Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PTS4 Final
Uploaded by
Elmenhor M Usman0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views4 pagesPlane and Topographic surveying Laboratory 4
Original Title
PTS4final
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPlane and Topographic surveying Laboratory 4
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views4 pagesPTS4 Final
Uploaded by
Elmenhor M UsmanPlane and Topographic surveying Laboratory 4
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Name: Naif M.
Patadon Year/Course/Section: 2-BSCE-B
Date: November 29, 2022
Laboratory Exercise 4
Determination of the Elevation of Points and Graphically Represent the Contour lines
Using Checkerboard Method
Materials:
Level
Tape measure
Pen and notebook
Leveling rod
Tripod
Procedure:
1. Prepare all the equipment needed in this type of survey.
2. Make a maximum rectangular dimension at the site where the survey will be
conducted using tape measure and record the width.
3. Divide the measured width to 4 so that there will be 5 equally spaced reference
point and take note the distance between them. (Remember to mark all the
points)
4. From your 5-reference point, start finding the location of other points in line to the
length of the rectangle using the recorded equally distance in procedure 3. Since
this survey uses Checkerboard Method to find elevation of each point, all points
should have equal distances between them.
5. Place your level where all points can be surveyed or can be seen. (It is
recommended to place it inside the rectangle as long as not above on your
designated points.)
6. Using leveling rod and the level, site first the benchmark and this will serve as the
backsight of all point throughout the survey.
7. Site all the defined points and record it. Those will be the foresights of each point.
8. Make a table out of the data you have gathered and find the elevation of each
point analytically.
9. With a contour interval of 1 meter, graphically represent the elevation data of the
survey.
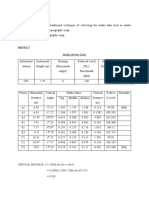
Table 1.1 Backsight, Foresight, Elevation Data
(BB)Benchmark Backsight= 1.08m HI= Benchmark Elev + Benchmark
backsight or
(BE)Benchmark Elevation= 100 HI=BB + BE
Elevation(xx)= HI - FS(xx)
Points Foresight Elevation Points Foresight Elevation
A1 1.11 99.97 E4 1.18 99.9
A2 1.15 99.93 E5 1.21 99.87
A3 1.15 99.93 F1 1.22 99.86
A4 1.16 99.92 F2 1.24 99.84
A5 1.15 99.93 F3 1.2 99.88
B1 1.15 99.93 F4 1.18 99.9
B2 1.18 99.9 F5 1.22 99.86
B3 1.14 99.94 G1 1.265 99.815
B4 1.19 99.89 G2 1.25 99.83
B5 1.19 99.89 G3 1.215 99.865
C1 1.15 99.93 G4 1.205 99.875
C2 1.15 99.93 G5 1.205 99.875
C3 1.14 99.94 H1 1.245 99.835
C4 1.16 99.92 H2 1.245 99.835
C5 1.21 99.87 H3 1.245 99.835
D1 1.185 99.895 H4 1.225 99.855
D2 1.185 99.895 H5 1.2 99.88
D3 1.07 100.02 I1 1.17 99.91
D4 1.17 99.91 I2 1.23 99.85
D5 1.21 99.87 I3 1.25 99.83
E1 1.23 99.85 I4 1.22 99.86
E2 1.22 99.86 I5 1.212 99.868
E3 1.14 99.94 J1 0.985 100.095
points Foresight elevation
J2 1.205 99.875
J3 1.215 99.865
J4 1.175 99.905
J5 1.175 99.905
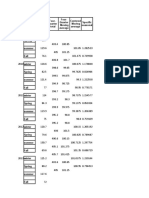
Table 1.2 Point Elevation Data
Station 1 2 3 4 5
Points
A 99.97 99.93 99.93 99.92 99.93
B 99.93 99.9 99.94 99.89 99.89
C 99.93 99.93 99.94 99.92 99.87
D 99.895 99.895 100.02 99.91 99.87
E 99.85 99.86 99.94 99.9 99.87
F 99.86 99.84 99.88 99.9 99.86
G 99.815 99.83 99.865 99.875 99.875
H 99.835 99.835 99.835 99.835 99.88
I 99.91 99.85 99.83 99.86 99.868
J 100.095 99.875 99.865 99.905 99.905
D(total width) = 11m
d=D/4 - square side dimension
d = 11 / 4 = 2.75m
Observation/Conclusion:
On a map, contour lines are curved, straight, or a combination of both lines that
show where a real or hypothetical surface intersects with one or more horizontal planes.
Map readers can deduce the relative gradient of a parameter and estimate that
parameter at specific locations thanks to the design of these contours. Contour lines
can be determined by using checkerboard method to pinpoint the exact location of the
contour lines.
