Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 2 - Signals
Uploaded by
hanxingg 020 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views9 pagesThis document provides an overview of key concepts related to signals, including:
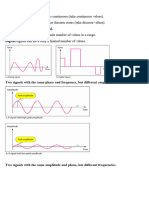
- Analog signals are continuous while digital signals take on discrete values.
- Periodic signals repeat over time while nonperiodic signals do not.
- Frequency and period are inverses, with examples of calculating period from frequency and vice versa.
- Phase describes the position of a waveform relative to a reference point in time.
- Signals can be represented in both the time and frequency domains, with a full sine wave in time domain appearing as a single spike in the frequency domain.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of key concepts related to signals, including:
- Analog signals are continuous while digital signals take on discrete values.
- Periodic signals repeat over time while nonperiodic signals do not.
- Frequency and period are inverses, with examples of calculating period from frequency and vice versa.
- Phase describes the position of a waveform relative to a reference point in time.
- Signals can be represented in both the time and frequency domains, with a full sine wave in time domain appearing as a single spike in the frequency domain.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views9 pagesTutorial 2 - Signals
Uploaded by
hanxingg 02This document provides an overview of key concepts related to signals, including:
- Analog signals are continuous while digital signals take on discrete values.
- Periodic signals repeat over time while nonperiodic signals do not.
- Frequency and period are inverses, with examples of calculating period from frequency and vice versa.
- Phase describes the position of a waveform relative to a reference point in time.
- Signals can be represented in both the time and frequency domains, with a full sine wave in time domain appearing as a single spike in the frequency domain.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
Tutorial 2
Quick Recap
• To be transmitted, data must be transformed to electromagnetic signals.
• The term analog signal refers to information that is continuous; digital signal
refers to information that has discrete states.
• Analog signal take on continuous values. Digital signal take on discrete values.
• Periodic and Nonperiodic Signals
• In data communications, we commonly use periodic analog signals and nonperiodic
digital signals.
Time period and frequency
• Frequency and period are the inverse of each
other.
• The power we use at home has a frequency of 60
Hz. The period of this sine wave can be
determined as follows:
Phase
• Phase describes the position of the
waveform relative to time 0.
Time and Frequency domain
• A complete sine wave in the time domain can be represented by one single
spike in the frequency domain.
Units of period and frequency
1. Given the frequencies listed below, calculate the corresponding periods.
a) 24Hz
b) 8 MHz
c) 40 KHz
2. Given the following periods, calculate the corresponding frequencies.
a. 5 s
b. 220 ns
3. Express a period of 100 ms in microseconds.
4. The period of a signal is 100 ms. What is its frequency in kilohertz?
Signal
1. Draw a sine wave with a frequency of 1Hz. Label this “Sine 1”
2. Draw a sine wave 90 degrees ahead of the earlier wave. Label this “Sine 2”.
3. Draw a sine wave double the frequency of Sine 1.
4. Draw another sine wave half the frequency of Sine 1.
5. Draw another sine wave double the amplitude of Sine 1.
6. Draw another sine wave half the amplitude of Sine 1.
7. Comparing Sine 1 and Sine 2, which sine wave will complete one cycle first? If so,
why?
Signals
8. Draw two sine wave and add them together. The sine wave are as follows
a) F(x) = sin (x)
b) G(x) = sin (x + π/2)
