Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Postpartum Care
Uploaded by
Christian Clyde N. JakosalemOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Postpartum Care
Uploaded by
Christian Clyde N. JakosalemCopyright:
Available Formats
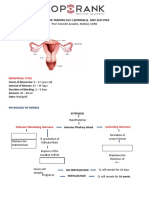
Postpartum care
Maternal Adaptation During
Postpartum Period Weight loss
Physiologic adaptation
Reproductive system ❖ Immediate 12 to 14 lb = baby, placenta, and
❖ Uterine contraction leads to amniotic fluid
involution(shrinking of the uterus ❖ 5 to 15 lb (early postpartum) = fluid loss from
❖ Measured by assessing fundal height diaphoresis, urinary excretion
❖ Factors promote, inhibit involution ❖ Return to prepregnancy weight six months after
❖ Afterpains childbirth (if within recommended weight gain
range)
assessment/ education ❖ In general, the breastfeeding woman tends to
lose weight faster than the woman who does not
Assess fundal height: Assess the location, breastfeed because of increased caloric
consistency, and height of the fundus through palpation. demands.
❖ If the uterus is not firm upon palpation,
massage it gently. Placing the infant on the
mother’s breast also aids in stimulating
Nursing interventions for
contractions.
postpartum care after cesarean birth
Assessment
Lochia: blood, mucus, tissue, WBC compose uterine Primary causes of maternal mortality post cesarean
discharge ❖ Anesthesia complications
❖ Rubra: first 3-4 days, small-mod amount, ❖ Postpartum infection
mostly blood and dark red with fleshy odor ❖ Hemorrhage
❖ Serosa: days 4-10, decreases to small amount, ❖ Thromboembolism
brownish/pink color Monitor
❖ Alba: after day 10, white-pale yellow, mostly ❖ Lungs; signs of respiratory depression
❖ IV for Sources of pain
WBCs ❖ PCA
Ovaries ❖ discomfort
❖ Ovulation can occur as soon as three weeks ❖ Incision; bowel sounds; urinary output
❖ Signs of thrombus formation
post-delivery
Cervix
❖ Vagina, perineum
❖ Never fully return to pregravid state; Kegel
❖
exercises
Lactation can lead to vaginal dryness, Nursing management & Discharge
Breasts
dyspareunia (painful intercourse)
planning
❖ Colostrum; prolactin ❖ Preventing injury from Rh-negative blood type or non immunity
Cardiovascular system to rubella
❖ High plasma fibrinogen levels and other ❖ Is the woman a candidate for Rho(D) immune globulin
coagulation factors mark postpartum period (RhoGAM) I'M within 24 hours of delivery. Given and checked
Vital signs as if you were administering a blood product.
❖ Temperature may be slightly elevated first 24 ❖ Providing patient teaching
❖ Breast care; fundal massage
hours
❖ Perineum and vaginal care
❖ Slow pulse a first, then WNL first week post
❖ Pain management
delivery ❖ Nutrition; constipation
❖ Blood pressure should not be elevated ❖ Proper rest
For every 250 mL of blood loss, the hemoglobin and ❖ Stress importance of prioritizing self-care
hematocrit (H&H) fall by one and two points, ❖ MMR (subq) right before DC if needed
respectively. So, if the woman’s H&H were 12 and 34, ❖ Evaluation: Goals and expected outcomes
then fall to 10 and 30, the approximate blood loss is
500 mL.
