Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grinding Machine Guide: A Complete Overview
Uploaded by
piravi66Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Grinding Machine Guide: A Complete Overview
Uploaded by
piravi66Copyright:
Available Formats
Grinding Machine
• Grinding is a metal removal process by the
action of a rotating abrasive wheel.
• An abrasive is a material whose particles are
extremely hard and can be used to machine
materials such as hardened steel, glass, carbides,
ceramics, etc.
• Grinding operation may be used for removing a
thick layer (about 0.5 mm) of material in general
class of work.
• Usually grinding is used for finishing & polishing
of parts produced by other machining process.
P R Venkatesh, Mech Dept, RVCE , B'lore
Abrasives
• Abrasive is the mineral material employed for
sharpening, grinding & polishing operations.
• Two types of abrasives are commonly used;
1. Natural abrasives
Ex: Emery, Sand stone, Quartz, Corundum,
Diamond.
(Corundum & Emery mainly consist of Aluminium oxide)
2. Artificial or synthetic abrasives.
Ex: Silicon carbide, Aluminium oxide, artificial
diamond.
P R Venkatesh, Mech Dept, RVCE , B'lore
Grinding Wheels
P R Venkatesh, Mech Dept, RVCE , B'lore
Grinding Wheel (Bonded Abrasives)
• In a grinding wheel, the abrasive grains are held
together by a bonding material.
• Grinding wheels are specified by the standardized
system of letters & numbers Indicating the type of
abrasive, grain size, grade, structure & bond type.
1. Abrasive type: The most commonly used abrasives
are
Aluminium oxide used to grind steel and its alloys.
Silicon carbide used to grind cast iron & non
ferrous metals.
Diamond used to grind carbides, marbles, gems,
P R Venkatesh, Mech Dept, RVCE , B'lore
2. Grain size: It is used to describe the fineness of
the mesh used in grading the abrasive grits
(particles).
• Coarse grains are used to grind soft, ductile
materials.
• Fine grains are used for hard and brittle
materials and also when close accuracy is
required.
3. Grade: It indicates the relative strength of the
bond that holds the abrasive particles in place.
P R Venkatesh, Mech Dept, RVCE , B'lore
4. Structure: It indicates the relative spacing of the abrasive
grains.
• A wheel with wide spacing between the grains is best
suited for grinding soft materials.
• A closely spaced structure is suitable for grinding hard
materials.
5. Bond: It is the medium that holds the grains together in
the form of a wheel.
The various bond materials generally used are
Vitrified : ( Feldspar & clay)
Silicate : (Silicate of soda)
Shellac : (resin secreted by a lac bug on a tree)
rubber : (pure rubber with sulphur as
vulcanizing agent)
P R Venkatesh, Mech Dept, RVCE , B'lore
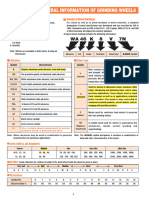
Standard Marking System of a grinding wheel
Prefix Abrasive Grain size Grade Structure Bond type Suffix
W A 46 K 5 V 17
Manufacturer's Manufacturer's
abrasive code bond code
A to Z 4 10
A - Aluminium oxide
C- Silicon Carbide (A-Softest) 5 11
Z- Zirconia Z-Hardest) 6 12
7 13
8 14
V- Vitrified
Coarse Fine S- Silicate
8 9 15
80 B- Resin
10 100
12 120 R- Rubber
14 150 E- Shellac
16 180 P- Epoxy
20 Very Fine
24 220
Medium 240
30 280
36 320
46 400
60 500
600
P R Venkatesh, Mech Dept, RVCE , B'lore
Grinding wheel structure
Typical structure of a grinding wheel.
P R Venkatesh, Mech Dept, RVCE , B'lore
Dressing of Grinding Wheel
• As the grinding wheel
is used, it gets loaded
with metal chips in
between the cavities
of the grains.
• Dressing is the process
of removing all dull
grains and chips from
the wheel surface and
exposing new sharp
grains.
• An abrasive stick is
used for dressing.
P R Venkatesh, Mech Dept, RVCE , B'lore
Truing of Grinding Wheel
• Grinding wheels lose
their geometry
during use.
• Truing is a dressing
operation by which a
wheel is restored its
original shape.
• A single point
diamond tool can be
used to true the
wheel.
P R Venkatesh, Mech Dept, RVCE , B'lore
Classification of Grinding Machines
Grinding machines are classified according to the
type of surface they produce.
