Professional Documents
Culture Documents
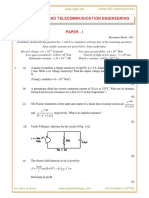
EEC Question Paper - III Test - Oct 2020
EEC Question Paper - III Test - Oct 2020
Uploaded by
Rajachedambaram RajachedambaraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EEC Question Paper - III Test - Oct 2020
EEC Question Paper - III Test - Oct 2020
Uploaded by
Rajachedambaram RajachedambaraCopyright:
Available Formats
ELECTRODICS AND ELECTROCATALYSIS
EL8502 – October 2020
Time: 1 hr 30 mins Maximum: 40 marks
PART A (5 2 = 10 marks)
Answer all questions
1. Draw Nyquist plots for a single electron transfer reversible diffusion controlled and charge
transfer controlled processes along with their suitable equivalent circuits.
2. Define potentiometric selectivity coefficient with an example.
3. Impedance response of Zn/Zn2+ redox couple recorded in an aqueous solution of 1M NaClO4
and 1mM perchloric acid using a disc shaped Au electrode in the frequency range of 20 Hz
to 20 kHz exhibits a resistance value of 0.5 cm2 at 20 kHz and the other intercept on X-
axis provides a resistance value of 3.15 cm2. Given that CZn=CZn2+= 8 µmoles/cm3, =
0.5 and Zmax observed at 1 kHz is 1.45 cm2. Calculate the charge transfer resistance (Rct)
and capacitance associated with this process.
4. What do you mean by ideally polarizable and non-plolarizable electrodes? Write one
examples for each.
5. Define the term electrical double Layer (EDL).
PART B (3 × 10 = 30 marks)
Answer all questions
1. (a) Derive the expressions and sketch the relations for input (E) and output (I) ac signals
when the circuits containing resistor only, capacitor only and a series combination of resistor
and capacitor are employed. (5)
(b) Derive the expressions for kinetic parameters such as charge transfer resistance (R ct),
electron transfer rate constant (ket), O, R and from the Faradaic impedance. (5)
2. (a) Define ion-selective electrode and explain the working principle of pH electrode with a
neat sketch. (5)
(b) Derive Lippman equation for liquid metal interface. (5)
3. Explain the following.
(i) Helmholtz double layer and (ii) Gouy-Chapman double layer.
You might also like
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1No ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- EDC Question-Papers Complete SetDocument13 pagesEDC Question-Papers Complete Setselvi04120% (1)
- Impedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and ApplicationsFrom EverandImpedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and ApplicationsEvgenij BarsoukovNo ratings yet
- dc82dbfbEndSem 2018Document2 pagesdc82dbfbEndSem 2018Aayush Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Time: Three Hours Answer ALL Questions Max Marks:100Document2 pagesTime: Three Hours Answer ALL Questions Max Marks:100Vijayalakshmi VijiNo ratings yet
- FY-BTech - ET - Electrical & Electronics Engineering - SEM-I - JAN 2023Document2 pagesFY-BTech - ET - Electrical & Electronics Engineering - SEM-I - JAN 2023kumbhalkarvalay8No ratings yet
- EC Question PaperDocument3 pagesEC Question PaperGna Senthil KumarNo ratings yet
- 15A04201 Network AnalysisDocument2 pages15A04201 Network AnalysisMahaboob SubahanNo ratings yet
- Anal Chem 3 - Test 1-2016Document4 pagesAnal Chem 3 - Test 1-2016Buhle BuhleNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument2 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentAksay SriramNo ratings yet
- Ee10002 Oct Autumn Mid Sas 23Document3 pagesEe10002 Oct Autumn Mid Sas 23mdabdularain655No ratings yet
- 2002 Qualifying ExamDocument5 pages2002 Qualifying ExamrujintoNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological University: InstructionsjayswamiiNo ratings yet
- SS - FTS - 04 (Online) - (Main) C - 2020-11-20 - 2020 - QDocument9 pagesSS - FTS - 04 (Online) - (Main) C - 2020-11-20 - 2020 - QjioNo ratings yet
- This PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For NEET & AiimsDocument13 pagesThis PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For NEET & Aiimsnil kumarNo ratings yet
- r059210204 Electromagnetic FieldsDocument8 pagesr059210204 Electromagnetic FieldsSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- EET285-Dynamic Circuits and SystemsDocument9 pagesEET285-Dynamic Circuits and SystemsDeepa M SNo ratings yet
- Electro Magnetic FieldDocument4 pagesElectro Magnetic FieldAnanya ParameswaranNo ratings yet
- Rr-10205-Edc Apr 2003Document8 pagesRr-10205-Edc Apr 2003mpssassygirlNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam #2 April 5, 2010: (Continue To Next Page)Document3 pagesMidterm Exam #2 April 5, 2010: (Continue To Next Page)Yenhao Philip ChenNo ratings yet
