Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Voltage Regulator 1666433031610
Uploaded by
Prashon G0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views4 pagesOriginal Title
voltage_regulator_1666433031610
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views4 pagesVoltage Regulator 1666433031610
Uploaded by
Prashon GCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
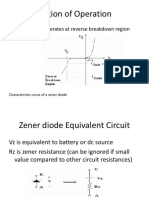
ZenerDiode
A Zener Diode is a special kind of diode which permits current to flow
in the forward direction as normal, but will also allow it to flow in the
reverse direction when the voltage is above the breakdown voltage or
‘zener’ voltage.
Zener diodes are designed so that their breakdown voltage is much
lower - for example just 2.4 Volts.
Function of Zener Diode
1. Zener diodes are a special kind of diode which permits current to
flow in the forward direction.
2. Zener diodes will also allow current tto
o flow in the reverse direction
when the voltage is above a certain value. This breakdown voltage
is known as the Zener voltage. In a standard diode, the Zener
voltage is high, and the diode is permanently damaged if a reverse
current above that value is aallowed to pass through it.
3. In the reverse bias direction, there is practically no reverse current
flow until the breakdown voltage is reached. When this occurs
there is a sharp increase in reverse current. Varying amount of
reverse current can pass through the diode without damaging it.
The breakdown voltage or zener voltage (VZVZ) across the diode
remains relatively constant.
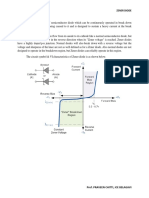
Zener Diode As A Voltage Regulator
A voltage regulator is an electronic circuit that provides a stable DC
voltage independent of tthehe load current, temperature and AC line
voltage variations.. A Zener diode of break down voltage VZ is reverse
connected to an input voltage source VI across a load resistance RL and a
series resistor RS. The voltage across the zener will remain steady at its
break down voltage VZ for all the values of zener current IZ as long as
the current remains in the break down region. Hence a regulated DC
output voltage V0=VZ is obtained across RL, whenever the input
voltage remains within a minimum and maximum volt voltage.
age.
Basically there are two type of regulations such as:
Line Regulation: In this type of regulation, series resistance and load
resistance are fixed, only input voltage is changing
changing.. Output voltage
remains the same as long as the input voltage is maintained
maintai above a
minimum value.
Load Regulation: In this type of regulation, input voltage is fixed and
the load resistance is varying. Output volt remains same, as long as the
load resistance is maintained above a minimum value.
Line Regulation Load Regulation
Figure:3
In Line Regulation, Load resistance is constant and input voltage
varies. VI must be sufficiently large to turn the Zener Diode ON.
ON
VL= VZ = VImin×RL / (RS+RL)
So, the minimum turn-on
on voltage VImin is :
VImin = VZ×(RS+RL)/RL
The maximum value of VI is limited by the maximum zener current IZmax
IRmax = IZmax+IL
IL is fixed at :
VZ/RL, Since,VL=VZ
So maximum VI is
VImax = VRmax+VZ
or,
VImax = IRmax×R+VZ
For VI<VZ, VO=VI
For VI>VZ, VO=VI−IS×RS
Load Regulation
In Load Regulation, input voltage is constant and Load resistance
varies. Too small a Load Resistance RL, will result in VTh<VZ and Zener
Diode will be OFF.
