Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Symmetrical Semi Converter
Uploaded by
Adi JohnsonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Symmetrical Semi Converter
Uploaded by
Adi JohnsonCopyright:
Available Formats
Symmetrical Semi converter
Symmetrical Semi converter is also known as a half controlled converter. A
Symmetrical semi converter utilizes SCRs(thyristor) and diodes to convert AC power to
DC power. Due to the utilization of diodes & thyristors, it provides limited control over
the level of DC output voltage.
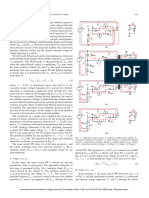
Circuit diagram of Symmetrical semi converter
The figure below shows the circuit dig. Of Symmetrical semi converter bridge
circuit. The bridge circuit consist of two thyristors(T1,T2) and two diodes(D1,D2) are
utilizing in the bridge connection while another diode (FD) is connected across thr
bridge circuit or load. The free wheeling diode (FD) finds it’s application in partialling
recovering the energy stored in the inductor back to the source.
The waveforms of Symmetrical semi converter
Operation
The operation of a Symmetrical semi-converter is discussed based on the above
waveform for definite time intervals.
1. At ωt=0 to ωt=π
During the interval of ωt =0 to ωt=α, thyristor T1 and diode D1 come into operation.
After ωt=0, thyristor T1 becomes forward biased only if Vmsinωt is greater than the load
circuit emf E. The thyristor T1 is then triggered at ωt=α during which Vmsinα > E.
When T1 is triggered, it gets ON and the load current io flows through the RLE load
through thyristor T1 and diode D1. The thyristor T1 will be conducting from ωt =α to
ωt=π.
During ωt=α to ωt=π, the voltage waveform across the load terminal(Vo) will be a
replica of the source voltage(VS).
2. At ωt =π to ωt=2π
Just after the ωt=π i.e. ωt=πt, the supply voltage gets negative, this causes thyristor T1 to
be reverse biased and it gets turned off. But on the other side, this reversal of supply
voltage at ωt=πt causes the freewheeling diode (FD) to be forward biased. So now the
load current io gets transferred from T1D1 to FD. As the freewheeling diode (FD) gets
forward biased, load terminals get short-circuited and the voltage across the load(Vo)
becomes zero.
During this period, thyristor T2 will be in reverse biased condition only if the source
voltage is greater than E. For ωt=π+α, source voltage (Vs) is greater than E, and T2 is
triggered from FD to T2 D2. After the T2 gets triggered, FD gets reverse biased.
3. After ωt=2π
Just after ωt=2π, the thyristor T2 gets reverse biased and is turned off and on the other
hand, FD gets forward biased, and load current io gets transferred to FD.
Role of Freewheeling Diode
In the Symmetrical semi converter, we can observe from its waveform that for time
intervals α to π, T1 D1 conducts and for the interval (π+α) to 2π, T2D2 conducts during
which power is supplied from the source o the RLE load.
During this period, a certain amount of energy is stored by the inductor(L), a definite
amount in the load circuit emf, and in the resistor (R), a certain amount of energy is
dissipated in the form of heat.
During the period π to π+α and 2π to 2π+α, the energy stored in the inductor is partially
fed back to the load circuit through the freewheeling diode(FD). This energy that is
being fed back to the load circuit is partially dissipated in the resistor as heat and
partially added to the load circuit emf E.
Hence, the freewheeling diode(FD) provides a freewheeling path for the energy that is
stored in the inductor during a certain interval to be fed back to the load again.
