Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Target Organs of The Thyroid Atf
Target Organs of The Thyroid Atf
Uploaded by
Ridwan PermanaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Target Organs of The Thyroid Atf
Target Organs of The Thyroid Atf
Uploaded by
Ridwan PermanaCopyright:
Available Formats
Last edited: 9/5/2021
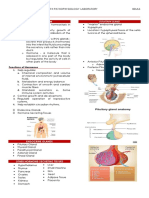
9. TARGET ORGANS OF THE THYROID
Endocrinology | Target Organs of the Thyroid Medical Editor: Ilia-Presiyan Georgiev
OUTLINE
I) EFFECTS ON THE CELL
II) EFFECTS ON THE LIVER
III) EFFECTS ON THE HEART
IV) EFFECTS ON THE CNS
V) EFFECTS ON THE BONES
VI) EFFECTS ON THE ADIPOSE TISSUE
VII) EFFECTS ON THE MUSCLES
VIII) EFFECTS ON THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
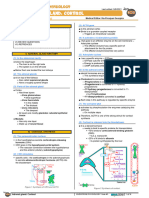
I) EFFECTS ON THE CELL
(1) Thyroid hormone (T3 and T4) Figure 1 Effects of TH on the cell.
circulates the bloodstream
o Bound to thyroxine binding globulin
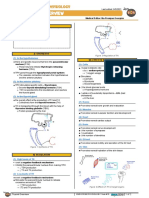
A protein made by the liver II) EFFECTS ON THE LIVER
o T4 (Thyroxine) is major component (1) TH exerts it effects
T4 passes through the lipid bilayer of the cellular
by a mechanism similar to the aforementioned and
membrane
produces proteins that stimulate
(2) Inside the cell o Glycogenolysis
The conversion of glycogen into glucose
the enzyme 5’-deiodinase removes an iodine form
• Glycogen is a polymer of glucose
thyroxine
o A storage molecule of glucose
o From the 5’-carbon atom
o Converts T4 into T3 (Triiodothyronine)
The active form of the thyroid hormone
o Gluconeogenesis
Another enzyme - 5-deiodinase can remove an iodine The conversion of non-carbohydrates into glucose
form thyroxine • Glycerol, amino acids and lactate (the
o From the 5-carbon atom conjugate base lactic acid) located in the liver
o Converts T4 reverse T3 o the expression of LDL receptors (LDL-R)
Inactive form
(3) T3 binds to
LDL - low-density lipoproteins (bad cholesterol)
a transcription factor
o To exert its effects, it needs retinoic acid (RXR) to
bind to the transcription factor as well
When both substances bind to the transcription factor
o It is activated
o Moves inside the nucleus
o Stimulates a specific gene sequence
(4) The gene sequence
undergoes transcription, translation and modifications Figure 2 Effects of TH on the liver.
o The end result is the synthesis of a protein
Sodium-potassium ATPase (Na⁺/K⁺-ATPase)
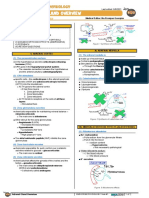
III) EFFECTS ON THE HEART
This protein merges with the cell membrane
o Acts as a sodium-potassium pump (1) TH exerts its effects on the cardiomyocytes
Pumps 3Na+ out of the cell Stimulates the expression of beta-1-adrenergic
Pumps 2K+ inside the cell receptors
Requires an ATP molecule to be convert to an o These receptors bind epinephrine and
ADP molecule for energy norepinephrine
(5) This leads to
increased number of sodium-potassium pumps
o Requires more energy
(2) TH also affects the non-contractile muscle cells
• Macromolecules (carbohydrates, fats, etc.) of the SA node and the AV node
Stimulates the expression of beta-1-adrenergic receptors
o These receptors bind epinephrine and norepinephrine
Target Organs of the Thyroid ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY: Note #9. 1 of 4
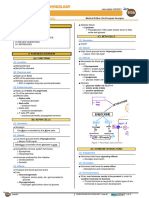
VI) EFFECTS ON THE ADIPOSE TISSUE
(1) TH stimulates lipolysis
The process of of breakdown of triglycerides into fatty
acids and glycerol by activating specific enzymes
o Triglycerides are the main component of the adipose
tissue
o The produced glycerol goes to the liver and is
converted into glucose via gluconeogenesis
Figure 3 Effects of TH on the heart.
IV) EFFECTS ON THE CNS
(1) TH affects the CNS in several ways
↑ dendrite formation
Figure 6 Effects of the TH on the adipose tissue.
↑ myelination
VII) EFFECTS ON THE MUSCLES
↑ number of synapses
(1) The protein metabolism
is the sum total of:
As a result of all this hyperthyroidism can lead to anxiety o Catabolism
and irritability Conversion of proteins to amino acids
o Anabolism
Conversion of amino acids into proteins
(2) TH regulates the activity of both
keeping them balanced
Figure 4 Effects of TH on the CNS. (3) Hyperthyroidism causes
the balance shifts to catabolism
V) EFFECTS ON THE BONES
(1) In the bones there are o not to be mistaken with lethargy
two types of important cells
o Osteoblasts
Responsible for bone deposition
o Osteoclasts
Responsible for bone resorption
(2) TH regulates
and maintains the balance between the two
o prevents excessive osteoblastic or osteoclastic
activity
o The process is called bone remodeling Figure 7 Effects of TH on the muscles.
