Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ged 212 - Assignment
Uploaded by
seri0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views3 pagesThis document outlines 10 major theories of development:
1. Freud's psychosexual theory which focuses on psychosexual stages from oral to genital and the roles of the id, ego and superego.
2. Piaget's cognitive development theory describes stages from sensorimotor to formal operations.
3. Bronfenbrenner's ecological systems theory examines environments from micro to macro and their influences.
4. Erikson's psychosocial theory outlines stages centered around developing trust, autonomy and initiative.
5. Vygotsky emphasized social learning and culture-specific tools in cognitive development.
Original Description:
THEORIES OF DEVELOPMENT AND KEY IDEAS
Original Title
GED 212- ASSIGNMENT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines 10 major theories of development:
1. Freud's psychosexual theory which focuses on psychosexual stages from oral to genital and the roles of the id, ego and superego.
2. Piaget's cognitive development theory describes stages from sensorimotor to formal operations.
3. Bronfenbrenner's ecological systems theory examines environments from micro to macro and their influences.
4. Erikson's psychosocial theory outlines stages centered around developing trust, autonomy and initiative.
5. Vygotsky emphasized social learning and culture-specific tools in cognitive development.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views3 pagesGed 212 - Assignment
Uploaded by
seriThis document outlines 10 major theories of development:
1. Freud's psychosexual theory which focuses on psychosexual stages from oral to genital and the roles of the id, ego and superego.
2. Piaget's cognitive development theory describes stages from sensorimotor to formal operations.
3. Bronfenbrenner's ecological systems theory examines environments from micro to macro and their influences.
4. Erikson's psychosocial theory outlines stages centered around developing trust, autonomy and initiative.
5. Vygotsky emphasized social learning and culture-specific tools in cognitive development.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
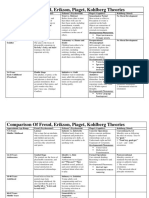
THEORIES OF DEVELOPMENT
PROPONENT THEORY KEY WORDS KEY IDEAS
1. Sigmund Freud Psychosexual Theory Psychosexual development: 1. Oral- fixation is in the mouth
Oral 2. Anal- fixation is in the anus
Anal -This is where the child is toilet
Phallic trained.
- Oedipus Complex *Anal retentive- orderly,
- Electra Complex perfectionist
Latency *Anal expulsive- messy,
Genital disorganized
3. Phallic- child began to explore
his/her genitals
*Oedipus complex- young boy
began to develop sexual desire
for his mother
*Electra complex- young girl
began to develop sexual desire
for his father
4. Latency- sexual impulses are
repressed
5. Genital- attraction towards
opposite sex
*Id- operates on the pleasure
Id principle; represents our urges,
Ego unconscious desires; wants
2. Sigmund Freud Psychoanalytic Theory Superego immediate gratification
*Ego- operates on the reality
principle; balances the id and
superego;
*Superego- operates on the
morality principles; our
conscience
3. Sigmund Freud Levels of consciousness Unconscious *Unconscious- outside our
Sub-conscious consciousness
Conscious *Sub-conscious- potentially be
brought to our conscious mind
*Conscious- awareness of the
reality
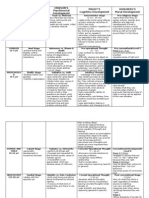
Sensorimotor stage It explores the development of
4. Jean Piaget Cognitive Development Preoperational knowledge, skills, problem
Theory stage solving and dispositions.
Concrete Sensorimotor stage: birth to 2
operational stage years
Formal operational Preoperational stage: ages 2 to
stage 7
Concrete operational stage:
ages 7 to 11
Formal operational stage: ages
12 and up
Microsystem Examine individuals'
5.Urie Ecological System Mesosystem relationships within
Bronfenbrenner Theory Exosystem communities and the wider
society
Microsystem: Refers to the
institutions and groups that
most immediately and directly
impact the child's development
including: family, school,
religious institutions,
neighborhood, and peers.
Mesosystem: Consists of
interconnections between the
microsystems, for example
between the family and
teachers or between the child’s
peers and the family.
Exosystem: Involves links
between social settings that do
not involve the child. For
example, a child's Macrosystem:
Describes the overarching
culture that influences the
developing child, as well as the
microsystems and mesosystems
embedded in those cultures.
6. Erik Erikson Psychosocial Trust vs Mistrust The infant will develop a
Development theory Autonomy vs Shame healthy balance
and doubt between trust and
Initiative vs Guilt mistrust if cared for and
responded consistently.