1. Surface grinding machine
(For finishing flat surfaces)
2. Cylindrical grinding machine
(For finishing the outside/inside diameter of
cylindrical workpiece)
3. Centerless grinder
( For grinding curved surfaces of long slender rods)
P R Venkatesh, Mech Dept, RVCE , B'lore
Surface Grinding Machine
P R Venkatesh, Mech Dept, RVCE , B'lore
Surface Grinding Machine
Grinding Spindle
wheel • Grinding of flat
surfaces is known as
Work surface grinding.
Table • Two general types of
machines are
Work reciprocates available; those with
Feed
reciprocating table &
the other with
rotating table.
• Each type has
possible variations
of having grinding
wheel spindle either
in horizontal position
or vertical position.
P R Venkatesh, Mech Dept, RVCE , B'lore
Cylindrical Grinding Machine
P R Venkatesh, Mech Dept, RVCE , B'lore
Cylindrical Grinding Machine
• Grinding of straight or
tapered cylindrical
surfaces is known as
cylindrical grinding.
• The work piece is
mounted between two
centers or in a chuck and
Grinding
wheel revolves in opposite
Spindle direction to that of
grinding wheel.
• The table which carries
the headstock & tailstock
centers and the work can
be reciprocated by a
Work piece
hydraulic drive.
P R Venkatesh, Mech Dept, RVCE , B'lore
Centerless Grinding
P R Venkatesh, Mech Dept, RVCE , B'lore
Centerless Grinding
• Centerless grinding is used for producing parallel, tapered or
contoured surfaces on long & slender rods.
• The work piece is not supported between centers and hence
the name centerless.
• The work piece rests on a work rest blade and is backed by a
second wheel called regulating wheel.
P R Venkatesh, Mech Dept, RVCE , B'lore
Centerless Grinding
• The regulating wheel is of rubber bonded abrasive having the
frictional characteristics to rotate the work piece at its own
rotational speed.
• The grinding wheel & the regulating wheel rotate in the same
direction.
• In through feed grinding, the axial movement of the work past
the grinding wheel is obtained by tilting the regulating wheel at
slight angle from the Phorizontal.
R Venkatesh, Mech Dept, RVCE , B'lore
Lapping
• Lapping is a precision
grinding technique
employed in finishing
of valve seats, cutting
edge of dies, optical
lenses, etc.
• It uses fluid suspension
of very small abrasive
particles (Lapping
compound) between
workpiece and lap
(tool)
P R Venkatesh, Mech Dept, RVCE , B'lore
Honing • Honing is also a
precision grinding
technique employed
in reshaping &
polishing cylinder
bores, gauges,
connecting rod bushes,
etc.
• It uses abrasive
bonded sticks known
as hones which will be
given combined rotary
& reciprocating
motions.
P R Venkatesh, Mech Dept, RVCE , B'lore
Honing• Abrasive process
performed by a set of
bonded abrasive sticks
using a combination of
rotational and oscillatory
motions.
• Common application is to
finish the bores of
internal combustion
engines
• Surface finishes of 0.12
m or better.
• Creates a characteristic
cross-hatched surface
that retains lubrication.
P R Venkatesh, Mech Dept, RVCE , B'lore
You might also like
- Millers Anesthesia - Sixth Edition - ANESTHESIA APPARATUS - 18Document6 pagesMillers Anesthesia - Sixth Edition - ANESTHESIA APPARATUS - 18Adriana VickNo ratings yet
- Drilling Training CourseDocument443 pagesDrilling Training Coursehama100% (8)
- Measuring Vibration InstrumentsDocument36 pagesMeasuring Vibration Instrumentssuresh505rameshNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure PacketDocument11 pagesAtomic Structure PacketJaznMonNo ratings yet
- Solved Board Problems - Geothermal Power PlantDocument6 pagesSolved Board Problems - Geothermal Power PlantFAMY Vazzim Soriano100% (1)
- Cunningham 2011Document3 pagesCunningham 2011januar fitrianaNo ratings yet
- Grinding and Finishing Processes: Unit 6Document49 pagesGrinding and Finishing Processes: Unit 6Sudharshan IyengarNo ratings yet
- 4.Grinding MachineDocument74 pages4.Grinding MachineShri Bhagwan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Grinding Wheel SpecificatonsDocument17 pagesGrinding Wheel Specificatonssample useNo ratings yet