VL=VZ=VImin×RL/(RS+RL)
So the minimum load resistance RL
RLmin = VZ×RS / VI−VZ
Any load resistance greater than R Lmin will make Zener Diode ON
IS=IL+IZ
RLmin will establish maximum IL as
ILmax = VL/RLmin = VZ/RLmin Since,VL=VZ
VS is the voltage drop across RS
VS=VImin−VZ
IS=VImin−VZ/RS
For RL < RLmin,
VO=VI
For RL > RLmin,
VO=VI−IS×RS
You might also like
- Practical File: Applied SciencesDocument12 pagesPractical File: Applied Scienceschikni babliNo ratings yet
- ANALOG ELECTRONICS LAB: ZENER DIODE & BJT EXPERIMENTSDocument21 pagesANALOG ELECTRONICS LAB: ZENER DIODE & BJT EXPERIMENTSdivye guptaNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode As Voltage RegulatorDocument2 pagesZener Diode As Voltage RegulatorAMIT KUMAR SINGHNo ratings yet
- Chapter I - RegulatorsDocument14 pagesChapter I - RegulatorsironmarkNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument6 pagesZener DiodeKumar shantanu BasakNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument36 pagesZener DiodeSurajguptarocks100% (1)
- Zener Diode Voltage RegulationDocument5 pagesZener Diode Voltage RegulationJoshua DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode Voltage Regulator ExplainedDocument3 pagesZener Diode Voltage Regulator ExplainedSURESH SURAGANINo ratings yet
- DIODE ZENER CIRCUIT AND APPLICATIONSDocument15 pagesDIODE ZENER CIRCUIT AND APPLICATIONSNurul HudaNo ratings yet
- Exp2 ZenerDocument6 pagesExp2 ZenerEdward Sevilla Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document81 pagesUnit 1Eswar suryaNo ratings yet
- Maintain Stable Power with Line and Load RegulationDocument4 pagesMaintain Stable Power with Line and Load RegulationAbhayNo ratings yet
- Zener RegulatorDocument3 pagesZener RegulatorBIBI MOHANANNo ratings yet
- BE UNIT-IIDocument12 pagesBE UNIT-IIhenryhorrid384No ratings yet
- Zener Diode AppliationsDocument19 pagesZener Diode AppliationsKartik GuptaNo ratings yet
- Voltage Regulators:: Fig - Zener Voltage RegulatorDocument7 pagesVoltage Regulators:: Fig - Zener Voltage RegulatorRamesh SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics-BTAB02003 MPSTME-NMIMS Shirpur Campus: Sem II (2015-16)Document20 pagesBasic Electronics-BTAB02003 MPSTME-NMIMS Shirpur Campus: Sem II (2015-16)virat gautamNo ratings yet
- Some Important and Interesting Topics: Ac & DCDocument3 pagesSome Important and Interesting Topics: Ac & DCsyed-md-shamsul-arifeen-459No ratings yet
- Region of Operation: - Zener Diode Operates at Reverse Breakdown RegionDocument16 pagesRegion of Operation: - Zener Diode Operates at Reverse Breakdown RegionRein AbreraNo ratings yet
- The Zener DiodeDocument4 pagesThe Zener DiodeKeshav JhaNo ratings yet
- Electronics-Tutorials - Ws-The Zener DiodeDocument10 pagesElectronics-Tutorials - Ws-The Zener DiodeVenki EdeNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodesDocument12 pagesZener DiodesnardnardNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode As Voltage Regulator (Theory)Document6 pagesZener Diode As Voltage Regulator (Theory)Rethika JeganNo ratings yet
- +zener Voltage RegulationDocument4 pages+zener Voltage RegulationtrshaaaNo ratings yet
- Voltage RegulatorDocument19 pagesVoltage RegulatorParth Upadhyay NokashichiriNo ratings yet
- CH 2 (Support) Power Supply CircuitsDocument30 pagesCH 2 (Support) Power Supply CircuitsFazreen Ahmad FuziNo ratings yet
- Zener Diodes Problems NotesDocument20 pagesZener Diodes Problems Notespsathishkumar1232544No ratings yet
- Zener Diode Tutorial: Understanding Voltage Regulation and Clipping CircuitsDocument7 pagesZener Diode Tutorial: Understanding Voltage Regulation and Clipping Circuitscelo81No ratings yet
- Ece20l 07Document7 pagesEce20l 07Diane Carina MendozaNo ratings yet
- ECE 201: Electronics I Semiconductors, PN Junction and DiodesDocument65 pagesECE 201: Electronics I Semiconductors, PN Junction and DiodesSameh AtallahNo ratings yet
- Lectures On Diodes 3Document14 pagesLectures On Diodes 3Tt RrtNo ratings yet
- Voltage Regulators ZenersDocument9 pagesVoltage Regulators Zenersnadlz3No ratings yet
