Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Name
Uploaded by
juss0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesDuty
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDuty
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesDrug Name
Uploaded by
jussDuty
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
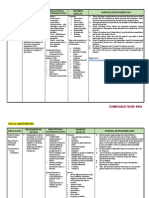
Drug
Name: Jessa B. Name
Alojado Classification Mechanism of Action BupivacaineIndication
Drug Study Contraindication Adverse Reactions Nursing Responsibilities
Generic Name: Local Bupivacaine is an Bupivacaine Hypersensitivity Hypersensitivity 1.) Obtain the signed consent for
Bupivacaine Anesthetics amide local anesthetic that is indicated to any of the local reactions, anginal administration of anesthesia.
provides local anesthesia for local anesthetic agent pain, anxiety, 2.) Monitor state of consciousness and vital
Brand Name: through blockade of nerve infiltration, of the amide type apprehension, signs, especially cardiac and respiratory
Marcaine impulse generation and peripheral nerve or to other blurred vision, status continuously in patients receiving
Sensorcaine conduction. These block, sympathetic components of bradycardia, retrobulbar and dental blocks.
impulses, also known as nerve block, and bupivacaine cardiovascular 3.) Monitor for signs of inadvertent
Dosage, Route & Frequency: action potentials, critically epidural and solutions. collapse, cardiac intravascular injection, which can produce a
Adult and Pediatric Dosages: depend on membrane caudal blocks. It is Obstretical arrhythmias, chills, transient "epinephrine response" within 45
Injectable solution depolarization produced sometimes used in paracervical block confusion, seconds in the unsedated patient and an
0.25% by the influx of sodium combination with anesthesia dizziness, increase by 20 bpm or more in heart rate
0.5% ions into the neuron epinephrine to drowsiness, for at least 15 seconds in sedated patient.
0.75% through voltage-gated prevent systemic edema, headache, 4.) Monitor for toxicity. CNS stimulation usually
sodium channels. It absorption and hypotension, occurs first, followed by CNS depression
Use in children <12 years is not crosses the neuronal extend the hypoventilation, (drowsiness, unconsciousness, respiratory
recommended; membrane and exerts its duration of action. nausea, loss of arrest). However, because stimulation is apt
> 12 years: Same as adult anesthetic action through The 0.75% (most consciousness, to be transient or absent, drowsiness may
dose: blockade of these channels concentrated) palpitations, be the first sign in some patients (especially
Causadal block: at the intracellular portion formulation is used respiratory arrest, children and older adults).
15-30 ml of 0.25% or 0.5% of their pore-forming in retrobulbar shivering, seizures, 5.) When appropriate, Inform the patient in
Epidural block: transmembrane segments. block. status advance that they may experience
10-20 ml of 0.25% - 0.5% The block is use- asthmaticus, temporary loss of sensation and motor
administered in 3-5 ml dependent, where tachycardia, activity, usually in the lower half of
increments allowing sufficient repetitive or prolonged tinnitus, tremors, the body, following proper administration
time to detect any toxic depolarization increases vomiting of caudal or epidural anesthesia.
manifestations of inadvertent sodium channel blockade. 6.) Assess dizziness that might affect gait,
intravenous or intrathecal Without sodium ions balance, and other functional activities.
administration passing through the Instruct the patient or family to report
Peripheral Nerve block: channel’s pore, balance problems and functional limitations
5 ml of 0.25% or 0.5%; bupivacaine stabilizes the to the physician and/or nursing staff, and
Max: 400 mg/day membrane at rest and caution the patient and family/caregivers to
Symphatetic nerve block: therefore prevents guard against falls and trauma.
20-50 ml of 0.25% (no neurotransmission.
epinephrine)
Local Anesthesia:
0.25% infiltrated locally.
