Professional Documents
Culture Documents
042 - Endocrinology Physiology) Growth Hormone
Uploaded by
یوسف رمضانOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
042 - Endocrinology Physiology) Growth Hormone
Uploaded by
یوسف رمضانCopyright:
Available Formats
Last edited: 9/4/2021
6. GROWTH HORMONE
Endocrinology | Growth Hormone Medical Editor: Ilia-Presiyan Georgiev
o The DNA undergoes transcription and produces
OUTLINE mRNA
o The mRNA goes to the ribosomes and is translated
I) SYNTHESIS into protein
II) EFFECTS OF GROWTH HORMONE o The protein undergoes modifications in the rough ER
III) EFFECTS OF IGF TYPE 1
and the Golgi apparatus and eventually is released in
IV) REVIEW QUESTIONS
V) REFRENCES the circulation
This protein is called Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)
type 1
(B) GLUCONEOGENESIS
(1) In the liver
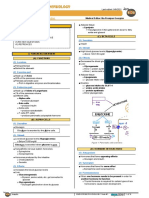
I) SYNTHESIS
GH also stimulates gluconeogenesis
(1) The arcuate nucleus o Increases the blood glucose levels by producing
in the hypothalamus secretes growth hormone glucose from non-carbohydrate sources
releasing hormone (GHRH) Glycerol
o Secondary triggers Odd chain fatty acids
↑ amino acid levels in the blood
↓ glucose levels in the blood
• Hypoglycemia
↓ fatty acid levels in the blood
Exercise
Healthy stressors
GHRH goes in the hypophyseal portal system
o The vascular connection between the hypothalamus Figure 2 Effects of growth hormone in the liver.
and the anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis) (C) LIPOLYSIS
GHRH stimulates specific cells - the somatotropes in the (1) GH binds to
adenohypophysis to secrete growth hormone (GH) into
the bloodstream receptors in adipose tissue
o Triggers an intracellular mechanism
Activates the enzyme hormone sensitive lipase
(HSL)
HSL initiates lipolysis
o The breaking down triglycerides into glycerol and fatty
acids
Glycerol and the odd chain fatty acids are used for
gluconeogenesis
Figure 3 Effect of growth hormone in adipose tissue.
Figure 1 Growth hormone synthesis. (D) AMINO ACID UPTAKE
(1) GH binds to
II) EFFECTS OF GROWTH HORMONE receptors present on the surface of skeletal muscle cells
o Activates specific signaling pathway
(A) IGF TYPE 1 PRODUCTION o Activates the nucleus
(1) Certain percentage of the secreted GH o The nucleus activates specific genes
Produces specific types of proteins
goes and binds to specific receptors in the liver
o Tyrosine kinase-like receptor These proteins activate specific channels for amino acids
o Has a specific part that activates the on the cell membrane
phosphorylation of specific types of amino acids o ↑ amino acid uptake
The enzyme Janus kinase (JAK) is activated
o Phosphorylates the signal transducer activator of
transcription (STAT)
(2) When activated STAT
goes to the nucleus
Binds to a specific gene sequence of DNA
Figure 4 Effect of growth hormone on the skeletal muscles.
Growth hormone ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY: Note #6. 1 of 3
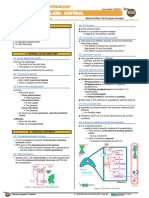
III) EFFECTS OF IGF TYPE 1 o Overall, the bones get bigger and thicker –
appositional growth
(A) EFFECTS ON THE SKELETAL MUSCLES The activated osteoblast and osteoclasts increase the
(1) IGF1 binds to endochondral ossification
receptors present on the surface of skeletal muscle cells (2) IGF type 1 also stimulates
o Activates specific signaling pathway protein synthesis which increases the density of the
o Activates the nucleus bones
o The nucleus activates specific genes o ↑ production of collagen type 1
Produces specific types of proteins
In the bones there is collagen type one
These proteins activate specific channels for amino acids
o ↑ increased production of proteoglycans
on the cell membrane
o ↑ amino acid uptake
(2) Inside the cell
another pathway stimulates the amino acids
o Amino acids link together and produce proteins
Myofibrils
• Actin
• Myosin
This causes hypertrophy of the muscles
o ↑ the overall size of the muscles
Figure 6 Effects of IGF type 1 on the bones.
