Professional Documents
Culture Documents
G8 HYPOCHLOREMIA Handout
Uploaded by
Risha Ethel BerondoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
G8 HYPOCHLOREMIA Handout
Uploaded by
Risha Ethel BerondoCopyright:
Available Formats
GROUP 8:
ALI, Hidjara M.
ANGDAO, Princess Saideh C.
PIMPING, Sittie Hafsa M.
HYPOCHLOREMIA
Hypochloremia is an electrolyte imbalance and is indicated by a low level of chloride
in the blood. This occurs when serum chloride levels fall below 96 mEq/L. The
normal adult value for chloride is 96-106 mEq/L.
Chloride in the blood is an important electrolyte and works to ensure that the
body’s metabolism is working correctly. It also helps the acid and base balance in
the body.
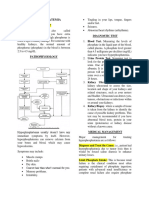
Pathophysiology
Hypochloremia can occur through this five main causes:
C - chloride loss from fluid loss through nausea or vomiting or by existing conditions,
diarrhea, diseases, severe diaphoresis, burns, or medications which results to dehydration.
H - hyponatremia. Hyponatremia is characterized by low sodium level. This is one of the
main causes of hypochloremia as chloride always follows sodium. If there's a low level in
sodium, and so with the chloride.
A - Addison's disease and adrenal crisis. Addison's disease, also called as adrenal
insufficiency, is an uncommon disease that occurs when the body does not make enough of
certain hormones. In Addison's the adrenal glands make too little aldosterone, a hormone
responsible for sodium and water regulation in the body by keeping sodium in and releasing
potassium from the body. A deficiency of aldosterone causes the body to excrete large
amounts of sodium and retain potassium, leading to low levels of sodium and high levels of
potassium in the blood. The person may experience diarrhea and vomiting.
M - medications. Primary renal chloride losses are due to the use of some diuretics such as
loop diuretics, thiazides, and acetazolamide which increase excretion of chloride as well as
sodium and potassium and person who experience this may feel dizziness, headache, and
dehydration.
P - pH imbalances from metabolic alkalosis. This is sodium and potassium deficiency that
affect acid-base or electrolyte balance, such as Addison’s disease. As I have mentioned
earlier, Addison's disease causes the adrenal glands to produce too little amount of
aldosterone which in turn releases more sodium and let the potassium retain in the body
which results to a pH imbalances particularly the metabolic alkalosis. Metabolic alkalosis is
an increase in bicarbonate in the blood that may occur due to kidney diseases. Chloride and
bicarbonate have an inverse relationship. When the level of one goes down, the level of the
other goes up which is why it results into metabolic alkalosis. The person may experience
fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and confusion.
Signs & Symptoms
1. fluid loss
2. dehydration
3. weakness or fatigue
4. difficulty breathing
5. diarrhea or vomiting, caused by fluid loss
Hypochloremia can also frequently accompany hyponatremia, a low amount of sodium
in the blood.
Diagnostic Tests
● Blood test to check your chloride level.
● Typically, blood chloride isn’t the only factor tested. It’ll be
included as part of a metabolic or electrolyte panel.
● An electrolyte panel is a blood test that measures chloride,
bicarbonate, potassium, and sodium.
● if the doctor suspects metabolic alkalosis, they may order a urine
chloride test and urine sodium test.
○ blood chloride test
○ urine chloride test
○ urine sodium test
Medical Management
✓ Treatment involves correcting the cause of hypochloremia and the contributing
electrolyte and acid–base imbalances.
✓ Normal saline (0.9% sodium chloride)
✓ Half-strength saline (0.45% sodium chloride) solution is given by IV to
replace the chloride
✓ Ammonium chloride, an acidifying IV agent, may be prescribed to treat
metabolic alkalosis
Nursing Management
✓ The nurse monitors the patient’s I&O, ABG values, and serum electrolyte levels.
✓ Changes in the patient’s level of consciousness and muscle strength and movement
are reported to the primary provider promptly.
✓ Vital signs are monitored, and respiratory assessment is carried out frequently.
✓ The nurse provides and educates the patient about foods with high chloride content.