Average and RMS Output Voltage
The expression for average output voltage (V o) of Symmetrical semi-converter is given
by
The expression for RMS output voltage (V orms) is
You might also like
- Unit 3Document23 pagesUnit 3Prema ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Small-Signal Analysis of Open-Loop PWM Flyback DCDC Converter For CCMDocument8 pagesSmall-Signal Analysis of Open-Loop PWM Flyback DCDC Converter For CCMAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- L-17 (Types of Basic DC-DC Converters)Document11 pagesL-17 (Types of Basic DC-DC Converters)Roberto HidroboNo ratings yet
- PSIM MANUAL For StudentsDocument23 pagesPSIM MANUAL For StudentsSomnath Khamaru75% (4)
- MSC Rectifier CorrectedDocument53 pagesMSC Rectifier CorrectedashammoudaNo ratings yet
- 10 InvertersDocument136 pages10 InverterszapzahtNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Switch-Mode Converters: Step-Down, Buck Converter GuideDocument35 pagesDC-DC Switch-Mode Converters: Step-Down, Buck Converter GuideNandu JagguNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Semi Converter With R, RL Loads For Continuous Conduction ModesDocument5 pagesSingle Phase Semi Converter With R, RL Loads For Continuous Conduction ModesSankar KaruppaiahNo ratings yet
- Single-Phase Inverters: Seminar by Supervised byDocument45 pagesSingle-Phase Inverters: Seminar by Supervised bynoor deenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02Document21 pagesLecture 02Abd El-Rahman DabbishNo ratings yet
- Buck ConverterDocument8 pagesBuck Converterhamza abdo mohamoudNo ratings yet
- 03 InverterDocument61 pages03 Inverterkamlesh jatNo ratings yet
- Assignment: AddedDocument39 pagesAssignment: Addedfuh kingsleyNo ratings yet
- SEPIC ConverterDocument16 pagesSEPIC ConverterDina GaranNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Converter Types Explained: Buck, Boost and Buck-Boost CircuitsDocument4 pagesDC-DC Converter Types Explained: Buck, Boost and Buck-Boost CircuitsJamir CalNo ratings yet
- Step down buck converter voltage regulatorDocument11 pagesStep down buck converter voltage regulatorYugendra RNo ratings yet
- PEI Mod2@AzDOCUMENTS - inDocument68 pagesPEI Mod2@AzDOCUMENTS - inINDIAN LEGENDSNo ratings yet
- Balanced ModulatorDocument4 pagesBalanced Modulatorramaiah2369No ratings yet
- Half-Bridge Inverters OverheadsDocument9 pagesHalf-Bridge Inverters OverheadsJuan E. JohnsonNo ratings yet
- 2095784617.power Electronics Unit IiDocument59 pages2095784617.power Electronics Unit IiSaranya. M SNSNo ratings yet
- Lec. 17Document22 pagesLec. 17Hira MunirNo ratings yet
- Astable Multivibrator Using TransistorsDocument10 pagesAstable Multivibrator Using TransistorsGangireddy SanjeevNo ratings yet
- Controlled Rectifiers and AC Voltage ControllersDocument35 pagesControlled Rectifiers and AC Voltage ControllersAishwaryaNo ratings yet
- MSC ChopperDocument6 pagesMSC ChopperashammoudaNo ratings yet
- How a Buck Converter Works to Lower VoltageDocument5 pagesHow a Buck Converter Works to Lower VoltageSubarna AdakNo ratings yet
- PC-EE-504-Module 5 Power Electronics: InvertersDocument39 pagesPC-EE-504-Module 5 Power Electronics: InvertersSanjoy PathakNo ratings yet
- Hafta1.compressedDocument28 pagesHafta1.compressedSersio BordiosNo ratings yet
- Foster Seeley DiscriminatorDocument2 pagesFoster Seeley DiscriminatorDebesh Bar100% (1)
- 210 AC 2013 StuentsDocument28 pages210 AC 2013 StuentsKieran CullenNo ratings yet
- Buck and Boost Converters With Transmission LinesDocument8 pagesBuck and Boost Converters With Transmission LinesVisu TamilNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 - AC To DC ConvertersDocument36 pagesChapter2 - AC To DC ConvertersYee Yen AppleNo ratings yet
