Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Research Participant (29.7 × 21 CM)
Uploaded by
Lutfia Arum PambudiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Research Participant (29.7 × 21 CM)
Uploaded by
Lutfia Arum PambudiCopyright:
Available Formats
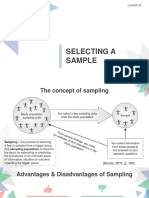
POPULATION
SAMPLE
Research
The Entire interest A group of
group individuals
Usually targeted
selected from and
(not everyone)
Participant
intended to
represent the
population
SAMPLING
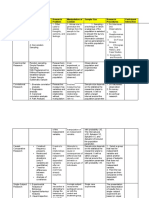
NON-PROBABILITY SAMPLING
METHODS
PR
PROBABILITY SAMPLING
1. Simple Random samplin
g mean that every
member of the population
has an equal and
independent chance 1. Simple Random sampling mean that every
2. Systematic Sampling (Ev member of the population has an equal and
ery kit element is
sampled) independent chance
3. Stratified Random (Po 2. Systematic Sampling (Every kit element is
pulation is divided into
strata and a Random Sam sampled)
ple is drawn from
each stratum) 3. Stratified Random (Population is divided into
4. Proportionate Random strata and a Random Sample is drawn from
means that there is an
even greater chance tha each stratum)
t the sample 4. Proportionate Random means that there is an
representative
5. Cluster (Used with a pop even greater chance that the sample
ulation that is large representative
6. Multistage sampling
5. Cluster (Used with a population that is large
Non Probability
6. Multistage sampling
Non Probability
Ninda Ma'uunatul. M -20202011 - TBI-B
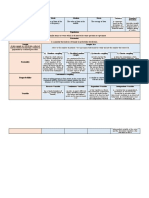
Definition Good research instruments
Type Of question
A Research Methodology addresses the question “How does
1. According to the kind of data
should be valid and reliable,
the researcher answer the questions stated in Chapter 1?”
(Quantied data, descriptive
based on the conceptual
data, degree of judgment, the
suitable and relevant data
intensity of feeling, reasoning,
based on the topic, find the
Understanding,
data that will be tested, the
2. According to form
data should answer the
The free-answer type
research question
The guided response type(Recal
type and recognition type
Ninda Ma'uunatul. M -20202011 - TBI-B
You might also like
- Neuroevolution: Fundamentals and Applications for Surpassing Human Intelligence with NeuroevolutionFrom EverandNeuroevolution: Fundamentals and Applications for Surpassing Human Intelligence with NeuroevolutionNo ratings yet
- Sampling MethodsDocument2 pagesSampling MethodsVernonNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 12: Selecting A SampleDocument2 pagesCHAPTER 12: Selecting A Samplealia.delareineNo ratings yet
- Details of Study: Sampling DesignDocument29 pagesDetails of Study: Sampling DesignharsimranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Quantitative SamplingDocument5 pagesChapter 8: Quantitative SamplingWahyu HidayatNo ratings yet
- Type of Sampling Description of Methodology Advantages DisadvantagesDocument2 pagesType of Sampling Description of Methodology Advantages DisadvantagesAfia TawiahNo ratings yet
- MethodologyDocument27 pagesMethodologyAngela Maxine BajarNo ratings yet
- 01 - Selecting The Study Subjects - Hulley, Designing Clinical Research, 4th Edition PDFDocument9 pages01 - Selecting The Study Subjects - Hulley, Designing Clinical Research, 4th Edition PDFDaniel Palma100% (1)
- C GEMTH MidtermsDocument4 pagesC GEMTH MidtermsKarl LintanNo ratings yet
- 5.+pre Class+act Population Sample SamplingDocument3 pages5.+pre Class+act Population Sample SamplingMuhammad ArifaNo ratings yet
- Selecting the Right SampleDocument5 pagesSelecting the Right SampleGracezel Evangelista GarciaNo ratings yet
- Sampling Distribution of the Sample MeanDocument4 pagesSampling Distribution of the Sample MeanMYRAVIE NOVESNo ratings yet
- How To Select A SampleDocument34 pagesHow To Select A SampleLÝ VŨ THỊ THIÊNNo ratings yet
- AP Statistics 핵심정리Document20 pagesAP Statistics 핵심정리Junho LeeNo ratings yet
- Business Research Methods (Session 3 - Sampling Techniques)Document6 pagesBusiness Research Methods (Session 3 - Sampling Techniques)Scorpions StingNo ratings yet
