Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NOTES
Uploaded by
Karen BautistaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NOTES
Uploaded by
Karen BautistaCopyright:
Available Formats
NON-MENDELIAN PATTERN OF INHERITANCE MORE ABOUT CHROMOSOMES AND GENES
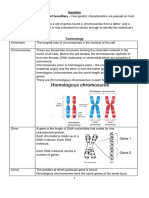
How do we refer to these characteristics that each individual Humans have 46 chromosomes or 23 pairs of chromosomes
person has?
Chromosomes come in pairs ; they re called homologous
TRAITS- observable inherited characteristics chromosomes
What determines a persons traits? Homologous chromosomes(1) have similar structure and
shape and (2) have genes that code for proteins that
GENES- functional unit of heredity found in chromosomes
expresses the same trait
which are in the nucleus of cell
Non- Mendelian Inheritance
This is the type inheritance where in the patterns of
Genes and MORE ABOUT CHROMOSOMES AND GENES
phenotypes does not coincide with those that was
presented in the Mendelian’s Laws of inheritance
It also describes the in heritance of traits linked to a
Like chromosomes, genes also come single gene in the chromosomes
in pairs
Term Meaning
Incomplete Dominance Pattern of heredity in which
Each parent passes along just one copy to make up the genes one allele is not completely
dominant over another
you have
Codominance Pattern of heredity in which
both alleles are
simultaneously expressed in
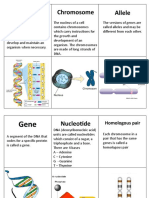
Alleles are different forms of the same gene which are the heterozygote
located on the same part of the chromosome. Multiple alleles A gene that is controlled by
more than two alleles
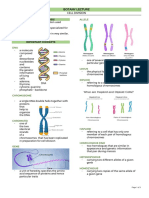
Chromosomes
Pleiotropy When one gene affects
multiple characteristics
All living things are made up of cells
Lethal allele Allele that results in the death
Inside the cells are smaller ORGANELLES of an individual
NUCLEUS- controls and regulates the activities of the cell; Polygenic trait Traits that are controlled by
multiple genes
contains the hereditary material
Inside the nucleus are threadlike structure called
CHROMOSOMES containing the genetic material
Phenotype- observable trait
CHROMATIN- unraveled condensed structure of DNA
Genotype- genetic make-up of an organism
CHROMOSOME- highly condensed structure of DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) - is a long molecule that
Incomplete Dominance
contains our unique genetic code; hereditary material in
humans and almost al other A case in which one
allele is not
What is the genes?
completely dominant
GENES- functional unit of heredity found in chromosomes over another
which are in the nucleus of the cell. It s a form of
inheritance which produces an intermediate trait
a heritable factor made of a length of DNA which Shows the actual appearance based on the GENE
influences a specific characteristic PAIR resulted once two pair combined
a long segment of the chromosome/ DNA that codes
for a certain trait
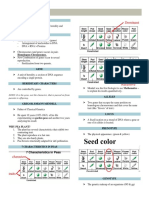
Problem :
Phenotype Genotype Gene Antibodies
Show the possible outcome of the cross between two pink Product Present
four o’clock flower plants by using the Punnett Square
Type A A A Antigen Anti-B
I I or I A
A
i
Type B B B B Antigen Anti-A
I I or I B
i
Type AB A B Antigen Neither
I I A and Anti-A nor
Antigen Anti-B
B
Genotype : 25% RR Type O ii none Anti-A and
Anti-B
25% WW
50% RW
Phenotype: 25% Red four o’clock plant
25% White four o’clock plant
50% Pink four o’clock plant
Codominance
Pattern of heredity in which both alleles are simultaneously
expressed in the heterozygote
Multiple Alleles
A gene that is controlled by more than two alleles
You might also like
- Protoonkogen OnkogenDocument22 pagesProtoonkogen OnkogenkurniawanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in General Biology Ii - KmbsDocument5 pagesReviewer in General Biology Ii - KmbsKSNo ratings yet
- Kenny's Boards 2 ReviewsDocument254 pagesKenny's Boards 2 ReviewsHuguette Marie NseleNo ratings yet
- Autism MALONICACIDDocument172 pagesAutism MALONICACIDMilan Valachovic100% (1)
- PRELIM Exam in Science 9Document5 pagesPRELIM Exam in Science 9Mohammad Javier D. DimaporoNo ratings yet
- t4 SC 409 Genes and Inheritance Match and DrawDocument2 pagest4 SC 409 Genes and Inheritance Match and DrawNubar MammadovaNo ratings yet
- PanosteitisDocument5 pagesPanosteitisElEffe100% (1)
- I.9. Classical Genetics FinalDocument50 pagesI.9. Classical Genetics FinalOrNo ratings yet