(C) EFFECTS ON THE CARTILAGE
(1) In the epiphyseal plates
IGF type 1 affects the chondroblasts
o ↑ differentiation into certain types of bone tissue
o ↑ size
o ↑ proliferation
As a result, the bones grow in length – interstitial
growth
Figure 5 Effects of IGF type 1 on the skeletal muscles.
(B) EFFECTS ON THE BONE
(1) IGF type 1 regulates
the osteoblasts and osteoclasts cells inside the bones
o Highly activates and regulates the activity of both Figure 7 Effects of IGF type 1 on the cartilage.
↑ bone deposition (osteoblasts)
↑ bone resorption (osteoclasts)
IV) APPENDIX
Adipose Skeletal
Liver Bones Cartilage
tissue muscles
Produces Insulin-
Growth like growth factor ↑ amino acid
Lipolysis
hormone type 1 uptake
Gluconeogenesis
↑ bone deposition
↑ amino acid ↑ differentiation
Insulin-like (osteoblasts)
uptake into certain types
↑ bone resorption
growth factor ↑ the overall of bone tissue
(osteoclasts)
type 1 size of the ↑ size
appositional growth
muscles ↑ proliferation
↑ endochondral ossification
2 of 3 ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY: Note #6. Growth hormone
V) REVIEW QUESTIONS VI) REFRENCES
Which nucleus secretes GHRH?
● Le T, Bhushan V, Sochat M, Chavda Y, Zureick A. First Aid for
a. Preoptic nucleus the USMLE Step 1 2018. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Medical; 2017
b. Supraoptic nucleus ● Marieb EN, Hoehn K. Anatomy & Physiology. Hoboken, NJ:
c. Arcuate nucleus Pearson; 2020.
● Boron WF, Boulpaep EL. Medical Physiology.; 2017.
d. Paraventricular nucleus ● Jameson JL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL,
Loscalzo J. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, Twentieth
Which is not a secondary trigger for GHRH Edition (Vol.1 & Vol.2). McGraw-Hill Education / Medical; 2018
● Hall JE, Hall ME. Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical
secretion? Physiology. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021.
a. ↓ amino acid levels in the blood
b. ↓ glucose levels in the blood
c. ↓ fatty acid levels in the blood
d. Exercise
Which cells are stimulated by the GHRH?
a. Corticotropes
b. Somatotropes
c. Thyrotropes
d. Gonadotropes
Which tissue is not affected directly by the growth
hormone?
a. Liver
b. Skeletal muscles
c. Adipose tissue
d. Bones
Which enzyme initiates the production of IGF type
1?
a. JAK
b. STAT
c. HSL
d. pkA
Which process is stimulated directly by the growth
hormone?
a. Glycogenosis
b. Glycolysis
c. Glycogenolysis
d. Gluconeogenesis
What is the main effect of the growth hormone in the
skeletal muscles?
a. Increased amino acid uptake
b. Increased protein synthesis
c. Both
d. Neither
IGF type 1 stimulates the productions of which
protein?
a. Glycerol
b. STAT
c. Myosin
d. growth hormone
Which protein increases bone density
a. Actin
b. Collagen type 1
c. Myosin
d. Collagen type 2
What is the name of the process where bones
increase in length?
