Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sheet (1) (Introduction)
Uploaded by
mostafa nasserOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sheet (1) (Introduction)
Uploaded by
mostafa nasserCopyright:
Available Formats
Faculty of Engineering
Computer and Systems Engineering Department
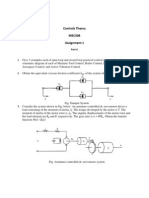
CSE 371: Control Engineering
Sheet 1: Introduction to Control Engineering
1. Many closed-loop and open-loop control systems may be found at home. List several
examples and describe them.
2. Give two examples in which a human acts as a feedback control system.
3. In the past, control systems used a human operator as part of a closed-loop control system.
Sketch the block diagram of the valve control system shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Flow control system
4. The accurate control of a nuclear reactor is important for power system generators. Assuming
the number of neutrons present is proportional to the power level, an ionization chamber is
used to measure the power level. The current io is proportional to the power level. The position
of the graphite control rods moderates the power level. Complete the control system of the
nuclear reactor shown in Figure 2. And sketch the block diagram describing the operation of
the feedback control loop.
Figure 2. Nuclear reactor control
5. A light-seeking control system used to track the sun is shown in Figure 3. The output shaft is
driven by the motor through a worm reduction gear, has a bracket attached on which are
mounted two photocells. Complete the closed loop system so that the system follows the light
source.
Figure 3. Sun tracking system
6. Consider the inverted pendulum in Figure 4. Sketch the block diagram of a feedback control
system to maintain the pendulum in upward position (=0).
Figure 4. Inverted pendulum control
7. A position control system converts a position input command to a position output response.
Position control finds widespread applications in antennas, robot arms, and computer disk
drives. The radio telescope antenna in Figure 5. is one example. The purpose of this system is
to have the azimuth angle output follow the input angle. The input command is an angular
displacement. The potentiometer converts the angular displacement into a voltage. Similarly,
the output angular displacement is converted to a voltage by the potentiometer in the feedback
path. The signal and power amplifiers boost the difference between the input and output
voltages. This amplified actuating signal drives the plant. The system operates to drive the
error to zero when the input and the output match, the error will be zero and the motor will not
run. Sketch the block diagram describing the operation of the feedback control loop.
Figure 5. Position control system
You might also like
- Electrical Correcting Elements in Automatic Control and Regulation CircuitsFrom EverandElectrical Correcting Elements in Automatic Control and Regulation CircuitsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document7 pagesLecture 1faridrahmanNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorNo ratings yet
- Tuning A PID Controller For A Digital Excitation Control SystemDocument8 pagesTuning A PID Controller For A Digital Excitation Control SystemSharat Chandra KeswarNo ratings yet
- Control of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesFrom EverandControl of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics Unit III and IV Question and AnswersDocument6 pagesMechatronics Unit III and IV Question and AnswersSaravanan MathiNo ratings yet
- Seminar Presentation On Controllers, Actuators and Control SystemsDocument30 pagesSeminar Presentation On Controllers, Actuators and Control SystemsOdinma AzuonwuNo ratings yet