- Poultry LEA ISUDocument139 pagesPoultry LEA ISULaila Ubando0% (1)
- Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI)Document102 pagesIntegrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI)Jasmin Jacob100% (2)
- Unit 1.2 Mendelian GeneticsDocument7 pagesUnit 1.2 Mendelian GeneticsRegine Coeli Menta LansanganNo ratings yet
- Waste Water Treatment and Use in AgricultureDocument148 pagesWaste Water Treatment and Use in AgricultureDaisyNo ratings yet
- Transmission NotesDocument14 pagesTransmission NotesurjaNo ratings yet
- Science Exam Preparations - Joel TDocument12 pagesScience Exam Preparations - Joel TvaughanNo ratings yet
- Mitosis vs. MeosisDocument1 pageMitosis vs. MeosisJULIANNE NICOLE LIMNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Genetics: GenesDocument6 pagesReviewer in Genetics: GenesKCrsNo ratings yet
- 11.3 Note-Taking PageDocument4 pages11.3 Note-Taking Pageangelina100906No ratings yet
- Gene Segregation and Interaction Hand Out BebDocument4 pagesGene Segregation and Interaction Hand Out Bebbsed.science.perezkristinejoyNo ratings yet
- Uppc Upcat Tutorials Science Part 5Document40 pagesUppc Upcat Tutorials Science Part 5Llen FabilaneNo ratings yet
- 00 Core Learning Checklist 2 Astrobio UnitDocument3 pages00 Core Learning Checklist 2 Astrobio UnitgaoNo ratings yet
- 2A GeneticsDocument47 pages2A GeneticsYashNo ratings yet
- LS 107 - Midterm 1 Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesLS 107 - Midterm 1 Cheat SheetAudrie L.No ratings yet
- 7 Priciple of Genetic 1Document22 pages7 Priciple of Genetic 1beyonduckNo ratings yet
- Genetics VocabularyDocument4 pagesGenetics Vocabularysnowy45.rmNo ratings yet
- BIO 2 2nd SemDocument7 pagesBIO 2 2nd SemKelly Misha NoolNo ratings yet
- Bio 152Document3 pagesBio 152Zas OlivaNo ratings yet
- NCM 108 - Lec 1 - Genetics and Genetic CounselingDocument6 pagesNCM 108 - Lec 1 - Genetics and Genetic CounselingNicole TomlinsonNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 Lesson 1Document8 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Lesson 1sydgosjrNo ratings yet
- 4 - Q - Genetic InheritanceDocument22 pages4 - Q - Genetic InheritanceNOOR JANNAH FIRDOUSE BINTI ISMAIL KM-Pensyarah100% (1)
- Chromosomes and Cell DivisionDocument6 pagesChromosomes and Cell DivisionEllaine Larren RazonNo ratings yet
- Human Develpment CHAPTER 3Document4 pagesHuman Develpment CHAPTER 3Alexa ProvidoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27Document58 pagesChapter 27Konishko DeyNo ratings yet
- Inquirey Question 4 Genetic VariationDocument6 pagesInquirey Question 4 Genetic VariationAnna BuiNo ratings yet
- General Genetics Notes With DR ChandleeDocument36 pagesGeneral Genetics Notes With DR ChandleeVenice CariñoNo ratings yet
- Mendelian LawsDocument46 pagesMendelian LawsFrancheska Faith BatallaNo ratings yet
- Inheritance and VariationDocument6 pagesInheritance and Variationabbas faresNo ratings yet
- Standard Level Long Questions: Question 1:distinguish Between Gene, Allele and Chromosome. 6Document2 pagesStandard Level Long Questions: Question 1:distinguish Between Gene, Allele and Chromosome. 6Tehreem AsadNo ratings yet
- Agents of DiseasesDocument3 pagesAgents of DiseasesRaymart DomingoNo ratings yet
- General Biology Genetics, Proteins, Origins of Life & BiotechnologyDocument31 pagesGeneral Biology Genetics, Proteins, Origins of Life & BiotechnologyAlexis Carla GahumanNo ratings yet
- Genetics Revision of Terms CardsDocument4 pagesGenetics Revision of Terms Cardsjenna cupidoNo ratings yet
- Biology Glossary Terms 3Document13 pagesBiology Glossary Terms 3Tim PopeNo ratings yet
- Science VocabularyDocument7 pagesScience VocabularychereewhaleNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Science Chapter 3: Heredity and Variation: 3.1 Cell DivisionDocument22 pagesForm 4 Science Chapter 3: Heredity and Variation: 3.1 Cell DivisionJia JiaNo ratings yet
- Pp6 Genetics An Inheritance JangeDocument31 pagesPp6 Genetics An Inheritance JangeoptimallethumusaNo ratings yet
- Science TestDocument2 pagesScience TestNaveed MendezNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2 Genetics To EvolutionDocument12 pagesGen Bio 2 Genetics To EvolutionLeonard CubeloNo ratings yet
- General Biology 11Document6 pagesGeneral Biology 11Nicks GelidoNo ratings yet
- Sec 2a Genetics ReviewerDocument4 pagesSec 2a Genetics ReviewerGeemaica MacaraigNo ratings yet
- Plant Genetics: Group 10 MembersDocument25 pagesPlant Genetics: Group 10 MembersJhemaeca PalisocNo ratings yet