a. Appositional growth
b. Interstitial growth
c. Endochondral ossification
d. Bone deposition
CHECK YOUR ANSWERS
Growth hormone ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY: Note #6. 3 of 3
You might also like
- Glycolysis Atf Ninja NerdDocument5 pagesGlycolysis Atf Ninja NerdLara GentNo ratings yet
- Food and NutritionDocument291 pagesFood and NutritionIonut Marius Barsan96% (25)
- 054 - Endocrinology Physiology) Pancreas Insulin FunctionDocument4 pages054 - Endocrinology Physiology) Pancreas Insulin FunctionLily Blossom100% (1)
- Pancreas Insulin Function AtfDocument3 pagesPancreas Insulin Function Atf2ymyccmvfcNo ratings yet
- 065 Endocrinology Pathology Hypothyroidism Physiology, PathophysiologyDocument6 pages065 Endocrinology Pathology Hypothyroidism Physiology, PathophysiologyLily BlossomNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland Cortisol AtfDocument4 pagesAdrenal Gland Cortisol Atf2ymyccmvfcNo ratings yet
- Target Organs of The Thyroid AtfDocument4 pagesTarget Organs of The Thyroid AtfRidwan PermanaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Anterior Pituitary GlandDocument35 pages2 - Anterior Pituitary GlandBHUWAN BASKOTANo ratings yet
- Wa0016.Document21 pagesWa0016.Survey IndiaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Viii Notes Prepared by Dr. Dhondiba Vishwanath Suryawanshi, GFGC KR Puram Bengaluru-36Document9 pagesChemistry-Viii Notes Prepared by Dr. Dhondiba Vishwanath Suryawanshi, GFGC KR Puram Bengaluru-36Dr. Dhondiba Vishwanath0% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDocument70 pagesEndocrine SystemKELVINNo ratings yet
- (Chappel S., Murphy W.) Growth Hormone (BookFi)Document16 pages(Chappel S., Murphy W.) Growth Hormone (BookFi)H.M.No ratings yet
- Growth Hormone - BDSDocument24 pagesGrowth Hormone - BDSxmarty.fazil100% (1)
- 10.1 Blood Sugar - RegulationDocument9 pages10.1 Blood Sugar - RegulationSadiqNo ratings yet
- Glucose regulation-RSKDocument4 pagesGlucose regulation-RSKdevilalshingh9525No ratings yet
- Physio 5Document15 pagesPhysio 5amjadNo ratings yet
- Glycogenolysis: BiochemistryDocument6 pagesGlycogenolysis: BiochemistryManila MedNo ratings yet
- Production of Growth Factors, Cytokines, and ChemokinesDocument16 pagesProduction of Growth Factors, Cytokines, and ChemokinesNina TrươngNo ratings yet
- SomatotrophinDocument42 pagesSomatotrophinSaqib SaeedNo ratings yet
- Multiple Effects of HormonesDocument35 pagesMultiple Effects of HormonesRokia GhariebNo ratings yet
- BasicsDocument120 pagesBasicsbiniam MesfinNo ratings yet
- Endo Other Hormones ElhDocument12 pagesEndo Other Hormones Elhodiodi57No ratings yet
- Protein Dan Enzimologi: Dewi - Erika.adriani@ulm - Ac.idDocument21 pagesProtein Dan Enzimologi: Dewi - Erika.adriani@ulm - Ac.idNur MaulidaNo ratings yet
- Joe JOE 22 0159Document11 pagesJoe JOE 22 0159AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument14 pagesEndocrine System NotesSteven100% (1)
- Adrenal RAAS, Vasopressin Lecture 37 PDFDocument9 pagesAdrenal RAAS, Vasopressin Lecture 37 PDFmubashirNo ratings yet
- Use of Soy Isoflavones For Stimulation of Skin Collagen SynthesisDocument3 pagesUse of Soy Isoflavones For Stimulation of Skin Collagen SynthesiserlanggawidyaputriNo ratings yet
- 5-Pituitary, Thyroid 1Document57 pages5-Pituitary, Thyroid 1tmqt2fbnzgNo ratings yet
- Cell-Cell Communication-Rumen MetabolismDocument11 pagesCell-Cell Communication-Rumen MetabolismChala Tekalign HareruNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Anterior Pituitary and HypothalamusDocument121 pagesDisorders of The Anterior Pituitary and Hypothalamusbiniam MesfinNo ratings yet
- 1.2 CorticosteroidsDocument9 pages1.2 Corticosteroidsua091031No ratings yet
- Control of Hormone SecretionDocument77 pagesControl of Hormone Secretionjohanna deguzmanNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesThe Endocrine SystemRODGIELYN MAE GEJONNo ratings yet
- Midterm - AnaphyDocument6 pagesMidterm - AnaphyJustine Mae OyongNo ratings yet
