Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 015
Uploaded by
Shade Elugbaju0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageChapter 015
Uploaded by
Shade ElugbajuCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Hubert: Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Professions, 6th
Edition
Chapter 15: Disorders of the Eyes, Ears and Other Sensory Organs
Answer Key to Study Questions
1. Mechanoreceptors—stimulated by mechanical force (touch, pressure)
Chemoreceptors—activated by change in chemical concentration (taste, smell)
Thermoreceptors—stimulated by temperature change (hot and cold)
Photoreceptors—respond to light (sight)
Nociceptors—respond to tissue damage (pain)
Osmoreceptors—detect changes in osmotic pressure of body fluids
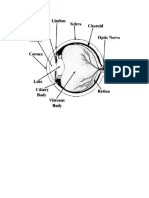
2. The sclera functions as a tough protective covering of the eyeball; the cornea is a
transparent covering, allowing passage of light rays into the pupil; the lens refracts
light rays to provide an accurate image on the retina; the choroid is a vascular structure
that provides nutrients to the retina, and pigment in it absorbs light rays; the ciliary
process secretes aqueous humor.
3. Acute glaucoma causes severe eye pain, photophobia, a cloudy bulging cornea, and
increased intraocular pressure. Chronic glaucoma causes loss of peripheral vision,
cupping of the optic disc, and increased intraocular pressure. Cataract causes blurred
vision. Detached retina causes an expanding dark area in one part of the visual field
and flashing lights.
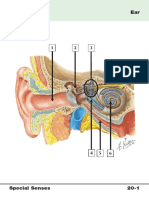
4. Sound is heard when an air wave enters the external auditory meatus; the tympanic
membrane vibrates; ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) vibrate; the oval window vibrates;
waves in the fluids (endolymph and perilymph) and movements of the membranes in
the cochlea stimulate the hair cells or nerve receptors in the organ of Corti, which
converts sound waves to electrical impulses in the auditory branch of cranial nerve
VIII; the impulses enter the brainstem and divide; half the nerve fibers go to the
auditory area in the temporal lobe on the same side, and half go to the contralateral
temporal lobe; impulses are received in the auditory cortex and interpreted in the
auditory association area.
5. Adhesions prevent vibration of the tympanic membrane or ossicles, or the tympanic
membrane ruptures and scar tissue prevents vibration.
6. Excess fluid affects movement of hair cells in both the cochlea and semicircular canals.
Copyright © 2014, 2011, 2006, 2002, 1997 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
You might also like
- Sensory Mechanism: Almozara Francisco Villaflores LorenzoDocument29 pagesSensory Mechanism: Almozara Francisco Villaflores LorenzoMerrylFranciscoNo ratings yet
- Sensory and Motor SystemDocument12 pagesSensory and Motor SystemrobertoNo ratings yet
- Sensory SystemsDocument25 pagesSensory SystemsGena Els100% (1)
- OB Exam 1 QuestionsDocument6 pagesOB Exam 1 QuestionsShade Elugbaju100% (1)
- 2022 OlfactionDocument46 pages2022 OlfactionRam LakshmanNo ratings yet
- Pharma Act 6Document7 pagesPharma Act 6Shade ElugbajuNo ratings yet
- Conjunctiva Lines The EyelidsDocument3 pagesConjunctiva Lines The EyelidsApril Hilarylynn Lawa JagunosNo ratings yet
- StimulusDocument3 pagesStimulusMiracle LakeNo ratings yet
- 5 Special SensesDocument45 pages5 Special SensesgenesyschloeNo ratings yet
- Visual Sensory System, Its Structure and Function?: Physiology Physiology Analyzers. Higher Nervous Activity of ManDocument15 pagesVisual Sensory System, Its Structure and Function?: Physiology Physiology Analyzers. Higher Nervous Activity of ManjimmyNo ratings yet
- Special Senses Study Guide KEYDocument7 pagesSpecial Senses Study Guide KEYBlade Henry100% (1)
- Module 8 Sensory SystemDocument11 pagesModule 8 Sensory SystemMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- PARAFRASEODocument4 pagesPARAFRASEOAllegroNo ratings yet
- U6 - Sensory Organs and Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesU6 - Sensory Organs and Nervous Systempovad44811No ratings yet
- Special SensesDocument8 pagesSpecial SensesChloe Gabrielle LlamasNo ratings yet
- 1589814423the Sensory SystemsDocument14 pages1589814423the Sensory SystemsYamanoor SamudriNo ratings yet
- Revalida ReviewerDocument63 pagesRevalida ReviewerJam ChuaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Ch. 9 The Senses NotesDocument7 pagesAnatomy Ch. 9 The Senses Notesprincepalestine100% (1)
- Special SensesDocument4 pagesSpecial SensesGrayson JamesNo ratings yet
- The Special Senses Powerpoint by VictoriaDocument16 pagesThe Special Senses Powerpoint by VictoriaParmesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Biok - A.3 - Perception of StimuliDocument16 pagesBiok - A.3 - Perception of StimuliMishaal IrfanNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Penginderaan: Ahmad Azwar Habibi Lab Anatomi FK UIN Syarif Hidayatullah JakartaDocument62 pagesAnatomi Penginderaan: Ahmad Azwar Habibi Lab Anatomi FK UIN Syarif Hidayatullah JakartaIin Widya Sari SiregarNo ratings yet
