Professional Documents
Culture Documents
051 Endocrinology Physiology Adrenal Medulla Catecholamines
Uploaded by
یوسف رمضانOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
051 Endocrinology Physiology Adrenal Medulla Catecholamines
Uploaded by
یوسف رمضانCopyright:
Available Formats
Last edited: 9/8/2021
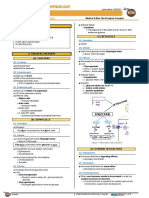
1. ADRENAL MEDULLA & CATECHOLAMINES
Endocrinology | Adrenal Medulla | Catecholamines Medical Editor: Ilia-Presiyan Georgiev
OUTLINE (4) In the LGH are located
the bodies of the preganglionic motor neurons of the SNS
I) MAIN HEADING IN o Their axons come out through the ventral ramus
II) CONTENT FORMATTING
o Move through sympathetic chain ganglia
III) APPENDIX
o Go the adrenal medulla
IV) REVIEW QUESTIONS
V) REFRENCES
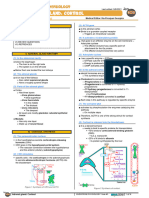
I) ADRENAL GLAND ANATOMY
(1) In the abdominal cavity
below the diaphragm
The liver is on the right side
The spleen is on the left side
Below them are located the two kidneys
(2) The adrenal glands
sit on top of the kidneys
Also called suprarenal glands
Have a roughly pyramid shape
(3) Parts of the adrenal gland
Cortex
o Has three layers
Zona glomerulosa Figure 1 Catecholamine synthesis part 1.
• Most superficial
Zona fasciculata
In most cases
• In the middle o Preganglionic neurons
• The thickest Short
Zona reticularis Go to the chain ganglia
• The deepest o Postganglionic neurons
o All layers are mostly glandular cuboidal epithelial Long
tissue Begin from the chain ganglia
Medulla The adrenal medulla is an exception
o Has only one layer o Preganglionic motor neurons
o Made up of neural tissue - chromaffin cells Long
Cell bodies of the postganglionic motor neurons of Reach the postganglionic cell bodies
o Postganglionic cell neurons
the sympathetic nervous system
Very short
Cell bodies located inside the actual organ
o This is called an intramural ganglion
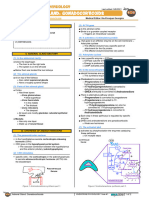
II) CATHECHOLAMINE SYNTHESIS
(5) Preganglionic motor neurons are cholinergic
(1) Th1 to L2 of the spinal cord
They release acetylcholine
is the sympathetic component o It binds to nicotinic receptors on the chromaffin cells
o The thoracolumbar outflow Cations (e.g. Na+) flow in
(2) Short term (acute) stress The cations activate specific action potentials
o Stimulate certain processes within the cell
is the primary stimulus of the sympathetic nervous system
(SNS) The depolarization of the cell activates certain enzymes
o “Fight or flight” situations o A specific biochemical pathway is triggered
e.g. escaping from a vicious orangutan
(6) Tyrosine is the building block of this pathway
(3) The hypothalamus activates Tyrosine is converted to L-DOPA
the SNS o By tyrosine hydroxylase
o Very strong regulator L-DOPA is converted to dopamine
o Has a sympathetic and a parasympathetic component o By DOPA decarboxylase
It sends presynaptic potential down Dopamine is converted to norepinephrine
o Through descending fibers o By dopamine beta hydroxylase
To the lateral gray horn (LGH) of the spinal cord
In Th1 to L2 Norepinephrine is converted to epinephrine
o By phenylethanolamine n-methyltransferase (PNMT)
Adrenal Medulla & Catecholamines ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY: Note #1. 1 of 4
(7) The synapse (5) Gluconeogenesis
of the axon of the postganglionic motor neurons secretes A process where non-carbohydrate sources are turned
o 80% epinephrine into glucose
o 20% norepinephrine o Amino acids and lactic acid form the muscles
Normally epinephrine and norepinephrine are o Glycerol and odd chain fatty acids from the adipose
presynthesized tissue
o Put into vesicles (6) The overall result
Located in the terminal bulb of the axon
of both glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis is glucose
(8) Na+ enters the cell
Action potentials are produced down the axon
o When they reach the terminal bulb • Hyperglycemia
The potential reaches positive 30 mV The glucose can be utilized by the muscles
o Ca++ channels located there, open o For contraction
Ca++ starts flowing in.
(9) Ca++ acts as a bridge
Causes the vesicles to merge with the cell membrane
o Epinephrine and norepinephrine are released into the
bloodstream
Figure 3 Effects of catecholamines on the liver.
