Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bi 6 Lab Ex 5-Fermentation
Uploaded by
CCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bi 6 Lab Ex 5-Fermentation
Uploaded by
CCopyright:
Available Formats
Bi 6 Biotechnology for Everyone, Laboratory
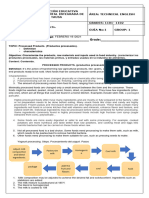
Fermentation
Yogurt is a fermented milk product produced by adding a "starter" of active yogurt containing
a mixed culture of Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus. These bacteria produce
lactic acid during fermentation of lactose. The lactic acid lowers the pH, makes the milk tart, causes
the milk protein to thicken and acts as a preservative since pathogenic (disease-causing) bacteria
cannot grow in acid conditions (with lids intact, this yogurt will keep at least a month or two in the
refrigerator). The partial digestion of the milk when these bacteria ferment milk makes yogurt easily
digestible. In addition, these bacteria will help settle gastrointestinal tract upset including that which
follows oral antibiotic therapy by replenishing non-pathogenic flora of the gastrointestinal tract.
Several factors are crucial for successful yogurt making:
good sterile technique (i.e., proper sterilization and cooling of milk, proper cleansing and heat
treatment of glassware and
keeping out unwanted bacteria)
proper incubation temperature (Lactobacilli and Streptococcus thermophilus are thermophilic
bacteria, meaning they prefer
elevated temperatures for growth. At such temperatures (50°C,
in this case) pathogenic or putrefactive bacteria are inhibited. However, even these
thermophilic bacteria are killed if exposed to temperatures over 55°C (130°F) and do not grow
well below 37°C (98°F))
protection of the starter from contamination (Do not open the starter until you are ready to
make the next batch)
Materials:
1 liter of fresh milk (not non-fat milk)
Yogurt starter (Nestle plain yogurt)
disposable spoon
Transparent microwavable containers (small, around 100 - 250 ml, 1 per group)
Procedure:
1. Make sure that the microwavable container is clean. Clean it using detergent and water. Rinse
thoroughly.
2. Pour boiled water on the containers and allow the water to stay for 5 minutes. This will kill
most bacteria that may
contaminate the yogurt. Repeat this step for the disposable spoons.
3. Label the containers with laboratory section and group number.
4. Pour the milk on the cleaned containers and put inside the microwave for 2 minutes. Cool the
milk to temperatures
between 40 to 60°C.
5. Add a teaspoon of yogurt starter to the milk and stir. Set aside in a warm room for at least 7
hours until set. Do not disturb.
6. To know whether the yogurt has set, tilt slightly the container to see if the yogurt retains its
shape. If it does, place it in the
refrigerator. This may serve as starter culture for another
batch of yogurt. Do not open it unless the materials to make
another batch of yogurt are
ready.
7. To enjoy the yogurt, add sugar or salt. Yogurt could also be substituted for sour cream in dips
and other recipes.
Department of Biology, School of Science and Engineering
Ateneo de Manila University
Bi 6 Biotechnology for Everyone, Laboratory
Exercise 5. Fermentation
Name:___________________________________________ Date: _______________________
Group No.: _______________________________________ Instructor: ___________________
Guide Questions:
1. What are the health benefits of yogurt? Cite at least two original scientific papers that support
the health benefits of yogurt.
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
2. Give a situation when your own body cells perform fermentation. Which body cells can
perform fermentation?