✓ A person who drinks free water (water without electrolytes) or bottled water and
excretes large amounts of chloride needs instruction to avoid drinking this kind of water
You might also like
- Hyperkalemia, (High Blood Potassium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHyperkalemia, (High Blood Potassium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Chloride Deficit LecDocument2 pagesChloride Deficit Leced123edNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Alkalosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandMetabolic Alkalosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- 11.chloride CDocument24 pages11.chloride CNgetwa TzDe TheWirymanNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte Imbalance, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandElectrolyte Imbalance, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Approach To Metabolic AlkalosisDocument11 pagesApproach To Metabolic AlkalosisJou ÁlvarezNo ratings yet
- Magnesium Levels DeficitsDocument8 pagesMagnesium Levels DeficitsAbegail DoriaNo ratings yet
- M5 - Electrolyte AbnormalitiesDocument44 pagesM5 - Electrolyte AbnormalitiesVishal KumarNo ratings yet
- By: Gisela G. LunaDocument26 pagesBy: Gisela G. LunaYusuf EspinaNo ratings yet
- Alkalosis Is A Condition of Excess BaseDocument18 pagesAlkalosis Is A Condition of Excess BaseDiana Deciu100% (1)
- Cheat Sheet Nursing Key PointsDocument3 pagesCheat Sheet Nursing Key PointsKristina EitelNo ratings yet
- Acidic-Base Imbalance: Under Supervision:Dr/Shimaa SabryDocument12 pagesAcidic-Base Imbalance: Under Supervision:Dr/Shimaa SabryAhoood ,No ratings yet
- Chloremia (Hypochloremia) & Acute and Chronic Respiratory Alkalosis (Carbonic Acid Deficit)Document4 pagesChloremia (Hypochloremia) & Acute and Chronic Respiratory Alkalosis (Carbonic Acid Deficit)KQarlo Luis Pestaño Maniaol100% (1)
- Description of Disease/condition: Metabolic Alkalosis, Information About Metabolic AlkalosisDocument6 pagesDescription of Disease/condition: Metabolic Alkalosis, Information About Metabolic AlkalosisJusterine Jade To-ong SiglosNo ratings yet
- Fluidsandelectrolytes 090224074347 Phpapp02Document102 pagesFluidsandelectrolytes 090224074347 Phpapp02IsaacJ22No ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte Final OutputDocument19 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Final OutputNatasha Alaine E. CayabyabNo ratings yet
- HyperkalemiaDocument9 pagesHyperkalemiaFabdul RaufNo ratings yet
- Concept Map - HyponatremiaDocument9 pagesConcept Map - HyponatremiaElleNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes & FluidimbalancesDocument80 pagesElectrolytes & FluidimbalancesDennis Nyambane MomanyiNo ratings yet
- Aguinaldo, Sophia Kaye M. Hypochloremia & HyperchloremiaDocument9 pagesAguinaldo, Sophia Kaye M. Hypochloremia & HyperchloremiaSophia Kaye AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Acid Base BalanceDocument24 pagesAcid Base BalanceHusam ShawagfehNo ratings yet
- Indications of Dialysis in Acute Renal Failure (ARF)Document3 pagesIndications of Dialysis in Acute Renal Failure (ARF)Tariku GelesheNo ratings yet
- Fluid Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument46 pagesFluid Electrolyte ImbalanceAxsa AlexNo ratings yet
- Fluid Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument46 pagesFluid Electrolyte ImbalanceAxsa Alex100% (1)
- Metabolic AlkalosisDocument2 pagesMetabolic AlkalosisKath ComodaNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Balance 2Document62 pagesAcid-Base Balance 2chimbimbNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte BalanceDocument52 pagesFluid and Electrolyte BalanceFrancis Appau100% (1)
- Chloride CompleteDocument8 pagesChloride CompleteGul Rehman GulNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Electrolyte Imbalances Part 1Document74 pagesLesson 4 - Electrolyte Imbalances Part 1Clark SavageNo ratings yet