Autonomy- self-reliance
or independence;
shame and doubt if not
properly trained by their
parents
Initiative- self-
confidence to perform
actions; Guilt results
from belief that an
action will draw
disapproval
Zone of Proximal Community plays a central role
7. Lev Vygotsky Sociocultural Theory Development in the process of "making
Culture-specific meaning."
tools
Private speech
Imitation Imitation- conscious learning
8. Gabriel Tarde Imitation-Suggestion Suggestion Suggestion- unconscious
Theory learning
9. Albert Bandura Social Learning Theory Observation It emphasizes the importance of
Imitation observing and modeling the
Modeling behaviors, attitudes, and
emotional reactions of others.
Unconditional Unconditional positive regard–
10. Carl Rogers Client-Centered Therapy positive regard a nonjudgmental caring for the
Genuineness client that is not dependent on
Empathetic the client’s behavior.
understanding Genuineness– realness or
congruence between what the
therapist feels and what he or
she says to the client.
Empathetic understanding– in
which the therapist senses the
feelings and personal meaning
from the client and
communicates this
understanding to the client.
You might also like
- Comprehensive Study Guide For NCEDocument73 pagesComprehensive Study Guide For NCEoscarcortina100% (6)
- Comparison of Freud, Erikson, Piaget, Kohlberg Theories: Developmental PhenomenaDocument3 pagesComparison of Freud, Erikson, Piaget, Kohlberg Theories: Developmental PhenomenaNorashia MacabandingNo ratings yet
- Sigmund Freud Psychosexual Theory Kohlberg's Theory of MoralityDocument1 pageSigmund Freud Psychosexual Theory Kohlberg's Theory of MoralityMary SutingcoNo ratings yet
- Stages of Growth and DevelopmentDocument3 pagesStages of Growth and DevelopmentJaney Cunanan100% (6)
- Theories of Development: Early Childhood)Document3 pagesTheories of Development: Early Childhood)Sofia Marie GalendezNo ratings yet
- Id, Ego, Super-EgoDocument24 pagesId, Ego, Super-EgoHerley Mendez0% (1)
- Psychosexual and Psychosocial Theory of DevelopmentDocument14 pagesPsychosexual and Psychosocial Theory of DevelopmentBea LiberatoNo ratings yet
- Psychoanalytic TheoryDocument9 pagesPsychoanalytic TheoryHeliosNo ratings yet
- Module 3.1 - The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesDocument10 pagesModule 3.1 - The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesMarkhill Veran TiosanNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Learner-Centered Teaching: Module 3 - Review of Theories Related To The Learners' DevelopmentDocument15 pagesFacilitating Learner-Centered Teaching: Module 3 - Review of Theories Related To The Learners' DevelopmentLou Jane YescaNo ratings yet
- Freud Psychoanalytic Theory PDFDocument1 pageFreud Psychoanalytic Theory PDFJackelyn TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Broota K D - Experimental Design in Behavioural Research - 3eDocument26 pagesBroota K D - Experimental Design in Behavioural Research - 3eRANJAN ROY67% (3)
- Freud's Components of The PersonalityDocument6 pagesFreud's Components of The PersonalityCelyn OrapaNo ratings yet
- Theories On Human DevelopmentDocument42 pagesTheories On Human DevelopmentHANS CHRISTIAN DELOS REYESNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing: 33 QuestionsDocument27 pagesReading and Writing: 33 QuestionsWonjae ChungNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment and Management PlanDocument70 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment and Management PlanWael AlmahdiNo ratings yet
- Freud's Psychoanalytic TheoryDocument6 pagesFreud's Psychoanalytic TheoryNina londoNo ratings yet
- ProfEd Reviewer 101Document21 pagesProfEd Reviewer 101Bella NameNo ratings yet
- Bistos BT-550 - CatalogoDocument3 pagesBistos BT-550 - CatalogoRobinsson Tafur FloridaNo ratings yet
- TOP Freud PsychoanalysisDocument3 pagesTOP Freud PsychoanalysisshantyNo ratings yet
- Soft Copy ReviewerDocument17 pagesSoft Copy ReviewerCecilia PejiNo ratings yet
- Educ 101 - Revised Developmental Theories and Other Relevant TheoriesDocument11 pagesEduc 101 - Revised Developmental Theories and Other Relevant TheoriesLi OchiaNo ratings yet
