Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Final Report
Uploaded by
Umais Ali MangiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Final Report
Uploaded by
Umais Ali MangiCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: Umais Ali Mangi
Registration no: 2135118
Program: MBA-36
• Measurement: Measurement is defined as process of associating numbers or symbols to
observation obtained in a research study.
• Measurement means assigning numbers or other symbols to characteristics of objects
• These observation could be qualitative or quantitative.
• It is difficult to measure qualitative characteristics than quantitative characteristics.
It is easy to measure properties like weight, height etc.
• But it difficult to measure properties like motivation, honesty, customers perception etc.
• Example:
We can record a person marital status as 1,2,3or 4 depending on whether the person is married, single,
or divorced. We cannot make comparison between these numbers but we can be count each number.
• Scaling
A scaling is a procedure for the assignment of numbers or other symbols to a property of objects
in order to import some of the characteristics of numbers to properties in questions.
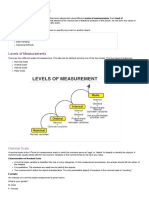
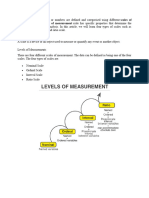
Characteristics of scales
• Nominal: Numbers to identify and classify.
it is simply a system of assigning number symbols to elements in order to label them.
E.g.; student’s numbers.
• Ordinal: ordinal scale places elements in order, it ranks objects or elements from one largest to
smallest or first to last.
E.g.; (quality ranking) ranking of students according to scores obtained by them.
• Interval scale: A scale in which numbers are used to rate objects such that numerically equal
distance on the scale represents equal distances in the characteristics being measured
E.g.; like Temperature scale.
• Ratio scale: ratio scale represents the actual amount of variables.
E.g.; measure of physical dimensions such as height, weight, distance etc.
You might also like
- 1.measurement and ScalingDocument44 pages1.measurement and ScalingGaganNo ratings yet
- Measurement ToolDocument30 pagesMeasurement ToolLekhnath SubediNo ratings yet
- Measurement and ScalingDocument70 pagesMeasurement and ScalingRitik ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Galaxy PDFDocument28 pagesGalaxy PDFTôi Yêu VNNo ratings yet
- Scales of Measurement: By-Yukti SharmaDocument15 pagesScales of Measurement: By-Yukti SharmaYukti SharmaNo ratings yet
- M7-Research MethodologyDocument20 pagesM7-Research MethodologyLarissa Rodrigues GCHSNo ratings yet
- Statistical Processes Are Usually Carried Out As A Part of Decision Making ProceduresDocument9 pagesStatistical Processes Are Usually Carried Out As A Part of Decision Making ProceduresShabir LettaNo ratings yet
- Measurement and ScaleDocument37 pagesMeasurement and ScaleNaman LadhaNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Scaling Techniques: Scales of Measurement, Sources of Error in MeasurementDocument12 pagesMeasurement and Scaling Techniques: Scales of Measurement, Sources of Error in MeasurementwickedramanNo ratings yet
- BA Group-4 .Document16 pagesBA Group-4 .Khan FaizanNo ratings yet
- M8-Research MethodologyDocument21 pagesM8-Research MethodologyLarissa Rodrigues GCHSNo ratings yet
- Measurement & Scaling Technique 1Document7 pagesMeasurement & Scaling Technique 1Nilanjana ChakrabartyNo ratings yet
- Business Research Methods Unit IiiDocument40 pagesBusiness Research Methods Unit IiirajnikantNo ratings yet
- Ch13 Zikmund Measurement and ScaleDocument31 pagesCh13 Zikmund Measurement and Scalerohitoberoi1175% (4)
- Business Research Methods Unit IIIDocument40 pagesBusiness Research Methods Unit IIIIsha BiswasNo ratings yet
- Measurement ScalesDocument13 pagesMeasurement ScalesVeena VaishyNo ratings yet
- Measurement - Scaling, Reliability, ValidityDocument42 pagesMeasurement - Scaling, Reliability, ValidityMadiha JavedNo ratings yet
- 05 Observations and Variable Statistics. Introduction To StatitsticsDocument11 pages05 Observations and Variable Statistics. Introduction To StatitsticsOnline EducationNo ratings yet
- CH IV. Measurement and ScalingDocument51 pagesCH IV. Measurement and ScalingBandana SigdelNo ratings yet
- PR 1 Lecture 10Document13 pagesPR 1 Lecture 10Mabell MingoyNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Scale Construction TechniquesDocument61 pagesMeasurement and Scale Construction TechniquesAbhishek kumarNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Measurement and Scaling-1Document94 pagesUnit IV Measurement and Scaling-1onlinep410No ratings yet