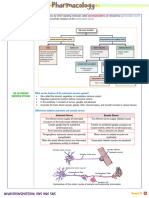
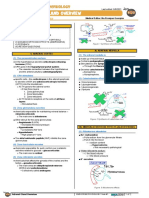
(B) EFFECTS ON THE ADIPOSE TISSUE
(1) Lipolysis
Catecholamines bind to a G protein-coupled receptor
o Activated the enzyme hormone sensitive lipase
(HSL)
Breaks down triglycerides into fatty acids and
glycerol
Figure 2 Catecholamine synthesis part 2.
The glycerol then goes to the liver
o Gets converted to glucose
III) CATECHOLAMINE EFFECTS The fatty acids go to the muscles
o Undergo beta oxidation and produce ATP
(A) EFFECTS ON THE LIVER o Helps with contraction
(1) Epinephrine goes
to the liver
Binds to a G protein-coupled receptor
o Triggers an intracellular cascade
(2) It activates a G stimulatory protein
that goes to an effector enzyme on the cell membrane –
Adenylate cyclase
o The effector enzyme has a specific point of Figure 4 Effects on adipose tissue.
attachment for the Gs protein
o The effector enzyme becomes very active (C) EFFECTS ON THE HEART
(3) Adenylate cyclase (1) Catecholamines exert their effects
has a specific enzyme – GTPase on the cardiomyocytes
o GTPase cuts the GTP and turns it into GDP Stimulates the expression of beta-1-adrenergic
o Energy is produced and used to convert ATP to cAMP receptors
o cAMP activates protein kinase A (pkA) o These receptors bind catecholamines
(4) Glycogenolysis
There is about 300g of glycogen in the liver
o Glycogen is a polymer of glucose
A storage molecule for glucose (2) Catecholamines also affect
Enzymes (glycogen phosphorylase, debranching
the non-contractile muscle cells
enzymes, etc.) cut up the glycogen into individual
of the SA node and the AV node
monomers – glucose
Stimulates the expression of beta-1-adrenergic
o The process is stimulated by catecholamines
receptors
Cortisol increases the sensitivity of the adrenergic
o These receptors bind catecholamines
receptors that bind them
2 of 4 ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY: Note #1. Adrenal Medulla & Catecholamines
(3) Catecholamines also bind to IV) REVIEW QUESTIONS
alpha-1-adrenergic receptors on some blood vessels
1) Which is the inner layer of the adrenal cortex
Cause vasoconstriction
a) Zona fasciculata
b) Zona reticularis
c) Zona glomerulosa
d) Zona pellucida
↑ blood pressure gets the nutrients to the vital tissue
o As much of nutrients as possible
o As quickly as possible 2) What tissue is the adrenal medulla made of?
a) Neural
b) Epithelial
c) Muscle
d) Connective
3) Which is the following is true for the adrenal
medulla?
a) Has three layers
b) Is made of glandular cuboidal epithelial tissue
c) Has one layer
d) That’s where aldosterone is synthesized
4) What is the primary stimulus of the SNS?
a) Acute stress
b) Resting
c) Reading
Figure 5 Effects on the heart. d) Eating
(D) EFFECTS ON THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
(1) Smooth muscle surrounds the bronchi 5) Which of these is the building block of the
epinephrine pathway?
Catecholamines act on those smooth muscle cells a) Dopamine
o By binding to alpha-2-adrenergic receptors b) Serotonin
Cause the bronchioles to dilate c) Histamine
d) Tyrosine
6) Which enzyme converts dopamine to
norepinephrine?
a) DOPA decarboxylase
b) Dopamine beta hydroxylase
c) Phenylethanolamine n-methyltransferase
d) Dopamine kinase
7) What are the effects of the catecholamines on the
liver?
a) Stimulating glycolysis
b) Inhibiting gluconeogenesis
c) Stimulating gluconeogenesis
d) Inhibiting glycogenolysis
8) What are the effects of the catecholamines on the
heart?
a) ↑ heart rate
b) ↑ cardiac output
c) ↑ stroke volume
Figure 6 Effects on the lungs. d) All of the above
(E) OTHER EFFECTS 9) Which of the following is an effect of the
catecholamines on the lungs?