On a topographic map, a contour line is a line drawn to denote a dip or elevation
of the ground. The vertical separation or elevation difference between contour lines is
known as a contour interval. Every sixth contour line has an index contour, which is a
bolder or thicker line.
The height of the terrain also rises if the numbers corresponding to particular
contour lines do. There is a decline in elevation if the numbers next to the contour lines
are declining. The contour lines turn upstream as they get closer to a stream, canyon, or
drainage area. They then cross the stream and make a "v"-shaped turn back along the
opposing bank of the stream. A rounded contour denotes a drainage or spur that is
flatter or wider. On ridge tops, which are frequently small or have very restricted spatial
extent, contour lines frequently enclose the smallest areas. Pointed ridges are indicated
by sharp contour points.
You might also like
- Cross Section LevelingDocument18 pagesCross Section Levelingzhalyan sardar100% (1)
- Highwall Miner HWM 300Document20 pagesHighwall Miner HWM 300Amit100% (1)
- 09 d01 Digsi 5 - Overview v1.1 En-UsDocument41 pages09 d01 Digsi 5 - Overview v1.1 En-UsAngie GinethNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Land LevelingDocument19 pagesChapter 4 Land LevelingAbra Semeneh100% (2)
- AristotleDocument126 pagesAristotlenda_naumNo ratings yet
- Countuor MapsDocument6 pagesCountuor MapsMuhammed SirwanNo ratings yet
- Final Survey CampDocument22 pagesFinal Survey CampLHDNo ratings yet
- LabReport5 2Document4 pagesLabReport5 2ss2fp7bkr6No ratings yet
- En Taqueometria IngDocument3 pagesEn Taqueometria IngDiogo FreitasNo ratings yet
- En Taqueometria IngDocument3 pagesEn Taqueometria IngDiogo FreitasNo ratings yet
- Zhalyan Sardar Ali - Cross Section LevelingDocument18 pagesZhalyan Sardar Ali - Cross Section Levelingzhalyan sardarNo ratings yet
- Plantillaword UPTC2024Document17 pagesPlantillaword UPTC2024spatinogaviriaNo ratings yet
- NumberDocument2 pagesNumberKarabo MonnanyanaNo ratings yet
- Recs Revised DormitoryDocument49 pagesRecs Revised DormitoryAgustin Velasco Jr.No ratings yet
- Slope-Degree, Gradient and Slope ConverterDocument14 pagesSlope-Degree, Gradient and Slope ConverterChristopher UcheNo ratings yet
- School of Architecture, Building and Design: Name Student IDDocument18 pagesSchool of Architecture, Building and Design: Name Student IDDaphne Tan 丽文No ratings yet
- CENG 50A LabExercise08Document5 pagesCENG 50A LabExercise08FRANCHESKA DUCHANo ratings yet
- Firing Tables mk19Document11 pagesFiring Tables mk19SSOpticsNo ratings yet
- Produccion SabaingoDocument12 pagesProduccion SabaingoRUCNo ratings yet
- Fatteh Singh OGLDocument10 pagesFatteh Singh OGLANKESH SHRIVASTAVANo ratings yet
- OBJECTIVEDocument2 pagesOBJECTIVEAnnisha IshaNo ratings yet
- Tabla 1 Tabla 2 Input Ke T KD KD (1-T) D% G Wacc NoplatDocument3 pagesTabla 1 Tabla 2 Input Ke T KD KD (1-T) D% G Wacc NoplatOscarDavidIturriagoHernandezNo ratings yet
- Table 03 21 102623Document4 pagesTable 03 21 102623kvlad3377No ratings yet
- 70 Additional Forms-Annex VDocument2 pages70 Additional Forms-Annex Vmotilal naikNo ratings yet
- Description Bs IS FS HI RL (M) RemarksDocument4 pagesDescription Bs IS FS HI RL (M) RemarksGsUpretiNo ratings yet
- Bahan Pivot 2Document6 pagesBahan Pivot 2Fadillah AryaNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 1 Section: Cv-A Roll No: 19L-0800Document23 pagesAssignment # 1 Section: Cv-A Roll No: 19L-0800ifsha akhlaqNo ratings yet
- Nova Assignment 1 - Surveying Finals (Autosaved) (Autosaved) Nova Assignment 1 - Surveying FinalsDocument10 pagesNova Assignment 1 - Surveying Finals (Autosaved) (Autosaved) Nova Assignment 1 - Surveying FinalsKenNo ratings yet
- Answer Some of The Following QuestionsDocument3 pagesAnswer Some of The Following QuestionsSalih MohayaddinNo ratings yet