- Zener Diode Applications 1. Zener Diode As A VoltageDocument3 pagesZener Diode Applications 1. Zener Diode As A VoltageSaravananNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode: As Voltage RegulatorDocument39 pagesZener Diode: As Voltage RegulatorRey Francis FamulaganNo ratings yet
- BEEE UNIT IV - Lecture 6Document31 pagesBEEE UNIT IV - Lecture 6Girish Shankar MishraNo ratings yet
- DiodeApplications 1spDocument32 pagesDiodeApplications 1spHakkı AKYÜZNo ratings yet
- CHAP 3 - Zener DiodeDocument65 pagesCHAP 3 - Zener DiodeAnees Ahmad100% (1)
- The Zener DiodeDocument8 pagesThe Zener DiodemaanibrahimNo ratings yet
- 2.08 Zener Diode Used As Voltage RegulatorDocument1 page2.08 Zener Diode Used As Voltage RegulatorVamsiMadupuNo ratings yet
- Special-Purpose Diodes: Zener, Varactor and Optical DiodesDocument45 pagesSpecial-Purpose Diodes: Zener, Varactor and Optical DiodesAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Electronic AnalysisDocument29 pagesElectronic Analysishabibur rahman khanNo ratings yet
- Zener PracticalDocument6 pagesZener PracticalAzim KhanNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument5 pagesZener DiodePraveen ChittiNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document31 pagesLab 3張博翔No ratings yet
- CHAP 1 - Zener DiodeDocument65 pagesCHAP 1 - Zener Diodeksreddy2002No ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document8 pagesChapter 10Captain AmericaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Diode Circuits (Clippers)Document12 pagesChapter 2 - Diode Circuits (Clippers)Devaraj VignesvaranNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument15 pagesZener DiodeTawki BakiNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode Voltage Regulation GuideDocument10 pagesZener Diode Voltage Regulation GuideAce HighNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode As A WaveshaperDocument15 pagesZener Diode As A WaveshaperpriyaNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Regulation With The Zener DiodeDocument5 pages5.1 Regulation With The Zener DiodeRMK BrothersNo ratings yet
- 07-Series RegulatorDocument4 pages07-Series Regulatormuraliece muralieceNo ratings yet
- The Zener Diode Voltage RegulatorDocument11 pagesThe Zener Diode Voltage RegulatorHuri MughalNo ratings yet
- Chapter3.PDFDocument69 pagesChapter3.PDFj2yshjzzsxNo ratings yet
- Name: Vikash Raj SCHOLAR ID: 2113047 Course: Btech 2 SEM Subject Code: Ec 111Document15 pagesName: Vikash Raj SCHOLAR ID: 2113047 Course: Btech 2 SEM Subject Code: Ec 111Felix KholhringNo ratings yet
- Output Voltage: VT Ve V Ve TLDocument2 pagesOutput Voltage: VT Ve V Ve TLRaghul RNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument8 pagesZener Diodekumar_9583No ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Metal Casting Processes-NVRDocument287 pagesUnit - 1 Metal Casting Processes-NVRPrashon GNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Cell Biology PDF 1669094660463Document113 pagesUnit 3 Cell Biology PDF 1669094660463Prashon GNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Notes 1668156102805Document76 pagesUnit 3 Notes 1668156102805Prashon GNo ratings yet
- MICROBIAL NUTRITION, GROWTH AND METABOLISMDocument31 pagesMICROBIAL NUTRITION, GROWTH AND METABOLISMPrashon GNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Probaiblity Random Varibles 1668156176285Document107 pagesUnit 4 Probaiblity Random Varibles 1668156176285Prashon GNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Problem Based On NPTEL 1665212445323Document23 pagesUnit 2 Problem Based On NPTEL 1665212445323Prashon GNo ratings yet
- MI Unit 1 2022 1662623571633Document108 pagesMI Unit 1 2022 1662623571633Prashon GNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Upload 1 1601876564420 1 1606990038157 1666265103888Document29 pagesUnit 3 Upload 1 1601876564420 1 1606990038157 1666265103888Prashon GNo ratings yet
- MI Unit 2 2022 Lecture Material 1665212363262Document115 pagesMI Unit 2 2022 Lecture Material 1665212363262Prashon GNo ratings yet