(1) The vessels going to the GI tract a) Bronchoconstriction
constrict and divert the blood to b) Bronchodilatation
o Skeletal muscles c) ↓ respiration
o Brain d) Bradypnea (slow breathing rate)
o Heart, etc. 10) Which of the following is WRONG for the effects of
↓ GI tract activity the catecholamines?
a) ↑ blood pressure
(2) The blood vessels going to the kidneys b) Stimulating glycogenolysis
constrict and divert the blood c) ↑ GI tract activity
d) Stimulating lypogenesis
(3) The blood vessels in the skin
CHECK YOUR ANSWERS
constrict and divert the blood
Adrenal Medulla & Catecholamines ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY: Note #1. 3 of 4
4 of 4 ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY: Note #1. Adrenal Medulla & Catecholamines
You might also like
- Endocrine SystemDocument20 pagesEndocrine SystemSheena Pasion100% (2)
- Riverside College, Inc. Department of Physical Therapy Physiology01 Module 4 Lesson 3 Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesRiverside College, Inc. Department of Physical Therapy Physiology01 Module 4 Lesson 3 Autonomic Nervous SystemNeonil Dequina CaceresNo ratings yet
- Chapmans ReflexesDocument10 pagesChapmans ReflexesNickosteo100% (9)
- Nervous SYSTESTDocument19 pagesNervous SYSTESTedwalk1250% (2)
- Introduction To ANS PharmacologyDocument34 pagesIntroduction To ANS PharmacologySebontu HasenNo ratings yet
- Physiology of 3 Gates (Qigong) or 3 Granthi (Yoga)Document10 pagesPhysiology of 3 Gates (Qigong) or 3 Granthi (Yoga)Test4DNo ratings yet
- AbPsych Reviewer 1 PDFDocument8 pagesAbPsych Reviewer 1 PDFSyndell PalleNo ratings yet
- Psychology Mnemonics CollectionDocument15 pagesPsychology Mnemonics Collectionapi-260339450100% (3)
- Negative Ions BenefitsDocument34 pagesNegative Ions BenefitsAl MarzolNo ratings yet
- Parasympathetic Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesParasympathetic Nervous SystemAdeelBaigNo ratings yet
- 041 - Endocrinology Physiology) Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)Document3 pages041 - Endocrinology Physiology) Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)یوسف رمضان100% (1)
- Funda Board ExamDocument107 pagesFunda Board Examjoan olanteNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Autonomic PharmacologyDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Autonomic PharmacologyChacha ChachaNo ratings yet
- NBDEDocument151 pagesNBDEfadi100% (1)
- Autonomic Nervous System HandoutDocument4 pagesAutonomic Nervous System HandoutJobelleNo ratings yet
- Science10 Q3 SLM7Document17 pagesScience10 Q3 SLM7PiaNo ratings yet
- Synapse and Muscle Physiology: Lecturer - I. Savinkova, PHD Department of PhysiologyDocument50 pagesSynapse and Muscle Physiology: Lecturer - I. Savinkova, PHD Department of PhysiologyИринаNo ratings yet
- Frando-Detailed Learning Module 7.2.Document15 pagesFrando-Detailed Learning Module 7.2.Ranz Kenneth G. FrandoNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitter: S P SutamaDocument22 pagesNeurotransmitter: S P Sutamaanon_134497206No ratings yet
- Neurological Disorders MCQSDocument78 pagesNeurological Disorders MCQSninestar102100% (2)
- Neurofunctional Blueprints Transcripts For Tempe, January 2015 PDFDocument82 pagesNeurofunctional Blueprints Transcripts For Tempe, January 2015 PDFAnonymous oCjRxyBP100% (3)
- Adrenal Gland Cortisol AtfDocument4 pagesAdrenal Gland Cortisol Atf2ymyccmvfcNo ratings yet
- (PHARMA 2A) 2.1 - Intro To Autonomics and Drugs Acting On The Parasympathetic Nervous System - Dr. OnaDocument16 pages(PHARMA 2A) 2.1 - Intro To Autonomics and Drugs Acting On The Parasympathetic Nervous System - Dr. OnaRONALDO CUANo ratings yet
- Hormonal Communication and SynapsesDocument15 pagesHormonal Communication and SynapsesNirav PandeyNo ratings yet
- Pharmacol Ogy PHL 313: Chapter 5-6-7 Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)Document14 pagesPharmacol Ogy PHL 313: Chapter 5-6-7 Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)Abdullah Al-TuraifiNo ratings yet
- International Post-Baccalaureate Pharmd. (Ipbp) Program Internal Assessment (Ia) Exam Study GuideDocument67 pagesInternational Post-Baccalaureate Pharmd. (Ipbp) Program Internal Assessment (Ia) Exam Study Guideapi-3752144No ratings yet
- Pharma 2Document12 pagesPharma 2MARIEMIL FOLLOSONo ratings yet
- ANS PharmacologyDocument181 pagesANS Pharmacologywizgrace12No ratings yet
