Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tables Nurology
Uploaded by
Razan Alayed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views5 pagesOriginal Title
tables nurology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views5 pagesTables Nurology
Uploaded by
Razan AlayedCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
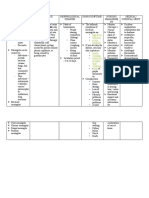
Subfalcine Downward Upward Cerebellar
herniation Transtentorial transtentorial tonsillar
herniation herniation herniation
Herniated cingulate gyrus inferomedial superior Downward
component slides underneath displacement of transtentorial displacement
the falx. the uncus through herniation of the of the
the tentorial notch cerebellar vermis cerebellar
due to posterior tonsils
fossa mass effect through
foramen
magnum
Compressed may rarely cause 1.ipsilateral CN III obstructive Compression
structure compression of the paresis hydrocephalus of medullary
anterior cerebral 2. compression of from aqueductal respiratory
artery PCA compression. centers is
Contralateral 3. Duret often fatal
hydrocephalus hemorrhages
may result from 4. compression of
foramen of Monro contralateral
obstruction cerebral peduncle
Allergic Fungal Sinusitis Acute Invasive Fugal Sinusitis
involves Opacification of multiple sinuses bilaterally Opacification of multiple
Favours ethmoid and maxillary sinuses. Stranding /
Extension into the fat around
the sinuses
Immune Normal Immune System (Asthma is common) immunocompromised
system - Neutropenic = Aspergillus
- Diabetic in DKA =
Zygomycetes / Mucor
CT Hyperdense centrally or with layers. Can Opacified Sinus with is NOT
erode and remodel sinus walls if chronic. hyperdense. Fat
stranding in the orbit,
masticator fat, pre-antral fat,
MRI Tl-T2 Dark Tl/T2 Dark. mucosa may not
Inflamed (T2 bright) mucosa which will enhance. The enhance (suggesting it is
glob of fungus snot will not enhance necrotic).
The extension of disease out of
the sinus will be
bright on STIR and enhance.
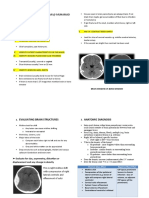
hyperacute acute infarct early subacute late subacute chronic infarct
infarct 0-6 6-72 hours infarct infarct
hours 1.5 days - 5 5 days - 2
days weeks
DWI Hyper hyper hyper Hyper iso
ADC hypo hypo resolving Iso or normal hyper
Diffusion restricted restricted Less restricted increased increased di-
diffusivity. usivity
T2w signal Normal or Hyper in grey Hyper T2/FLAIR T2/FLAIR
subtle hyper matter involving both hyperintense hyperintense
grey and
white matter
Mass effect ---------- Increasing peaks at 3-4 reduction …….
peaks at 3-4 days in mass effect.
days
enhancement ---------- --------- gyriform ………
enhancement
6 d to 6 wks
Perfusion decreased increase in Perfusion
cerebral blood size of the imaging shows
volume of the infarct core continued
infarct core+/- with expansion of
penumbra resultant the infarct
decrease in core and
size of the further
penumbra. reduction in
penumbra
Type of cytotoxic vasogenic vasogenic resolving resolving
edema edema
Traumatic pseudoaneurysm:Arteries close to bony structures (such as the basilar and vertebral
artery) are prone to dissecting aneurysms.
Saccular Fusiform Mycotic Oncotic Traumatic
aneurysm aneurysm aneurysm aneurysm pseudoaneurysm
cause combination Atherosclerosis Bacterial neoplasm trauma
of chronic endocarditis
hemodynamic dissection
stress and
acquired
degeneration
of the vessel
wall.
location arising at a Posterior distal arterial distal arterial
branch point circulation circulation, circulation
in the circle of beyond the
Willis circle of Willis
Other can be do not occur at A benign left Arteries close to
classified as branch point atrial bony structures
small (<1 cm), myxoma may (such as the
medium (>1 peripherally basilar and
cm and <2.5 embolize and vertebral artery)
cm), and giant cause a distal are prone to
(>2.5 cm). oncotic dissecting
aneurysm aneurysms.
