Professional Documents
Culture Documents
046 - Endocrinology Physiology) Thyroid Overview
Uploaded by
یوسف رمضانOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
046 - Endocrinology Physiology) Thyroid Overview
Uploaded by
یوسف رمضانCopyright:
Available Formats
Last edited: 9/5/2021
10. THYROID OVERVIEW
Endocrinology | Thyroid Overview Medical Editor: Ilia-Presiyan Georgiev
OUTLINE
I) MAIN HEADING IN
II) CONTENT FORMATTING
III) APPENDIX
IV) REVIEW QUESTIONS
V) REFRENCES
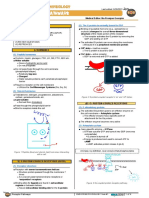
I) SYNTHESYS
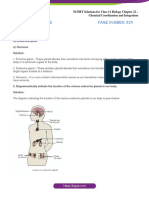
Figure 2 Regulation of TH.
(1) In the hypothalamus
III) EFFECTS ON TARGET ORGANS
there are specific neurons that form the paraventricular
nucleus (PVN) (1) Cells
o Those neurons release thyrotropin releasing
↑ basal metabolic rate
hormone (TRH)
o by ↑ sodium-potassium ATPase
TRH goes through the hypophyseal portal system
o The vascular connection between the hypothalamus
Stimulates
and the anterior pituitary
o Lipolysis
(2) In the anterior pituitary o Glycolysis
o Gluconeogenesis
TRH stimulates specific cells – thyrotropes
o Secrete thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) ↑ the blood glucose levels
o TSH is secreted into the bloodstream and reaches o A hyperglycemic hormone
the thyroid gland ↑ uptake of low-density lipoproteins – LDL (bad
(3) In the thyroid gland cholesterol)
o In the liver
the overall effect is the production of T3 and T4
o Collectively form the thyroid hormone (TH) (2) Bones
TH is transported through the blood with the help of Promotes normal bone growth and maturation
thyroxine binding globulin (TBG)
(3) Muscles
o Protein produced by the liver
Promotes normal muscular function and development
(4) Heart
Promotes normal cardiac output
(5) Brain
Promotes normal nerve development
↑ the number of synapses
↑ myelination
↑ the number of dendrites
(6) GI tract
Promotes normal motility and secretion of the GI tract
Figure 1 Synthesis of TH. (7) Skin
Promotes normal hydration of the skin tissue
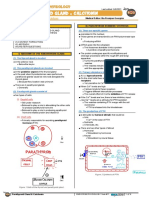
II) REGULATION
(1) High levels of TH
• exert a negative feedback mechanism
• Inhibits the paraventricular nucleus from making TRH
(2) Low levels of TH
exert a negative feedback mechanism
Stimulate the paraventricular nucleus to release
excessive amounts of TRH
Figure 3 Effects of TH on target organs.
Thyroid Overview ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY: Note #10. 1 of 2
IV) REVIEW QUESTIONS V) REFRENCES
● APA citation guide. (2016). http://www.bibme.org/citation-
1) Which hormone is produced by the anterior pituitary
guide/apa/
gland? ● Lipson, C. (2011). Cite right: A quick guide to citation styles –
a) TRH MLA, APA, Chicago, the sciences, professions, and more (2nd ed).
b) TSH United States of America: The University of Chicago Press, Ltd.,
London.
c) TH ● Ferraro, A. (Photographer). (2014). Liberty enlightening the
d) TGB world [digital image]. Retrieved from
https://www.flickr.com/photos/afer92/ 14278571753/in/set-
72157644617030616
2) Which cells are stimulated by TRH?
a) Neurons in the PVN
b) Follicular cells
c) Thyrotropes
d) Hepatocytes
3) Which two substances collectively form the TH
a) Thyroglobulin colloid and iodine
b) Tyrosine and thyroid peroxidase
c) Diiodotyrosine and monoiodotyrosine
d) Thyroxine and triiodothyronine
4) Which substance binds TH in the bloodstream?
a) Albumin
b) Thyroxine binding globulin
c) Thyroglobulin
d) Iodide
5) What is NOT correct about the effects of T3 on the
cell?
a) ↑ number of sodium-potassium pumps
b) ↑ the cellular ATP levels
c) ↑ in burning fuel
d) ↑ heat production
6) What is WRONG about the effects of TH on the CNS?