- Neurotransmitters - 2016Document183 pagesNeurotransmitters - 2016AdminNo ratings yet
- Pineal Gland AtfDocument2 pagesPineal Gland AtfSambit DashNo ratings yet
- Med Chem ANS DrugsDocument168 pagesMed Chem ANS Drugshailu tasheNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology 011 - ANS 3Document9 pagesPharmacology 011 - ANS 3Kaye NeeNo ratings yet
- 2013B Pathology CNS1Document8 pages2013B Pathology CNS1Christian Bryan TANNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland Gonadocorticoids AtfDocument2 pagesAdrenal Gland Gonadocorticoids Atf2ymyccmvfcNo ratings yet
- Pharma - Neurotransmission Ans and SnsDocument10 pagesPharma - Neurotransmission Ans and SnsksescletoNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitter 2Document37 pagesNeurotransmitter 2Preety ShresthaNo ratings yet
- 11 - Endocrine - 2021 Edition EndpointsDocument80 pages11 - Endocrine - 2021 Edition Endpointsgksah711No ratings yet
- Kuliah Pengantar Fisiologi Neuromuskuloskeletal 2021Document43 pagesKuliah Pengantar Fisiologi Neuromuskuloskeletal 2021rifkaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument37 pagesNervous Systemmariam1.ashrafNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitters and PsychopathologyDocument6 pagesNeurotransmitters and PsychopathologytakenotesanyaNo ratings yet
- Ans For PCL 301Document26 pagesAns For PCL 301olowoyoanjolaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of NeurotransmittersDocument7 pagesBiochemistry of NeurotransmittersHyphophysis 2015No ratings yet
- The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument42 pagesThe Autonomic Nervous SystemArkene LevyNo ratings yet
- 2autonomic Nervous SystemDocument28 pages2autonomic Nervous SystemSolomon H.No ratings yet
- The Autonomic System 2019Document50 pagesThe Autonomic System 2019TheBoss 20No ratings yet
- AP 18 Endocrine OverviewDocument19 pagesAP 18 Endocrine OverviewMARICRIS NEBIARNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesNervous SystemanneNo ratings yet
- NCM 205 - Pharma Lab IDocument7 pagesNCM 205 - Pharma Lab Isunwonloml0No ratings yet
- Part I. Principles of PsychopharmacologyDocument12 pagesPart I. Principles of PsychopharmacologyGauri SharmaNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument36 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemWed LodNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System (Introduction)Document33 pagesAutonomic Nervous System (Introduction)Abdelrahman GalalNo ratings yet
- 1 Nervous System OutlinesDocument45 pages1 Nervous System OutlinesTestingAccNo ratings yet
- PL-10 Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument24 pagesPL-10 Autonomic Nervous SystemFoong Zhen HinNo ratings yet
- Saqs - (Very Important)Document67 pagesSaqs - (Very Important)BRIGHTON JOSHUANo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System MedicationsDocument12 pagesCentral Nervous System MedicationsMARY JEANINA ALBANo ratings yet
- Kuliah VIII - Sistem Endokrin - KKPMT IIDocument50 pagesKuliah VIII - Sistem Endokrin - KKPMT IIRae SenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Endocrine SystemDocument13 pagesChapter 11 - Endocrine SystemIvy CustodioNo ratings yet
- Pain ControlDocument4 pagesPain Control381a53c99bNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument130 pagesAutonomic Nervous Systempmm21d229No ratings yet
- NP1 PDFDocument32 pagesNP1 PDFRajat AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument70 pagesNervous SystemStephen MartinNo ratings yet
- Neural Control and Coordination Notes For NEET Download PDF - pdf-20Document7 pagesNeural Control and Coordination Notes For NEET Download PDF - pdf-20Legendary KingNo ratings yet
- Synapse, The Concept of Antidote, Curare and Exotoxins PoisoningDocument39 pagesSynapse, The Concept of Antidote, Curare and Exotoxins PoisoningCLEMENTNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Peripheral Nervous System Pharmacology: Dr. M. IchwanDocument85 pagesIntroduction To Peripheral Nervous System Pharmacology: Dr. M. IchwanGarry B GunawanNo ratings yet
- PAS113 Block 2 NotesDocument41 pagesPAS113 Block 2 NotesAngela WuNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitters and Neuronal TractsDocument16 pagesNeurotransmitters and Neuronal TractsSravani MeesalaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Chemical ControlDocument36 pagesEndocrine System: Chemical ControlGary VlaicuNo ratings yet