Rhomboencephalosynapsis joubert syndrome
vermis absent Absent or small
cerebellum abnormal fusion of the cerebellum Small Cerebellum
Classic imaging Transversely oriented single lobed "Molar Tooth" appearance
appearance cerebellum
4th ventricle small Large 4th Ventricle
"Batwing Shaped"
Fastigial point and primary Rounded Fastigial Point, Absent Fastigial Point,
fissure Absent Primary Fissure Absent Primary Fissure
association Holoprosencephaly Spectrum Retinal dysplasia (50%),
Multicystic dysplastic
kidneys (30%).
Liver Fibrosis ("COACH"
Syndrome)
Chiari type I II III
features Tonsillar descend more here is relatively less features of of Chiari 2
that 5 mm from BO tonsillar herniation, plus
line but more cerebellar Occipital
vermian Encephalocele
displacement
Imaging features Clival Hypoplasia Encephalocele
Low Lying Torcula containing cerebellum
Thinned Corpus and/ or the brainstem,
Callosum occipital lobe, and
Tectal Beak sometimes even
Interdigitated Cerebral the fourth ventricle
Gyri
association Syrinx Lumbar • Syrinx ( cervical)
Klippel-Feil Syndrome. myelomeningocele / • Tethered cord
NOT associated with a Spina Bifida • Hydrocephalus
neural tube defect Only seen in patients • Agenesis of the
with a neural tube corpus
defect callosum
pseudotumor Thyroid ophthalmopathy
unilateral bilateral
painful painless
Involves the myotendinous insertion Spares the myotendinous insertion
most commonly involves the lateral rectus I aM SlOw
Inferior, Middle, Superior, Lateral, Oblique
You might also like
- EKG Study GuideDocument45 pagesEKG Study GuideBrawner100% (6)
- Musculoskeletal ChartsDocument27 pagesMusculoskeletal Chartssurviving nursing school100% (3)
- Physio 2.05 Bloodphysiology2 HemostasisDocument9 pagesPhysio 2.05 Bloodphysiology2 HemostasisSimon Peter Familara100% (1)
- @MedicalBooksStore 2014 MusculoskeletalDocument423 pages@MedicalBooksStore 2014 MusculoskeletalRazan Alayed100% (5)
- Method Statement For PlasteringDocument14 pagesMethod Statement For Plasteringjameel100% (1)
- Path CNS Robbins Outline: Owl Club Review Sheets 1Document37 pagesPath CNS Robbins Outline: Owl Club Review Sheets 1Coy NuñezNo ratings yet
- Dams Flash Cards PDFDocument315 pagesDams Flash Cards PDFKritika P SoroutNo ratings yet
- NEURO2 3.05 Neurosurgical Management of Stroke and CNS Infection - Dr. Domingo PDFDocument3 pagesNEURO2 3.05 Neurosurgical Management of Stroke and CNS Infection - Dr. Domingo PDFPatricia Nicole AlcarazNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of HydrocephalusDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of HydrocephalusJan Rae Barnatia AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Dr. Subagia - Neuro RadiologyDocument94 pagesLecture - Dr. Subagia - Neuro RadiologySyaimee Annisa AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Physical Diagnosis Overview Guide ScribdDocument117 pagesPhysical Diagnosis Overview Guide ScribdTrisNo ratings yet
- Using The Vineland 3 On Q Global Pearsonclinical Com AuDocument16 pagesUsing The Vineland 3 On Q Global Pearsonclinical Com AuAndreia SilvaNo ratings yet
- Nosotros NoDocument2 pagesNosotros NoAlcindorLeadonNo ratings yet
- Anxiety NeurosisDocument34 pagesAnxiety Neurosisilakkiya ilakkiyaNo ratings yet
- Paraplegia-Types, Causes and DiagnosisDocument59 pagesParaplegia-Types, Causes and Diagnosiskashmala afzalNo ratings yet
