Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2 8 Creating Histograms
Uploaded by
NinaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2 8 Creating Histograms
Uploaded by
NinaCopyright:
Available Formats
NAME: __________________________________________ DATE: ________
IB Math Studies Year 1 – Creating Histograms PERIOD:______
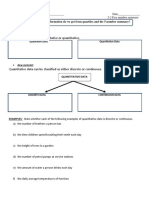
Summary of Lesson 2-7
What is a Bar Graph? A bar graph can be used to display and compare data. There should be spaces between
the bars. The height of each bar shows the frequency of each data value. A bar graph is commonly used to
represent discrete data.
What is a Histogram? A histogram is a bar graph with no spaces between the bars. The height of each bar
shows the frequency of data within that interval. The intervals of a histogram are of equal size and do not
overlap. A histogram is commonly used to represent continuous data.
Histograms (no gaps) can be used with used to represent data values
with or without a range! See examples below.
WARM-UP: Express the following histograms as a frequency table!
PRACTICE WITH TYPING HISTOGRAM DATA INTO THE CALCULATOR
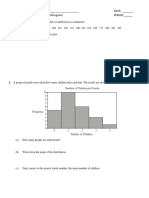
1. The following histogram shows the age distribution of teachers who smoke at Laughlin High School.
5
frequency
(# of 4
smokers) 3
2
1
20 30 40 50 60 70
ages
(a) How many teachers are represented?
(b) Write down the modal class of the distribution.
(c) In which class is the median?
(d) Calculate an estimate of the mean and standard deviation of the ages.
How do you enter the histogram into your
calculator to find the answers to parts (c) and (d)?
PRACTICE CREATING A HISTOGRAM GIVEN A FREQUENCY TABLE
2. The following table shows the times, to the nearest minute, taken by 100 students to complete a mathematics
task.
Time (t) minutes 10 ≤ 𝑡 < 15 15 ≤ 𝑡 < 20 20 ≤ 𝑡 < 25 25 ≤ 𝑡 < 30 30 ≤ 𝑡 < 35 35 ≤ 𝑡 < 40
Number of 7 13 25 28 20 7
students
(a) Calculate an estimate of the mean time in minutes.
(b) On the following grid, construct a histogram to represent this data.
TICKET TO HOMEWORK
3. A marine biologist records as a frequency distribution the lengths (L), measured to the nearest centimetre, of
100 mackerel. The results are given in the table below.
Length of mackerel Number of
(L cm) mackerel
27 < L ≤ 29 2
29 < L ≤ 31 4
31 < L ≤ 33 8
33 < L ≤ 35 21
35 < L ≤ 37 30
37 < L ≤ 39 18
39 < L ≤ 41 12
41 < L ≤ 43 5
(a) Calculate the following:
(i) the median length of mackerel;
(ii) the interquartile range of mackerel length.
(b) On the following grid, construct a histogram to represent this data.
You might also like
- Statistics For The Behavioral Sciences 3rd Edition Ebook PDFDocument61 pagesStatistics For The Behavioral Sciences 3rd Edition Ebook PDFantonia.connor78998% (45)
- Unesco Als Ls3 Math m06 SGDocument32 pagesUnesco Als Ls3 Math m06 SGals midsayap1100% (2)
- Gcse Data Work Book Compiled by MR BradfordDocument80 pagesGcse Data Work Book Compiled by MR Bradfordapi-655636980% (1)
- Cumulative Frequency Review For Final ExamDocument10 pagesCumulative Frequency Review For Final ExamapalokaNo ratings yet
- 2 6 Review of Lessons 2 1 Through 2 5Document5 pages2 6 Review of Lessons 2 1 Through 2 5NinaNo ratings yet
- ES 01 Central and DispersionDocument21 pagesES 01 Central and DispersionTaimoor Hassan KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document19 pagesChapter 3Ahmad baderNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios IB Media Moda MedianaDocument11 pagesEjercicios IB Media Moda MedianadiegocueNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics: Definition 10.2.1Document16 pagesDescriptive Statistics: Definition 10.2.1anipa mwaleNo ratings yet
