Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EIA Task5
Uploaded by
Ahmed HosneyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EIA Task5
Uploaded by
Ahmed HosneyCopyright:
Available Formats
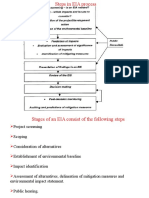
Approaches of screening to EIA
Most countries focus on identifying the types of projects, their size and potential
impacts to determine the need for an EIA. Overall, we can distinguish two different
.approaches to screening
Prescriptive or standardized approaches: Categories for different types of
development proposals are outlined in legislation and regulations. Proponents can
often decide whether their project will need an EIA based on these standardized
:approaches. These could include
.Legal (or policy) definitions of proposals to which EIA does or does not apply -
Inclusion lists of projects (with or without thresholds) for which an EIA is -
.automatically required
Exclusion lists of activities that do not require an EIA because they are insignificant -
.or are exempt by law (e.g., national security or emergency activities)
Customized approaches: Proposals are screened on an individual or case-by-
.case base, using indicative guidance with categories
Different countries and international agencies combine these types of screening
procedures. Most often, a simple categorization (such as A – C or 1 – 3) is used.
These categories help proponents and licensing agencies decide when a full EIA is
.needed
For high-impact projects: A full EIA is required because these are likely to have -1
significant serious adverse environmental impacts (i.e., result in irreversible damage,
affect vulnerable ethnic minorities, involve involuntary resettlement, or affect
:cultural heritage sites). These often include
.Dams and reservoirs
.Forestry and production projects
.Industrial plants (large-scale)
.Irrigation, drainage, and flood control (large-scale)
.Mining and mineral development (including oil and gas)
.Port and harbor development
.Reclamation, resettlement and new land development
.Thermal and hydropower development
Manufacture, transportation, and use of pesticides and other hazardous and/or toxic
.materials
For medium-impact projects (those likely to have adverse environmental impacts -2
that are less significant than those of in the previous category): Normally a limited
EIA will be undertaken to identify suitable mitigation and management measures
:and incorporate them into the project. These often include
Agro-industries, Electrical transmission; rural electrification
Aquaculture, irrigation and drainage (small-scale), Renewable energy, Tourism, Rural
.water supply and sanitation
For low-impact projects (Those that are likely to have minimal or no adverse
environmental impacts): No EIA is required. For example
Construction of small buildings, Community garden development, Development of
.wells in a community, Outdoor recreation
:Advantages of screening approaches
Timesaving for local authorities and developers;
Cost reduction to local authorities and developers;
Reducing unnecessary EIAs.
Alternative option of submitting screening direction through the secretary of state.
Avoided impacts and violations of laws and regulations.
Avoided treatment/cleanup costs.
Disadvantages of screening approaches
There is no distinction between urban and rural areas, despite the qualities of the
areas being are significantly different;
The increase in hectares was too large, particularly in urban areas;
Subjectivity to housing size and height;
Smaller projects collectively can account for larger impacts, which may eventually
become detrimental.
Smaller projects are now overlooked
Screening Approaches to EIA in Egypt: The system encompasses a
flexible screening system and projects are classified into three groups or
classes reflecting different levels of environmental impact assessment
according to severity of possible environmental impacts.
The List Approach (Customized) in Egypt:
The list approach depends on screening projects into three categories based on different levels
of EIA required according to severity of possible environmental impacts as follows:
1. The "A" list projects for establishments/projects with minor environmental impact.
2. The "B" list projects for establishments/projects which may result in substantial
environmental impact.
3. The "C" list projects for establishments/projects which require complete EIA due to
their potential impacts.