- Genetics and HeredityDocument56 pagesGenetics and HeredityHnin NandarNo ratings yet
- Bio DefinitionsDocument2 pagesBio DefinitionsChloe TanNo ratings yet
- Key Answer Exercise 7Document6 pagesKey Answer Exercise 7diezelNo ratings yet
- PP6. Genetics and Inheritance - TerminologyDocument39 pagesPP6. Genetics and Inheritance - Terminologylebohangcandy8No ratings yet
- Common Genetic Problems and Diseases, Stem Cell Research: Rebecca ChinDocument48 pagesCommon Genetic Problems and Diseases, Stem Cell Research: Rebecca ChinJacky Lam JackyNo ratings yet
- Ndsi BioDocument26 pagesNdsi BioMarc Augustine BelgaNo ratings yet
- Basic Genetic Principles in Blood BankingDocument4 pagesBasic Genetic Principles in Blood BankingchippaiNo ratings yet
- 17 - InheritanceDocument4 pages17 - InheritanceAvyay TopraniNo ratings yet
- Genes and Inheritance: GCE Study Buddy BiologyDocument38 pagesGenes and Inheritance: GCE Study Buddy BiologyPeace FulNo ratings yet
- Genetics DifferencesDocument5 pagesGenetics DifferencesOoga ChakaNo ratings yet
- Gamete: Inheritance MatchingDocument2 pagesGamete: Inheritance MatchingdaliaNo ratings yet
- Cytogen Lesson 1Document3 pagesCytogen Lesson 1STEM-A CHRISTINE TRIBUNALONo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. DevpsychDocument7 pagesChapter 3. DevpsychEdralyn EgaelNo ratings yet
- Genetics 2024Document63 pagesGenetics 2024davidmajutla87No ratings yet
- 18 InheritanceDocument46 pages18 Inheritances1139221No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesCell DivisionChristina DaligconNo ratings yet
- CYTOGENETICSDocument2 pagesCYTOGENETICShassan hanisaNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics 3Document6 pagesCytogenetics 3Jessamin Velasco Sta RomanaNo ratings yet
- Deb-Kar-33-2017-255-Ppr-Msc Cosmetic Science PDFDocument28 pagesDeb-Kar-33-2017-255-Ppr-Msc Cosmetic Science PDFDivya UmmenthalaNo ratings yet
- Genetics ExercisesDocument3 pagesGenetics ExercisesJowell Obra OañaNo ratings yet
- Genetics: Punnett SquareDocument11 pagesGenetics: Punnett SquareZhai RielleNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Resistance Among Uropathogenic Escherichia ColiDocument13 pagesAntibiotic Resistance Among Uropathogenic Escherichia ColiSyed AmanNo ratings yet
- First Quarter Periodic TestDocument2 pagesFirst Quarter Periodic TestNur ShaNo ratings yet
- Children of Lourdes Academy - Cauayan Inc.: Curriculum MapDocument3 pagesChildren of Lourdes Academy - Cauayan Inc.: Curriculum MapNhorielyn Joy Disbaro BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Phytochemistry of Medicinal Plants (PDFDrive)Document369 pagesPhytochemistry of Medicinal Plants (PDFDrive)Albania StarNo ratings yet
- Presentation HaemoparasiteDocument112 pagesPresentation HaemoparasiteMedicine 0786No ratings yet
- STM123 - General BiologyDocument126 pagesSTM123 - General BiologyLEONIEVEVE L LIMBAGANo ratings yet
- NEET Biology SyllabusDocument8 pagesNEET Biology SyllabusNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Genetics and Genomics in Nursing and Health Care 2nd Edition by BeeryDocument151 pagesTest Bank For Genetics and Genomics in Nursing and Health Care 2nd Edition by BeeryabbieNo ratings yet
- Anthracnose Pathogen of The Succulent Plant Echeveria Perle Von NürnbergDocument4 pagesAnthracnose Pathogen of The Succulent Plant Echeveria Perle Von NürnbergJosue RomanNo ratings yet
- Gene Manipulation in CultureDocument9 pagesGene Manipulation in CultureImran KhanNo ratings yet
- Prelim HPCTDocument37 pagesPrelim HPCTMariaangela AliscuanoNo ratings yet
- Ajpgi 00008 2022Document18 pagesAjpgi 00008 2022Jéssica Thandara GosseNo ratings yet
- Banana Buch Top Disease PDFDocument2 pagesBanana Buch Top Disease PDFDomenico CappelloNo ratings yet
- BP Environmental CleaningDocument250 pagesBP Environmental CleaningFaruque SathiNo ratings yet
- UG Zoology PDFDocument54 pagesUG Zoology PDFPritha GhoshNo ratings yet
- PL-Microbiology Specimen Collection Guidelines (2020.07.22)Document14 pagesPL-Microbiology Specimen Collection Guidelines (2020.07.22)Anonymous fgRHAEIMrHNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Epidemiology and Control A Global PerspectiveDocument329 pagesCommunicable Disease Epidemiology and Control A Global PerspectiveMarisela FuentesNo ratings yet
- Labreportnew PDFDocument8 pagesLabreportnew PDFLuCky100% (1)
- Chapter 13:meiosis and Sexual Life CyclesDocument7 pagesChapter 13:meiosis and Sexual Life Cycleskuitang100% (1)