Max: 175 mg
You might also like
- 3 Bupivacain Drug StudyDocument4 pages3 Bupivacain Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RLE PDFDocument15 pagesDrug Study RLE PDFCzarina Isabela Tuazon100% (1)
- Drug Study 1Document15 pagesDrug Study 1Czarina Isabela TuazonNo ratings yet
- Bupivacaine Merk 4Document2 pagesBupivacaine Merk 4PutuNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Indication Contraindication Mechanism of Actions Side Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesName of Drug Indication Contraindication Mechanism of Actions Side Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesLloyd Adrian GaffudNo ratings yet
- SUMMARY DRUG CompletedDocument10 pagesSUMMARY DRUG CompletedNor haztini Mohd zainNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Local and General AnesthesiaDocument8 pagesDrugs For Local and General AnesthesiaApple MaeNo ratings yet
- RLE OR - Drug StudyDocument6 pagesRLE OR - Drug Studyelijahdale.guillergan-05No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studytaurus_gm27No ratings yet
- Frcem Sba Preparation Set 1Document107 pagesFrcem Sba Preparation Set 1jacknaim7090100% (2)
- Drug Study JSGSDocument8 pagesDrug Study JSGSJohannes SantosNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument9 pagesDrug AnalysisKyle DapulagNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Nov. 12Document6 pagesDrug Study Nov. 12Jenny Ajoc100% (4)
- Drug Study (Epinephrine, Lidocaine, Diazepam)Document6 pagesDrug Study (Epinephrine, Lidocaine, Diazepam)Abigaile Operiano100% (2)
- Case Study Module 5Document56 pagesCase Study Module 5Khylamarie VillalunaNo ratings yet
- Spinal Anes Drug StudyDocument12 pagesSpinal Anes Drug StudyNicosia Mae FerrerNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic InterventionsDocument8 pagesPharmacologic InterventionsYsabelle De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Forcadilla Drug Study 3.3 PDFDocument10 pagesForcadilla Drug Study 3.3 PDFkint manlangitNo ratings yet
- DRug Study PhenytoinDocument1 pageDRug Study Phenytoinmichelle marquezNo ratings yet
- Patient 1 Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPatient 1 Drug StudyCharlyn JenselNo ratings yet
- The SURGICAL Experience: AnesthesiaDocument43 pagesThe SURGICAL Experience: AnesthesiaAngela CamilleNo ratings yet
- LidocaineDocument2 pagesLidocaineRomwella May AlgoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument24 pagesDrug StudySittie Nashieva A. UsmanNo ratings yet
- Biperiden HCLDocument2 pagesBiperiden HCLivy_tan_6No ratings yet
- General Surgery Lecture N: 1. Anaesthesia. - Medical Uses - TechniquesDocument18 pagesGeneral Surgery Lecture N: 1. Anaesthesia. - Medical Uses - TechniquesAmal ShereefNo ratings yet
- LidocaineDocument4 pagesLidocaineAhmad Fauzi100% (1)
- Pedia Drug StudyDocument3 pagesPedia Drug StudyAnna LaritaNo ratings yet
- White and Blue Pharmaceutical Science Trifold BrochureDocument2 pagesWhite and Blue Pharmaceutical Science Trifold BrochureHanna Violeza Velasco CayetanoNo ratings yet
- Er Drug Study 1Document3 pagesEr Drug Study 1Rey Jean GarciaNo ratings yet
- 50321-Article Text-72499-1-10-20100129Document3 pages50321-Article Text-72499-1-10-20100129rosy.pearl.auNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyWTRNo ratings yet
- Suxamethonium Dosage, Side Effect MIMS - Com PhilippinesDocument2 pagesSuxamethonium Dosage, Side Effect MIMS - Com PhilippinesWay LyanNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Side Effects Before:: Ventricular ArrhythmiasDocument4 pagesGeneric Name Side Effects Before:: Ventricular ArrhythmiasElizabeth Ivory ChuaNo ratings yet
- Leukupenia, Neutropenia, ThrombocytopeniaDocument3 pagesLeukupenia, Neutropenia, ThrombocytopeniaVANESSANo ratings yet
- DuaventDocument2 pagesDuaventKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Cesarean SectionDocument31 pagesCesarean Sectionjovan teopizNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY-LidocaineDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY-LidocaineCarissa Mae Tapec Estrada100% (1)
- YAWAADocument10 pagesYAWAAZyrene CapulongNo ratings yet
- Cesarean Section CASEDocument32 pagesCesarean Section CASEjovan teopizNo ratings yet
- NimodipineDocument5 pagesNimodipineGwyn Rosales100% (1)
- 9 PropofolDocument2 pages9 PropofolAbdelhafiz Susmiran100% (3)
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug Studykarenkaren09No ratings yet
- OxytocinDocument2 pagesOxytocinFernandez, Florence NicoleNo ratings yet
- AnestesiDocument59 pagesAnestesiJeffrey EkaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Can Affects The CnsDocument9 pagesDrugs Can Affects The CnsDayan CabrigaNo ratings yet
- DroperidolDocument1 pageDroperidolIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- JAMBALOS JERALDEEN BSN 4 2 DRUG STUDY FormatDocument3 pagesJAMBALOS JERALDEEN BSN 4 2 DRUG STUDY FormatJeraldeen JambalosNo ratings yet