9. What is the phase shift for the foIlowing?
a) A sine wave with the maximum amplitude at time zero
b) A sine wave with maximum amplitude after 1/4 cycle
c) A sine wave with zero amplitude after 3/4 cycle and increasing
Review Questions
1. Differentiate between an analog and a digital signal.
2. What are three important characteristics of an analog signal?
3. How many radians are there in a complete circle of 360 degrees?
4. What is the relationship between the wavelength and frequency of a sine wave?
5. What is the relationship between a spectrum and its bandwidth?
You might also like
- DC Module2 (Chapter1)Document71 pagesDC Module2 (Chapter1)Mayank RajNo ratings yet
- Analog Digital Chap3Document50 pagesAnalog Digital Chap3NirmalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ExercisesDocument3 pagesChapter 3 ExercisesarrgantenNo ratings yet
- Tutorial2 ModelanswerDocument5 pagesTutorial2 ModelanswerIhsan ul HaqNo ratings yet
- DDDocument284 pagesDDawaazdevNo ratings yet
- 3-Data and SignalDocument48 pages3-Data and SignalIman FahimNo ratings yet
- Data Transmission CH 2Document71 pagesData Transmission CH 2Prïñčé Äl ŜåmádNo ratings yet
- DataCommunication (5CCI02) Module2 Part1Document131 pagesDataCommunication (5CCI02) Module2 Part1hafsatamer03No ratings yet
- Week 04 SignalDocument36 pagesWeek 04 SignalikonNo ratings yet
- Physical Layer and MediaDocument56 pagesPhysical Layer and MediaVarunNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital DataDocument11 pagesAnalog and Digital DatamgayananNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 2Document73 pagesPertemuan 2GalihNo ratings yet
- D Ata & SignalsDocument20 pagesD Ata & Signalssectheta01No ratings yet
- 1 Signal Transmission 2.2Document7 pages1 Signal Transmission 2.2mrx3925No ratings yet
- DCN Unit - 2Document143 pagesDCN Unit - 2Rohan SaiNo ratings yet
- Name: Hassan Ahmed Khan Roll No: 201907008 Section: 6 SemesterDocument3 pagesName: Hassan Ahmed Khan Roll No: 201907008 Section: 6 SemesterHassan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Signals: Data Communication & Networking Mca 2 Sem. 2021Document28 pagesSignals: Data Communication & Networking Mca 2 Sem. 2021Rahul AryanNo ratings yet
- CMSC 137 Lecture Notes 3Document21 pagesCMSC 137 Lecture Notes 3Rheymart TugadoNo ratings yet
- Analog SignalsDocument20 pagesAnalog SignalsLenard Erasmo Mari MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document16 pagesLecture 3mzmalek6No ratings yet
- Data Communication: Data Communications and Networking, 4rd Edition, Behrouz A. ForouzanDocument59 pagesData Communication: Data Communications and Networking, 4rd Edition, Behrouz A. ForouzanJakia ChyNo ratings yet
- Seismic Processing 3Document169 pagesSeismic Processing 3Temitayo Ologun100% (1)
- 3.10 Practice Set: Review QuestionsDocument4 pages3.10 Practice Set: Review QuestionsscpNo ratings yet
- Data Communication & Networking NotesDocument13 pagesData Communication & Networking NotesEman100% (1)
- Chapter 3Document62 pagesChapter 3dhewk98No ratings yet
- Introduction To Physical LayerDocument96 pagesIntroduction To Physical LayerBimal GajeraNo ratings yet
- Nor Azimah Khalid FSKM, Uitm Shah AlamDocument50 pagesNor Azimah Khalid FSKM, Uitm Shah AlamNOl ShAnahNo ratings yet
- CSU07204-Lecture 4.CSU07204-Physical Layer-AnalogDocument46 pagesCSU07204-Lecture 4.CSU07204-Physical Layer-AnalogElikana BarikiNo ratings yet
- Data and SignalsDocument58 pagesData and SignalsBilal AwanNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document56 pagesLec 2AbdullahNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering & Technology: Heet ATA RansmissionDocument2 pagesCollege of Engineering & Technology: Heet ATA RansmissionAyu Hotmaida NaiborhuNo ratings yet