- SOCSCI1 ReviewerDocument6 pagesSOCSCI1 ReviewerCHRISTIAN KAYE UMALINo ratings yet
- Psychosexual Theory - Abms 1Document22 pagesPsychosexual Theory - Abms 1barbiehans14No ratings yet
- TablesDocument4 pagesTablesColeen DajonNo ratings yet
- Human Development TheoryDocument3 pagesHuman Development TheoryMaribel Pascual FloresNo ratings yet
- Personal DevelopmentDocument7 pagesPersonal DevelopmentRenz PanaliganNo ratings yet
- Top WorksheetDocument29 pagesTop WorksheetmaerucelNo ratings yet
- Prefinal - GEC 1 - Understanding The SelfDocument3 pagesPrefinal - GEC 1 - Understanding The SelfKatherine RaferNo ratings yet
- Comparison Theories PDFDocument3 pagesComparison Theories PDFエド パジャロンNo ratings yet
- Child Psychology PedodonticsDocument44 pagesChild Psychology Pedodonticsswechchha gupta100% (1)
- Module 5Document3 pagesModule 5Dhaze OjanoNo ratings yet
- Sarahina CI EDUC2 A2Document8 pagesSarahina CI EDUC2 A2sarahinacamilaNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document3 pagesModule 5Dhaze OjanoNo ratings yet
- Biological and Environmental Factors.": Perdev'T ExamDocument1 pageBiological and Environmental Factors.": Perdev'T ExamMikka RoqueNo ratings yet
- TFN FinalssssDocument2 pagesTFN FinalssssDimple Lexiry GloriaNo ratings yet
- Perdev Q3Document5 pagesPerdev Q3Sam VillegasNo ratings yet
- Developmental Psychology: Don Mariano Marcos Memorial State University College of Arts and SciencesDocument9 pagesDevelopmental Psychology: Don Mariano Marcos Memorial State University College of Arts and SciencesVaflor Esteve KevinNo ratings yet
- UTS D. Until LastDocument10 pagesUTS D. Until LastROWENA VILLAMINNo ratings yet
- Theories PDFDocument3 pagesTheories PDFPunitNo ratings yet
- Session Iv: Theories of PersonalityDocument17 pagesSession Iv: Theories of PersonalitydevipriyaindiaNo ratings yet
- Child PsychologyDocument11 pagesChild PsychologySandeep RajaNo ratings yet
- Developmental Stages and TasksDocument4 pagesDevelopmental Stages and TasksRafaelNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Perspective of Human DevelopmentDocument79 pagesTheoretical Perspective of Human DevelopmentJanice FurioNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Developmental Theories and Other Relevant Theories: I. II. Iii. IV. V. VIDocument15 pagesUnit 3 - Developmental Theories and Other Relevant Theories: I. II. Iii. IV. V. VIPrince AguilarNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument21 pagesReviewermain.marivic.masicapNo ratings yet
- Trocio - Psy 3145 Seniors In-Service Training - Top - Summary of ConceptsDocument12 pagesTrocio - Psy 3145 Seniors In-Service Training - Top - Summary of ConceptsmaerucelNo ratings yet
- About PersonalityDocument36 pagesAbout PersonalityAman SinhaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 To 6 Developmental Theories 1Document22 pagesLesson 3 To 6 Developmental Theories 1Allyson Lois BacucangNo ratings yet
- Raising Our Children, Raising OurselvesDocument2 pagesRaising Our Children, Raising OurselvesTrisha GalangNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Developmental Theories and Other Relevant TheoriesDocument9 pagesUnit 3: Developmental Theories and Other Relevant TheoriesHemera BacarezaNo ratings yet
- Psychological View of The SelfDocument31 pagesPsychological View of The SelfQueen KwengNo ratings yet
- ELERIA - Theories of Personality - Fil Psych NotesDocument41 pagesELERIA - Theories of Personality - Fil Psych NotesKiyo SaitoNo ratings yet
- ReviewersDocument2 pagesReviewersRodeth Ann MendozaNo ratings yet
- GordonDocument6 pagesGordonIzat UmayrahNo ratings yet
- NCM 117 Week 4Document6 pagesNCM 117 Week 4Ljae NatinoNo ratings yet
- Developing The Whole Person Holistic Development I. Physiological Development II. Cognitive DevelopmentDocument2 pagesDeveloping The Whole Person Holistic Development I. Physiological Development II. Cognitive DevelopmentAstxilNo ratings yet
- Devpsy ReviewerDocument15 pagesDevpsy Reviewerfabrigaselijahron.prNo ratings yet
- Psychoanalytic Theory - Sigmund FreudDocument5 pagesPsychoanalytic Theory - Sigmund FreudKesiah SorianoNo ratings yet
- 3-Chriszia Mae AlfonsoDocument29 pages3-Chriszia Mae Alfonsofrondajamaica81No ratings yet