- Grinding: Abrasive Machine Process GrinderDocument29 pagesGrinding: Abrasive Machine Process GrinderMuhammad AneesNo ratings yet
- Ceramics Properties ApplicationsDocument24 pagesCeramics Properties ApplicationsAluNo ratings yet
- Surface RoughnessDocument8 pagesSurface RoughnessGyagenda NasserNo ratings yet
- GRINDINGDocument24 pagesGRINDINGYash SahaniNo ratings yet
- Grinding Wheel Specification PDFDocument17 pagesGrinding Wheel Specification PDFPENONVVNo ratings yet
- Module 5 PDFDocument85 pagesModule 5 PDFMar CialNo ratings yet
- Abbressive WheelDocument38 pagesAbbressive WheelFarrukh AhmadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 07) GrindingDocument22 pagesLecture 07) GrindingMat MatttNo ratings yet
- Material Removal Processes (IM 213) : Arab Academy For Science, Technology, and Maritime TransportDocument22 pagesMaterial Removal Processes (IM 213) : Arab Academy For Science, Technology, and Maritime TransportNicolas EleftheriouNo ratings yet
- Brochure OTR CAT - PDF Bridgestone PDFDocument20 pagesBrochure OTR CAT - PDF Bridgestone PDFFilipposNo ratings yet
- Abrasive SDocument3 pagesAbrasive SmurusaNo ratings yet
- MP Unit 4 GrindingDocument25 pagesMP Unit 4 GrindingJ S VAISHNAVNo ratings yet
- GRINDING OF TOOL STEELDocument16 pagesGRINDING OF TOOL STEELSubodh RanjanNo ratings yet
- Master Grinding WheelsDocument82 pagesMaster Grinding WheelsHouariKouadriNo ratings yet
- Grinding Wheel Specificatons: Presentation By:-Bhubaneswar FombDocument17 pagesGrinding Wheel Specificatons: Presentation By:-Bhubaneswar Fombcipet imphalNo ratings yet
- Grinding Wheel Specifications and Selection GuideDocument50 pagesGrinding Wheel Specifications and Selection GuidegillawatNo ratings yet
- AMP Unit 4 BDocument24 pagesAMP Unit 4 BAjai BaskarNo ratings yet
- Cutting Off Wheels: Bond Type Resinoid Shellac RubberDocument17 pagesCutting Off Wheels: Bond Type Resinoid Shellac RubberaloordominicNo ratings yet
- SRJ Rubber Track & Pad CatalogDocument39 pagesSRJ Rubber Track & Pad CatalogeduardoNo ratings yet
- Master Grinding Wheel BrochureDocument72 pagesMaster Grinding Wheel BrochureSgk Manikandan100% (1)
- Grinding Wheel Basic TrainingDocument38 pagesGrinding Wheel Basic Trainingsomu.cp100% (1)
- A36I9B-specification DetailsDocument1 pageA36I9B-specification DetailsKarim HakimNo ratings yet
- Proses Manufaktur - Abrasive ProcessDocument35 pagesProses Manufaktur - Abrasive ProcessRandy NainggolanNo ratings yet
- ME 480 GrindingDocument32 pagesME 480 GrindingSiva Kumar SalumuriNo ratings yet
- GrindingDocument105 pagesGrindingPrashant Rao Meshram100% (1)
- Chapter 13 - Applications and Processing of CeramicsDocument26 pagesChapter 13 - Applications and Processing of CeramicsAngelino PimentelNo ratings yet
- Applications and Processing of CeramicsDocument13 pagesApplications and Processing of CeramicsGonzalo CamposNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document58 pagesUnit 5Palak NaikNo ratings yet
- Applications and Processing of Ceramics: Pablo Borbon Main II, Alangilan Batangas CityDocument8 pagesApplications and Processing of Ceramics: Pablo Borbon Main II, Alangilan Batangas CityChristine De la RamaNo ratings yet
- Ceramic and GlassDocument27 pagesCeramic and Glasskautsar muafaNo ratings yet
- MT&A - Unit 4Document52 pagesMT&A - Unit 4Yashvanth H LNo ratings yet
- Abrasive Machining Processes GuideDocument29 pagesAbrasive Machining Processes GuideRaghuNo ratings yet
- Abrasive Machining Processes: N. Sinha, Mechanical Engineering Department, IIT KanpurDocument29 pagesAbrasive Machining Processes: N. Sinha, Mechanical Engineering Department, IIT KanpurAbin BrothersNo ratings yet
- TDS Hardcarb 70 (#ET - EN - 20.1)Document2 pagesTDS Hardcarb 70 (#ET - EN - 20.1)Jimit ShahNo ratings yet
- Krishna Engineering College Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument4 pagesKrishna Engineering College Department of Mechanical EngineeringVivek BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Lubrication & BearingsDocument91 pagesLubrication & BearingsRohan SinghNo ratings yet