a) ↑ quality of synapses
b) ↑ dendrite formation
c) ↑ the number of the neural connections
d) ↑ myelination
CHECK YOUR ANSWERS
2 of 2 ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY: Note #10. Thyroid Overview
You might also like
- Science Essentials 9 For NSW Stage 5 Australian Curriculum EditionDocument3 pagesScience Essentials 9 For NSW Stage 5 Australian Curriculum Editionapi-374582387No ratings yet
- Quiz EndocrineDocument84 pagesQuiz EndocrineMedShare92% (12)
- Thyroid and Thyroid DiseasesDocument22 pagesThyroid and Thyroid DiseasesAnushka Sharma82% (17)
- (Morris, David Morris) Stereochemistry (Tutorial C (B-Ok - Xyz)Document179 pages(Morris, David Morris) Stereochemistry (Tutorial C (B-Ok - Xyz)anushka100% (2)
- 26-1208-01 Evolution of Silicon-Based Technology in CoatingsDocument10 pages26-1208-01 Evolution of Silicon-Based Technology in Coatingskreci1No ratings yet
- 041 - Endocrinology Physiology) Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)Document3 pages041 - Endocrinology Physiology) Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)یوسف رمضان100% (1)
- Types of Malware and Importance of Malware AnalysisDocument10 pagesTypes of Malware and Importance of Malware AnalysisshaletNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedFrom EverandThyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Midterms 88%Document18 pagesMidterms 88%jrence80% (5)
- Static Var CompensatorDocument29 pagesStatic Var CompensatorCarlos Fabian GallardoNo ratings yet
- Seam 325 Prelim Exam ReviewerDocument6 pagesSeam 325 Prelim Exam ReviewerKyle Steven CaymeNo ratings yet
- Target Organs of The Thyroid AtfDocument4 pagesTarget Organs of The Thyroid AtfRidwan PermanaNo ratings yet
- Slide Webinar TiroidDocument28 pagesSlide Webinar TiroidmariaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument71 pagesChemical Coordination and IntegrationAditiya SaxenaNo ratings yet
- 065 Endocrinology Pathology Hypothyroidism Physiology, PathophysiologyDocument6 pages065 Endocrinology Pathology Hypothyroidism Physiology, PathophysiologyLily BlossomNo ratings yet
- 12 Poll - Z-12 (20 Ques.)Document2 pages12 Poll - Z-12 (20 Ques.)lixanNo ratings yet
- AP1 Lab16 Endocrine System FA2021Document11 pagesAP1 Lab16 Endocrine System FA2021daleng subNo ratings yet
- Not Testable Subject Matter, Just Know Endocrine System Works With Other SystemsDocument23 pagesNot Testable Subject Matter, Just Know Endocrine System Works With Other Systemsjnoah111No ratings yet
- Homeostasis Practice QuizDocument2 pagesHomeostasis Practice QuizRofekiNo ratings yet
- AP Bio - Chapter 40 OutlineDocument8 pagesAP Bio - Chapter 40 OutlineEllen LiNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions June6 For Class 11 Biology Chapter 22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument8 pagesNcert Solutions June6 For Class 11 Biology Chapter 22 Chemical Coordination and Integrationginnisingh524No ratings yet
- Endocrine Hand OutDocument10 pagesEndocrine Hand OutbetazenNo ratings yet
- The Thyroid Gland: Physiology and Pathophysiology: Endocrine Series #6Document16 pagesThe Thyroid Gland: Physiology and Pathophysiology: Endocrine Series #6نذير الشرعبيNo ratings yet
- Enr Saqs 2Document5 pagesEnr Saqs 2Mahnoor KhanNo ratings yet
- XI CH - 22 Chemical Control and CoordinationDocument16 pagesXI CH - 22 Chemical Control and Coordinationali imranNo ratings yet
- 1016MSC T1 2023 Module 5 Tutorial WorksheetsDocument21 pages1016MSC T1 2023 Module 5 Tutorial WorksheetsTina HussainiNo ratings yet
- Biology: Topic - Endocrine System Class-VIII Board - ICSEDocument3 pagesBiology: Topic - Endocrine System Class-VIII Board - ICSEItu DeyNo ratings yet
- CH 16 Endocrine TableDocument9 pagesCH 16 Endocrine TablebetazenNo ratings yet
- Thyroid FinalDocument19 pagesThyroid FinalMariela AlvarezNo ratings yet
- 052 - Endocrinology Physiology) Adrenal Gland OverviewDocument2 pages052 - Endocrinology Physiology) Adrenal Gland Overviewیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- MCQs On Chemical Coordination and ControlDocument18 pagesMCQs On Chemical Coordination and ControlPukazhvanthen ParamanandhanNo ratings yet