- Beliefs: Knowing Yourself Means Understanding Your StrengthsDocument8 pagesBeliefs: Knowing Yourself Means Understanding Your StrengthsKathy suNo ratings yet
- SIGMUND FREUD: Psychoanalysis: What Is Personality?Document19 pagesSIGMUND FREUD: Psychoanalysis: What Is Personality?CutecutefaceNo ratings yet
- Gecolea, ME143-2 Sample QuestionsDocument25 pagesGecolea, ME143-2 Sample QuestionsJazztine Andrei GecoleaNo ratings yet
- Modeling in Gnu Mathprog Language - A Short Introduction: Paweł Zieli NskiDocument38 pagesModeling in Gnu Mathprog Language - A Short Introduction: Paweł Zieli NskiSeptimus PierreNo ratings yet
- Sample Informational Interview ChecklistDocument1 pageSample Informational Interview ChecklistPhạm TúUyênNo ratings yet
- Comparison of MPPT Algorithms For PV Systems Based DC-DC ConverterDocument11 pagesComparison of MPPT Algorithms For PV Systems Based DC-DC ConverterLeandro SouzaNo ratings yet
- Astrovision May 2020Document81 pagesAstrovision May 2020Poornima100% (1)
- Azrak Pipe ScheduleDocument1 pageAzrak Pipe ScheduleErcan YilmazNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation On Fly Ash Bricks Using Industrial WasteDocument7 pagesExperimental Investigation On Fly Ash Bricks Using Industrial WasteIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Brandix Apparel BD LTD: Hazard Identification and Risk Assesment (HIRA) of Compressor RoomDocument4 pagesBrandix Apparel BD LTD: Hazard Identification and Risk Assesment (HIRA) of Compressor RoomShoaibNo ratings yet
- Week 011-Understanding Data and Ways To Systematically Collect DataDocument13 pagesWeek 011-Understanding Data and Ways To Systematically Collect DataLeona April DarriguezNo ratings yet
- Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences: Naseem Ahmad Charoo, Mark Durivage, Ziyaur Rahman, Mohamad Haitham AyadDocument6 pagesJournal of Pharmaceutical Sciences: Naseem Ahmad Charoo, Mark Durivage, Ziyaur Rahman, Mohamad Haitham Ayadmehrdarou.qaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Municipal Solid WasteDocument5 pagesResearch Paper On Municipal Solid Wasteaflbtrnpf100% (1)
- GCSE Mathematics 1MA1 Problem-Solving Questions 1: Higher TierDocument21 pagesGCSE Mathematics 1MA1 Problem-Solving Questions 1: Higher TierMorena PotenzaNo ratings yet
- Final PSYCH625r5 Wk2 Probability Statistical AnalysisDocument5 pagesFinal PSYCH625r5 Wk2 Probability Statistical AnalysisJessica Paone LaraNo ratings yet
- SYM Starter U04 OSEWorksheetDocument4 pagesSYM Starter U04 OSEWorksheetCarolinaNo ratings yet
- Lexicology Unit 8Document24 pagesLexicology Unit 8Business EnglishNo ratings yet
- Translating Isaac Bashevis SingerDocument4 pagesTranslating Isaac Bashevis SingerDavid StrombergNo ratings yet
- Rubric For Industrial Training Report MGT666 & HRM666 Semester March 2021Document5 pagesRubric For Industrial Training Report MGT666 & HRM666 Semester March 2021Nursyazana AnuarNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Computer Science: Yi Hong, Jiandong Liu, Deying Li, Chuanwen Luo, Mengjie ChangDocument11 pagesTheoretical Computer Science: Yi Hong, Jiandong Liu, Deying Li, Chuanwen Luo, Mengjie ChangDinda AisyNo ratings yet
- CS201 Mathematics For Computer Science I: Manindra Agrawal CS201: Lecture 1Document16 pagesCS201 Mathematics For Computer Science I: Manindra Agrawal CS201: Lecture 1Mohan RaghuNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal Template APADocument8 pagesResearch Proposal Template APASameen FaisalNo ratings yet
- The Horace Mann Record: Model Congress Hosts First ConferenceDocument6 pagesThe Horace Mann Record: Model Congress Hosts First ConferenceJeff BargNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Measurement and Vectors PDFDocument27 pagesUnit 1 Measurement and Vectors PDFSharneet ChettyNo ratings yet
- DESIGNDocument29 pagesDESIGNerick kazindukiNo ratings yet
- Krauss - Photography's Discursive Spaces - Landscape-View - 1982Document10 pagesKrauss - Photography's Discursive Spaces - Landscape-View - 1982Noam GonnenNo ratings yet
- Re91485 2016-10 PDFDocument108 pagesRe91485 2016-10 PDFNicolas AguilarNo ratings yet
- Processes of Ideal GasesDocument20 pagesProcesses of Ideal Gasesemmarie llantinoNo ratings yet