- Overlap in Rectifiers Overlap in Rectifiers: Advance Power Electronics Advance Power ElectronicsDocument10 pagesOverlap in Rectifiers Overlap in Rectifiers: Advance Power Electronics Advance Power ElectronicsJunaid AlviNo ratings yet
- Converts Alternating Current Directcurrent InverterDocument10 pagesConverts Alternating Current Directcurrent InverterDevansh SinghNo ratings yet
- "Single Phase Full Wave Rectifier": Power Point Presentation OnDocument12 pages"Single Phase Full Wave Rectifier": Power Point Presentation Onshadan alamNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Rectifier: Convert AC to DC Efficiently in 40 CharactersDocument21 pagesFull Wave Rectifier: Convert AC to DC Efficiently in 40 CharactersbaradhanNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document21 pagesModule 2Anandu DipukumarNo ratings yet
- Eee 513 Lecture Module IiDocument30 pagesEee 513 Lecture Module Iistephenhuncho22No ratings yet
- 106Document6 pages106vinay kumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: DC-DC Conversion: DC ChoppersDocument55 pagesChapter Four: DC-DC Conversion: DC Choppersfor lifeNo ratings yet
- Switching Losses PDFDocument4 pagesSwitching Losses PDFleonardo_arévalo_28No ratings yet
- Battery Eliminator: High Voltage Alternating CurrentDocument12 pagesBattery Eliminator: High Voltage Alternating CurrentAnishka KadiyanNo ratings yet
- Rectifying CircuitsDocument13 pagesRectifying Circuitssina981No ratings yet
- Electrical-Engineering Engineering Power-Electronics Inverters NotesDocument22 pagesElectrical-Engineering Engineering Power-Electronics Inverters NotesAbdelrahman Magdy EbrahimNo ratings yet
- Boost ConverterDocument8 pagesBoost Converterhamza abdo mohamoudNo ratings yet
- Transformer & Electrical MachinesDocument31 pagesTransformer & Electrical Machinesam20300% (1)
- CHAPTER 3 Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument29 pagesCHAPTER 3 Electronic Devices and CircuitsDaniel EkassiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 PowDocument10 pagesLecture 6 PowPamela ChemutaiNo ratings yet
- A Single Phase Power Factor Correction ConverterDocument30 pagesA Single Phase Power Factor Correction ConverterAnanth NoorithayaNo ratings yet
- 1 Phase Controlled RectifierDocument34 pages1 Phase Controlled RectifierAfiq BobbyNo ratings yet
- DC TO AC INVERTERDocument93 pagesDC TO AC INVERTERABCDNo ratings yet
- High-Efficiency Single-Input Multiple-Output DC-DC ConverterDocument35 pagesHigh-Efficiency Single-Input Multiple-Output DC-DC ConverterHathiram Pawar50% (2)
- Thyristor Commutation: Mode Equivalent Circuits. Questions, NumericalsDocument22 pagesThyristor Commutation: Mode Equivalent Circuits. Questions, NumericalsSanjoy PathakNo ratings yet
- Phase Controlled Rectifier Circuit TypesDocument107 pagesPhase Controlled Rectifier Circuit TypesVarun Singh IndaNo ratings yet
- Smps 1Document23 pagesSmps 1Tewodros ShegawNo ratings yet
- Mod2 150324001504 Conversion Gate01 PDFDocument33 pagesMod2 150324001504 Conversion Gate01 PDFJay The PerfectNo ratings yet
- Authorized Licensed Use Limited To: Rutgers University. Downloaded On May 17,2021 at 01:24:20 UTC From IEEE Xplore. Restrictions ApplyDocument1 pageAuthorized Licensed Use Limited To: Rutgers University. Downloaded On May 17,2021 at 01:24:20 UTC From IEEE Xplore. Restrictions ApplyElyes MbarekNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- FCC PART 15.407 IC RSS-210, ISSUE 8, DEC 2010 Test and Measurement ReportDocument86 pagesFCC PART 15.407 IC RSS-210, ISSUE 8, DEC 2010 Test and Measurement ReportaslamNo ratings yet
