Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A2 14.2 Circuit Switching Packet Switching
Uploaded by
Maryam NuurCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A2 14.2 Circuit Switching Packet Switching
Uploaded by
Maryam NuurCopyright:
Available Formats
Compiled by: Ghaus Muhammad Maqsood – Headstart school ISB
14 Communication and internet technologies
14.2 Circuit switching, packet switching
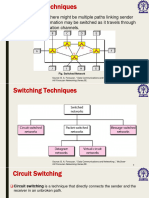
Circuit switching v/s packet switching:
Circuit switching is a type of switching in which a dedicated channel or circuit is established
for the duration of communications, a method used by the old traditional telephone call-
carried over the public switched telephone network (PSTN) it is also referred to as the plain
old telephone service (POTS).
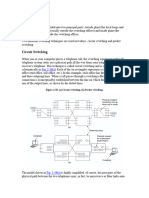
Working of circuit switching:
A traditional telephone network
The PSTN networks are connected through central offices which act as telephone exchanges,
each serving a certain geographical area. For example, person A calls to person B:
1|Circuit-switched v/s packet-switched networks – Chapter 14
Compiled by: Ghaus Muhammad Maqsood – Headstart school ISB
The telephone network is trying different circuits to find an available channel.
A connection must be established before they start their conversations.
Once the channel is decided, it guarantees the full bandwidth and remains connected for the
duration of the communication session until users terminate their connections. When you are
making a traditional/PSTN call, you are actually renting the lines. That is why international
telephone call or long distance phone call was expensive.
Working of Packet switching:
Packet switching uses different methods.
Packet switching networks are connected through many routers
2|Circuit-switched v/s packet-switched networks – Chapter 14
Compiled by: Ghaus Muhammad Maqsood – Headstart school ISB
Each router is serving different segment of networks.
Data is broken into packets before it is transported.
3|Circuit-switched v/s packet-switched networks – Chapter 14
Compiled by: Ghaus Muhammad Maqsood – Headstart school ISB
In packet switching, packets can travel any path on the network to their destination because
each packet contains an IP address and sequencing information. Therefore they don’t need
to follow each other, they can travel any network path and they can find the fastest channel
available at any instant. They don’t need to arrive in sequence because they can re-
assemble together at the destination.
(a)
(b)
The internet is based on a packet switching protocol. TCP/IP
Circuit-switched networks and packet-switched networks have traditionally occupied different
spaces within corporations.
Circuit-switched networks are ideal for communication which requires data to be transmitted
in real-time (video conferencing for example).
4|Circuit-switched v/s packet-switched networks – Chapter 14
Compiled by: Ghaus Muhammad Maqsood – Headstart school ISB
Packet switched networks are more flexible and more efficient if some amount of delay is
acceptable (e-mail for example).
The circuit-switched networks are normally used for traditional telephone calls while the
packet-switched networks normally handle digital data.
But nowadays, you can get phone service delivered over the internet just like digital data
packets. This new technology is called Voice over IP or simply VOIP.