- Problems With Sodium and PotassiumDocument34 pagesProblems With Sodium and PotassiumJemima Nove JapitanaNo ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument5 pagesDiabetic KetoacidosisJill Catherine Cabana100% (3)
- SodiumDocument48 pagesSodiumSanchita SahaNo ratings yet
- Acidosis AlkalosisDocument5 pagesAcidosis Alkalosisaljosa_21No ratings yet
- Acid-Base Balance (Burn and Scalds or Shock)Document10 pagesAcid-Base Balance (Burn and Scalds or Shock)SalinKaurNo ratings yet
- Wa0003Document30 pagesWa0003محمد رزاق مزهر جبرNo ratings yet
- AlkalosisDocument5 pagesAlkalosisAnila zafarNo ratings yet
- Unit II Water and ElectrolytesDocument8 pagesUnit II Water and ElectrolytesSantosh P JosephNo ratings yet
- Harrison MCQ NephrologyDocument7 pagesHarrison MCQ Nephrologydrtpk80% (15)
- Dr. Ali's Uworld Notes For Step 2 CKDocument15 pagesDr. Ali's Uworld Notes For Step 2 CKBoogy WoogyNo ratings yet
- ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesElectrolytesArham HarunNo ratings yet
- Sodium, and 350-500 Meq/L of Chloride. The Combined Effects of Serum Hyperosmolarity, Dehydration, and Acidosis Result in Increased Osmolarity in Brain Cells That ClinicallyDocument5 pagesSodium, and 350-500 Meq/L of Chloride. The Combined Effects of Serum Hyperosmolarity, Dehydration, and Acidosis Result in Increased Osmolarity in Brain Cells That ClinicallyMorgan Mitchell100% (10)
- HyponatremiaDocument6 pagesHyponatremiaJaymart Saclolo CostillasNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument74 pagesAcid BaseMiracle For NursesNo ratings yet
- Fluid N Electrolyte BalanceDocument60 pagesFluid N Electrolyte BalanceAnusha Verghese67% (3)
- Determination of PH QFRDocument2 pagesDetermination of PH QFRsyareeisyeeNo ratings yet
- Pleno Minggu 2 Blok 3.4Document84 pagesPleno Minggu 2 Blok 3.4Devi Yunita PurbaNo ratings yet
- M5 3 HypokalemiaDocument6 pagesM5 3 HypokalemiaVishal KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes ImbalanceDocument10 pagesElectrolytes ImbalanceSilver DrakeNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Values: Serum SodiumDocument3 pagesLaboratory Values: Serum SodiumVincentNo ratings yet
- Anaemia PDFDocument3 pagesAnaemia PDFrian hadiNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes - HypernatraemiaDocument20 pagesElectrolytes - HypernatraemiamympomNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte-2013Document91 pagesFluid and Electrolyte-2013shwetaNo ratings yet
- Medical EmergenciesDocument12 pagesMedical EmergenciesBSN 2 - Sasis, Rusmaryte C.No ratings yet
- Complete Metabolic PanelDocument12 pagesComplete Metabolic PanelimperiouxxNo ratings yet
- Hyperchloremia: Group 11 Singh, Joshua Silverio, Silver John Tabarnilla, Michiko Unico, Paula Villa, JustinaDocument15 pagesHyperchloremia: Group 11 Singh, Joshua Silverio, Silver John Tabarnilla, Michiko Unico, Paula Villa, JustinaKyle De Sagun OtedaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism.: Abdelmoniem Saeed Mohammed Er SpecialistDocument49 pagesDisorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism.: Abdelmoniem Saeed Mohammed Er SpecialistYousef Al-AmeenNo ratings yet
- CULLA - Activity 2Document2 pagesCULLA - Activity 2SheenaGuinoCullaNo ratings yet
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument9 pagesFluids and ElectrolytesLeahandJosh NadhernyNo ratings yet
- Hypokalemiaand Hyperkalemia: Jesse Theisen-ToupalDocument17 pagesHypokalemiaand Hyperkalemia: Jesse Theisen-ToupalMattya SalazarNo ratings yet
- HyponatremiaDocument20 pagesHyponatremiamanjaruNo ratings yet
- VASCULITIS (Group 6 Fact Sheet)Document3 pagesVASCULITIS (Group 6 Fact Sheet)Risha Ethel BerondoNo ratings yet
- Kaposi Sarcoma CompiledDocument5 pagesKaposi Sarcoma CompiledRisha Ethel BerondoNo ratings yet
- Group 11 Hyperphosphatemia HandoutsDocument2 pagesGroup 11 Hyperphosphatemia HandoutsRisha Ethel BerondoNo ratings yet
- Hypermagnesemia Handouts Group 9Document3 pagesHypermagnesemia Handouts Group 9Risha Ethel BerondoNo ratings yet
- Protist PacketDocument7 pagesProtist PacketAyesha MartiniNo ratings yet