- 03 - Physics - March 2007Document6 pages03 - Physics - March 2007Bernardo Gonzalez GarciaNo ratings yet
- CT It 2 S1Document4 pagesCT It 2 S1Raja pandiyanNo ratings yet
- Online Test On Electrochemistry PDFDocument2 pagesOnline Test On Electrochemistry PDFrvignesh2809No ratings yet
- Introductory Chemistry WorksheetDocument1 pageIntroductory Chemistry WorksheetAyanthi ShashikalaNo ratings yet
- Hours: ExaminationDocument2 pagesHours: Examinationapi-279049687No ratings yet
- Physics Cc13Document2 pagesPhysics Cc13b718535740No ratings yet
- Phy543 HW Combo PDFDocument3 pagesPhy543 HW Combo PDFAbdul Jalil MondalNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper 2: General InstructionDocument9 pagesCBSE Sample Paper 2: General Instructionkg4freeNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics I (8.04) Spring 2016 Assignment 2: Problem Set 2Document5 pagesQuantum Physics I (8.04) Spring 2016 Assignment 2: Problem Set 2Fabian M Vargas FontalvoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves and Transmission Lines Question PaperDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic Waves and Transmission Lines Question PaperelimelekNo ratings yet
- R5100207-Electronic Devices & CircuitsDocument2 pagesR5100207-Electronic Devices & CircuitssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- NANJA CH 110. Tutorial Sheet 6 (Atomic Structure) - FM 2024.Document2 pagesNANJA CH 110. Tutorial Sheet 6 (Atomic Structure) - FM 2024.nzalamsundayNo ratings yet
- 07a4ec10-Em Waves and Transmission LinesDocument5 pages07a4ec10-Em Waves and Transmission LinesSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Bee MT - Ii Question Paper CseDocument2 pagesBee MT - Ii Question Paper Cseviju001No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Worksheet - ElectrochemistryDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Worksheet - ElectrochemistryArya VermaNo ratings yet
- CHE-221 Question Bank (09.06.10), PDFDocument5 pagesCHE-221 Question Bank (09.06.10), PDFnazmulsustNo ratings yet
- Problems: I Ijk J K IDocument1 pageProblems: I Ijk J K INeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- EE Con-1 Mock-2Document8 pagesEE Con-1 Mock-2shishirgupta2007No ratings yet
- Prework Questions For KI-1Document5 pagesPrework Questions For KI-1Danial SadiqNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper 1: General InstructionDocument8 pagesCBSE Sample Paper 1: General InstructionRavi RavisankarNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics (Theory)Document6 pages12 Physics (Theory)Bhaswati SurNo ratings yet
- IES Conventional BNNNDocument10 pagesIES Conventional BNNNVivek ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 19A02401T Electrical Circuit AnalysisDocument2 pages19A02401T Electrical Circuit Analysisfepov48405No ratings yet
- II PUC Physics Paper 1Document2 pagesII PUC Physics Paper 1narayanammagnarayanamma90No ratings yet
- A10 ET&TL (ECE) SuppDocument2 pagesA10 ET&TL (ECE) SuppManeesha MonuNo ratings yet
- .Theory of Electrical Engineering Exam July 2020Document3 pages.Theory of Electrical Engineering Exam July 2020James kaundaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Monthly Test 2016-17 (JULY)Document3 pagesClass 12 Monthly Test 2016-17 (JULY)rahulNo ratings yet
- IAS Previous Year Test PapersDocument4 pagesIAS Previous Year Test PapersRavinder Singh100% (2)
- Spring K MassDocument4 pagesSpring K MasshamedNo ratings yet
- Year 1991Document4 pagesYear 1991Tamizh E STNo ratings yet
- AssignmenticsDocument4 pagesAssignmenticssattar280% (1)
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document0 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Bala SubramanianNo ratings yet
- R5102303-Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument1 pageR5102303-Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Subatomic Problem Set 1: Radioactivity and Nuclear StabilityDocument32 pagesSubatomic Problem Set 1: Radioactivity and Nuclear StabilityDiego M GranziolNo ratings yet
- bt21R0718 p1 18 11 09rahulDocument30 pagesbt21R0718 p1 18 11 09rahulAnonymous nTxB1EPvNo ratings yet
- CHEM10101 2011 Exam AnswersDocument9 pagesCHEM10101 2011 Exam Answersyasemin19921No ratings yet
- Chemistry Holiday Assignment Class 10Document9 pagesChemistry Holiday Assignment Class 10Uday Prakash SahuNo ratings yet
- BSC II Year - Physics Paper-II - 2017Document3 pagesBSC II Year - Physics Paper-II - 2017Tharun TharunNo ratings yet
- Semester-1 - Chemistry Stream - Mid+end PaperDocument15 pagesSemester-1 - Chemistry Stream - Mid+end PaperGopiNo ratings yet