5|Circuit-switched v/s packet-switched networks – Chapter 14
You might also like
- Packet SwitchingDocument21 pagesPacket SwitchingMuhammad Faiz MasroorNo ratings yet
- ch4Document49 pagesch4zekiNo ratings yet
- 05 Communication Fundamentals B PDFDocument20 pages05 Communication Fundamentals B PDFRobinNo ratings yet
- Circuit-Switched vs Packet-Switched Networks ExplainedDocument23 pagesCircuit-Switched vs Packet-Switched Networks ExplainedswethaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document9 pagesTutorial 4susmita lamsalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SwitchingDocument103 pagesChapter 2 SwitchingmulugetaNo ratings yet
- Nat142 ADocument15 pagesNat142 AAnin MembreveNo ratings yet
- Assignment-01: Student ID: 170021038Document4 pagesAssignment-01: Student ID: 170021038Muntequa Imtiaz Siraji, 170021038No ratings yet
- A Wide Area NetworkDocument16 pagesA Wide Area NetworkDeejay Jay MehtaNo ratings yet
- Packet SwitchingDocument72 pagesPacket SwitchingSalman JawedNo ratings yet
- Cs52 Computer Networks Unit Iii 9 Circuit Switching vs. Packet Switching / Packet Switched Networks - IP - ARP - RARP - DHCP - ICMPDocument33 pagesCs52 Computer Networks Unit Iii 9 Circuit Switching vs. Packet Switching / Packet Switched Networks - IP - ARP - RARP - DHCP - ICMPsamueljamespeterNo ratings yet
- Network Layer Design IssuesDocument6 pagesNetwork Layer Design Issuessravan kumarNo ratings yet
- Week # 04: Data Communication & NetworkDocument32 pagesWeek # 04: Data Communication & NetworkSaad Ashfaq XaadNo ratings yet
- Wireless Mobile Network AssignmentDocument9 pagesWireless Mobile Network AssignmentCHALCHISA TAMIRUNo ratings yet
- Performance Enhancement of TCP in Mobile IP Based Networks: Satish@whut - Edu.cn Xuwenjun@whut - Edu.cnDocument6 pagesPerformance Enhancement of TCP in Mobile IP Based Networks: Satish@whut - Edu.cn Xuwenjun@whut - Edu.cnSatish NaiduNo ratings yet
- General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Document8 pagesGeneral Packet Radio Service (GPRS)DeepakNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii: Telephony: Multiplexing-WDM, TDM, FDM, Switching Data Link Control ProtocolsDocument84 pagesUnit-Iii: Telephony: Multiplexing-WDM, TDM, FDM, Switching Data Link Control ProtocolsTaru GoelNo ratings yet
- Switching Networks: Circuit, Packet & MessageDocument20 pagesSwitching Networks: Circuit, Packet & MessageShalini Kumari GuptaNo ratings yet
- Comparing Communication SystemsDocument32 pagesComparing Communication SystemsReenav ShuklaNo ratings yet
- P Resented byDocument14 pagesP Resented bysekhar2014No ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Circuit and Packet SwitchingDocument39 pagesLecture 5 Circuit and Packet SwitchingHamza IqbalNo ratings yet
- Network Switching ExplainedDocument7 pagesNetwork Switching ExplainedMarinette MedranoNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Computer Networks and the InternetDocument40 pagesIntroduction to Computer Networks and the InternetSUNDAS FATIMANo ratings yet
- Circuit Switching Vs Packet SwitchingDocument3 pagesCircuit Switching Vs Packet SwitchingJonathan JaegerNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Switching TechniquesDocument7 pagesResearch Paper On Switching Techniquesfznn7hzd100% (1)
- Unit-3 Network ModelDocument28 pagesUnit-3 Network Modeljaydipzinzuvadiya098No ratings yet
- Switching TechniquesDocument45 pagesSwitching TechniquesFarzeen FatimaNo ratings yet
- SwitchingDocument5 pagesSwitchingAjay SahreNo ratings yet
- Unit-7: Packet SwitchingDocument21 pagesUnit-7: Packet SwitchingSubeksha PiyaNo ratings yet
- Definition and OverviewDocument24 pagesDefinition and Overviewmanish1403kumarNo ratings yet
- Packet Vs Circuit Switch Newworks, CDPD, and WLL Sep 2022Document39 pagesPacket Vs Circuit Switch Newworks, CDPD, and WLL Sep 2022Janet MuendiNo ratings yet
- Circuit and Packet SwitchingDocument29 pagesCircuit and Packet SwitchingAastha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Write The Full Form of The Following:: Communication Technology - 10 MarksDocument12 pagesWrite The Full Form of The Following:: Communication Technology - 10 MarksanithasancsNo ratings yet