❖ Musculoskeletal system: Abdomen is soft,
sagging immediately postpartum
❖ Gastrointestinal system: Very hungry;
constipation
❖ Urinary system: Transient glycosuria,
proteinuria, and ketonuria are normal
immediately postpartum
❖ Voiding issues
❖ Integumentary system: Copious diaphoresis
common
❖ Striae (stretch marks) on abdomen and breasts
You might also like
- Pregnancy Decoded: A Comprehensive Handbook for Today's Expectant MomsFrom EverandPregnancy Decoded: A Comprehensive Handbook for Today's Expectant MomsNo ratings yet
- 2 - Pre Gestational ConditionDocument11 pages2 - Pre Gestational ConditionAngelica Dalit MendozaNo ratings yet
- GEMS Obstetrics and GynaecologyDocument59 pagesGEMS Obstetrics and GynaecologyUMARRA SHAFIQUENo ratings yet
- 2023 Labdiagnostic Proceduresm101Document60 pages2023 Labdiagnostic Proceduresm101Alezandra LabusNo ratings yet
- POSTPARTUMDocument31 pagesPOSTPARTUMLeo D' GreatNo ratings yet
- Gestational 1Document8 pagesGestational 1RoseAngelyne VicenteNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of The High Risk Pregnant Client With Gestational ConditionDocument55 pagesNursing Care of The High Risk Pregnant Client With Gestational ConditionMarc FresNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgBadmrbzR Zbaf9LIsgA4xz3BXrf4T JrmRyxu5 5bkJFOaK1lMBnJ2 AUVEbPfI17GyIzBlEKvmA QY2 MBlLC8PHYkavITBEfKLN2rz Ns UV ETHtZJ3GVrlvuohWjtap7LzQ0YgxbfDocument37 pagesACFrOgBadmrbzR Zbaf9LIsgA4xz3BXrf4T JrmRyxu5 5bkJFOaK1lMBnJ2 AUVEbPfI17GyIzBlEKvmA QY2 MBlLC8PHYkavITBEfKLN2rz Ns UV ETHtZJ3GVrlvuohWjtap7LzQ0YgxbfBiraito TakanaNo ratings yet
- At I Maternal NewbornDocument24 pagesAt I Maternal NewbornEunice Cortés100% (2)
- Maternal Reviewer FinalsDocument36 pagesMaternal Reviewer FinalsHannah QuindipanNo ratings yet
- Normal Pregnancy - 094218Document67 pagesNormal Pregnancy - 094218Beatrice habukuwie BaahNo ratings yet
- Puerperium NotesDocument5 pagesPuerperium NotesCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Norzagaray DutyprojectDocument25 pagesNorzagaray DutyprojectSven OrdanzaNo ratings yet
- Gestational DisordersDocument30 pagesGestational DisordersGwyneth GuintuNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Physical AssessmentDocument60 pagesPostpartum Physical Assessmentalmyr_rimandoNo ratings yet
- Gestational Conditions 1Document14 pagesGestational Conditions 1Fatima TañedoNo ratings yet
- Pre Natal Care Book BasedDocument9 pagesPre Natal Care Book BasedAngelaTrinidadNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Physical AssessmentDocument60 pagesPostpartum Physical AssessmentJhgrace Mary Pacaña Gallo100% (1)
- Labor ReadinessDocument1 pageLabor ReadinessEvidence ChaibvaNo ratings yet
- Early Pregnancy ComplicationDocument31 pagesEarly Pregnancy ComplicationHizami NorddinNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care During Labor and Pain Management2015Document51 pagesNursing Care During Labor and Pain Management2015christopher ebarbNo ratings yet
- ABORTIONDocument40 pagesABORTIONLiangkiuwiliuNo ratings yet
- 2F Compiled Oral Revalida 1Document75 pages2F Compiled Oral Revalida 1Mary Loise VillegasNo ratings yet
- Precipitate Labor To Uterine Inversion 1.28.22Document42 pagesPrecipitate Labor To Uterine Inversion 1.28.22coco brillqnteNo ratings yet
- Obstetricsafetyprotocols PDFDocument10 pagesObstetricsafetyprotocols PDFLoraine CastilloNo ratings yet
- Uterine Atony: Cudanin, Regine R. Kimaykimay, Angeline PDocument31 pagesUterine Atony: Cudanin, Regine R. Kimaykimay, Angeline PregNo ratings yet