- 2 11 Practice With Cumulative FrequencyDocument5 pages2 11 Practice With Cumulative FrequencyNinaNo ratings yet
- G10 U8 Statistics Practice Test 23-34Document6 pagesG10 U8 Statistics Practice Test 23-34ACADEMIA CIRCULO INGENIONo ratings yet
- Statistics Mid Question Sec A&BDocument2 pagesStatistics Mid Question Sec A&BSahadat Hosen ArnavNo ratings yet
- Representations of Data and Correlation - Test A (50 Mins) : Graph Paper NeededDocument1 pageRepresentations of Data and Correlation - Test A (50 Mins) : Graph Paper NeededHo Lam, Trish LauNo ratings yet
- Statistics Teaching Notes For Exams: Mean, Median and ModeDocument15 pagesStatistics Teaching Notes For Exams: Mean, Median and ModeLombeNo ratings yet
- Histogram With Unequal Class Width - Step by Step Solutions PDFDocument5 pagesHistogram With Unequal Class Width - Step by Step Solutions PDFNeha MunneeNo ratings yet
- MathsrevisionDocument17 pagesMathsrevisionbold bananaNo ratings yet
- Home Work January 26Document1 pageHome Work January 26caroline_amideast8101No ratings yet
- 4 Numerical Methods For Describing DataDocument50 pages4 Numerical Methods For Describing DataKrung KrungNo ratings yet
- 30 Graphical Representations of DataDocument18 pages30 Graphical Representations of Datakousik70No ratings yet
- Statistics 1: Pelangi Kasih School JakartaDocument7 pagesStatistics 1: Pelangi Kasih School JakartaTest BigbenNo ratings yet
- Trial Maths M Term 2 (2014) SmartDocument6 pagesTrial Maths M Term 2 (2014) SmartIrenaeus MartinNo ratings yet
- Binder 2Document79 pagesBinder 2oscholten06No ratings yet
- Simple StatDocument10 pagesSimple Statbader alsaloumNo ratings yet
- Organization and Presentation of Data: Graphs: What Is The Difference Between A Bar Chart and A Histogram?Document4 pagesOrganization and Presentation of Data: Graphs: What Is The Difference Between A Bar Chart and A Histogram?Joni Czarina AmoraNo ratings yet
- Measures of The Centre AdvDocument42 pagesMeasures of The Centre AdvLight ChristopherNo ratings yet
- BusDocument18 pagesBusSudip SahaNo ratings yet
- Cumulative Frequency and Box Whisker PPQDocument4 pagesCumulative Frequency and Box Whisker PPQEmma LAI [12U24]No ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument16 pagesStatisticsmlustgaNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument5 pagesAssignmentheidiNo ratings yet
- Question PaperDocument6 pagesQuestion Paperbkbalaji110No ratings yet
- Statistics Notes SPM Add MathsDocument10 pagesStatistics Notes SPM Add MathsNiceman NatiqiNo ratings yet
- CS3332 (01) Course DescriptionDocument11 pagesCS3332 (01) Course DescriptionJazyrin M. PullanNo ratings yet
- TRIAL STPM Mathematics M 2 (KEDAH) SMK KhirJohariDocument9 pagesTRIAL STPM Mathematics M 2 (KEDAH) SMK KhirJohariSKNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Assessment of Learning UploadDocument13 pagesModule 3 Assessment of Learning Uploadreyes.jenniferNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Week 4 1Document30 pagesPresentation - Week 4 1Zeynep KerimoğluNo ratings yet
- Worksheet For EngineersDocument2 pagesWorksheet For EngineersAdmasu100% (2)
- Probability and Statistics June July 2022Document10 pagesProbability and Statistics June July 2022sriramulaharish748No ratings yet
- Basic StatisticsDocument23 pagesBasic StatisticsZAKAYO NJONYNo ratings yet
- CHP 2 Mat161Document12 pagesCHP 2 Mat161Ammar KamilNo ratings yet
- Representation of DataDocument27 pagesRepresentation of DataEdgardo LeysaNo ratings yet
- G-7 Math QuizDocument6 pagesG-7 Math QuizExer ArabisNo ratings yet