- System Programming Unit-4 by Arun Pratap SinghDocument83 pagesSystem Programming Unit-4 by Arun Pratap SinghArunPratapSinghNo ratings yet
- 13 Network LayerDocument32 pages13 Network Layeranushka aroraNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Telecommunication Network Model and TypesDocument19 pagesLecture - Telecommunication Network Model and TypesMOHAMMED FAYEZ KHANNo ratings yet
- Dedicated vs. Switched WAN Technologies: Video TranscriptDocument3 pagesDedicated vs. Switched WAN Technologies: Video TranscriptPkNo ratings yet
- HS BackHaul WhitepaperDocument4 pagesHS BackHaul Whitepaperpepe_shadeNo ratings yet
- Mblevins NTC242 Week 4 AssignmentDocument4 pagesMblevins NTC242 Week 4 AssignmentmdblevinsNo ratings yet
- 3 On Tap NWC203c Sum23Document20 pages3 On Tap NWC203c Sum23ntnanh.hwNo ratings yet
- MANET Literature ReviewDocument29 pagesMANET Literature Reviewengineeringwatch100% (2)
- Mpls For VoipDocument10 pagesMpls For Voipquanghung91No ratings yet
- Packet SwitchingDocument4 pagesPacket SwitchingAnkit BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Switching TechniquesDocument28 pagesSwitching TechniquesSuhirt MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Network Layer and Circuit SwitchingDocument47 pagesNetwork Layer and Circuit Switchingapi-3825972No ratings yet
- Simplify Network Migration With Smart SFPDocument13 pagesSimplify Network Migration With Smart SFPTom SlegterNo ratings yet
- Sunny GprsDocument18 pagesSunny GprsSumit KumarNo ratings yet
- Leonardi Notes Gabriele DiVittorio DiCaroDocument21 pagesLeonardi Notes Gabriele DiVittorio DiCaroKshitij SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit III NotesDocument20 pagesUnit III NotesPraveen RajNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Computer NetworksDocument31 pagesLecture 2 Computer Networksahmedehab1772002No ratings yet
- 13 Network LayerDocument38 pages13 Network LayerRakesh CharyNo ratings yet
- Light Trails: Sub-Wavelength Solution for Optical NetworkingDocument5 pagesLight Trails: Sub-Wavelength Solution for Optical NetworkingMiguel Angel Sarmiento AcostaNo ratings yet
- Wide Area NetworkingDocument8 pagesWide Area NetworkingKashif AmjadNo ratings yet
- Report Ip Over WDMDocument16 pagesReport Ip Over WDMGunawanNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Cs NotesDocument27 pagesComputer Network Cs NotesDeepti DubeyNo ratings yet
- Switching SystemDocument49 pagesSwitching SystemjansarveshNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Packet Switching and Circuit SwitchingDocument20 pagesIntroduction to Packet Switching and Circuit SwitchingUtsav Kakkad100% (1)
- Submitted by Md. Ahsan SG - 196415 Amiete - EtDocument17 pagesSubmitted by Md. Ahsan SG - 196415 Amiete - EtShanky KumarNo ratings yet
- Concise Guide to OTN optical transport networksFrom EverandConcise Guide to OTN optical transport networksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- A2 A Star Algo AI 27 9 2022Document2 pagesA2 A Star Algo AI 27 9 2022Maryam NuurNo ratings yet
- One Belt One Road China S New Grand StrategyDocument18 pagesOne Belt One Road China S New Grand StrategyMaryam NuurNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Capital Asset Pricing ModelDocument19 pagesAn Introduction To Capital Asset Pricing ModelMaryam NuurNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9618/33Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9618/33Maryam NuurNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9618/32Document12 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9618/32Maryam NuurNo ratings yet
- AS Prime Composite Code 24 1 2022Document1 pageAS Prime Composite Code 24 1 2022Maryam NuurNo ratings yet
- Formation of PolyestersDocument26 pagesFormation of PolyestersMaryam NuurNo ratings yet
- PMT CH (2) Elements Compounds and Mixtures PDFDocument4 pagesPMT CH (2) Elements Compounds and Mixtures PDFEric TTLNo ratings yet