- Facial Nerve: by Dona Mariam Sam Third Year BDS Reg No 170021349Document26 pagesFacial Nerve: by Dona Mariam Sam Third Year BDS Reg No 170021349DONA MARIAM SAMNo ratings yet
- PAN India Empanelled Hospital List - OICDocument423 pagesPAN India Empanelled Hospital List - OICBHARAT BHUSHANNo ratings yet
- mgmt404 Final Project HMPDocument22 pagesmgmt404 Final Project HMPapi-25526962850% (2)
- 4 Dohns May 2004Document7 pages4 Dohns May 2004rizwan afzalNo ratings yet
- Batangas State University NSTP Project on Community GardeningDocument17 pagesBatangas State University NSTP Project on Community Gardeningjaerald estiocoNo ratings yet
- Macroscopic Diagnostic GuideDocument21 pagesMacroscopic Diagnostic Guidekapil pancholiNo ratings yet
- M100 ActivityDocument5 pagesM100 ActivityAira Galinato CabrasNo ratings yet
- PPT Ilmiah Spine Cerebellar DisordersDocument17 pagesPPT Ilmiah Spine Cerebellar DisordersVito MasagusNo ratings yet
- Brain AbscessDocument3 pagesBrain AbscessAndrew JavierNo ratings yet
- Complications of Suppurative Otitis MediaDocument2 pagesComplications of Suppurative Otitis MediaAnmarNo ratings yet
- Case 2 Reva Question HydrocephalusDocument6 pagesCase 2 Reva Question HydrocephalusApril Marie MolenoNo ratings yet
- Hypertrophic Olivary Degeneration Secondary - 2015 PDFDocument2 pagesHypertrophic Olivary Degeneration Secondary - 2015 PDFSamuel MorenoNo ratings yet
- Neck Anatomy: Lymph NodesDocument5 pagesNeck Anatomy: Lymph NodesKiara GovenderNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Distress Seizures Patent Ductus ArteriosusDocument1 pageRespiratory Distress Seizures Patent Ductus ArteriosusReno Jun NagasanNo ratings yet
- Neuroradiology: Dr. Dhanti Erma, SP - RadDocument64 pagesNeuroradiology: Dr. Dhanti Erma, SP - RadizzkibipNo ratings yet
- Patho RevDocument21 pagesPatho RevJo CastilloNo ratings yet
- Surgery Long case Viva questions updatedDocument54 pagesSurgery Long case Viva questions updatedthehexhealthNo ratings yet
- Neuro AnatomyDocument4 pagesNeuro AnatomyMarianne Abnasan100% (1)
- ANatomiDocument5 pagesANatomieren akayNo ratings yet
- PathoBCA CNSBonesWBC VisionDocument14 pagesPathoBCA CNSBonesWBC VisionNicole SarcosNo ratings yet
- B20M1L7 - Facial NerveDocument3 pagesB20M1L7 - Facial NerveGokul PoudelNo ratings yet
- High Fever Stiff Neck Severe HeadacheDocument3 pagesHigh Fever Stiff Neck Severe HeadacheDiana Jane LauretaNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics2 Se4 High2Document23 pagesPediatrics2 Se4 High2Daryl Gay NanoNo ratings yet
- Blue Boxes For Head and NeckDocument11 pagesBlue Boxes For Head and NeckhajajyNo ratings yet
- Blumenfeld Neuroanatomy Ch. 5 SummaryDocument5 pagesBlumenfeld Neuroanatomy Ch. 5 SummaryMeeraNo ratings yet
- Talley Sum Up ExaminationDocument57 pagesTalley Sum Up ExaminationGroup 14No ratings yet
- Neuro Lo 3 Week 5Document16 pagesNeuro Lo 3 Week 5Donna MaharaniNo ratings yet
- The MeningesDocument23 pagesThe Meningesanjhulz0% (1)
- Intradural Extramedullary TumorsDocument10 pagesIntradural Extramedullary TumorsFaizyab AhmedNo ratings yet
- IntraCranial HemorrhageDocument1 pageIntraCranial HemorrhageTasya MeidyNo ratings yet
- 8 - HerniaDocument12 pages8 - HerniaPrincyNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Pearls For Pain ManagementDocument24 pagesDiagnostic Pearls For Pain ManagementpuchioNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck Clinicals Shared by Drs of 2027-28Document5 pagesHead and Neck Clinicals Shared by Drs of 2027-28muhammadshayan416No ratings yet