- 1538 Exam 1 ReproductionDocument22 pages1538 Exam 1 ReproductionJade EdanoNo ratings yet
- OB 1st PNCUDocument8 pagesOB 1st PNCUAngelo Erispe100% (1)
- ObsGyn - OSCE NotesDocument69 pagesObsGyn - OSCE NotesMatt McCannNo ratings yet
- Intrapartal ComplicationsDocument8 pagesIntrapartal ComplicationsLizeth Querubin100% (4)
- Ob Final ReviewDocument13 pagesOb Final Reviewraquel maniegoNo ratings yet
- ObstetricsDocument34 pagesObstetricshassanwejdan1No ratings yet
- Prenatal CareDocument77 pagesPrenatal Caredavidbuena0920No ratings yet
- Complication of PregnancyDocument44 pagesComplication of PregnancyJharaNo ratings yet
- Maternity Nursing NotesDocument7 pagesMaternity Nursing NotesazitaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Post Partal Care 7Document36 pagesPost Partal Care 7Christian OpinaldoNo ratings yet
- Puerperium and ManagementDocument38 pagesPuerperium and ManagementWadhha AlsenaidiNo ratings yet
- Revised OB Handout Part 2 MAY 2023 PNLE RefresherDocument9 pagesRevised OB Handout Part 2 MAY 2023 PNLE RefresherMatelyn OargaNo ratings yet
- English Report 4Document5 pagesEnglish Report 4Marie Ashley CasiaNo ratings yet
- 14 USI-Diagnosis of PregnancyDocument19 pages14 USI-Diagnosis of PregnancyEugene LancasterNo ratings yet
- Management of Postnatal CareDocument31 pagesManagement of Postnatal Caresinuaish syaNo ratings yet
- Revised OB Handout Part 1 MAY 2023 PNLE RefresherDocument15 pagesRevised OB Handout Part 1 MAY 2023 PNLE RefresherMatelyn OargaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5.1 Student JLBDocument26 pagesUnit 5.1 Student JLBkendrabooboooNo ratings yet
- Postnatal CareDocument72 pagesPostnatal CareDIPENDRA KUMAR KUSHAWAHANo ratings yet
- Antepartum HaemorrhageDocument21 pagesAntepartum HaemorrhageDavina DakapNo ratings yet
- PUERPERIUMDocument38 pagesPUERPERIUMChikky ChikyNo ratings yet
- OB Final Exam Study GuideDocument14 pagesOB Final Exam Study GuideMarissa SolanoNo ratings yet
- Incompetent Cervix Group 4Document9 pagesIncompetent Cervix Group 4bbaltazarjaniceNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 - Normal Changes During PregnancyDocument4 pagesTopic 5 - Normal Changes During PregnancyREANNE MAE ABRERANo ratings yet
- Post Partum SF 1 - 1Document19 pagesPost Partum SF 1 - 1John MajanNo ratings yet
- DR Devdatt Laxman Pitale, Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist, High Risk Preganancy and ReproductiveDocument31 pagesDR Devdatt Laxman Pitale, Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist, High Risk Preganancy and ReproductiveDrDevdatt Laxman PitaleNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 High Risk PregnancyDocument11 pagesNCM 109 High Risk PregnancyLea BorceNo ratings yet
- Placenta AbruptioDocument30 pagesPlacenta AbruptioArchana MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Highlights, Elmar P. SakalaDocument47 pagesObstetric Highlights, Elmar P. Sakaladukelist5660% (1)
- Lesson 3 - PregnancyDocument4 pagesLesson 3 - PregnancyA CNo ratings yet
- 2 Nursing Care of The Pregnant Client Gestational ConditionDocument120 pages2 Nursing Care of The Pregnant Client Gestational ConditionjustinjareddNo ratings yet
- MCHNDocument6 pagesMCHNJohn KenNo ratings yet
- OB Stages of Labor and Care in The Stages of Labor With VideoDocument45 pagesOB Stages of Labor and Care in The Stages of Labor With VideodsmagallanesNo ratings yet
- OB ATI Study Guide: Initial Prenatal VisitDocument26 pagesOB ATI Study Guide: Initial Prenatal Visitxoxo318No ratings yet