- Year Quarter Sales Four-Quarter Total Four - Quarter Moving Average Centered Moving Average Specific SeasonalDocument1 pageYear Quarter Sales Four-Quarter Total Four - Quarter Moving Average Centered Moving Average Specific SeasonalAnonymous Bo6hZiSJzNo ratings yet
- Surveying Camp - FromatDocument12 pagesSurveying Camp - Fromatalluru Venu gopalNo ratings yet
- Portfolios in RotorDocument75 pagesPortfolios in RotorMojtaba HasanluNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Levelling and ContouringDocument30 pagesModule 6 - Levelling and ContouringAbdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Zhalyan Sardar Ali - Profile LevelingDocument9 pagesZhalyan Sardar Ali - Profile Levelingzhalyan sardarNo ratings yet
- Survey Lab ReportDocument8 pagesSurvey Lab ReportJames Michael ChuNo ratings yet
- Close RangeDocument5 pagesClose RangenuruljannatiNo ratings yet
- Hand Beam CalculationDocument7 pagesHand Beam CalculationAhsan UlNo ratings yet
- Roting Waduk (Autorecovered)Document46 pagesRoting Waduk (Autorecovered)irmanovitaNo ratings yet
- Investment Ass#6 - Daniyal Ali 18u00265Document3 pagesInvestment Ass#6 - Daniyal Ali 18u00265Daniyal Ali100% (1)
- 1.2-1.4 and 1.8 - S2-3 Section 5.6Document20 pages1.2-1.4 and 1.8 - S2-3 Section 5.6shenkaheiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2C - Seasonal Analysis and ForecastingDocument15 pagesChapter 2C - Seasonal Analysis and Forecastingdeklerkkimberey45No ratings yet
- Engineering Department ENGR 370 - Surveying: Student NamesDocument9 pagesEngineering Department ENGR 370 - Surveying: Student Nameszhalyan sardarNo ratings yet
- Price Index PDFDocument4 pagesPrice Index PDFAfif Taufiiqul HakimNo ratings yet
- ContoursDocument45 pagesContoursSaileshNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7Document4 pagesTutorial 7HENG QUAN PANNo ratings yet
- Computation of Earthwork EmbankmentDocument2 pagesComputation of Earthwork EmbankmentsnsNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document3 pagesLab 3yaredNo ratings yet
- Appendix PDFDocument12 pagesAppendix PDFSITI NUR ATIQAH BINTI AMINUDDIN / UPMNo ratings yet
- Nivel de Ruido PDFDocument2 pagesNivel de Ruido PDFJavier Alfredo Arancibia BernalNo ratings yet
- Compaction RegisterDocument73 pagesCompaction Registersuraj ChinttuNo ratings yet
- 33Document8 pages33Farah AymanNo ratings yet
- Klasifikasi Medan: Titik A Titik BDocument10 pagesKlasifikasi Medan: Titik A Titik BCynthiaSinagaNo ratings yet
- Tugas 3Document2 pagesTugas 3firda hestiNo ratings yet
- HBS Table No. 160 - Quarterly Estimates of Gross Domestic Product at Factor Cost (At Constant Prices) (New Series) (Base - 2004-05)Document18 pagesHBS Table No. 160 - Quarterly Estimates of Gross Domestic Product at Factor Cost (At Constant Prices) (New Series) (Base - 2004-05)Arijit DasNo ratings yet
- Hand Column CalculationDocument10 pagesHand Column CalculationAhsan UlNo ratings yet
- Mensuration and CalculationDocument23 pagesMensuration and CalculationMARJORE PLAZANo ratings yet
- Pratik Nandan Choudhary-1902030023Document8 pagesPratik Nandan Choudhary-1902030023Ritesh Agarwal OYOwalaNo ratings yet
- AyabaDocument20 pagesAyabaAdams IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Wind Load (Diphragm Load Per Floor) - AhnafDocument4 pagesWind Load (Diphragm Load Per Floor) - AhnafahnafNo ratings yet
- tp04 TopgraphieDocument5 pagestp04 TopgraphieAziz NefzaouiNo ratings yet
- Report Contour SurveyDocument10 pagesReport Contour SurveyOzair AtalNo ratings yet
- CBR.2 TemplateDocument4 pagesCBR.2 TemplateBenjamin DagbeyNo ratings yet
- Excuse LetterDocument5 pagesExcuse LetterElmenhor M UsmanNo ratings yet
- SDG Infomercial ScriptDocument8 pagesSDG Infomercial ScriptElmenhor M UsmanNo ratings yet