- 113resuelto Procesamiento-Ceramicos ch13Document26 pages113resuelto Procesamiento-Ceramicos ch13Isac NumNo ratings yet
- Automotive Mitsubishi Tooling PDFDocument24 pagesAutomotive Mitsubishi Tooling PDFAlex GăuruşNo ratings yet
- SWR SRB Product SheetDocument2 pagesSWR SRB Product SheetCarlo AguiluzNo ratings yet
- Holex 2017-2018Document8 pagesHolex 2017-2018Krakovchi LorandNo ratings yet
- CERAMICSDocument27 pagesCERAMICSErika RamosNo ratings yet
- Kinematical Limit Analysis MethodDocument4 pagesKinematical Limit Analysis MethodJemal JibrilNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document5 pagesCH 2alsltanyhasanNo ratings yet
- Sterling AbrasivesDocument78 pagesSterling AbrasivesITL200_UNo ratings yet
- Drilling Fluid - 2021 - Handouts - 16 September 2022Document87 pagesDrilling Fluid - 2021 - Handouts - 16 September 2022Egis KrismaNo ratings yet
- Grinding Final NotesDocument21 pagesGrinding Final NotesGaikwad Aniket100% (1)
- Ordering from Kemet Materials GuideDocument24 pagesOrdering from Kemet Materials Guidevantuan17792No ratings yet
- Grinding TextDocument10 pagesGrinding TextASIST MechNo ratings yet
- Wear Plate LeafletDocument4 pagesWear Plate LeafletumeshNo ratings yet
- Abrasive Machining and Finishing OperationsDocument40 pagesAbrasive Machining and Finishing OperationsBody NassifNo ratings yet
- Lecture 06 Grinding AMS Jan29 23Document69 pagesLecture 06 Grinding AMS Jan29 23QAQC GCCNo ratings yet
- 1 GrindingDocument36 pages1 GrindingswarnnaNo ratings yet
- Rock Blasting: A Practical Treatise on the Means Employed in Blasting Rocks for Industrial PurposesFrom EverandRock Blasting: A Practical Treatise on the Means Employed in Blasting Rocks for Industrial PurposesNo ratings yet
- CAEG Solutions (21ME16)Document55 pagesCAEG Solutions (21ME16)piravi66No ratings yet
- MOM 12ME33 Test 1 Sept 2015Document1 pageMOM 12ME33 Test 1 Sept 2015piravi66No ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibrations ExplainedDocument64 pagesMechanical Vibrations Explainedpiravi66No ratings yet
- 18ME54 - Keerthi KumarDocument136 pages18ME54 - Keerthi KumarAravindNo ratings yet
- Undamped Free Vibrations: Free Vibration or Natural VibrationDocument81 pagesUndamped Free Vibrations: Free Vibration or Natural Vibrationpiravi66No ratings yet
- 4.forced VibrationsDocument62 pages4.forced Vibrationspiravi66No ratings yet
- Unit 3&4Document65 pagesUnit 3&4piravi66No ratings yet
- Unit 2 SFEEDocument19 pagesUnit 2 SFEEpiravi66No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Heat and WorkDocument31 pagesUnit 2 Heat and Workpiravi66No ratings yet
- UNIT 2-Basics AerodynamicsDocument23 pagesUNIT 2-Basics Aerodynamicspiravi66No ratings yet
- Problem 2 LawDocument5 pagesProblem 2 Lawpiravi66No ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibrations (10 ME 74) DampingDocument44 pagesMechanical Vibrations (10 ME 74) Dampingpiravi66No ratings yet
- Turbomachinery: (Third Edition)Document404 pagesTurbomachinery: (Third Edition)piravi66100% (1)
- Introduction to Space Flight OrbitsDocument14 pagesIntroduction to Space Flight Orbitspiravi66No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Aircraft StructuresDocument12 pagesUnit 4 Aircraft Structurespiravi66No ratings yet
- Unit 2 First Law-Closed System ProblemsDocument11 pagesUnit 2 First Law-Closed System Problemspiravi66No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Notes-Basics of Aerospace Engg To StudentsDocument10 pagesUnit 1 Notes-Basics of Aerospace Engg To Studentspiravi66No ratings yet
- Three Types of Altitude Defined and ExplainedDocument13 pagesThree Types of Altitude Defined and Explainedpiravi66No ratings yet
- Unit 2-Basic AerodynamicsDocument63 pagesUnit 2-Basic Aerodynamicspiravi66No ratings yet
- Aerospace Propulsion ExplainedDocument23 pagesAerospace Propulsion Explainedpiravi66No ratings yet