- Q2 L4 HandoutDocument4 pagesQ2 L4 HandoutmiatamayoqtNo ratings yet
- The Senses: Eugene Flor Lindawan Ulpindo, MSNDocument67 pagesThe Senses: Eugene Flor Lindawan Ulpindo, MSNayoNo ratings yet
- Sense Organ Ear Eye and Skin NoteDocument29 pagesSense Organ Ear Eye and Skin NoteAnkit SubediNo ratings yet
- Lab Act Special SensesDocument7 pagesLab Act Special SensesJhia TorreonNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Sensory PathwaysDocument10 pagesExperiment 3 Sensory PathwaysJenward HostalleroNo ratings yet
- Special Senses Long ActivityDocument4 pagesSpecial Senses Long Activity26jmuzychenkoNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Sensitive OrgansDocument4 pages2.1 Sensitive OrgansSOFI ULLISKYNo ratings yet
- Meniere's DiseaseDocument26 pagesMeniere's DiseasenandaanggiNo ratings yet
- Sensory Physiology-B: Lecturer: Dr. R. AhangariDocument27 pagesSensory Physiology-B: Lecturer: Dr. R. AhangariSylv IaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - An Introduction To The Special Senses: Taste HairsDocument4 pagesChapter 17 - An Introduction To The Special Senses: Taste Hairstomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- Bio 6 AslidessensoryreceptorscDocument59 pagesBio 6 Aslidessensoryreceptorscapi-285078865No ratings yet
- Kuliah PPDS - Cranial NerveDocument68 pagesKuliah PPDS - Cranial Nervederi rivanoNo ratings yet
- NUR131 + 132 Week 10Document6 pagesNUR131 + 132 Week 10mariamNo ratings yet
- Biology SS3 Summer School E-NotesDocument27 pagesBiology SS3 Summer School E-Notespraiseforever90No ratings yet
- First Term Biology Ss3Document29 pagesFirst Term Biology Ss3Stella OgunsajuNo ratings yet
- 8 KandleDocument7 pages8 KandleKezia KurniaNo ratings yet
- Final Review 2401Document7 pagesFinal Review 2401miralieNo ratings yet
- 15SPECIALSENSESDocument5 pages15SPECIALSENSESDaniellaRuth Cajurao CanalesNo ratings yet
- MODULE 16 HANDOUTS Special SensesDocument6 pagesMODULE 16 HANDOUTS Special SensesMichaela PoNo ratings yet
- Senses: 13.1 Sensory Receptors and SensationsDocument2 pagesSenses: 13.1 Sensory Receptors and SensationsJimina ParkNo ratings yet
- Sharon's Geri AssignmentDocument6 pagesSharon's Geri AssignmentSharon OlowoNo ratings yet
- Do You Hear What I Hear?:: A Lecture On The Auditory SenseDocument39 pagesDo You Hear What I Hear?:: A Lecture On The Auditory Sensecherub23No ratings yet
- Special SensesDocument26 pagesSpecial SensesWadabiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5: Sensation and Perception: ThresholdsDocument8 pagesLecture 5: Sensation and Perception: ThresholdsT-Bone02135No ratings yet
- Communication HSC BiologyDocument55 pagesCommunication HSC BiologyRubaiyat Jannat100% (1)
- Week 4 Lab Exercise - Special SensesDocument12 pagesWeek 4 Lab Exercise - Special SensesJoselito JardielNo ratings yet
- The Special Senses: Vision Auditory Sense Equilibrium Olfactory Sense Gustatory SenseDocument19 pagesThe Special Senses: Vision Auditory Sense Equilibrium Olfactory Sense Gustatory SenseGlen VillenaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Sensory Motor MechanismDocument4 pagesLesson 8 Sensory Motor Mechanismcabahugmarlon2.5No ratings yet
- 01 - What Controls Breath Rate?: Achou Algum Erro? Corrija!! E Passe Adiante!!Document8 pages01 - What Controls Breath Rate?: Achou Algum Erro? Corrija!! E Passe Adiante!!Carlos Eduardo BeckerNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and EarDocument2 pagesHuman Eye and Earshathurjanan.jana5No ratings yet
- Sense Organs General Senses Taste Smell Hearing Equilibrium VisionDocument50 pagesSense Organs General Senses Taste Smell Hearing Equilibrium VisionjosephNo ratings yet
- SENSORY SYSTEM (Draft) Group 5Document6 pagesSENSORY SYSTEM (Draft) Group 5Karl Angelo Velasco PorrasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Sensory and Motor MechanismDocument8 pagesLesson 8 Sensory and Motor MechanismBrent PatarasNo ratings yet
- Senses SpeDocument47 pagesSenses SpeStef FieNo ratings yet
- B.SC Term 2Document33 pagesB.SC Term 2jackcarter981No ratings yet
- Biological Psychology Lesson 5 NotesDocument24 pagesBiological Psychology Lesson 5 Notesjeyn100% (1)
- 4 Development of The EarDocument38 pages4 Development of The EarBryan AtasNo ratings yet
- E Learning FinalsDocument7 pagesE Learning Finalsnorma BernardoNo ratings yet
- B (Sensory Receptors)Document43 pagesB (Sensory Receptors)AROOJ ASLAMNo ratings yet
- Sem 4 Math TestDocument38 pagesSem 4 Math TestShade ElugbajuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document37 pagesChapter 1Shade ElugbajuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Prep U.odtDocument9 pagesChapter 20 Prep U.odtShade ElugbajuNo ratings yet
- Practice Final Summer 2022Document14 pagesPractice Final Summer 2022Shade ElugbajuNo ratings yet
- Care Plan 1 CPDocument1 pageCare Plan 1 CPShade ElugbajuNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment Chapter 13Document6 pagesHealth Assessment Chapter 13Shade ElugbajuNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment Chapter 12Document4 pagesHealth Assessment Chapter 12Shade ElugbajuNo ratings yet