- Common Sense Cardio Training by Nick Mitchell - UP FitnessDocument13 pagesCommon Sense Cardio Training by Nick Mitchell - UP FitnessSean DrewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document38 pagesChapter 1synap5esNo ratings yet
- Immunology 1Document2 pagesImmunology 1darxide39No ratings yet
- Dave GrossmanDocument3 pagesDave Grossmantrainingalot100% (1)
- Lesson1 The Human Organism GRRRDocument5 pagesLesson1 The Human Organism GRRRqueen grazildaNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Motility and Sensory.16Document7 pagesGastrointestinal Motility and Sensory.16AnaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Meiosis NotesDocument7 pagesMitosis Meiosis NotesSophia Cook100% (1)
- PBL GM 2Document41 pagesPBL GM 2SleepyHead ˋωˊNo ratings yet
- Neural Signal Processing: ELEC 548 - Fall 2015 Tuesday/Thursday 09:25AM - 10:40AM BRC 284Document31 pagesNeural Signal Processing: ELEC 548 - Fall 2015 Tuesday/Thursday 09:25AM - 10:40AM BRC 284marcaumggNo ratings yet
- How It Works Book of The Human Body (Kalinel - Du)Document180 pagesHow It Works Book of The Human Body (Kalinel - Du)AMFA100% (4)
- A Gut Feeling - Hoffman2018Document3 pagesA Gut Feeling - Hoffman2018Francini MontemarNo ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia (SeminarDocument38 pagesHypoglycemia (SeminarDawitNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Bone: Dr. Ross G. Cooper Senior Lecturer Division of Physiology School of Health & Policy StudiesDocument70 pagesPhysiology of Bone: Dr. Ross G. Cooper Senior Lecturer Division of Physiology School of Health & Policy StudiesnannaraNo ratings yet
- The Evil Russian SpeaksDocument13 pagesThe Evil Russian SpeaksDmitriKartikeya100% (1)
- Chapter 20: Medicine - Set ADocument4 pagesChapter 20: Medicine - Set ABernard Paul GuintoNo ratings yet
- IDA Maharashtra State Branch Dental Dialogue July-September2012Document40 pagesIDA Maharashtra State Branch Dental Dialogue July-September2012kkarkhanisNo ratings yet
- Formal Report: Stability of ProteinsDocument7 pagesFormal Report: Stability of ProteinsQueenie Tenedero100% (2)
- Module 2 - Cell Structure & Function (Student Guide)Document24 pagesModule 2 - Cell Structure & Function (Student Guide)greggcllam619076100% (7)
- Corrosion Inh MSDSDocument8 pagesCorrosion Inh MSDSfructoraNo ratings yet
- Nicu Picu IccuDocument10 pagesNicu Picu IccumiraNo ratings yet
- Ectopia Lentis PDFDocument7 pagesEctopia Lentis PDFBeerappaJanpetNo ratings yet
- Marieb Ch11aDocument23 pagesMarieb Ch11aapi-229554503No ratings yet
- Bhagani 2018Document7 pagesBhagani 2018rifky kurniawanNo ratings yet
- Eye Pathology: Dr. Jusuf FantoniDocument8 pagesEye Pathology: Dr. Jusuf Fantonitutor tujuhNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes-Growth Kinetics - Growth PhasesDocument24 pagesLecture Notes-Growth Kinetics - Growth Phasesbioenviron100% (1)
- The Ultimate 2 Week Fat Loss DietDocument132 pagesThe Ultimate 2 Week Fat Loss DietDr Rushen Singh100% (7)
- Fisiologi Biota LautDocument40 pagesFisiologi Biota LautSakti Bachmid100% (1)
- BIOL 2P98 D2 2017FW Lab 4Document18 pagesBIOL 2P98 D2 2017FW Lab 4TumuhimbiseMosesNo ratings yet
- Formula Guide NewestDocument60 pagesFormula Guide Newesteran76No ratings yet
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (23)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (80)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosFrom Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (207)
- How to ADHD: The Ultimate Guide and Strategies for Productivity and Well-BeingFrom EverandHow to ADHD: The Ultimate Guide and Strategies for Productivity and Well-BeingNo ratings yet
- An Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyFrom EverandAn Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningFrom EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Troubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassFrom EverandTroubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (26)