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
3. It is said to be possible for lactose intolerant individuals to eat yogurt. Why?
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
Department of Biology, School of Science and Engineering
Ateneo de Manila University
You might also like
- LabDocument4 pagesLabMaria Cecille Sarmiento GarciaNo ratings yet
- Yogurt Fermentation With Lactobacillus CulturesDocument5 pagesYogurt Fermentation With Lactobacillus Culturesjorgearreola85504350% (2)
- Leaflet - Milk FermentationDocument3 pagesLeaflet - Milk FermentationNoor SultanNo ratings yet
- Yogurt LabDocument2 pagesYogurt Labapi-697400605No ratings yet
- Reinvent Your Dairy at Home - Your Ultimate Guide to Being Healthier Without LactoseFrom EverandReinvent Your Dairy at Home - Your Ultimate Guide to Being Healthier Without LactoseNo ratings yet
- Milk Substitute Recipes: 12 Tasty Milk Substitute Recipes for Weight LossFrom EverandMilk Substitute Recipes: 12 Tasty Milk Substitute Recipes for Weight LossNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Yoghurt:: Methods of ProcessingDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Yoghurt:: Methods of ProcessingMaheshchandra PatilNo ratings yet
- LAB PT Yogurt FermentationDocument7 pagesLAB PT Yogurt Fermentationvince.ortegaNo ratings yet
- Let's Cut The CheeseDocument11 pagesLet's Cut The CheeseJanelle BurgosNo ratings yet
- 1025 Lab 11 Preparation of YogurtDocument1 page1025 Lab 11 Preparation of YogurtMohd NabeelNo ratings yet
- Science Fair Scrap BookDocument23 pagesScience Fair Scrap BookChitra KavivannanNo ratings yet
- Pro BioticDocument3 pagesPro BioticSoundarya GajendranNo ratings yet
- Robsaan KootiDocument8 pagesRobsaan KootiDhugaan GalgalaafNo ratings yet
- YoghurtDocument2 pagesYoghurtIngrid AlvesNo ratings yet
- Lactate Fermentation Student Version Final-2Document15 pagesLactate Fermentation Student Version Final-21chaudhryibrNo ratings yet
- Got Milk? Background: Food Processing and PreservationDocument7 pagesGot Milk? Background: Food Processing and PreservationRaja VeluNo ratings yet
- Fs 173 EmakingyogurtDocument7 pagesFs 173 EmakingyogurtKonesi Ronald100% (1)
- Milk Processing: Pathogen SterilizationDocument5 pagesMilk Processing: Pathogen SterilizationSurya AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Milk ProcessingDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Milk ProcessingMintesnot Bogale100% (1)
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Introductionbalajir65No ratings yet
- Nestlé: Ice Cream Product LineDocument31 pagesNestlé: Ice Cream Product LineMary Anne AntenorNo ratings yet
- Vegan Dairy: Making milk, butter and cheese from nuts and seedsFrom EverandVegan Dairy: Making milk, butter and cheese from nuts and seedsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Healthy Alternative To Conventional Infant FormulaDocument16 pagesHealthy Alternative To Conventional Infant FormulaCarlos AdanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 - The Anaerobic Fermentation ProcessDocument5 pagesExperiment 4 - The Anaerobic Fermentation ProcessFatimatuzzahra' Binti Hardiyono FISNo ratings yet
- Unit 5.FDMDocument11 pagesUnit 5.FDMAgam SindhwaniNo ratings yet
- The Making of Yoghurt, Conventional Biotechnology ProductDocument3 pagesThe Making of Yoghurt, Conventional Biotechnology ProductMariaNapituNo ratings yet
- Malunggay YogurtDocument7 pagesMalunggay YogurtEljoy AgsamosamNo ratings yet
- Nestle PresentationDocument24 pagesNestle PresentationGunjan Goel100% (1)
- Safety and Hygienic Practices in Storing DessertsDocument3 pagesSafety and Hygienic Practices in Storing DessertsMARY JOY VILLARUEL100% (2)
- Conserver ses Aliments grâce à la LactofermentationFrom EverandConserver ses Aliments grâce à la LactofermentationNo ratings yet
- Bio SBA (P-D) The Investigative ProjectDocument9 pagesBio SBA (P-D) The Investigative Projectferrongeneva01No ratings yet
- Nutribullet Recipes: Top 51 Nutribullet Smoothie Recipes for Weight Loss, Beautiful Skin, Anti-agingFrom EverandNutribullet Recipes: Top 51 Nutribullet Smoothie Recipes for Weight Loss, Beautiful Skin, Anti-agingNo ratings yet
- How To Make YogurtDocument1 pageHow To Make YogurtMukhtiNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcomes:: Lesson ViDocument11 pagesLearning Outcomes:: Lesson ViYuhan AliwateNo ratings yet