- Stages of LaborDocument1 pageStages of LaborChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Fetal Heart TonesDocument1 pageFetal Heart TonesChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Complete-Head MergedDocument85 pagesComplete-Head MergedChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument1 pageSkeletal SystemChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs Normal RangeDocument1 pageVital Signs Normal RangeChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Testamentary Succession CasesDocument69 pagesTestamentary Succession CasesGjenerrick Carlo MateoNo ratings yet
- WT WIAB Reworked CH 3 FullDocument5 pagesWT WIAB Reworked CH 3 Fulljack3314sonyNo ratings yet
- Travisa India ETA v5Document4 pagesTravisa India ETA v5Chamith KarunadharaNo ratings yet
- FRA - Project - NHPC - Group2 - R05Document29 pagesFRA - Project - NHPC - Group2 - R05DHANEESH KNo ratings yet
- The Approach of Nigerian Courts To InterDocument19 pagesThe Approach of Nigerian Courts To InterMak YabuNo ratings yet
- EMCEE ScriptDocument3 pagesEMCEE ScriptSunshine Garson84% (31)
- ThesisDocument44 pagesThesisjagritiNo ratings yet
- Short Run Decision AnalysisDocument31 pagesShort Run Decision AnalysisMedhaSaha100% (1)
- Unit Test 11 PDFDocument1 pageUnit Test 11 PDFYONo ratings yet
- NZAA ChartsDocument69 pagesNZAA ChartsA340_600100% (5)
- International PositioningDocument37 pagesInternational PositioningMansi A Kathuria100% (1)
- Organization and ManagementDocument65 pagesOrganization and ManagementIvan Kirby EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Albanian DialectsDocument5 pagesAlbanian DialectsMetaleiroNo ratings yet
- Coorg Chicken CurryDocument1 pageCoorg Chicken CurryAnitha VinukumarNo ratings yet
- Depreciation, Depletion and Amortization (Sas 9)Document3 pagesDepreciation, Depletion and Amortization (Sas 9)SadeeqNo ratings yet
- Ekotoksikologi Kelautan PDFDocument18 pagesEkotoksikologi Kelautan PDFMardia AlwanNo ratings yet
- Notes (Part 1) : Accounting Policies, Changes in Estimates and ErrorsDocument13 pagesNotes (Part 1) : Accounting Policies, Changes in Estimates and ErrorsPaula Bautista100% (2)
- A Study On Cross Cultural PracticesDocument56 pagesA Study On Cross Cultural PracticesBravehearttNo ratings yet
- General Concepts and Principles of ObligationsDocument61 pagesGeneral Concepts and Principles of ObligationsJoAiza DiazNo ratings yet
- Singles Inferno SpreekexamensDocument10 pagesSingles Inferno SpreekexamensIlhamNo ratings yet
- Shop Decjuba White DressDocument1 pageShop Decjuba White DresslovelyNo ratings yet
- Ch.6 TariffsDocument59 pagesCh.6 TariffsDina SamirNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument2 pagesDocumentHP- JK7No ratings yet
- Cuthites: Cuthites in Jewish LiteratureDocument2 pagesCuthites: Cuthites in Jewish LiteratureErdincNo ratings yet
- 4-Cortina-Conill - 2016-Ethics of VulnerabilityDocument21 pages4-Cortina-Conill - 2016-Ethics of VulnerabilityJuan ApcarianNo ratings yet
- Resume-Pam NiehoffDocument2 pagesResume-Pam Niehoffapi-253710681No ratings yet
- Crime and Punishment Vocabulary 93092Document2 pagesCrime and Punishment Vocabulary 93092Rebeca Alfonso Alabarta50% (4)
- Calendario General 2Document1 pageCalendario General 2Santiago MuñozNo ratings yet
- General Terms Conditions For Sales Purchases LPG and Chemical TankersDocument34 pagesGeneral Terms Conditions For Sales Purchases LPG and Chemical TankersSally AhmedNo ratings yet
- Vayigash BookletDocument35 pagesVayigash BookletSalvador Orihuela ReyesNo ratings yet