- Energetic Processes in Follow-Up Electrical Control Systems: International Series of Monographs on Electronics and InstrumentationFrom EverandEnergetic Processes in Follow-Up Electrical Control Systems: International Series of Monographs on Electronics and InstrumentationNo ratings yet
- 1) Theoretical Background: 1-1) Function and DefinitionDocument13 pages1) Theoretical Background: 1-1) Function and DefinitionH. ZNADNo ratings yet
- Radio Telescope Antenna Control System Modelling For Antenna Azimuth Position Using Simulink/MatlabDocument4 pagesRadio Telescope Antenna Control System Modelling For Antenna Azimuth Position Using Simulink/MatlabFahmy R. SaputriNo ratings yet
- Assignment1Document2 pagesAssignment1Manoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Rotary Inverted PendulumDocument8 pagesRotary Inverted PendulumEduardo BittencourtNo ratings yet
- Documentation For The Bytronic Pendulum Control System: (Version 2.1)Document37 pagesDocumentation For The Bytronic Pendulum Control System: (Version 2.1)Mohamed Elsayed HasanNo ratings yet
- Unit No - II: Block Diagram RepresentationDocument56 pagesUnit No - II: Block Diagram RepresentationNamrta DeokateNo ratings yet
- Principles of Automatic ControlDocument26 pagesPrinciples of Automatic ControlMesut OzilNo ratings yet
- Self Balancing Two Wheeled Robot ReportDocument11 pagesSelf Balancing Two Wheeled Robot Reportnetlvr0No ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document22 pagesChapter 01Abiyot egataNo ratings yet
- Power System Dynamics ETH NoteDocument107 pagesPower System Dynamics ETH Noteabs4everonline100% (1)
- Chapter Eight Root Locus Control Design: Figure 8.1: A Common Controller-Plant ConfigurationDocument44 pagesChapter Eight Root Locus Control Design: Figure 8.1: A Common Controller-Plant ConfigurationVijay GargNo ratings yet
- Tuning A PID Controller For A Digital Excitation Control SystemDocument11 pagesTuning A PID Controller For A Digital Excitation Control SystemMahmoud SamyNo ratings yet
- Case Study PneumaticDocument16 pagesCase Study PneumaticHazwan Jamhuri100% (6)
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument18 pagesChapter 1 IntroductionSśēmǾǿ ŔämáďañNo ratings yet
- Inverted PendulumDocument60 pagesInverted PendulumMauricio OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Ece IV Control Systems (10es43) Notes1Document205 pagesEce IV Control Systems (10es43) Notes1Nithindev GuttikondaNo ratings yet
- Autotronics and Vehicle Intelligence : Aeng6205Document25 pagesAutotronics and Vehicle Intelligence : Aeng6205Abubaker MuzayinNo ratings yet
- (P1) Modul DC Motor Speed Control SystemDocument13 pages(P1) Modul DC Motor Speed Control SystemTito Bambang Priambodo - 6726No ratings yet
- Closed Loop SystemsDocument11 pagesClosed Loop SystemsMohamed RashidNo ratings yet
- 000 Digital Control LecturesDocument67 pages000 Digital Control LecturesPX PRNo ratings yet
- Unit Control Concepts PDFDocument7 pagesUnit Control Concepts PDFasotozuazuaNo ratings yet
- Pendulum Positioning System Actuated by Dual Motorized PropellersDocument4 pagesPendulum Positioning System Actuated by Dual Motorized Propellerspatmos666No ratings yet
- 6 TH Sem 2022Document23 pages6 TH Sem 2022AnkitNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Control Systems: Theme 1Document16 pagesIntroduction To Control Systems: Theme 1Murphy's LawNo ratings yet
- Acs 2017s1 Assn1Document5 pagesAcs 2017s1 Assn1MiraelNo ratings yet
- Control System4Document115 pagesControl System4Wilson BethuelNo ratings yet
- c4 3rdyearDocument4 pagesc4 3rdyearMark Chow Khoon Keat0% (1)
- A New Approach On Stabilization Control of An InveDocument5 pagesA New Approach On Stabilization Control of An Inveseyed mohsen SalehiNo ratings yet
- Step ResponseDocument6 pagesStep Responsenew007007No ratings yet