- Tumors of The Orbit by Dr. Jonathan Del Prado 082708Document3 pagesTumors of The Orbit by Dr. Jonathan Del Prado 082708CitrusNo ratings yet
- Anterior NeckDocument1 pageAnterior NeckCarlo BarriosNo ratings yet
- Neuron2 0331Document77 pagesNeuron2 0331baharehNo ratings yet
- Tumours of Nasopharynx DhingraDocument8 pagesTumours of Nasopharynx DhingraIkmal ShahromNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Clients With Upper Airway or Respiratory DisordersDocument6 pagesNursing Care of Clients With Upper Airway or Respiratory DisordersVinzii DrtNo ratings yet
- Template CT Scan (Amirul)Document5 pagesTemplate CT Scan (Amirul)Amirul MukminNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Spinal Cord and RootsDocument9 pagesDisorders of The Spinal Cord and RootsMariana Hoyos GallegoNo ratings yet
- Most Common Malignant Primary Tumor in Childhood: Malignanttumors RhabdomyosarcomaDocument2 pagesMost Common Malignant Primary Tumor in Childhood: Malignanttumors RhabdomyosarcomaMarissa AsimNo ratings yet
- Cephalocaudal KemerutDocument10 pagesCephalocaudal KemerutKIANA LOUISE ROMANONo ratings yet
- Abses Cerebri (Ham)Document23 pagesAbses Cerebri (Ham)Yanti SoelistyawanNo ratings yet
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: (Anatomy, Physiology, Etiology & Diagnosis)Document31 pagesCarpal Tunnel Syndrome: (Anatomy, Physiology, Etiology & Diagnosis)Sabran Jamil PulubuhuNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound (2) Edit2Document53 pagesUltrasound (2) Edit2RahmanandhikaNo ratings yet
- Diseases of the Nervous System SummaryDocument12 pagesDiseases of the Nervous System SummaryWade JacksonNo ratings yet
- Epidural Hematoma, Subdural Hematoma, Meningitis vs Encephalitis, Ischemic vs Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument12 pagesEpidural Hematoma, Subdural Hematoma, Meningitis vs Encephalitis, Ischemic vs Hemorrhagic StrokeCres Padua QuinzonNo ratings yet
- Brain Tumor DDDocument9 pagesBrain Tumor DDbebbyNo ratings yet
- SalivaryDocument20 pagesSalivaryTicky TomNo ratings yet
- Spinal TuberculosisDocument54 pagesSpinal TuberculosisGagandeep YadavNo ratings yet
- 5-Bronchogenic Carcinoma & ParamalignantDocument20 pages5-Bronchogenic Carcinoma & ParamalignantMayar JaradNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: InflammatoryDocument6 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis: InflammatoryAlyssa BatasNo ratings yet
- Head Injury Diagnosis and ManagementDocument41 pagesHead Injury Diagnosis and ManagementChristian Dave EndinoNo ratings yet
- Vasculitis StepDocument2 pagesVasculitis Stepcsa yanisis hernandezNo ratings yet
- Liver Study MaterialDocument17 pagesLiver Study MaterialRazan AlayedNo ratings yet
- Vascular AnomaliesDocument77 pagesVascular AnomaliesRazan AlayedNo ratings yet
- Q Banks Notes GUDocument30 pagesQ Banks Notes GURazan AlayedNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Image Quality When Evaluating Blood Flow atDocument25 pagesOptimizing Image Quality When Evaluating Blood Flow atRazan AlayedNo ratings yet
- ShoulderDocument91 pagesShoulderRazan AlayedNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal (Gi) Contrast Media in Adults: Indications and GuidelinesDocument60 pagesGastrointestinal (Gi) Contrast Media in Adults: Indications and GuidelinesRazan AlayedNo ratings yet