- Lect. 04. Data and SignalDocument56 pagesLect. 04. Data and SignalSoy ChandaraNo ratings yet
- Ch03 Introduction To Physical LayerDocument69 pagesCh03 Introduction To Physical LayerBilal MughalNo ratings yet
- Semana 05: Conceptos de RadiofrecuenciaDocument58 pagesSemana 05: Conceptos de RadiofrecuenciaciberfoxNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital SignalsDocument32 pagesAnalog and Digital SignalsMehran ShabeerNo ratings yet
- 1 Computer Networks Data and Signals 3rdDocument39 pages1 Computer Networks Data and Signals 3rdMuhammad Taha AamirNo ratings yet
- Unit-2:: Physical LayerDocument44 pagesUnit-2:: Physical LayerVishal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 ITT400 CS2302A Group 4Document10 pagesTutorial 1 ITT400 CS2302A Group 4fatin farhanahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Data and Signals Exercise Question With SolutionDocument10 pagesChapter 3 Data and Signals Exercise Question With SolutionStevs Shamim100% (3)
- EE366-Digital Signal Processing: Muhammad Nafees NaveedDocument44 pagesEE366-Digital Signal Processing: Muhammad Nafees NaveedAyesha KhanNo ratings yet
- Periodic Analog SignalsDocument3 pagesPeriodic Analog Signalsroysayanccp05No ratings yet
- Chap 3Document39 pagesChap 3Siti ZulaikhaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Data Communication PrinciplesDocument19 pagesUnit 2 Data Communication PrinciplesMarumamula Santosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document1 pageTutorial 1DanielNo ratings yet
- Waves: Name - TeacherDocument47 pagesWaves: Name - TeachersaadNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - Signals (More)Document6 pagesTutorial 3 - Signals (More)hanxingg 02No ratings yet
- Data and SignalsDocument54 pagesData and SignalsFr SunnyNo ratings yet
- Data Communication & NetworksDocument52 pagesData Communication & NetworksSajid MumtazNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02-Physical Layer-Transmission Terminology-1920Document80 pagesLecture 02-Physical Layer-Transmission Terminology-1920Arvin 97No ratings yet
- 3.3 Waves AnswersDocument66 pages3.3 Waves Answersmarkmattesz06No ratings yet
- Physical Layer - Data & Signals: M.S. H Hu NH PhongDocument96 pagesPhysical Layer - Data & Signals: M.S. H Hu NH PhongrerNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Raza POC Lab 3 Sir Hamza Saleem 18/04/2021Document5 pagesMuhammad Raza POC Lab 3 Sir Hamza Saleem 18/04/2021ziaulhaqNo ratings yet
- 2nd Week Data Communications Data and SignalsDocument24 pages2nd Week Data Communications Data and SignalsIvano Harris WidwiarsantoNo ratings yet
- CSE 315 Lecture-No.3 (Spring 2022) - Transmission Media and Channel CapacityDocument63 pagesCSE 315 Lecture-No.3 (Spring 2022) - Transmission Media and Channel CapacityShajjad Hossain ShisherNo ratings yet
- Analog DigitalDocument30 pagesAnalog DigitalReggie GustiloNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform Experiment ManualDocument10 pagesFourier Transform Experiment Manualf20212358No ratings yet
- Chapter - 3Document44 pagesChapter - 3B72l7nanNo ratings yet
- JBL Audio Engineering for Sound ReinforcementFrom EverandJBL Audio Engineering for Sound ReinforcementRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Tutorial 5 - Transmission Media (Unguided)Document7 pagesTutorial 5 - Transmission Media (Unguided)hanxingg 02No ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - Signals (More)Document6 pagesTutorial 3 - Signals (More)hanxingg 02No ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 - Transmission Media & Channel CapacityDocument5 pagesTutorial 4 - Transmission Media & Channel Capacityhanxingg 02No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document9 pagesTutorial 1hanxingg 02No ratings yet