- Discrete Structures Lab 9 Graph: 2.1. Adjacency Matrix - Weighted MatrixDocument5 pagesDiscrete Structures Lab 9 Graph: 2.1. Adjacency Matrix - Weighted Matrixhuy phanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade 11Document22 pagesMathematics Grade 11Wan ImamNo ratings yet
- Statistics II QDocument5 pagesStatistics II QHANS0% (1)
- Chapter 2 - Representing Sample Data: Graphical DisplaysDocument16 pagesChapter 2 - Representing Sample Data: Graphical DisplaysdeimanciukasNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions in This SectionDocument2 pagesAnswer All Questions in This SectionSTPMmaths100% (1)
- Sample QuesDocument8 pagesSample QuesMD. MAHABUB RANA SAIKATNo ratings yet
- 02 - Creating ScatterplotsDocument3 pages02 - Creating ScatterplotsValeria Pinzón NiñoNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Qoirul Purwanto - PMS JDocument6 pagesMuhammad Qoirul Purwanto - PMS JQoirul PurwantoNo ratings yet
- His To GramsDocument15 pagesHis To GramsMaryam HasanNo ratings yet
- Additional Practice Questions: Time (T Seconds) FrequencyDocument8 pagesAdditional Practice Questions: Time (T Seconds) FrequencyAinee100% (1)
- Name: - : InstructionsDocument8 pagesName: - : Instructionszul123No ratings yet
- 2 9 Cumulative Frequency TablesDocument6 pages2 9 Cumulative Frequency TablesNinaNo ratings yet
- BBA (N) - 103 Presentation of DataDocument15 pagesBBA (N) - 103 Presentation of DataPratyum PradhanNo ratings yet
- The Sampling Distribution of The Sample MeanDocument22 pagesThe Sampling Distribution of The Sample MeanMohd Nazri OthmanNo ratings yet
- 6 Cumulative FrequencyDocument8 pages6 Cumulative FrequencyJosephine FuNo ratings yet
- Sheet 02Document4 pagesSheet 02TimoNo ratings yet
- Quiz Review 2014 With More SpaceDocument6 pagesQuiz Review 2014 With More SpaceAzka Hamdah (Yr. 22-24)No ratings yet
- ! - Statistics Test PYQs 2 SolutionDocument50 pages! - Statistics Test PYQs 2 Solutionvishmon09041104No ratings yet
- محاضرة اولى -احصاء هندسيDocument10 pagesمحاضرة اولى -احصاء هندسيalhaswbalshkhsy969No ratings yet
- Representation and Summary of Data - Location (Questions)Document4 pagesRepresentation and Summary of Data - Location (Questions)Hassan HussainNo ratings yet
- HPCOpen House 2012Document21 pagesHPCOpen House 2012NinaNo ratings yet
- 2 3 Box and Whisker PlotsDocument6 pages2 3 Box and Whisker PlotsNinaNo ratings yet
- 2 5 Frequency TablesDocument6 pages2 5 Frequency TablesNinaNo ratings yet
- 1 7 Applications of Unit ConversionsDocument4 pages1 7 Applications of Unit ConversionsNinaNo ratings yet
- 2 1 Intro To StatsDocument6 pages2 1 Intro To StatsNinaNo ratings yet
- 2 2 Five Number SummaryDocument4 pages2 2 Five Number SummaryNinaNo ratings yet
- 2 7 HistogramsDocument6 pages2 7 HistogramsNinaNo ratings yet
- 1 9 Unit 1 Review SheetDocument3 pages1 9 Unit 1 Review SheetNinaNo ratings yet
- 2 4 Find A Missing Data Value Given MeanDocument6 pages2 4 Find A Missing Data Value Given MeanNinaNo ratings yet
- 1 5 Operations With Scientific NotationDocument4 pages1 5 Operations With Scientific NotationNinaNo ratings yet
- 1 3 Practice With Rounding and Significant FiguresDocument3 pages1 3 Practice With Rounding and Significant FiguresNinaNo ratings yet
- 2 2 HomeworkDocument2 pages2 2 HomeworkNinaNo ratings yet
- 1 1 Place Value and Rounding UpdatedDocument4 pages1 1 Place Value and Rounding UpdatedNinaNo ratings yet
- 1 6 International System of Conversion UpdatedDocument4 pages1 6 International System of Conversion UpdatedNinaNo ratings yet
- 2 11 Practice With Cumulative FrequencyDocument5 pages2 11 Practice With Cumulative FrequencyNinaNo ratings yet
- 1 2 Significant FiguresDocument4 pages1 2 Significant FiguresNinaNo ratings yet
- 1 9 Unit 1 Study GuideDocument5 pages1 9 Unit 1 Study GuideNinaNo ratings yet