- EXCI360 Ch75 IntroductionDocument19 pagesEXCI360 Ch75 Introduction5xfz6hjkpgNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland Clinical Chemistry 2 (Laboratory) : LessonDocument4 pagesThyroid Gland Clinical Chemistry 2 (Laboratory) : LessonCherry Ann ColechaNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Thyroid Disorders and Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument6 pagesReview Article: Thyroid Disorders and Chronic Kidney DiseaseMariano CadeNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument13 pagesEndocrineElyka Alivan Valdez PolonioNo ratings yet
- Chemical Signals in Animals: Egg Larva Pupa AdultDocument29 pagesChemical Signals in Animals: Egg Larva Pupa AdultMENWER ALJOHANINo ratings yet
- Endocrine PhysiologyDocument26 pagesEndocrine Physiologysam bossaNo ratings yet
- Previous Year Questions Control - CoordinationDocument13 pagesPrevious Year Questions Control - CoordinationsinghejouraaritNo ratings yet
- Dawood ThesisDocument50 pagesDawood ThesisDawood khanNo ratings yet
- 11 - Chem Coordination and Integration PDFDocument37 pages11 - Chem Coordination and Integration PDFANo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System,: Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVMDocument23 pagesThe Endocrine System,: Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVMiLeyNNo ratings yet
- Te-Control and Coordination Final Revisor (2023-24)Document69 pagesTe-Control and Coordination Final Revisor (2023-24)Gautam SharrmaNo ratings yet
- NorcetDocument95 pagesNorcetDiksha DhillonNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland (Mam Suba)Document2 pagesThyroid Gland (Mam Suba)Mark Vincent SahagunNo ratings yet
- Sample RUDocument25 pagesSample RUmaria riza lagromaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Control N Cordboard QTN ScienceDocument3 pagesLesson 7 Control N Cordboard QTN ScienceSarvesh KotkarNo ratings yet
- Bio Control and CoordinationDocument3 pagesBio Control and CoordinationR.Pearlsis SophiNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders 1Document29 pagesThyroid Disorders 1zxcvbzaki123No ratings yet
- VND Ms-Powerpoint&rendition 1Document49 pagesVND Ms-Powerpoint&rendition 1Muhammad SamiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument8 pagesChemical Coordination and IntegrationsuryababaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise 13Document18 pagesLaboratory Exercise 13Jessa SuacitoNo ratings yet
- ICSE-X Biology Chap-11 (Endocrine System)Document14 pagesICSE-X Biology Chap-11 (Endocrine System)TAHMEENA ZAFARNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism Cats Part IDocument10 pagesHyperthyroidism Cats Part IFabiola Andrea Abril ParraNo ratings yet
- Endocrine-System Important-Qs Important-QuestionsDocument4 pagesEndocrine-System Important-Qs Important-Questionssshashvat810No ratings yet
- Name# Khursheed Ali Reg No# 17-ARID-6126Document15 pagesName# Khursheed Ali Reg No# 17-ARID-6126shahzeb bilalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Co OrdinationDocument6 pagesChemical Co Ordinationtunganasyam966No ratings yet
- Dopa - 22Document6 pagesDopa - 22hhNo ratings yet
- Ch45 EndocrineSystemDocument3 pagesCh45 EndocrineSystemCristie SumbillaNo ratings yet
- EXCI360 Ch75 IntroductionDocument21 pagesEXCI360 Ch75 Introduction5xfz6hjkpgNo ratings yet
- BOARD EXAM QUESTION PAPER 2023 Biology (Chapter 1, 2)Document8 pagesBOARD EXAM QUESTION PAPER 2023 Biology (Chapter 1, 2)Anisha ThomasNo ratings yet
- RenalHormoneRegLecture Zeman (Spring2020)Document50 pagesRenalHormoneRegLecture Zeman (Spring2020)Sahil ParikhNo ratings yet
- Enr SaqsDocument4 pagesEnr SaqsMahnoor KhanNo ratings yet
- Artículo de InvestigaciónDocument18 pagesArtículo de InvestigacióngabrielaNo ratings yet
- BasicsDocument120 pagesBasicsbiniam MesfinNo ratings yet
- Lecture10 CommunicationIII 1Document30 pagesLecture10 CommunicationIII 1Liana Rose MeregildoNo ratings yet