- PMT CH (2) Elements Compounds and Mixtures PDFDocument4 pagesPMT CH (2) Elements Compounds and Mixtures PDFEric TTLNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry States of Matter NotesDocument3 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Chemistry States of Matter NotesRS123No ratings yet
- Top Anime Series to Watch in 2021Document1 pageTop Anime Series to Watch in 2021Maryam NuurNo ratings yet
- PMT CH (2) Elements Compounds and Mixtures PDFDocument4 pagesPMT CH (2) Elements Compounds and Mixtures PDFEric TTLNo ratings yet
- LTE - Voice Call HandoverDocument36 pagesLTE - Voice Call HandoverMervat AbuElkheir100% (1)
- Indonesia's Growing Mobile-First Internet and E-Commerce MarketDocument75 pagesIndonesia's Growing Mobile-First Internet and E-Commerce MarketwaladNo ratings yet
- Drilling Communications: Dep SpecificationDocument30 pagesDrilling Communications: Dep SpecificationHamidNo ratings yet
- Knowlarity Salesforce CTI SolutionDocument11 pagesKnowlarity Salesforce CTI SolutionmohitNo ratings yet
- 49 17402-Axb25005 8uen - DyDocument95 pages49 17402-Axb25005 8uen - DyAhmedNo ratings yet
- G.ix. Chapter 1.1 & 1.2 WorksheetDocument5 pagesG.ix. Chapter 1.1 & 1.2 WorksheetMangesh RahateNo ratings yet
- Kalaia Money Scandal 2003 NewDocument22 pagesKalaia Money Scandal 2003 NewsiaapaNo ratings yet
- Real Solutions ProfileDocument12 pagesReal Solutions ProfileFahad MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Voucher: Accounts Payable LiabilityDocument3 pagesVoucher: Accounts Payable LiabilityNiño Rey LopezNo ratings yet
- Accounts Receivable Job Interview Preparation GuideDocument8 pagesAccounts Receivable Job Interview Preparation Guideganesanmani1985No ratings yet
- Different Types of Bank Accounts in The PhilippinesDocument14 pagesDifferent Types of Bank Accounts in The PhilippinesAngel MarieNo ratings yet
- Project On Home InsuranceDocument55 pagesProject On Home InsuranceAbbas Taher Pocketwala71% (17)
- Yes Bank - 29 1 2019 PDFDocument8 pagesYes Bank - 29 1 2019 PDFADNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice: This Activity Contains 15 QuestionsDocument4 pagesMultiple Choice: This Activity Contains 15 QuestionsRavi SatyapalNo ratings yet
- Resume For Bookkeeping JobDocument8 pagesResume For Bookkeeping Jobjgsjzljbf100% (2)
- Import Foreign Used Car To T&TDocument5 pagesImport Foreign Used Car To T&TShekinah FergusonNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 5 Networks Comp SciDocument38 pagesLecture Notes 5 Networks Comp SciDe Shad BosticNo ratings yet
- 47 CCNA Security Interview Questions Answers GuideDocument5 pages47 CCNA Security Interview Questions Answers GuideomerNo ratings yet
- BankDocument3 pagesBankRavi Ragavan PonnusamyNo ratings yet
- An Inclusive Research On Bharat PeDocument7 pagesAn Inclusive Research On Bharat PesimranNo ratings yet
- WestgardRulesWorksheets PDFDocument4 pagesWestgardRulesWorksheets PDFDayledaniel SorvetoNo ratings yet
- Acct 220 Final Exam UmucDocument10 pagesAcct 220 Final Exam UmucOmarNiemczyk0% (2)
- M1.1 Introduction To Logistics in CLIPDocument58 pagesM1.1 Introduction To Logistics in CLIPArmieta AmeliaNo ratings yet
- Hadiza Bala Usman's Access Bank Account StatementDocument1 pageHadiza Bala Usman's Access Bank Account StatementSahara ReportersNo ratings yet
- Audit Committee PDFDocument13 pagesAudit Committee PDFChoo YieNo ratings yet
- Best Wishes From Maxcure Hospitals!: Urology and Bariatric Procedure To All Your Needy Patients According To TheDocument2 pagesBest Wishes From Maxcure Hospitals!: Urology and Bariatric Procedure To All Your Needy Patients According To TheMunnangi NagendrareddyNo ratings yet
- Final Report On BankingDocument70 pagesFinal Report On Bankingbharat sachdevaNo ratings yet
- Walmart'S Business Strategy: A Case Study of Cost Leadership and Technological InnovationDocument9 pagesWalmart'S Business Strategy: A Case Study of Cost Leadership and Technological InnovationJAYASREE K.KNo ratings yet
- Listening - Guess The Answers. Listen To CheckDocument2 pagesListening - Guess The Answers. Listen To CheckNicolás GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Basic Call FDDocument447 pagesBasic Call FDangela.guevara.sandovalNo ratings yet