- 1 4 Scientific NotationDocument4 pages1 4 Scientific NotationNinaNo ratings yet
- 1 8 Percent ErrorDocument4 pages1 8 Percent ErrorNinaNo ratings yet
- 1 3 Do NowDocument1 page1 3 Do NowNinaNo ratings yet
- 2 8 HomeworkDocument2 pages2 8 HomeworkNinaNo ratings yet
- Name: - DateDocument6 pagesName: - DateNinaNo ratings yet
- 2 10 Cumulative Frequency Graphs1Document6 pages2 10 Cumulative Frequency Graphs1NinaNo ratings yet
- 2 9 Cumulative Frequency TablesDocument6 pages2 9 Cumulative Frequency TablesNinaNo ratings yet
- Math 7 Module 4.3 Statistical GraphsDocument2 pagesMath 7 Module 4.3 Statistical GraphsSpree AbysNo ratings yet
- Chapter02 0Document17 pagesChapter02 0ASaqar0% (1)
- MMW StatisticsDocument5 pagesMMW StatisticsCastro, Lorraine Marre C.No ratings yet
- Preliminary Edition of Statistics Learning From Data 1st Edition Roxy Peck Test BankDocument26 pagesPreliminary Edition of Statistics Learning From Data 1st Edition Roxy Peck Test BankDianaChangmtyx100% (35)
- Sta404 Chapter 02Document55 pagesSta404 Chapter 02Ibnu Iyar100% (1)
- 4 - Organizing DataDocument42 pages4 - Organizing DataAhtisham AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Prob - Performance Task - MidtermDocument17 pagesStatistics and Prob - Performance Task - Midtermdr8ryryz25No ratings yet
- Question Bank 1Document11 pagesQuestion Bank 1Pooja MBANo ratings yet
- Straight Sprinting Is The Most Frequent Action in Goal SituationsDocument8 pagesStraight Sprinting Is The Most Frequent Action in Goal SituationsMarcelo PadilhaNo ratings yet
- Math 7 Pre Test SY 23-24Document3 pagesMath 7 Pre Test SY 23-24Jelly Ann CandidoNo ratings yet
- LDR Maths CafcDocument57 pagesLDR Maths Cafcswalihm868No ratings yet
- Statistics IntroductionDocument37 pagesStatistics Introductionramana606No ratings yet
- Module 4 Educ 105 FinalDocument35 pagesModule 4 Educ 105 FinalMaria Zobel CruzNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics CourseDocument100 pagesBiostatistics CourseAlamgir Hossain100% (1)
- Graphical Presentation of DataDocument36 pagesGraphical Presentation of DataPRIYANK100% (2)
- Module 3 PDFDocument24 pagesModule 3 PDFyoonginismNo ratings yet
- Teching Matrial For StatsicsDocument31 pagesTeching Matrial For Statsicsadisu yirgaNo ratings yet
- Doroh Efemena Edu 821 Research and Statistics Course Note 3Document9 pagesDoroh Efemena Edu 821 Research and Statistics Course Note 3CelestineNo ratings yet
- Paper III Fundamental of StaticsDocument111 pagesPaper III Fundamental of Staticspeer javaid ahmadNo ratings yet
- Me Module 3 Data Presentation and Interpretation May 2Document28 pagesMe Module 3 Data Presentation and Interpretation May 2Assistant RegistrarNo ratings yet
- Statistics Chapter 7Document11 pagesStatistics Chapter 7KunikaNo ratings yet
- 4TH QTR Percentiles For Grouped DataDocument5 pages4TH QTR Percentiles For Grouped DataAubrey Elaine MagpusaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Elementary StatisticsDocument13 pagesChapter 2 Elementary StatisticsTrixie Kayle CroduaNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2022-23 MAT5007 ETH VL2022230105838 Reference Material I 22-09-2022 IntroductionToStatisticsDocument37 pagesFALLSEM2022-23 MAT5007 ETH VL2022230105838 Reference Material I 22-09-2022 IntroductionToStatisticsRishav Nath PatiNo ratings yet
- Wa0011.Document4 pagesWa0011.SabaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 0 CPE105 Review On StatisticsDocument12 pagesMODULE 0 CPE105 Review On StatisticsKishiane Ysabelle L. CabaticNo ratings yet
- Math 7 - Q4, WK4 LasDocument12 pagesMath 7 - Q4, WK4 LasNiña Romina G. NavaltaNo ratings yet
- Midterm ExamDocument2 pagesMidterm ExamJomin Dennis MiembroNo ratings yet