- Fisiopatologia de La Crisis HipoglicemicaDocument11 pagesFisiopatologia de La Crisis HipoglicemicaLemur DaJuliNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument5 pagesChemical Coordination and Integrationbansarigadhvi23No ratings yet
- Name of The GlandDocument3 pagesName of The GlandSajeevNo ratings yet
- Glycogenolysis AtfDocument3 pagesGlycogenolysis AtfDivyaa VisvalingamNo ratings yet
- L13 - Cancer Cell Signalling-Part 1-S23Document24 pagesL13 - Cancer Cell Signalling-Part 1-S23waNo ratings yet
- Cytokines IN PeriodonticsDocument72 pagesCytokines IN PeriodonticsInduNo ratings yet
- J Ajo 2006 02 047Document9 pagesJ Ajo 2006 02 047Zuni TriyantiNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - MNT For Metabolic StressDocument14 pagesReviewer - MNT For Metabolic StressimjuuNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Physiology and Pathophysiology (Part 1)Document34 pagesEndocrine System Physiology and Pathophysiology (Part 1)ayaessam392002No ratings yet
- Ch45 EndocrineSystemDocument3 pagesCh45 EndocrineSystemCristie SumbillaNo ratings yet
- Ant. Pituitary Hormones: 1. Growth HormoneDocument21 pagesAnt. Pituitary Hormones: 1. Growth HormoneGriffinNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Hormones and AgingDocument10 pagesBiochemistry of Hormones and AgingTushar ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Hormones and AgingDocument10 pagesBiochemistry of Hormones and AgingTushar ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Lec-3 The Pituitary Gland-IDocument37 pagesLec-3 The Pituitary Gland-IMowlidAbdirahman Ali madaaleNo ratings yet
- 052 - Endocrinology Physiology) Adrenal Gland OverviewDocument2 pages052 - Endocrinology Physiology) Adrenal Gland Overviewیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- Hormones GlandsDocument1 pageHormones GlandsCHEN GAONo ratings yet
- 037 - Endocrinology Physiology) Receptor PathwaysDocument4 pages037 - Endocrinology Physiology) Receptor Pathwaysیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- Block 1Document46 pagesBlock 1Yash YadavNo ratings yet
- Summary 3 - Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesSummary 3 - Endocrine SystemAurélNo ratings yet
- Functions of Growth HormoneDocument19 pagesFunctions of Growth HormoneRezaul RazibNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6-Repair & Healing - 382Document33 pagesLecture 6-Repair & Healing - 382MirghaniNo ratings yet
- Growth Hormone and Craniofacial Tissues. An Update: George LitsasDocument8 pagesGrowth Hormone and Craniofacial Tissues. An Update: George LitsaspuspitaNo ratings yet
- 09 - Endocrine System - AADocument39 pages09 - Endocrine System - AAMenalqueNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Clinical Endocrinology: Professor Dr. Najat A. HasanDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Clinical Endocrinology: Professor Dr. Najat A. HasanToukir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Proteins SchematicDocument9 pagesProteins SchematicRuchie Ann Pono BaraquilNo ratings yet
- Lec No 3Document50 pagesLec No 3X And ZNo ratings yet
- Lipid MediatorsFrom EverandLipid MediatorsFiona M. CunninghamNo ratings yet
- 051 Endocrinology Physiology Adrenal Medulla CatecholaminesDocument4 pages051 Endocrinology Physiology Adrenal Medulla Catecholaminesیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- 041 - Endocrinology Physiology) Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)Document3 pages041 - Endocrinology Physiology) Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)یوسف رمضان100% (1)