- Design of An Antenna Azimuth Position Control SystemDocument12 pagesDesign of An Antenna Azimuth Position Control SystemUche PaulNo ratings yet
- Inverted PendulumDocument18 pagesInverted PendulumLingxi HuangNo ratings yet
- Control 2021 UngappedDocument58 pagesControl 2021 Ungapped周暐凱No ratings yet
- Closedloop PID Control of Universal MotorDocument9 pagesClosedloop PID Control of Universal MotorabhywaNo ratings yet
- Ball-And-Beam Laboratory System Controlled by Simulink Model Through Dedicated Microcontrolled-Matlab Data Exchange ProtocolDocument11 pagesBall-And-Beam Laboratory System Controlled by Simulink Model Through Dedicated Microcontrolled-Matlab Data Exchange ProtocolIrawan MalikNo ratings yet
- EEE 441 - Note IIDocument4 pagesEEE 441 - Note IIAlex Peter OnojaNo ratings yet
- Control Systems and Task of Control Engineers 1.1 Introduction To Control EngineeringDocument7 pagesControl Systems and Task of Control Engineers 1.1 Introduction To Control EngineeringMagarsaa Qana'iiNo ratings yet
- Control System PresentationDocument10 pagesControl System PresentationVikneshwaran Keluan SinghNo ratings yet
- Final Lab ReportDocument17 pagesFinal Lab Reportapi-556975313No ratings yet
- 1, March 47: of ForDocument8 pages1, March 47: of Forcarlos gomez reyesNo ratings yet
- Control EngineeringDocument19 pagesControl EngineeringAmirul Zahim AzharNo ratings yet
- A Simple Fuzzy Excitation Control System (Avr)Document6 pagesA Simple Fuzzy Excitation Control System (Avr)Mmillion AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- Control System 1Document15 pagesControl System 1swatiagrawal_ecNo ratings yet
- Feedback and Control Systems: Engr. Joey P. Sarmiento, PECEDocument160 pagesFeedback and Control Systems: Engr. Joey P. Sarmiento, PECERAINIER RamosNo ratings yet
- DESIGNING THE PROPORTIONAL (P) AND PROPORTIONAL-INTEGRAL (PI) CONTROLLERS Control SystemDocument7 pagesDESIGNING THE PROPORTIONAL (P) AND PROPORTIONAL-INTEGRAL (PI) CONTROLLERS Control SystemjayxcellNo ratings yet
- Design of Magnetic Levitation System Undergraduate: A Control An ProjectDocument5 pagesDesign of Magnetic Levitation System Undergraduate: A Control An ProjectIshrat JamalNo ratings yet
- Power System Stabilizers As Undergraduate Control Design ProjectsDocument8 pagesPower System Stabilizers As Undergraduate Control Design Projectsabhikirk99No ratings yet
- Double Closed-Loop PI Controller Tuning For MotorDocument8 pagesDouble Closed-Loop PI Controller Tuning For MotorvrajakisoriDasiNo ratings yet
- Accumulator TensionDocument4 pagesAccumulator TensionMostafa MehrjerdiNo ratings yet
- Automated Emergency Response System For Nuclear Reactor: Final Report OnDocument11 pagesAutomated Emergency Response System For Nuclear Reactor: Final Report OnSaibNo ratings yet
- Space Engineering Lab Manual MDocument43 pagesSpace Engineering Lab Manual Mmanikandan_murugaiahNo ratings yet
- Control Engineering Instructional Module LecturesDocument13 pagesControl Engineering Instructional Module LecturesJohn Kenneth Santiago PaulinoNo ratings yet
- Sheet (3) (Block Diagrams)Document2 pagesSheet (3) (Block Diagrams)mostafa nasserNo ratings yet
- Sheet (5) (Modelling)Document2 pagesSheet (5) (Modelling)mostafa nasserNo ratings yet
- Sheet (2) (Laplace Transform)Document3 pagesSheet (2) (Laplace Transform)mostafa nasserNo ratings yet
- Sheet (6) (State Space Modelling)Document2 pagesSheet (6) (State Space Modelling)mostafa nasserNo ratings yet
- Design Verification With e 0131413090 9780131413092 CompressDocument410 pagesDesign Verification With e 0131413090 9780131413092 CompressQUÂN LÊ HỒNGNo ratings yet
- Networking Devices and Networking Topologies PDFDocument25 pagesNetworking Devices and Networking Topologies PDFAli AlwesabiNo ratings yet