- Belden Cable 101 PresentationDocument152 pagesBelden Cable 101 PresentationJerans100% (1)
- Power Distribution System For Construction Design (Re Produced) PDFDocument122 pagesPower Distribution System For Construction Design (Re Produced) PDFabdullahiqbalNo ratings yet
- Mk60 Wiring InstructionsDocument6 pagesMk60 Wiring InstructionsAnas KhalilNo ratings yet
- CM-UFD.M31: Grid Feeding Monitoring According To VDE-AR-N 4105 and BDEWDocument17 pagesCM-UFD.M31: Grid Feeding Monitoring According To VDE-AR-N 4105 and BDEWZaharia MarianNo ratings yet
- Quantum Energy Generator - Free Energy Device BlueprintsDocument35 pagesQuantum Energy Generator - Free Energy Device Blueprintsenerchi111181% (16)
- Insulation Coordination Studies For 400 KV Gis in A Hydroelectric Project in IndiaDocument6 pagesInsulation Coordination Studies For 400 KV Gis in A Hydroelectric Project in IndiaAchint KumarNo ratings yet
- LED Lighting Applications Design GuideDocument20 pagesLED Lighting Applications Design GuideBank100% (3)
- AD5593RDocument28 pagesAD5593RTrooll LoolNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety ClearanceDocument6 pagesElectrical Safety Clearanceswanujay12No ratings yet
- Millimeter-Wave Technology For Automotive Radar Sensors in The 77 GHZ Frequency BandDocument16 pagesMillimeter-Wave Technology For Automotive Radar Sensors in The 77 GHZ Frequency BandSaif KamalNo ratings yet
- Manual Motor Starter PDFDocument35 pagesManual Motor Starter PDFEbrahim ArzaniNo ratings yet
- Technology and Livelihood Education: Exploratory Course in Electrical Installation and MaintenanceDocument13 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education: Exploratory Course in Electrical Installation and MaintenanceSteven Escarmosa100% (1)
- Ax 063Document1 pageAx 063Al Fakhamah LiftsNo ratings yet
- BasicElectronicsbyDebashisDe 1 PDFDocument836 pagesBasicElectronicsbyDebashisDe 1 PDFKhalid YahyaNo ratings yet
- C1 - TQBM-D609017-Q172717DEI-65FT2v02Document2 pagesC1 - TQBM-D609017-Q172717DEI-65FT2v02carlosconstructor1No ratings yet
- PRC 119 (F) Student Guide v09 (1) .12.09Document143 pagesPRC 119 (F) Student Guide v09 (1) .12.09tomfriis0% (1)
- Ul508a SCCR enDocument10 pagesUl508a SCCR enoladipoo1No ratings yet
- Three-Phase Sensorless Pump Driver IC A89303: Features and Benefits DescriptionDocument22 pagesThree-Phase Sensorless Pump Driver IC A89303: Features and Benefits Description박남수No ratings yet
- Jr. Engg. Electrical-ADocument16 pagesJr. Engg. Electrical-Azahidkhursheed786No ratings yet
- REVERSIBLE STAR DELTA MOTOR CONTROLLER CONTROL CIRCUIT DIAGRAM GUIDEDocument6 pagesREVERSIBLE STAR DELTA MOTOR CONTROLLER CONTROL CIRCUIT DIAGRAM GUIDEAbdul Haleem100% (3)
- CapacitorDocument37 pagesCapacitorAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Icest 2011 977 930Document8 pagesIcest 2011 977 93001666754614No ratings yet
- Ask-Psk-FskDocument15 pagesAsk-Psk-Fskhamza mohsenNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Mir 20200330 Web PDFDocument31 pagesRenewable Energy Mir 20200330 Web PDFJuan Carlos CastroNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/62Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/62Desire KandawasvikaNo ratings yet
- LV 25 PDocument2 pagesLV 25 Pgacongnghiep7786No ratings yet
- AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism - Electrostatics ReviewDocument17 pagesAP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism - Electrostatics ReviewDarkAgesGamerVNo ratings yet
- BTK2233 - Lab Module 1Document9 pagesBTK2233 - Lab Module 1FishNo ratings yet
- As19 h1g PDFDocument12 pagesAs19 h1g PDFronald sosaNo ratings yet