- 043 - Endocrinology Physiology) ProlactinDocument3 pages043 - Endocrinology Physiology) Prolactinیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- 038 Endocrinology Physiology Hypothalamus Posterior Pituitary ConnectionDocument3 pages038 Endocrinology Physiology Hypothalamus Posterior Pituitary Connectionیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- 037 - Endocrinology Physiology) Receptor PathwaysDocument4 pages037 - Endocrinology Physiology) Receptor Pathwaysیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- 040 - Endocrinology Physiology) OxytocinDocument3 pages040 - Endocrinology Physiology) Oxytocinیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- 052 - Endocrinology Physiology) Adrenal Gland OverviewDocument2 pages052 - Endocrinology Physiology) Adrenal Gland Overviewیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- 046 - Endocrinology Physiology) Thyroid OverviewDocument2 pages046 - Endocrinology Physiology) Thyroid Overviewیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- 047 Endocrinology Physiology Parathyroid Gland CalcitoninDocument4 pages047 Endocrinology Physiology Parathyroid Gland Calcitoninیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- Flavour Fiesta Magazine - Issue 1Document44 pagesFlavour Fiesta Magazine - Issue 1divya_yadava2586No ratings yet
- Fat Burning Cardio Workout - 37 MinDocument2 pagesFat Burning Cardio Workout - 37 MinCarlos MartinezNo ratings yet
- Bakeshop IngredientsDocument12 pagesBakeshop IngredientsJulia Mae TagabNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 - 1ST QuarterDocument122 pagesGrade 3 - 1ST QuarterMary Grace SanchezNo ratings yet
- Short Bowel SyndromeDocument20 pagesShort Bowel SyndromeMohamed El-sayedNo ratings yet
- Screening For Microalbuminuria in Patients With Diabetes: How? Why?Document2 pagesScreening For Microalbuminuria in Patients With Diabetes: How? Why?Abhishek SenNo ratings yet
- Nutritional AssessmentDocument34 pagesNutritional AssessmentEli Zza Koirala100% (2)
- Enhanced CDC NS Monitoring Form Masterlist of Beneficiaries and LGU Consolidation of NS ReportDocument4 pagesEnhanced CDC NS Monitoring Form Masterlist of Beneficiaries and LGU Consolidation of NS ReportluffyNo ratings yet
- Ucm 492225Document451 pagesUcm 492225popov357No ratings yet
- Intertrigo and Secondary Skin InfectionsDocument5 pagesIntertrigo and Secondary Skin Infectionskhalizamaulina100% (1)
- Food and EneryDocument31 pagesFood and EneryShrimoyeeNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 15 PBL 2Document26 pagesKelompok 15 PBL 2Riqah Nefiyanti WardanaNo ratings yet
- Using Apple Cider Vinegar For Weight Management On A Re-Stricted DietDocument6 pagesUsing Apple Cider Vinegar For Weight Management On A Re-Stricted DietZaphan ZaphanNo ratings yet
- Food Related Dissertation TopicsDocument6 pagesFood Related Dissertation TopicsPaperWritingServicesLegitimateCanada100% (1)
- PSQCA Banaspati Anisidine ValueDocument21 pagesPSQCA Banaspati Anisidine ValueHemendra_Sango_7630% (1)
- Internal DiseaseDocument55 pagesInternal Diseaseshilpa sekhar278No ratings yet
- HYper and Hypo TGDocument43 pagesHYper and Hypo TGRiajoy AsisNo ratings yet
- Livelong Performance Fat Loss KickstarterDocument10 pagesLivelong Performance Fat Loss KickstarterHArsh AroraNo ratings yet
- Living With BearsDocument2 pagesLiving With BearsScott FranzNo ratings yet
- TIA BrochureDocument2 pagesTIA Brochureward2713No ratings yet
- (Energy Balance and Cancer 13) Nathan A. Berger, Ann H. Klopp, Karen H. Lu (Eds.) - Focus On Gynecologic Malignancies (2018, Springer International Publishing) PDFDocument317 pages(Energy Balance and Cancer 13) Nathan A. Berger, Ann H. Klopp, Karen H. Lu (Eds.) - Focus On Gynecologic Malignancies (2018, Springer International Publishing) PDFasfwegereNo ratings yet
- Executive Summary: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2010Document7 pagesExecutive Summary: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2010mir-medicinaNo ratings yet
- Flex UK - October 2018Document148 pagesFlex UK - October 2018安建平 澳门南湖区100% (1)
- Metabolic Changes in Diabetes: R. D. G. Leslie LondonDocument4 pagesMetabolic Changes in Diabetes: R. D. G. Leslie LondonManuNo ratings yet
- The Diabetes Handbook by DK - Parte2Document20 pagesThe Diabetes Handbook by DK - Parte2CarlosPutnamNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes NCP-3Document2 pagesGestational Diabetes NCP-3Jeffrey RasonabeNo ratings yet
- To H-1Document17 pagesTo H-1Nor AnnisaNo ratings yet
- Icecream 2Document11 pagesIcecream 2lnaveenkNo ratings yet