- Milk FortificationDocument11 pagesMilk FortificationPrak0% (1)
- Yogurt MakingDocument21 pagesYogurt Makingsnookylein100% (3)
- Pasturization, Sterilizationo and FermentationDocument36 pagesPasturization, Sterilizationo and Fermentationkwagala joshuaNo ratings yet
- Plant-Based Yoghurt-Style Products: White PaperDocument24 pagesPlant-Based Yoghurt-Style Products: White PaperЕлена КоваленкоNo ratings yet
- HE CG Lesson 1 Topic 3Document5 pagesHE CG Lesson 1 Topic 3rem grimsNo ratings yet
- Make Your Own FormulaDocument8 pagesMake Your Own FormulaTony FontanaNo ratings yet
- Production of Yogurt PDFDocument2 pagesProduction of Yogurt PDFZaki SyedNo ratings yet
- Nestlé S.A. Is A Swiss Multinational Food and Drink Processing Conglomerate CorporationDocument15 pagesNestlé S.A. Is A Swiss Multinational Food and Drink Processing Conglomerate CorporationHalle TeferiNo ratings yet
- Vita GenDocument5 pagesVita GenAliia HamdanNo ratings yet
- Operation Management - Midterm ReportDocument23 pagesOperation Management - Midterm ReportNhiHoangNo ratings yet
- Dairy QNS and AnsDocument19 pagesDairy QNS and Ansaadnanafridi76No ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument22 pagesChemistry Investigatory ProjectAnurag Mishra100% (1)
- Fernmentation Guide On YogurtDocument3 pagesFernmentation Guide On YogurtPaolo Miguel DomingoNo ratings yet
- The Preppers Guide to Drying, Canning and Preserving Your Own Survival Food: Survival Family Basics - Preppers Survival Handbook SeriesFrom EverandThe Preppers Guide to Drying, Canning and Preserving Your Own Survival Food: Survival Family Basics - Preppers Survival Handbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Production of YoghurtDocument63 pagesProduction of YoghurtIbe Collins100% (3)
- Blues The ClueDocument3 pagesBlues The CluevishveshwarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory Project: Name: Sanjana Tiwari Class: Xii A' (Science) - ROLL NO: 23. SESSION: 2021-22Document13 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project: Name: Sanjana Tiwari Class: Xii A' (Science) - ROLL NO: 23. SESSION: 2021-22Sanjana TiwariNo ratings yet
- Guia1 Grupo1 Inglestecnico11 Periodo1Document2 pagesGuia1 Grupo1 Inglestecnico11 Periodo1Lina Mercedes Rozo BanoyNo ratings yet
- Canning & Preserving Food for Weight Loss: Improve Your Health, Fitness and Diet By Canning and Preserving FoodFrom EverandCanning & Preserving Food for Weight Loss: Improve Your Health, Fitness and Diet By Canning and Preserving FoodNo ratings yet
- Dairy Fermentation: Object: Making Chocolate Bars of Fermented MilkDocument9 pagesDairy Fermentation: Object: Making Chocolate Bars of Fermented MilkJibran NaeemNo ratings yet
- Reasons For Developing Food ProductsDocument5 pagesReasons For Developing Food Productssheela baralNo ratings yet
- JeBouffe Home Canning Step by Step Guide (second edition) Revised and ExpandedFrom EverandJeBouffe Home Canning Step by Step Guide (second edition) Revised and ExpandedNo ratings yet
- Bi 6 Lab Ex 6-MicroorganismsDocument2 pagesBi 6 Lab Ex 6-MicroorganismsCNo ratings yet
- Bi 6 Lab Ex 7-BlbDocument3 pagesBi 6 Lab Ex 7-BlbCNo ratings yet
- Bi 6 Lab Ex 1 MicropipettorDocument3 pagesBi 6 Lab Ex 1 MicropipettorCNo ratings yet
- Bi 6 Lab Ex 3-Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument6 pagesBi 6 Lab Ex 3-Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsCNo ratings yet
- Bi 6 Lab Ex 9-Dna IsolationDocument2 pagesBi 6 Lab Ex 9-Dna IsolationCNo ratings yet
- Bi 6 Lab Ex 10-AgeDocument3 pagesBi 6 Lab Ex 10-AgeCNo ratings yet
- Preventing DiabetesDocument2 pagesPreventing DiabetesCNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 - Project Management.rDocument23 pagesTopic 8 - Project Management.rCNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Basics of Operations ManagementDocument20 pagesTopic 2 - Basics of Operations ManagementCNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Total Quality in OrganizationDocument28 pagesTopic 1 - Total Quality in OrganizationCNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Focusing CustomersDocument23 pagesTopic 3 - Focusing CustomersCNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 - Product and Process DesignDocument49 pagesTopic 5 - Product and Process DesignCNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Internet MarketingDocument35 pagesChapter 3 - Internet MarketingCNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Internet Advertising & Customer Acquisition 2Document29 pagesChapter 4 - Internet Advertising & Customer Acquisition 2CNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce Law in The Phil 2Document34 pagesE-Commerce Law in The Phil 2CNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Ecommerce Presence and Internet Value ChainDocument57 pagesChapter 2 Ecommerce Presence and Internet Value ChainCNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 E-Business and E-Commerce IntroductionDocument46 pagesChapter 1 E-Business and E-Commerce IntroductionCNo ratings yet
- Yield and Fruit Quality of New Bulgarian Peach Cultivars: Argir Zhivondov, Sashka SavchovskaDocument1 pageYield and Fruit Quality of New Bulgarian Peach Cultivars: Argir Zhivondov, Sashka SavchovskaMirko PetrićNo ratings yet
- General Guidelines On Sampling (Codex Alimentarius)Document69 pagesGeneral Guidelines On Sampling (Codex Alimentarius)Janelle100% (1)
- Articol Stiinfitic 16 - Apple Varieties in AlabamaDocument8 pagesArticol Stiinfitic 16 - Apple Varieties in AlabamaOlgaNo ratings yet
- Effa GGuidance Document Attachment X On Flavourings With Modifying Properties FmpsDocument3 pagesEffa GGuidance Document Attachment X On Flavourings With Modifying Properties FmpsBrianlee1970No ratings yet
- Consultation CardDocument1 pageConsultation CardxrxaxnxNo ratings yet
- Footprint Without Feet SummaryDocument14 pagesFootprint Without Feet SummaryABPCLASSESNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument4 pagesBusiness PlanAprinfel TimaanNo ratings yet
- Assignment MEGDocument4 pagesAssignment MEGRaheel AbbasNo ratings yet
- Lesson01 PDFDocument9 pagesLesson01 PDFJuan Tercero TabladaNo ratings yet
- Bottle Catalogue 22Document7 pagesBottle Catalogue 22Pan SoapNo ratings yet
- Peanut Research PaperDocument9 pagesPeanut Research PaperrosoproductsNo ratings yet
- Gmo EssayDocument5 pagesGmo Essayapi-605318233No ratings yet
- DLP AdjectivesDocument8 pagesDLP AdjectivesNina Rica BautistaNo ratings yet
- Felix: FELIX: The Master of Its ArtDocument2 pagesFelix: FELIX: The Master of Its ArtMIGUEL IVAN REYES TORRESNo ratings yet
- Caregiving LAS GrimesDocument13 pagesCaregiving LAS GrimesJade MillanteNo ratings yet
- Potato MurukkuDocument4 pagesPotato MurukkuabgutihNo ratings yet
- Daily Activities Bahasa InggrisDocument5 pagesDaily Activities Bahasa InggrisMiftahul JannahNo ratings yet
- 5.1. Pig BreedsDocument43 pages5.1. Pig BreedsChristian Ramos NievesNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - My Day: Have A Nice Day!Document6 pagesUnit 3 - My Day: Have A Nice Day!daniela almendaresNo ratings yet
- Soy Sauce Chicken - The Woks of LifeDocument2 pagesSoy Sauce Chicken - The Woks of Lifeeian kaziaNo ratings yet
- Principle of Seeds StorageDocument10 pagesPrinciple of Seeds StorageChan ChanNo ratings yet
- APE - AvaliaçãoDocument7 pagesAPE - AvaliaçãoLana Araújo FernandesNo ratings yet
- Tapescript - CBNDocument5 pagesTapescript - CBNhậu đoànNo ratings yet
- Reflect Listening & Speaking 1: Unit 1 Vocabulary ListDocument8 pagesReflect Listening & Speaking 1: Unit 1 Vocabulary ListThùy TrangNo ratings yet
- Biology O Level Paper 1 MCQs Topical Pas 1Document43 pagesBiology O Level Paper 1 MCQs Topical Pas 1Muhammad Ali Usman AsifNo ratings yet
- Pillsbury AnswerDocument15 pagesPillsbury AnswerHarry Novianto KaiNo ratings yet
- Golden State Enterprise Is A Malaysian Milkshake and Pizza CompanyDocument43 pagesGolden State Enterprise Is A Malaysian Milkshake and Pizza CompanyDhivyashene RajaendranNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Nov.23 2022Document17 pagesCHAPTER 1 Nov.23 2022Daniella TiansayNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1: Cho dạng đúng của các động từ trong ngoặc.: Iii. Đáp ÁnDocument10 pagesExercise 1: Cho dạng đúng của các động từ trong ngoặc.: Iii. Đáp ÁnNguyen Thi Kim DungNo ratings yet
- Sw1570629192-Majina Ya Wanachuo Waliochaguliwa Kujiunga Na Vyuo Vya Wakala Ya Mafunzo Ya MifugoDocument35 pagesSw1570629192-Majina Ya Wanachuo Waliochaguliwa Kujiunga Na Vyuo Vya Wakala Ya Mafunzo Ya MifugofenyofelixNo ratings yet