- Population and Sample: Producing Data: SamplingDocument4 pagesPopulation and Sample: Producing Data: SamplingEnrica SalursoNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Research Approaches and Types of Data CollectedDocument2 pagesQuantitative Research Approaches and Types of Data CollectedJoseph Mark BaldomarNo ratings yet
- Stats ReviewerDocument4 pagesStats ReviewerJao CodmNo ratings yet
- Sample DesignDocument7 pagesSample DesignShubhankar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 Participants of The StudyDocument3 pagesPractical Research 2 Participants of The StudyAbegail Decasa100% (7)
- 1c - Sampling MethodsDocument35 pages1c - Sampling MethodsNezlyn D'SouzaNo ratings yet
- Epi Cheatsheet PDFDocument4 pagesEpi Cheatsheet PDFDrbee10No ratings yet
- SMS3033Document4 pagesSMS3033HaooonNo ratings yet
- Populasi, Sampel dan Teknik SamplingDocument14 pagesPopulasi, Sampel dan Teknik Samplingafri ifthiharNo ratings yet
- Statistical Analysis - Identify VariablesDocument4 pagesStatistical Analysis - Identify VariablesAbigail BantilloNo ratings yet
- Last Handour Research 2Document8 pagesLast Handour Research 2Maria ElizaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Sampling: Why Sample?Document16 pagesIntroduction To Sampling: Why Sample?SANTHOSH KUMAR VNo ratings yet
- 6 - Population and SamplingDocument13 pages6 - Population and SamplingSanele TshibeNo ratings yet
- Pros and Cons of Different Sampling Techniques: Gaganpreet SharmaDocument4 pagesPros and Cons of Different Sampling Techniques: Gaganpreet SharmaKyla RodriguezaNo ratings yet
- PR2 - Reviewer Learning JournalDocument2 pagesPR2 - Reviewer Learning JournalImee Kaye RodillaNo ratings yet
- Sampling TechniquesDocument40 pagesSampling Techniquesmorrispogi33No ratings yet
- Research Population & SampleDocument10 pagesResearch Population & SampleSakina NoviandaniNo ratings yet
- 1 Random Sampling Parameter StatisticsDocument3 pages1 Random Sampling Parameter StatisticsWilliam RamosNo ratings yet
- Sampling Methodology: It Is Cheaper It Is FasterDocument5 pagesSampling Methodology: It Is Cheaper It Is FasterLaish Christle CapiendoNo ratings yet
- 4.lesson Plan Education 4 Types of SamplingDocument12 pages4.lesson Plan Education 4 Types of SamplingYashoda Satpute100% (1)
- Lecture 7Document20 pagesLecture 7Javaria EhsanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Stat MidtermDocument4 pagesReviewer Stat MidtermSeok Jin KimNo ratings yet
- Types of Sampling Methods ExplainedDocument4 pagesTypes of Sampling Methods ExplainedJANE MARIEL ATIENZANo ratings yet
- Sampling, Sampling Distributions and EstimationDocument8 pagesSampling, Sampling Distributions and EstimationMamtha KumarNo ratings yet
- Types of Sampling: Probability Sampling Nonprobability Sampling 2. Purposive SamplingDocument16 pagesTypes of Sampling: Probability Sampling Nonprobability Sampling 2. Purposive SamplingSANTHOSH KUMAR VNo ratings yet
- Gate Scholorship Work - October: Sampling FundamentalsDocument13 pagesGate Scholorship Work - October: Sampling Fundamentalssiva sankariNo ratings yet
- Stats Reviewer CompleteDocument8 pagesStats Reviewer CompleteLewAndrewCortesNo ratings yet
- Experiment Design Basic PrinciplesDocument68 pagesExperiment Design Basic PrinciplesAngy Ruiz MarquezNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics Exam 1 PreparationDocument3 pagesBusiness Statistics Exam 1 Preparationmailt32.fptNo ratings yet
- Eba U1 A1 OsrnDocument10 pagesEba U1 A1 OsrnhelemNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Sampling and Sampling Methods: (Assignment For Research Methodology)Document9 pagesAssignment On Sampling and Sampling Methods: (Assignment For Research Methodology)ALI ASGHERNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Statistical ThinkingDocument6 pagesStatistics and Statistical ThinkingMarietoni PallanNo ratings yet
- RMM 3Document18 pagesRMM 3porseenaNo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument13 pagesSamplingThithiksha JNo ratings yet
- Pros and Cons of Sampling-With-Cover-Page-V2Document5 pagesPros and Cons of Sampling-With-Cover-Page-V2musawar420No ratings yet