- Data Structures Using C, 2e Reema TharejaDocument23 pagesData Structures Using C, 2e Reema TharejaseravanakumarNo ratings yet
- Systems Analysis and Design by Dennis AllanDocument4 pagesSystems Analysis and Design by Dennis AllanGrace Ann Aceveda Quinio100% (1)
- Synopsys Low Power Solutions For ASIC Design FlowDocument31 pagesSynopsys Low Power Solutions For ASIC Design FlowApoorva Bhatt100% (1)
- Beyond UVM Registers Better, Faster, Smarter: Rich Edelman, Bhushan Safi Mentor Graphics, US, IndiaDocument17 pagesBeyond UVM Registers Better, Faster, Smarter: Rich Edelman, Bhushan Safi Mentor Graphics, US, Indiapinakin4uNo ratings yet
- 13A99101 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering PDFDocument1 page13A99101 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering PDFsubbuNo ratings yet
- DSC System PCEI99339pdfDocument17 pagesDSC System PCEI99339pdfNeelam RanjanNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: B. Sc. Computer ScienceDocument79 pagesSyllabus: B. Sc. Computer SciencedrabdulsamathNo ratings yet
- A Brushless DC Motor Drive-763Document5 pagesA Brushless DC Motor Drive-763Harshal VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Workbench Installation Guide: Create and Customize User Interfaces For Router ControlDocument29 pagesWorkbench Installation Guide: Create and Customize User Interfaces For Router ControlArdian AriefNo ratings yet
- LiteWave Switch DatasheetDocument3 pagesLiteWave Switch Datasheetpaul esparagozaNo ratings yet
- SS Chapter 01 Introduction To A Machine ArchitectureDocument47 pagesSS Chapter 01 Introduction To A Machine ArchitectureNaveen Kumar TripathiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 18 Intro To Network Layer 12052021 024156pm 1 10012022 105155am 1 22062022 095946am 26122022 101336amDocument79 pagesChapter - 18 Intro To Network Layer 12052021 024156pm 1 10012022 105155am 1 22062022 095946am 26122022 101336amNoor fatimaNo ratings yet
- Genius Publications ListDocument5 pagesGenius Publications ListArun Trichal25% (4)
- Versant English Placement Test - Technical Requirements ENGDocument17 pagesVersant English Placement Test - Technical Requirements ENGmuller.eshetu12No ratings yet
- Thyristor Product CatalogDocument224 pagesThyristor Product CatalogMohamed ReyadNo ratings yet
- M3000 Firmware UpgradeDocument23 pagesM3000 Firmware UpgradeBiswajit DasNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityMihir RanaNo ratings yet
- Small Engine EFI Tuning GuideDocument189 pagesSmall Engine EFI Tuning GuideFabio GuedesNo ratings yet
- R5905112 04 ReleaseNoteDocument16 pagesR5905112 04 ReleaseNotejcll lopezNo ratings yet
- 6 Class NotesDocument19 pages6 Class NotesSAMPATH CHINDAMNo ratings yet
- 9.2.9 Packet Tracer - Examine The ARP Table - ILMDocument4 pages9.2.9 Packet Tracer - Examine The ARP Table - ILMRenato ValverdeNo ratings yet
- Batch 2017 3rd Semester CSEDocument27 pagesBatch 2017 3rd Semester CSEAnkur GiriNo ratings yet
- Installing Executable-Image GEMPACK Prior To Laptop-Based CourseDocument6 pagesInstalling Executable-Image GEMPACK Prior To Laptop-Based CourseSigit WaskithoNo ratings yet
- NTE46 Silicon NPN Transistor Darlington, General Purpose Amplifier, Preamp, DriverDocument2 pagesNTE46 Silicon NPN Transistor Darlington, General Purpose Amplifier, Preamp, DriverAbel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Addresses, Protocols, and Ports (PDFDrive)Document16 pagesAddresses, Protocols, and Ports (PDFDrive)rootNo ratings yet
- Contoller Replacement InstructionsDocument4 pagesContoller Replacement InstructionsRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- BRZ Electrical Wiring DiagramDocument404 pagesBRZ Electrical Wiring DiagramBagas Hanadi YudoNo ratings yet
- Philips SDK ManualDocument16 pagesPhilips SDK ManualMartin HríbikNo ratings yet