- Measurement and ScalingDocument23 pagesMeasurement and Scalingtshiringtmg7No ratings yet
- Psychometrics CH 2Document34 pagesPsychometrics CH 2Dejene DayNo ratings yet
- Levels of Measurement FinalDocument41 pagesLevels of Measurement FinalMary SutingcoNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Scaling Techniques1Document42 pagesMeasurement and Scaling Techniques1Ankush ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology: Presentation On Measurement-Meaning, Definition and Scales of MeasurementDocument10 pagesResearch Methodology: Presentation On Measurement-Meaning, Definition and Scales of MeasurementaashitiNo ratings yet
- Research MethodologyDocument36 pagesResearch Methodologyसागर मोहन पाटील33% (3)
- Measurement and Scalingt EchniquesDocument56 pagesMeasurement and Scalingt Echniqueswcf.fellowsNo ratings yet
- Measurement of VariablesDocument41 pagesMeasurement of VariablesTiara AdrianaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document11 pagesUnit 3maNo ratings yet
- Level of MeasurementDocument4 pagesLevel of Measurementpegtimaryjoy091No ratings yet
- Research Methodology Unit 2Document35 pagesResearch Methodology Unit 2swathisweetu91No ratings yet
- Topic 4Document39 pagesTopic 4sid suchakNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Measurement ScalesDocument11 pagesMeasurement and Measurement ScalesmaNo ratings yet
- Measurement and ScalingDocument4 pagesMeasurement and ScalingSwapnaNo ratings yet
- BRM Unit 3&4 Complete1Document69 pagesBRM Unit 3&4 Complete114122001riya2001No ratings yet
- Measurement & Scaling: Asst - Prof .Seena Alappatt Dept - Management StudiesDocument13 pagesMeasurement & Scaling: Asst - Prof .Seena Alappatt Dept - Management Studiesseena15No ratings yet
- PPT2 Types and Classification of VariablesDocument13 pagesPPT2 Types and Classification of VariablesMary De CastroNo ratings yet
- Module 5-6 - Research DesignDocument46 pagesModule 5-6 - Research DesignvoiceofmehmoodNo ratings yet
- Measurement and ScalingDocument14 pagesMeasurement and ScalingabcdNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Scaling ConceptDocument20 pagesMeasurement and Scaling ConceptVãńšh WädhwåNo ratings yet
- Principle Measurement Scales Social Science by Assoc Prof DR Caroline Geetha AP B ArokiadasanDocument29 pagesPrinciple Measurement Scales Social Science by Assoc Prof DR Caroline Geetha AP B ArokiadasanGirmaw YeshanbelNo ratings yet
- BRM Chap 13Document46 pagesBRM Chap 13pallavi412No ratings yet
- Business Research MethodsDocument94 pagesBusiness Research MethodsMahima SinghNo ratings yet
- DATA ANALYSIS SampleDocument29 pagesDATA ANALYSIS SampleCindy LapazNo ratings yet
- Levels of MeasurementDocument26 pagesLevels of MeasurementKristine Love Q. MorenoNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts OF Measurement, Assessment & EvaluationDocument6 pagesBasic Concepts OF Measurement, Assessment & EvaluationfierrepaoloatencioNo ratings yet
- BRM4Document2 pagesBRM4Preeti BarkerNo ratings yet
- MeasurementDocument11 pagesMeasurementRidhima jainNo ratings yet
- Scales of Measurement - Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and RatioDocument2 pagesScales of Measurement - Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and RatioDESHRAJ MEENANo ratings yet
- Research Design DefiningDocument14 pagesResearch Design Definingmanaqib ahmadNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document25 pagesUnit 3Yash SonkarNo ratings yet
- Measurement: Measurement Is The Process of Observing andDocument88 pagesMeasurement: Measurement Is The Process of Observing andmahima singhNo ratings yet
- Measurement and ScalingDocument66 pagesMeasurement and Scalingritam chakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Scaling Techniques: Presented By: Sem ShaikhDocument18 pagesMeasurement and Scaling Techniques: Presented By: Sem ShaikhponnasaikumarNo ratings yet
- Measurement and ScalingDocument12 pagesMeasurement and ScalingShafak MahajanNo ratings yet
- Fdocuments - in t4 Measurement and ScalingDocument39 pagesFdocuments - in t4 Measurement and ScalingDEVADATTA B KOTENo ratings yet
- Brand Strategies of Tiger BrandDocument2 pagesBrand Strategies of Tiger BrandUmais Ali MangiNo ratings yet
- Rearch ProposalDocument6 pagesRearch ProposalUmais Ali MangiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document23 pagesUnit 3Umais Ali MangiNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management JournalDocument1 pageStrategic Management JournalUmais Ali MangiNo ratings yet
- No Code Low CodeDocument12 pagesNo Code Low CodeUmais Ali MangiNo ratings yet
- Mision and Vision AssignmentDocument3 pagesMision and Vision AssignmentUmais Ali MangiNo ratings yet