4.Projects that have Special Conditions
You might also like
- Saep 13 PDFDocument24 pagesSaep 13 PDFbrecht1980100% (4)
- Hazardous Substances and Human Health: Exposure, Impact and External Cost Assessment at the European ScaleFrom EverandHazardous Substances and Human Health: Exposure, Impact and External Cost Assessment at the European ScaleNo ratings yet
- ConclusionDocument7 pagesConclusionMolshree Bhatnagar0% (1)
- ScreeningDocument35 pagesScreeningNmn FaltuNo ratings yet
- Sadik Zakir EIADocument24 pagesSadik Zakir EIAsufian abdo jilo100% (1)
- History of EIA in IndiaDocument31 pagesHistory of EIA in IndiaanaghaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment Report For Cement Industry (Guide)Document10 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment Report For Cement Industry (Guide)Arsalan Khan100% (2)
- September - 2020 - Environmental - Impact - Assessment ResarchDocument26 pagesSeptember - 2020 - Environmental - Impact - Assessment Resarchboussaidy609No ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment 1Document6 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment 1Mrīgendra Narayan UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact AssessmentDocument8 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessmentjunaid khanNo ratings yet
- Philippine Environmental Impact Statement System (PEISS)Document8 pagesPhilippine Environmental Impact Statement System (PEISS)Kristine KristineeeNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact AssessmentDocument20 pagesEnvironmental Impact AssessmentDanish RaisNo ratings yet
- Eia 2020Document6 pagesEia 2020Aditi SharmaNo ratings yet
- EIA Assignment 3Document4 pagesEIA Assignment 3hebahesham.12.2000No ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment (16.01.24)Document27 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment (16.01.24)Tarakasish GhoshNo ratings yet
- 1.4. Environmental Impact AssessmentDocument6 pages1.4. Environmental Impact Assessmentsiva ramanNo ratings yet
- Terms of References (Tors) For Eias: Digital Assignment-IiiDocument6 pagesTerms of References (Tors) For Eias: Digital Assignment-IiiArun KumarNo ratings yet
- EIA Ba LLB Revised 22-11-2019Document54 pagesEIA Ba LLB Revised 22-11-2019Palak JoshiNo ratings yet
- EIA Ba LLB Revised 22-11-2019Document54 pagesEIA Ba LLB Revised 22-11-2019Palak JoshiNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment (Eia)Document12 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment (Eia)RyuuNo ratings yet
- Environment Impact AssessmentDocument5 pagesEnvironment Impact AssessmentSuresh ManiNo ratings yet
- EIADocument32 pagesEIAHershita SinghNo ratings yet
- Environment Impact AssessmentDocument4 pagesEnvironment Impact AssessmentAdib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) : Project Management CourseDocument33 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment (EIA) : Project Management Courseg.suvoNo ratings yet
- 3 - EIA ProcessDocument65 pages3 - EIA ProcessAbdanur JihadNo ratings yet
- Environment Impact AssessmentDocument15 pagesEnvironment Impact AssessmentAyush BhadauriaNo ratings yet
- Adaptation To The Impacts of Sea Level Rise in EgyptDocument20 pagesAdaptation To The Impacts of Sea Level Rise in EgyptmijazNo ratings yet
- L1 - Basic ConceptsDocument67 pagesL1 - Basic Conceptsshivani100% (1)
- Environment Law NotesDocument17 pagesEnvironment Law Notesmitalirakhecha19.solNo ratings yet
- The Millenium Ecosystem Assessment (MA) - Greenorg SiteDocument5 pagesThe Millenium Ecosystem Assessment (MA) - Greenorg Siteamelia klejmentNo ratings yet
- The Legal Process of Environment Impact AssessmentDocument14 pagesThe Legal Process of Environment Impact AssessmentNi TanshaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment (Eia)Document44 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment (Eia)Abdul Aziz100% (1)
- Basis For Projects Categorization, and Safeguards Instruments-FDocument31 pagesBasis For Projects Categorization, and Safeguards Instruments-FMelikteNo ratings yet
- Eia Q & ADocument10 pagesEia Q & AAnkur YashNo ratings yet
- Tek Home Test EnviroDocument14 pagesTek Home Test EnviroTrarubo ArimaNo ratings yet
- Sample Answer: Govt. of Bihar Muzaffarpur Institute of Technology, Muzaffarpur, Bihar - 842003Document7 pagesSample Answer: Govt. of Bihar Muzaffarpur Institute of Technology, Muzaffarpur, Bihar - 842003Ankit100% (1)