- CommitteeDocument2 pagesCommitteeElmenhor M UsmanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 (Thesis Sample)Document23 pagesCHAPTER 1 (Thesis Sample)Elmenhor M UsmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Alperto Bajalan Espadera Necesito TejamDocument7 pagesChapter 4 Alperto Bajalan Espadera Necesito TejamElmenhor M UsmanNo ratings yet
- RecommendationDocument2 pagesRecommendationElmenhor M UsmanNo ratings yet
- Hayde U WahabDocument1 pageHayde U WahabElmenhor M UsmanNo ratings yet
- Kath UtsDocument2 pagesKath UtsElmenhor M UsmanNo ratings yet
- Physics SS2 Term 2 Dec 2022Document71 pagesPhysics SS2 Term 2 Dec 2022TahmidNo ratings yet
- 2.lecture 1-Basics and PrecedenceDocument30 pages2.lecture 1-Basics and PrecedenceBhavesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Luke Diosiek Fun With Electricity and MagnetismDocument21 pagesLuke Diosiek Fun With Electricity and MagnetismseablueNo ratings yet
- UACE BIO PAPER TWO SET 3 2023-JusanDocument3 pagesUACE BIO PAPER TWO SET 3 2023-JusanCampbell OGENRWOTNo ratings yet
- DDP400 Open-Frame and U-Chassis :: ROAL Living EnergyDocument12 pagesDDP400 Open-Frame and U-Chassis :: ROAL Living EnergyroalscribdNo ratings yet
- CHE504 - Lab Report On Gas Absorption L8 PDFDocument23 pagesCHE504 - Lab Report On Gas Absorption L8 PDFRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 02a-2 V-Can2 Xlrteh4300g033850Document1 page02a-2 V-Can2 Xlrteh4300g033850Daniel PricopNo ratings yet
- Development of A Continuous Microchannel CrystallizerDocument4 pagesDevelopment of A Continuous Microchannel CrystallizerchenabeelNo ratings yet
- Asme Se-165 2004Document25 pagesAsme Se-165 2004Kamalnath KpNo ratings yet
- Properties of Gray Cast Iron - Engineer's HandbookDocument2 pagesProperties of Gray Cast Iron - Engineer's Handbookkus satria dNo ratings yet
- Process Cooling System Chiller and Tower Sizing FormualsDocument2 pagesProcess Cooling System Chiller and Tower Sizing FormualsChuen Hau TanNo ratings yet
- Mrs - Sanjana Jadhav: Mobile No-9422400137Document3 pagesMrs - Sanjana Jadhav: Mobile No-9422400137Sanjana JadhavNo ratings yet
- Celonis Configuration Store Setup Guide 1.6Document11 pagesCelonis Configuration Store Setup Guide 1.6Venugopal JujhavarappuNo ratings yet
- Mahesh - Informatica DeveloperDocument5 pagesMahesh - Informatica DeveloperMadhav GarikapatiNo ratings yet
- Quality Control Tests For Emulsions, Syrups, Tinctures, Elixirs, Ointments and OthersDocument11 pagesQuality Control Tests For Emulsions, Syrups, Tinctures, Elixirs, Ointments and OthersMuhammad Masoom Akhtar100% (2)
- Properties in Shear: (Eg. Ssy 0.5sy)Document34 pagesProperties in Shear: (Eg. Ssy 0.5sy)Yusuf SahinNo ratings yet
- Neeraj Pal 2Document1 pageNeeraj Pal 2NeerajPalNo ratings yet
- Question Bank 4th SemesterDocument16 pagesQuestion Bank 4th SemesterJeevanandam ShanmugasundaramNo ratings yet
- Functions Equations Question BankDocument101 pagesFunctions Equations Question BankParth DesaiNo ratings yet
- Case Study - CCNA - Sem1 - Cosmin Daniel POCRISTEDocument7 pagesCase Study - CCNA - Sem1 - Cosmin Daniel POCRISTEcosmin_horusNo ratings yet
- Test For CarbohydratesDocument15 pagesTest For CarbohydratesKevin SangNo ratings yet
- 3681 113533 1 SM - , mutasiCVKaroseriLaksanaDocument14 pages3681 113533 1 SM - , mutasiCVKaroseriLaksanataufiq hidayatNo ratings yet
- Janitza-Main catalogue-2015-ENDocument418 pagesJanitza-Main catalogue-2015-ENOchoa Para La BandaNo ratings yet
- Digital Image ProcessingDocument71 pagesDigital Image ProcessingPratibha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mechanism Analysis of Gas Solid Flow Non-Uniformity Problem of 330 MW CFB BoilerDocument10 pagesMechanism Analysis of Gas Solid Flow Non-Uniformity Problem of 330 MW CFB BoilerTan Nguyen HuuNo ratings yet
- Cennamo - Intransitivity, Object Marking and Event StructureDocument16 pagesCennamo - Intransitivity, Object Marking and Event StructureAugusto PérezNo ratings yet
- Vacuum TubeDocument1 pageVacuum Tubejose condoriNo ratings yet