- KetamineDocument24 pagesKetamineMalik Arif UllahNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument21 pagesDrug StudyShelvin Jules LayvaNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics-Respiratory Disorders of The Newborn: Diseases Clinical Manifestations Diagnosis & Prognosis ManagementDocument9 pagesPediatrics-Respiratory Disorders of The Newborn: Diseases Clinical Manifestations Diagnosis & Prognosis ManagementJonathan ZumakpehNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY-Lidocaine RyreyDocument1 pageDRUG-STUDY-Lidocaine RyreyJanelle Cabida SupnadNo ratings yet
- CH19-25 PharmaDocument20 pagesCH19-25 Pharmakwon nanaNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy: Signs & Symptoms / Pathophysiology / Drug Studies / Ncps / Health TeachingsDocument22 pagesCerebral Palsy: Signs & Symptoms / Pathophysiology / Drug Studies / Ncps / Health TeachingsGeoffrey Sintaan RiveraNo ratings yet
- PHENYLEPHRINEDocument3 pagesPHENYLEPHRINERoger Jr PumarenNo ratings yet
- Regional Anesthesia: Pembimbing: Dr. Dewa, Span Oleh: Annisa Aulia WidyantiDocument22 pagesRegional Anesthesia: Pembimbing: Dr. Dewa, Span Oleh: Annisa Aulia WidyantimuhammadfahmanNo ratings yet
- Drug 2Document2 pagesDrug 2Sheika BanwagenNo ratings yet
- Sedation Reading TestDocument22 pagesSedation Reading TestJyothy AthulNo ratings yet
- DS NorepinephrineDocument4 pagesDS NorepinephrineReign RaineNo ratings yet
- Week 17-18Document8 pagesWeek 17-18jussNo ratings yet
- Unconventional DeliveryDocument4 pagesUnconventional DeliveryjussNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanjussNo ratings yet
- Grieving in ElderlyDocument29 pagesGrieving in Elderlyjuss100% (1)
- Path o PhysiologyDocument3 pagesPath o PhysiologyjussNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Readings in Philippine HistoryDocument2 pagesReviewer in Readings in Philippine HistoryjussNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management OF Git Problems Gastric and Duodenal DisordersDocument109 pagesNursing Management OF Git Problems Gastric and Duodenal DisorderstantanbaragoNo ratings yet
- Table of Contents YjcafDocument3 pagesTable of Contents Yjcafntsn3100No ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument20 pagesMuscle TissueDheeraj MenezesNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument29 pagesChronic Renal Failuregeorgia.langNo ratings yet
- PhysioEx Exercise 5 Activity 4Document3 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 5 Activity 4lucisNo ratings yet
- GIT OSPE Pathology - Final-2 PDFDocument29 pagesGIT OSPE Pathology - Final-2 PDFafaq alismailiNo ratings yet
- KARDIOLOGIDocument120 pagesKARDIOLOGIEsti IvanaNo ratings yet
- Medicine OSPE Pre AnnualDocument17 pagesMedicine OSPE Pre AnnualMunawarNo ratings yet
- Neonate With AcrocyanosisDocument4 pagesNeonate With Acrocyanosisnurul noviarisaNo ratings yet
- Cardiology I WorkbookDocument68 pagesCardiology I WorkbookPharmacist DinaNo ratings yet
- NCM 118 Skills Lab (Week 8)Document4 pagesNCM 118 Skills Lab (Week 8)kNo ratings yet
- General Basis of Pathologic ConditionDocument24 pagesGeneral Basis of Pathologic Conditionallexa jimlaniNo ratings yet
- ECG ReadingDocument11 pagesECG ReadingSuresh Shrestha100% (1)
- Thrombolytics-1Document3 pagesThrombolytics-1Shayan ShayanNo ratings yet
- Names and Functions of The Human AnatomiesDocument92 pagesNames and Functions of The Human AnatomiesShania Kate Ledesma ManabatNo ratings yet
- 3 - PancreaseDocument12 pages3 - PancreasemyarjddbzNo ratings yet
- Diver Medical FormDocument3 pagesDiver Medical FormJeanne PianoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestations of Hypothyroidism - UpToDateDocument9 pagesClinical Manifestations of Hypothyroidism - UpToDatedixama9519No ratings yet
- Enoxaparin - Safe Prescribing - Check It Out 1Document3 pagesEnoxaparin - Safe Prescribing - Check It Out 1Zaid DewachiNo ratings yet
- Amiloidosis Cardiaca AHA 2020Document16 pagesAmiloidosis Cardiaca AHA 2020Guillermo CenturionNo ratings yet
- Pne ThoraxDocument16 pagesPne ThoraxfyfvNo ratings yet
- CardiomyopathyDocument18 pagesCardiomyopathyDimpal Choudhary100% (1)
- Hemorragia SubaracnoideaDocument10 pagesHemorragia SubaracnoideaAna TeresaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Expenditure Burden of Disease and Management in 5 Eu CountriesDocument123 pagesDiabetes Expenditure Burden of Disease and Management in 5 Eu CountrieszilahparviNo ratings yet
- Common Pulmonary Diseases: Emmanuel R. Kasilag, MD, FPCP, FPCCPDocument74 pagesCommon Pulmonary Diseases: Emmanuel R. Kasilag, MD, FPCP, FPCCPDivine Grace FernandezNo ratings yet
- Nephrology CalciumDocument2 pagesNephrology CalciumAeroplane HubNo ratings yet
- Section A: Select Any 60 Consecutive Multiple Choice Questions. For Each Question Circle One Best AlternativeDocument17 pagesSection A: Select Any 60 Consecutive Multiple Choice Questions. For Each Question Circle One Best AlternativeJeshuah JehopioNo ratings yet
- Paediatric PSGDocument21 pagesPaediatric PSGFayhaa NadeemNo ratings yet
- Vetoryl Package InsertDocument1 pageVetoryl Package InsertBlaze DiazNo ratings yet
- NCM116 Module 3 Cerebrovascular Disease QuizDocument5 pagesNCM116 Module 3 Cerebrovascular Disease QuizIvan FernandezNo ratings yet