- Environmental Impact AssessmentDocument12 pagesEnvironmental Impact AssessmentSekelani LunguNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment and Introduction To Environmental AuditingDocument22 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment and Introduction To Environmental AuditingBAGUMA NELSON100% (1)
- Research Paper On EiaDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Eiagvzftaam100% (1)
- ReportDocument66 pagesReportMailene UmadhayNo ratings yet
- Eia Full NotesDocument56 pagesEia Full Notesorangeideas7No ratings yet
- Module 5Document44 pagesModule 5DIPTANU SAHANo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument86 pagesUnit IShrutiNo ratings yet
- 2.eia StepsDocument45 pages2.eia StepspushprajNo ratings yet
- OVER SEAS, March, 2002: The Philippine Environment Impact Statement System and What It EntailsDocument15 pagesOVER SEAS, March, 2002: The Philippine Environment Impact Statement System and What It EntailsSam Sy-HenaresNo ratings yet
- Screening and ScopingDocument24 pagesScreening and ScopingJesa MoradaNo ratings yet
- Saep 13Document23 pagesSaep 13Bernardo ZiliottoNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact AssessmentDocument19 pagesEnvironmental Impact AssessmentbbnNo ratings yet
- A. What Is Environmental Impact Assessment (Eia) ?Document5 pagesA. What Is Environmental Impact Assessment (Eia) ?Gnihc SicnarfNo ratings yet
- Consolidated EspsDocument45 pagesConsolidated EspsEzzadin BabanNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) : Project Management CourseDocument33 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment (EIA) : Project Management Courseg4goharNo ratings yet
- Saep 13Document24 pagesSaep 13iikh3ansNo ratings yet
- Landfill WasteDocument10 pagesLandfill WasteShawn PattonNo ratings yet
- QDocument8 pagesQSudipta kumar muduliNo ratings yet
- CET415 - M3 - Ktunotes - inDocument63 pagesCET415 - M3 - Ktunotes - inTheerthaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment and Emss: An IntroductionDocument17 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment and Emss: An IntroductionMunashe Josiah ChipatisoNo ratings yet
- Presidential Decree No. 1586: Philippine Environment Impact Statement System (PEISS)Document44 pagesPresidential Decree No. 1586: Philippine Environment Impact Statement System (PEISS)Benz Clyde Bordeos Tolosa100% (1)
- Direct Impacts:: Types of Environmental ImpactsDocument37 pagesDirect Impacts:: Types of Environmental ImpactsHang TranNo ratings yet
- Eiamethods NotesDocument5 pagesEiamethods NotesRoubina NuckcheddyNo ratings yet
- New sanitation techniques in the development cooperation: An economical reflectionFrom EverandNew sanitation techniques in the development cooperation: An economical reflectionNo ratings yet
- Final ExamDocument3 pagesFinal ExamAhmed HosneyNo ratings yet
- XIII Lecture 2020Document47 pagesXIII Lecture 2020Ahmed HosneyNo ratings yet
- Audit Report Template 37Document52 pagesAudit Report Template 37Ahmed Hosney100% (1)
- VIII Lecture 2020Document46 pagesVIII Lecture 2020Ahmed HosneyNo ratings yet
- VI Lecture 2020Document41 pagesVI Lecture 2020Ahmed HosneyNo ratings yet
- XI Lecture 2020Document47 pagesXI Lecture 2020Ahmed HosneyNo ratings yet
- XII Lecture 2020Document52 pagesXII Lecture 2020Ahmed HosneyNo ratings yet
- VII Lecture 2020Document45 pagesVII Lecture 2020Ahmed HosneyNo ratings yet
- Audit Report Template 11Document5 pagesAudit Report Template 11Ahmed HosneyNo ratings yet
- Audit Report Template 13Document5 pagesAudit Report Template 13Ahmed HosneyNo ratings yet
- Audit Report Template 05Document6 pagesAudit Report Template 05Ahmed HosneyNo ratings yet
- Annex 2 To The Law On EIA-2017Document8 pagesAnnex 2 To The Law On EIA-2017Ahmed HosneyNo ratings yet
- Audit Report Template 12Document1 pageAudit Report Template 12Ahmed HosneyNo ratings yet
- EIA MidDocument12 pagesEIA MidAhmed HosneyNo ratings yet
- Audit Report Template 01Document9 pagesAudit Report Template 01Ahmed HosneyNo ratings yet
- TL enDocument98 pagesTL enAhmed HosneyNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment in EgyptDocument17 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment in EgyptAhmed HosneyNo ratings yet
- Eia Hannan Airport NiueDocument21 pagesEia Hannan Airport NiueAhmed HosneyNo ratings yet