- (Ultrasonic Technology) K. A. Naugol'nykh (Auth.), L. D. Rozenberg (Eds.) - High-Intensity Ultrasonic Fields-Springer US (1971) PDFDocument419 pages(Ultrasonic Technology) K. A. Naugol'nykh (Auth.), L. D. Rozenberg (Eds.) - High-Intensity Ultrasonic Fields-Springer US (1971) PDFAcbal AchyNo ratings yet
- GE Krautkramer USN58L BrochureDocument2 pagesGE Krautkramer USN58L BrochureIslamNo ratings yet
- Ic 60 Users Manual V1.0 111008Document32 pagesIc 60 Users Manual V1.0 111008Eric Sanhueza GuíñezNo ratings yet
- XR2206 DIY Kit ManualDocument13 pagesXR2206 DIY Kit ManualCol Sanjay BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Relay Js PanasonicDocument4 pagesRelay Js Panasonicsalimos12No ratings yet
- Ee-8661 Power Electronics and Drives Lab ManualDocument88 pagesEe-8661 Power Electronics and Drives Lab ManualgangshNo ratings yet
- EPOCH 600 Training Presentation 3-2014Document193 pagesEPOCH 600 Training Presentation 3-2014Jhon R CPNo ratings yet
- Basic Vibration Analysis IDocument43 pagesBasic Vibration Analysis ISUNILNo ratings yet
- New 2 Si Doping in GaN PDFDocument4 pagesNew 2 Si Doping in GaN PDFQazi Zahid HusainNo ratings yet
- Oscilaoscopio OS-5040B 40MHz Manual OperaçãoDocument30 pagesOscilaoscopio OS-5040B 40MHz Manual OperaçãoanselmoNo ratings yet
- Zero Crossing Rate PDFDocument7 pagesZero Crossing Rate PDFPaul HeatchoteNo ratings yet
- Power Systems PDFDocument172 pagesPower Systems PDFSiva Agora KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- 100 Minute 100 Questions With Solution.-1Document27 pages100 Minute 100 Questions With Solution.-1shubhamNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document16 pagesCH 5Iratechaos100% (1)
- GBPC3562 PDFDocument6 pagesGBPC3562 PDFSantosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Fluke 164Document10 pagesFluke 164maxbit77No ratings yet
- S C S C: Ignal Onditioning and Ignal OnditionersDocument22 pagesS C S C: Ignal Onditioning and Ignal OnditionersWan LynnNo ratings yet
- Ac PDFDocument159 pagesAc PDFArunNo ratings yet
- Electrical Workshop: Module 4: Study of Measurement and Test EquipmentDocument24 pagesElectrical Workshop: Module 4: Study of Measurement and Test EquipmentMark RyceNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document209 pagesModule 1Athulya M ArunNo ratings yet
- AM TheoryDocument60 pagesAM TheoryChiranjivi KuthumiNo ratings yet
- Effect of Light On GravityDocument5 pagesEffect of Light On GravityDezso SarkadiNo ratings yet
- Motors:: The Past Is PresentDocument6 pagesMotors:: The Past Is Presenteko bagus sunaryoNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 1st Sep 2021 Shift 2 Physics EmbibeDocument12 pagesJEE Main 1st Sep 2021 Shift 2 Physics EmbibeDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- A Practical Approach To The Interpretation of Cement Bond Logs @Document10 pagesA Practical Approach To The Interpretation of Cement Bond Logs @Gilberto Garcia de la PazNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On Skinput TechnologyDocument19 pagesSeminar Report On Skinput TechnologyNISHANo ratings yet
- Predict The Frequency and Magnitude of The Primary Phase Truncation SpurDocument4 pagesPredict The Frequency and Magnitude of The Primary Phase Truncation Spurravi010582No ratings yet
- Adaptive Delta ModulationDocument15 pagesAdaptive Delta ModulationVinita DahiyaNo ratings yet
- Electrohydraulic Proportional Controls: User's Guidelines: A Due Stadi, Pilotate, Dimensioni ISO/Cetop 07 e 08Document5 pagesElectrohydraulic Proportional Controls: User's Guidelines: A Due Stadi, Pilotate, Dimensioni ISO/Cetop 07 e 08haggNo ratings yet
- Signals and Data TransferDocument73 pagesSignals and Data TransferVinod GandhiNo ratings yet