- 051 Endocrinology Physiology Adrenal Medulla CatecholaminesDocument4 pages051 Endocrinology Physiology Adrenal Medulla Catecholaminesیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- 043 - Endocrinology Physiology) ProlactinDocument3 pages043 - Endocrinology Physiology) Prolactinیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- 038 Endocrinology Physiology Hypothalamus Posterior Pituitary ConnectionDocument3 pages038 Endocrinology Physiology Hypothalamus Posterior Pituitary Connectionیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- 037 - Endocrinology Physiology) Receptor PathwaysDocument4 pages037 - Endocrinology Physiology) Receptor Pathwaysیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- 040 - Endocrinology Physiology) OxytocinDocument3 pages040 - Endocrinology Physiology) Oxytocinیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- 052 - Endocrinology Physiology) Adrenal Gland OverviewDocument2 pages052 - Endocrinology Physiology) Adrenal Gland Overviewیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- 042 - Endocrinology Physiology) Growth HormoneDocument3 pages042 - Endocrinology Physiology) Growth Hormoneیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- 047 Endocrinology Physiology Parathyroid Gland CalcitoninDocument4 pages047 Endocrinology Physiology Parathyroid Gland Calcitoninیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- GSE580Document132 pagesGSE580Anonymous g4wR41qNeNo ratings yet
- Rationale of Employee Turnover: An Analysis of Banking Sector in NepalDocument8 pagesRationale of Employee Turnover: An Analysis of Banking Sector in Nepaltempmail5598No ratings yet
- Application Form Safety Program Pg1Document1 pageApplication Form Safety Program Pg1Mark Jayson GarciaNo ratings yet
- Information TechnologyDocument7 pagesInformation TechnologyDEVANAND ANo ratings yet
- Subject: SRE (Software Requirement Engineering) Topic: SRS Document of Project. Project: Medical Store Management. Group MembersDocument9 pagesSubject: SRE (Software Requirement Engineering) Topic: SRS Document of Project. Project: Medical Store Management. Group Membersabdullah amjadNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Legal EthicalDocument22 pagesUnit 7 Legal Ethicalapi-462777064No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Divisions of Rashis - Ancient Vedic Texts !Document4 pagesChapter 7 - Divisions of Rashis - Ancient Vedic Texts !SN WijesinheNo ratings yet
- Top Talkers SOPv1Document3 pagesTop Talkers SOPv1Gaurav NayakNo ratings yet
- Quiet Healing CentreDocument12 pagesQuiet Healing CentredoliamahakNo ratings yet
- DOH Breast Cancer Guidelines FinalDocument123 pagesDOH Breast Cancer Guidelines Finalsupratimbiswas073380No ratings yet
- English: Quarter 1 - Module 1Document34 pagesEnglish: Quarter 1 - Module 1Roel MabbayadNo ratings yet
- Tele BRANCHES 01.06.2021Document23 pagesTele BRANCHES 01.06.2021Abhishek BarwalNo ratings yet
- Progress Audio Script 2Document1 pageProgress Audio Script 2groniganNo ratings yet
- Micro PPT FinalDocument39 pagesMicro PPT FinalRyan Christopher PascualNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument3 pagesQuestionsRajani NairNo ratings yet
- Material No 982981Document23 pagesMaterial No 982981Yelena ObyazovaNo ratings yet
- En 1 6 009 M 146000Document22 pagesEn 1 6 009 M 146000David AriasNo ratings yet
- MISSISSIPPI Chanery ClerksDocument7 pagesMISSISSIPPI Chanery Clerks2PlusNo ratings yet
- Effect of Pitting Corrosion On The Mechanical Properties of 316 Grade Stainless SteelDocument6 pagesEffect of Pitting Corrosion On The Mechanical Properties of 316 Grade Stainless SteelAnilNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Crime Scene Investigation andDocument1 page2.2 Crime Scene Investigation andFatima Sarpina HinayNo ratings yet
- Bioshock Audio DiariesDocument6 pagesBioshock Audio DiariesGeorge CuriosoNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi Electric MSZ-FH VE Remote Controller Eng PDFDocument1 pageMitsubishi Electric MSZ-FH VE Remote Controller Eng PDFShadi MattarNo ratings yet
- Methods of Teaching 1 and 6Document68 pagesMethods of Teaching 1 and 6BUEN, RENZZELLE JOY B.No ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between The Puncture and The Flashover of An Insulator - QuoraDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between The Puncture and The Flashover of An Insulator - QuorasanjuNo ratings yet