- Edc 1663667070358Document1 pageEdc 1663667070358Prashon GNo ratings yet
- Maths 2Document5 pagesMaths 2Prashon GNo ratings yet
- Limiting Error Problem 1663238067304Document34 pagesLimiting Error Problem 1663238067304Prashon GNo ratings yet
- Final Hydrogen Fuel Cell VehicleDocument8 pagesFinal Hydrogen Fuel Cell VehiclePrashon GNo ratings yet
- Measuring Instruments Static CharacteristicsDocument9 pagesMeasuring Instruments Static CharacteristicsPrashon GNo ratings yet
- 2N60 Series: N-Channel Power MosfetDocument8 pages2N60 Series: N-Channel Power MosfetMarcos PrestesNo ratings yet
- Dsa0066344 PDFDocument6 pagesDsa0066344 PDFJosé AdelinoNo ratings yet
- FireFinder PLUS Fire Brigade Response GuideDocument128 pagesFireFinder PLUS Fire Brigade Response GuidePeter van der BurgNo ratings yet
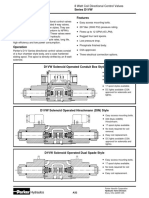
- Proportional Pressure Relief Valve Poppet Type, Direct-Acting, Metric Cartridge - 350 BarDocument4 pagesProportional Pressure Relief Valve Poppet Type, Direct-Acting, Metric Cartridge - 350 BarSakahi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electronics: A Telemetry, Tracking, and Command Antennas System For Small-Satellite ApplicationsDocument15 pagesElectronics: A Telemetry, Tracking, and Command Antennas System For Small-Satellite ApplicationsDavid KenyoNo ratings yet
- Martina: Available Colors For This VersionDocument2 pagesMartina: Available Colors For This VersionUmeshNo ratings yet
- Bray s70 OM ManualDocument23 pagesBray s70 OM ManualRoberto Reyes LaraNo ratings yet
- Network Topology NoteDocument12 pagesNetwork Topology NoteHaftamu HailuNo ratings yet
- Using Cadence Virtuoso IC617 To Simulate VI Characteristic CurveDocument15 pagesUsing Cadence Virtuoso IC617 To Simulate VI Characteristic Curvecarpet909No ratings yet
- Lightening Arrester 500kVTest Report EnglishDocument20 pagesLightening Arrester 500kVTest Report Englishashwani2101No ratings yet
- Vlsi Final Notes Unit4Document21 pagesVlsi Final Notes Unit4RohitParjapatNo ratings yet
- 0l1500 B SMM ModuleDocument2 pages0l1500 B SMM ModulereinaldomdNo ratings yet
- Tufting Gun User ManualDocument11 pagesTufting Gun User Manualgabs100% (6)
- 2502 A 002Document10 pages2502 A 002Mohamed ElmakkyNo ratings yet
- Real Case: Lithium Ion NMC-2170 Battery CellDocument15 pagesReal Case: Lithium Ion NMC-2170 Battery CellValic GuiterezNo ratings yet
- IRF540 N-Channel Power MOSFETDocument6 pagesIRF540 N-Channel Power MOSFETAntonio Carlos BassoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Guido GonzalezDocument10 pagesUnit 1 Guido GonzalezGuido Gonzalez PosadaNo ratings yet
- Design Studio: Shin Yang Development SDN BHDDocument1 pageDesign Studio: Shin Yang Development SDN BHDcRi SocietyNo ratings yet
- Eaton 290376 NZMH4 VE800 S1 en - GBDocument10 pagesEaton 290376 NZMH4 VE800 S1 en - GBkarthik01heroNo ratings yet
- Project DefinitionsDocument29 pagesProject Definitionsabhiram403No ratings yet
- STi7105 PDFDocument313 pagesSTi7105 PDFkernuNo ratings yet
- Sohail CV PDFDocument3 pagesSohail CV PDFSohail LarikNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Filters: Engr RenDocument29 pagesLesson 3 - Filters: Engr RenRennel MallariNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis and Power CalculationDocument13 pagesCircuit Analysis and Power CalculationThiv TriNo ratings yet
- Micrologic 2.3 630ADocument2 pagesMicrologic 2.3 630ADEADMANNo ratings yet
- HV Power Cable TestDocument9 pagesHV Power Cable TestMohammad Nasar100% (1)
- DAHandbook SectionDocument20 pagesDAHandbook SectionbpchimeraNo ratings yet
- Pat Document BnjpoDocument64 pagesPat Document BnjpoMohammadNo ratings yet
- Virtual-Circuit Networks: Frame Relay and ATMDocument24 pagesVirtual-Circuit Networks: Frame Relay and ATMdil_18100% (1)
- DIS-300G Series Managed Industrial Gigabit Ethernet Switch Quick Installation GuideDocument8 pagesDIS-300G Series Managed Industrial Gigabit Ethernet Switch Quick Installation GuideproletproletNo ratings yet