- 054 - Endocrinology Physiology) Pancreas Insulin FunctionDocument4 pages054 - Endocrinology Physiology) Pancreas Insulin FunctionLily Blossom100% (1)
- FINALSDocument19 pagesFINALSOdyNo ratings yet
- Direct Acting CholinomimeticsDocument64 pagesDirect Acting CholinomimeticsAmirAmeer AliNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitter (Dr. Devi) - 2Document71 pagesNeurotransmitter (Dr. Devi) - 2nazyaNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Pharmacology OverviewDocument44 pagesAutonomic Pharmacology OverviewChipego NyirendaNo ratings yet
- Neurology 1Document47 pagesNeurology 1Sonu CanNo ratings yet
- Cholinesterases: A Histochemical Contribution to the Solution of Some Functional ProblemsFrom EverandCholinesterases: A Histochemical Contribution to the Solution of Some Functional ProblemsNo ratings yet
- 043 - Endocrinology Physiology) ProlactinDocument3 pages043 - Endocrinology Physiology) Prolactinیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- 038 Endocrinology Physiology Hypothalamus Posterior Pituitary ConnectionDocument3 pages038 Endocrinology Physiology Hypothalamus Posterior Pituitary Connectionیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- 037 - Endocrinology Physiology) Receptor PathwaysDocument4 pages037 - Endocrinology Physiology) Receptor Pathwaysیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- 040 - Endocrinology Physiology) OxytocinDocument3 pages040 - Endocrinology Physiology) Oxytocinیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- 052 - Endocrinology Physiology) Adrenal Gland OverviewDocument2 pages052 - Endocrinology Physiology) Adrenal Gland Overviewیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- 047 Endocrinology Physiology Parathyroid Gland CalcitoninDocument4 pages047 Endocrinology Physiology Parathyroid Gland Calcitoninیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- 042 - Endocrinology Physiology) Growth HormoneDocument3 pages042 - Endocrinology Physiology) Growth Hormoneیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- 046 - Endocrinology Physiology) Thyroid OverviewDocument2 pages046 - Endocrinology Physiology) Thyroid Overviewیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- Q Bank Physio 30Document30 pagesQ Bank Physio 30haleemeltayebNo ratings yet
- Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 12th Ed - p0776Document3 pagesGuyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 12th Ed - p0776Maryama AflahaNo ratings yet
- Units 1-7 OutlinesDocument64 pagesUnits 1-7 OutlinesSungmin ChuNo ratings yet
- Health Psychology An Interdisciplinary Approach To Health 2nd Edition Deborah Test BankDocument39 pagesHealth Psychology An Interdisciplinary Approach To Health 2nd Edition Deborah Test Bankjakebradyt0x9100% (16)
- CH 7 The Nervous System NotesDocument21 pagesCH 7 The Nervous System Notesbiswa217No ratings yet
- SecretinDocument10 pagesSecretinerwilli5No ratings yet
- TVP 2016 0102 OO AnisocoriaDocument7 pagesTVP 2016 0102 OO AnisocoriaRocioNo ratings yet
- Manuel, Christine D.-Bsed 2e-Anatomy and Physiology-Module 10Document2 pagesManuel, Christine D.-Bsed 2e-Anatomy and Physiology-Module 10Christine ManuelNo ratings yet
- The Brain and Nervous System (Psychology) Unit 14: An Academic ReportDocument7 pagesThe Brain and Nervous System (Psychology) Unit 14: An Academic ReportOlatokunbo SinaayomiNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Health Psychology 3rd Canadian EditionDocument38 pagesTest Bank For Health Psychology 3rd Canadian EditionCarrie Stavis100% (36)
- Nervous System Part 2Document89 pagesNervous System Part 2VEA DE LEONNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Eccrine Sweat Glands and SweatingDocument8 pagesDisorders of The Eccrine Sweat Glands and SweatingAnnisa Chaerani BurhanuddinNo ratings yet
- Chap 14Document16 pagesChap 14larryeNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Nervous System PDFDocument92 pages1.2 Nervous System PDFtess_15No ratings yet
- Autonomic InnervationDocument3 pagesAutonomic InnervationIana Gaia MartiniNo ratings yet
- Conservative Treatment of Pulp TissueDocument212 pagesConservative Treatment of Pulp TissueBer CanNo ratings yet
- 24 Cerebral Blood FlowDocument31 pages24 Cerebral Blood FlowZuhaib Ahmed100% (1)