- 7-Welding Belts LubricationDocument46 pages7-Welding Belts LubricationS.m. ChandrashekarNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Beams & Dynamic AnalysisDocument66 pagesUnit 4 Beams & Dynamic Analysispiravi66No ratings yet
- 2 Unit V FEM (Heat Transfer) PDFDocument28 pages2 Unit V FEM (Heat Transfer) PDFsidguru chincholeNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 2-D CST ElementDocument68 pagesUnit 3 2-D CST Elementpiravi66No ratings yet
- Vibration-Based Analysis of Damage in CompositesDocument10 pagesVibration-Based Analysis of Damage in CompositesRohithsai PasupuletiNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Methods Unit 2Document84 pagesFinite Element Methods Unit 2piravi66No ratings yet
- July 14, 2005 10:3 WSPC/175-IJN 00313: Ion Beam Lithography and Nanofabrication: A ReviewDocument18 pagesJuly 14, 2005 10:3 WSPC/175-IJN 00313: Ion Beam Lithography and Nanofabrication: A Reviewmoviemac7No ratings yet
- 09-08-15 SR - Iit-Iz-Co-Spark Jee Adv Rpta-2 (2013 p2) Q'paperDocument33 pages09-08-15 SR - Iit-Iz-Co-Spark Jee Adv Rpta-2 (2013 p2) Q'paperKumar Prasad100% (1)
- RESIN - TRANSFER - MOLDING - FINAL - REPORT With RefDocument37 pagesRESIN - TRANSFER - MOLDING - FINAL - REPORT With RefI DKNo ratings yet
- Sample ReportDocument39 pagesSample Reportgerman esteban rodriguez baqueroNo ratings yet
- Temperature and Heat 3Document18 pagesTemperature and Heat 3Samud MorrisNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Answer Key PDFDocument1 pageChemistry Answer Key PDFMark FuentesNo ratings yet
- Micro Digital Media 2e Lab Book-3Document101 pagesMicro Digital Media 2e Lab Book-3string440% (1)
- PH and BuffersDocument24 pagesPH and BuffersJoshua LewisNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment No1 Turbidity and PHDocument5 pagesLaboratory Experiment No1 Turbidity and PHEmmanuel CausonNo ratings yet
- Bureau of Indian Standards - PCD12Document15 pagesBureau of Indian Standards - PCD12Divya BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Journal of Cleaner Production: Amit Madhu, J.N. ChakrabortyDocument20 pagesJournal of Cleaner Production: Amit Madhu, J.N. ChakrabortyNagender SinghNo ratings yet
- Kilfrost Winter Best Practice Guide - Edition 3Document44 pagesKilfrost Winter Best Practice Guide - Edition 3DimitriosMonogios100% (1)
- Hydrogenation of AlkenesDocument2 pagesHydrogenation of AlkenesNur FarahinNo ratings yet
- Super Kit ManualDocument22 pagesSuper Kit ManualFabiana ChusitNo ratings yet
- Modscour BLDocument21 pagesModscour BLpalanmadhukantNo ratings yet
- Water Problems SolutionsDocument6 pagesWater Problems SolutionsHarshitha LokeshNo ratings yet
- DR Hugo Touchette (NITheP Stellenbosch)Document11 pagesDR Hugo Touchette (NITheP Stellenbosch)Rene KotzeNo ratings yet
- 4th FM Lecture Notes-Units and Scales of Pressure MeasurementDocument8 pages4th FM Lecture Notes-Units and Scales of Pressure MeasurementMike BuzmionNo ratings yet
- ControTrace Saves Customer $100KDocument4 pagesControTrace Saves Customer $100KmarraezNo ratings yet
- UEP (July2013) Paper 1Document4 pagesUEP (July2013) Paper 1Irfan AliNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Consumibles Cromatografia de Gases y Espectrometria de Gases Parte3 PDFDocument218 pagesCatalogo Consumibles Cromatografia de Gases y Espectrometria de Gases Parte3 PDFTaranom SpNo ratings yet
- Photomultiplier Tube: FeaturesDocument2 pagesPhotomultiplier Tube: Featuresابو حميد ابو حميدNo ratings yet
- F84C-5 - Sat - MSDSDocument4 pagesF84C-5 - Sat - MSDSDenise Koh Chin HuiNo ratings yet
- Exercise # I: Chemical BondingDocument34 pagesExercise # I: Chemical BondingIndranilNo ratings yet
- Titration - FinalDocument2 pagesTitration - FinalHitesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bronze & Brass Valves: JIS 5K/10K, ASME Class 125/150/300, KITZ Type 100/125/150/300/400/600Document52 pagesBronze & Brass Valves: JIS 5K/10K, ASME Class 125/150/300, KITZ Type 100/125/150/300/400/600roshan jaiswalNo ratings yet