- Tipk enDocument106 pagesTipk enAhmed HosneyNo ratings yet
- EIA Task 8Document1 pageEIA Task 8Ahmed HosneyNo ratings yet
- EIA Task 7Document2 pagesEIA Task 7Ahmed HosneyNo ratings yet
- EIA Task4Document28 pagesEIA Task4Ahmed HosneyNo ratings yet
- EIA Task2Document1 pageEIA Task2Ahmed HosneyNo ratings yet
- EIA Task3Document2 pagesEIA Task3Ahmed HosneyNo ratings yet
- Mangroves StudyDocument7 pagesMangroves StudyTeresa Marie Yap CorderoNo ratings yet
- General Creteria GM Leed: Green Mark and Leed ComparisonDocument47 pagesGeneral Creteria GM Leed: Green Mark and Leed ComparisonNguyên Trịnh CaoNo ratings yet
- O' Level Geo Sir Salman HashmiDocument74 pagesO' Level Geo Sir Salman HashmiXantron Robins100% (1)
- 17 Sustainable Development GoalsDocument62 pages17 Sustainable Development Goalspacul.jeweljadeNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Notes 06 Student GoodDocument6 pagesGlobal Warming Notes 06 Student GoodTammara WallaceNo ratings yet
- Types of Environmental PollutionDocument1 pageTypes of Environmental PollutionLing Siew EeNo ratings yet
- Academic Session:-2020-2021: Presentation On Types of Biological Pest ControlDocument13 pagesAcademic Session:-2020-2021: Presentation On Types of Biological Pest ControlNishthaNo ratings yet
- SST New FormatDocument8 pagesSST New FormatKOVID PRAPANNANo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Case Studies (International) : 1.1 Case 1 Mitigation of The Heat Island Effect in Urban New JerseyDocument14 pagesChapter 1 Case Studies (International) : 1.1 Case 1 Mitigation of The Heat Island Effect in Urban New JerseyShirjana ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Go Green ProjectDocument1 pageGo Green ProjectMinh Tâm PhạmNo ratings yet
- I Am Sharing 'OE Question Bank' With YouDocument55 pagesI Am Sharing 'OE Question Bank' With YouVishva DesaiNo ratings yet
- Coastal Mitigation and Adaptation MeasuresDocument5 pagesCoastal Mitigation and Adaptation Measuresjames kaririNo ratings yet
- Script : - Marine EnvironmentDocument22 pagesScript : - Marine Environmentanishc007No ratings yet
- PDF Assignment Business Ethics Governance and Risk 20 11 2018Document3 pagesPDF Assignment Business Ethics Governance and Risk 20 11 2018devang asherNo ratings yet
- ES200SWMDocument37 pagesES200SWMRuchi Aayush MehtaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Issues in Developing CountriesDocument3 pagesEnvironmental Issues in Developing Countriesmohinman100% (1)
- Organic AgricultureDocument13 pagesOrganic AgricultureGabriela Nicoleta EremiaNo ratings yet
- 2018 Laudato Si ConferenceDocument24 pages2018 Laudato Si ConferenceCari AzoresNo ratings yet
- (Wildlife Management and Conservation) Michael L. Morrison, Heather A. Mathewson-Wildlife Habitat Conservation - Concepts, Challenges, and Solutions-Johns Hopkins University Press (2015)Document198 pages(Wildlife Management and Conservation) Michael L. Morrison, Heather A. Mathewson-Wildlife Habitat Conservation - Concepts, Challenges, and Solutions-Johns Hopkins University Press (2015)Víctor Hugo Guzman CalderonNo ratings yet
- Alaska Climate Action Plan RecommendationsDocument40 pagesAlaska Climate Action Plan RecommendationsKevin GullufsenNo ratings yet
- Q1 Week 6 Day 1Document22 pagesQ1 Week 6 Day 1Eddierlyn ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Rayya DataDocument46 pagesRayya DataParth DuggalNo ratings yet
- Jordan Odor Thesis DraftDocument22 pagesJordan Odor Thesis DraftrutkrtkNo ratings yet
- March 2nd DLL Catch Up FridayDocument3 pagesMarch 2nd DLL Catch Up FridayJecel FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Final Demo - Ecological RelationshipDocument7 pagesFinal Demo - Ecological RelationshipDareen CuetoNo ratings yet
- Sarihay 3rd IssueDocument16 pagesSarihay 3rd Issuefpe_scribdNo ratings yet
- Thesis Water QualityDocument7 pagesThesis Water Qualitydwr11wf4100% (2)
- Kampala City Solar Street Lighting Project: Mandating Authority: Expected Project CAPEXDocument2 pagesKampala City Solar Street Lighting Project: Mandating Authority: Expected Project CAPEXDouglas OngomNo ratings yet
- EST (25 To 30) Micro ProjectDocument12 pagesEST (25 To 30) Micro ProjectVishal JadhavNo ratings yet
- Transition of Ecosystem Services Based On Urban Agro EcologyDocument20 pagesTransition of Ecosystem Services Based On Urban Agro EcologyAna C. PonticelliNo ratings yet