- Cystic Focal Liver Lesions in The Adult: Differential CT and MR Imaging FeaturesDocument35 pagesCystic Focal Liver Lesions in The Adult: Differential CT and MR Imaging FeaturesRazan AlayedNo ratings yet
- DR Orwa Congenital Skeletal AnomaliesDocument6 pagesDR Orwa Congenital Skeletal AnomaliesRazan AlayedNo ratings yet
- Types of Cerebral Herniation and Their Imaging FeaturesDocument42 pagesTypes of Cerebral Herniation and Their Imaging FeaturesRazan AlayedNo ratings yet
- GI anatomy and neuroradiology of the brainDocument36 pagesGI anatomy and neuroradiology of the brainRazan AlayedNo ratings yet
- Gac 311 NotesDocument26 pagesGac 311 NotesZAINABU OLANDONo ratings yet
- Handling Downsizing in The Process Industries - pg11 - 17Document7 pagesHandling Downsizing in The Process Industries - pg11 - 17Soeryanto SlametNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Understanding of OptimismDocument8 pagesConceptual Understanding of OptimismUDITA PARIKHNo ratings yet
- Jalaja Jeewa G-11 SDocument149 pagesJalaja Jeewa G-11 SKelum AthapaththuNo ratings yet
- Timetable Odd Semester 2021Document2 pagesTimetable Odd Semester 2021NIkhil GuptaNo ratings yet
- RFP 23-031 Electronic & Physical Site SecurityDocument31 pagesRFP 23-031 Electronic & Physical Site SecurityElle PolonNo ratings yet
- Improving Project ProposalsDocument2 pagesImproving Project ProposalsNancy Nicasio SanchezNo ratings yet
- Academic Compare and Contrast Essay TopicsDocument53 pagesAcademic Compare and Contrast Essay Topicszzcpllaeg100% (3)
- Effect of Ethanol Leaf Extract of Chromolaena Odorata On Lipid Profile of Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Wistar Albino RatsDocument9 pagesEffect of Ethanol Leaf Extract of Chromolaena Odorata On Lipid Profile of Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Wistar Albino RatsPUBLISHER JOURNALNo ratings yet
- ExampleDocument12 pagesExampleEmma May De MesaNo ratings yet
- Day 3-Social, Cultural and Political PhenomenaDocument67 pagesDay 3-Social, Cultural and Political PhenomenaEleazar, Jr. RanesesNo ratings yet
- Importance of Sustainable Development GoalsDocument2 pagesImportance of Sustainable Development GoalsDyas FerNo ratings yet
- Alexthymia in Sexual Disorder Clinic PatientsDocument7 pagesAlexthymia in Sexual Disorder Clinic PatientsFélix Aníbal Acuña OlivosNo ratings yet
- Ps DM - Ogl 365-Module 6 PaperDocument3 pagesPs DM - Ogl 365-Module 6 Paperapi-573130450No ratings yet
- Ndian Nstitute of Ourism & Ravel Anagement: I T T MDocument69 pagesNdian Nstitute of Ourism & Ravel Anagement: I T T Msilly_chilly100% (4)
- Curriculum Vitae: Amir E. Ibrahim, M.DDocument11 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Amir E. Ibrahim, M.DkendoNo ratings yet
- Cdmgens00160 PDFDocument111 pagesCdmgens00160 PDFMohammadMasoomParwezNo ratings yet
- How Do Barangay Nutrition Committees Contribute To Better Nutrition?Document20 pagesHow Do Barangay Nutrition Committees Contribute To Better Nutrition?Angelito CortunaNo ratings yet
- 1393un 2023-03Document94 pages1393un 2023-03Marcela Martínez100% (1)
- Activity 3.3.2 - Measuring Lung Capacity - Human Body SystemsDocument13 pagesActivity 3.3.2 - Measuring Lung Capacity - Human Body SystemsHerman Henson [Northwest CTA]No ratings yet
- Research Proposal 4Document3 pagesResearch Proposal 4api-385647692No ratings yet