- Epidemiological Concepts ExplainedDocument8 pagesEpidemiological Concepts ExplainedMelodic DubzNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics Fundamentals for Experimental Design and SamplingDocument11 pagesBiostatistics Fundamentals for Experimental Design and SamplingDeepak ThakurNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 DMS 411 Population & SamplingDocument19 pagesLecture 6 DMS 411 Population & SamplingWanjikuNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Population, Sample and Sampling: ObjectivesDocument8 pagesUnit 4 Population, Sample and Sampling: Objectivesvikas yadavNo ratings yet
- Sampling Techniques ExplainedDocument40 pagesSampling Techniques Explainedeyob bitewNo ratings yet
- Probabilitysampling 160409091802Document18 pagesProbabilitysampling 160409091802Aiza Rhea SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PDFDocument8 pagesChapter 2 PDFparklong16No ratings yet
- Evolutionary Computation Algorithms For Cryptanalysis A StudyDocument5 pagesEvolutionary Computation Algorithms For Cryptanalysis A StudyAMJAD HUSSAIN ZAHIDNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Management Unit 2 NoteDocument24 pagesStatistics For Management Unit 2 Noteeee2014.rvsNo ratings yet
- Sampling MethodsDocument7 pagesSampling Methodsapi-552158438No ratings yet
- Tange Awbrey ResumeDocument2 pagesTange Awbrey Resumeapi-264168595No ratings yet
- Finanacial Restructuring 2Document48 pagesFinanacial Restructuring 2Jim Mathilakathu100% (2)
- RN332 Business Process Framework Release Notes R15.0.0Document16 pagesRN332 Business Process Framework Release Notes R15.0.0ibrahim_nfsNo ratings yet
- Sample PPT Presentation For DefenseDocument57 pagesSample PPT Presentation For DefenseFreda Jeminez100% (1)
- Study on Performance of SBI Merchant BankingDocument73 pagesStudy on Performance of SBI Merchant BankingSonia Jacob50% (4)
- Globe at Home E-Bill - 884810304-2020-10-06 PDFDocument2 pagesGlobe at Home E-Bill - 884810304-2020-10-06 PDFParciNo ratings yet
- Final PPT On US BANKING and Bank of AmericaDocument74 pagesFinal PPT On US BANKING and Bank of AmericaSahil GuptaNo ratings yet
- Oracle Database Security PDFDocument43 pagesOracle Database Security PDFChidi OkerekeNo ratings yet
- Objectives and QuestionnaireDocument9 pagesObjectives and Questionnaireutcm770% (2)
- PMP Full ExamDocument51 pagesPMP Full Examrvsreddy197285% (26)
- Amity School of Business: Marketing Management - IIDocument38 pagesAmity School of Business: Marketing Management - IIOrange NoidaNo ratings yet
- BEC 3 Outline - 2015 Becker CPA ReviewDocument4 pagesBEC 3 Outline - 2015 Becker CPA ReviewGabrielNo ratings yet
- Infrastructure Management May 2009 Report - FinalDocument16 pagesInfrastructure Management May 2009 Report - FinalWazzupdude101No ratings yet
- Just To DownloadDocument217 pagesJust To DownloadhondaNo ratings yet
- FY 2008 SMGR Semen+Indonesia (Persero) TBKDocument89 pagesFY 2008 SMGR Semen+Indonesia (Persero) TBKRiki Ariyadi 2002110906No ratings yet
- From Idea To OpportunityDocument29 pagesFrom Idea To OpportunityDanica SolisNo ratings yet
- Andrea Rubio Online ResumeDocument2 pagesAndrea Rubio Online Resumeapi-235925145No ratings yet
- Business Continuity Planning at The Bank of JapanDocument11 pagesBusiness Continuity Planning at The Bank of Japanblue_l1No ratings yet
- Resume - December 2018 - Soren DahlDocument1 pageResume - December 2018 - Soren Dahlapi-381738033No ratings yet
- Purchase Order for Tires and Rims from Sharma InternationalDocument1 pagePurchase Order for Tires and Rims from Sharma InternationalMICHAELNo ratings yet
- Increasing Model Dairy Sales Through Effective DistributionDocument91 pagesIncreasing Model Dairy Sales Through Effective DistributionVenkatesh GuntiNo ratings yet
- NExitDocument164 pagesNExitdanuckyNo ratings yet
- Ra 8425 Poverty Alleviation ActDocument14 pagesRa 8425 Poverty Alleviation ActZyldjyh C. Pactol-Portuguez0% (1)
- 微观经济学笔记Document130 pages微观经济学笔记Alyse97No ratings yet
- Us GaapDocument3 pagesUs GaapHaneen Abdulla100% (1)
- Evaluating Marine Suppliers for Hai An CompanyDocument78 pagesEvaluating Marine Suppliers for Hai An CompanyHuy ChuNo ratings yet
- Joint Ventures ChecklistDocument2 pagesJoint Ventures ChecklistcityrenNo ratings yet
- Internet Bill For Aug-2022Document2 pagesInternet Bill For Aug-2022rased ahkcNo ratings yet
- Foreign Investors Dominate Vietnamese Real Estate MarketDocument36 pagesForeign Investors Dominate Vietnamese Real Estate MarketChau TranNo ratings yet
- Stock ExchangeDocument32 pagesStock ExchangeHassaan Zafar50% (2)