(3) TH affects the chondrocytes
in the epiphyseal plates VIII) EFFECTS ON THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
o The chondrocytes undergo
Proliferation (1) Layers of the skin
Hypertrophy Epidermis
Eventually ossification o Stratum Corneum
o This causes the bones to grow in length o Stratum Lucidum
o Interstitial growth Only found in thick skin
o Stratum Granulosum
(4) TH stimulates
o Stratum Spinosum
Endochondral ossification o Stratum Basale
o Turning cartilage into bone
Dermis
Contains the blood vessels that provide nutrition
Figure 8 Layers of the skin.
Figure 5 Effects of TH on the bones.
2 of 4 ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY: Note #9. Target Organs of the Thyroid
(2) TH increases
the metabolic rate
o the body tries to regulate it
Blood vessels dilate and increase the blood flow
o The skin to look soft and flushed
o Skin radiates heat
The apocrine and merocrine sweat glands start producing
sweat
TH ↑ the sweat glands sensitivity to catecholamines
o Epinephrine
o Norepinephrine
(3) Hypothyroidism causes
Brittle nails and thin hair
(4) Hyperthyroidism causes
Thick hair
IX) EFFECTS ON THE GI TRACT
(1) TH stimulates the secretions
of the entire GI tract
o Alkaline fluid
o Intestinal fluid, etc.
(2) TH enhances the motility
of the entire GI tract
o Stimulates the contractions of the smooth muscle
cells
(3) Hyperthyroidism causes
Diarrhea
(4) Hypothyroidism causes
Constipation
Figure 9 Effects of the TH on the GI tract.
Target Organs of the Thyroid ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY: Note #9. 3 of 4
X) REVIEW QUESTIONS
1) Which enzyme produces active triiodothyronine?
a) Thyroid peroxidase
b) 5-deiodinase
c) 5’-deiodinase
d) T3-oxigenase
2) What substance is required for T3 to exert its effects?
a) Retinoic acid
b) Thyroid binding globulin
c) Oxygen
d) Sodium
3) What is NOT correct about the effects of T3 on the
cell?
a) ↑ number of sodium-potassium pumps
b) ↑ the cellular ATP levels
c) ↑ in burning fuel
d) ↑ heat production
4) Which effect of TH is NOT exerted on the liver?
a) Glygenolysis
b) Gluconeogenesis
c) Increased LDL uptake
d) Lipolysis
5) Which effect of the TH does NOT result from
cardiomyocyte stimulation?
a) ↑ the contractility
b) ↑ stroke volume
c) ↑ the blood pressure
d) ↑ the heart rate
6) What is WRONG about the effects of TH on the CNS?
a) ↑ quality of synapses
b) ↑ dendrite formation
c) ↑ the number of the neural connections
d) ↑ myelination
7) What effect of the TH is NOT exerted on the
chondrocytes?
a) Proliferation
b) Hypertrophy
c) Remodeling
d) Ossification
8) Which is stimulated by TH?
a) Catabolism
b) Anabolism
c) Both
d) Neither
9) Which layer of the epidermis is only found in thick
skin?
a) Stratum Corneum
b) Stratum Lucidum
c) Stratum Granulosum
d) Stratum Spinosum
10) Hypothyroidism may cause which symptom?
a) Diarrhea
b) Constipation
c) Thick hair
d) Anxiety
CHECK YOUR ANSWERS
4 of 4 ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY: Note #9. Target Organs of the Thyroid
You might also like
- MCQ of HematologyDocument22 pagesMCQ of Hematologydrafq200063% (8)
- Chapter 9 Test Bank: Multiple ChoiceDocument21 pagesChapter 9 Test Bank: Multiple ChoicePayalNo ratings yet
- Biological Functions of Each of The Following Peptides: (2 PTS)Document3 pagesBiological Functions of Each of The Following Peptides: (2 PTS)Gio PosadasNo ratings yet
- (D. J. Begley BSC, PHD, J. A. Firth MA, PHD, J. R. PDFDocument259 pages(D. J. Begley BSC, PHD, J. A. Firth MA, PHD, J. R. PDFali razaNo ratings yet
- Promoter BashingDocument2 pagesPromoter Bashingrio candra pratamaNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland Cortisol AtfDocument4 pagesAdrenal Gland Cortisol Atf2ymyccmvfcNo ratings yet
- 065 Endocrinology Pathology Hypothyroidism Physiology, PathophysiologyDocument6 pages065 Endocrinology Pathology Hypothyroidism Physiology, PathophysiologyLily BlossomNo ratings yet
- 046 - Endocrinology Physiology) Thyroid OverviewDocument2 pages046 - Endocrinology Physiology) Thyroid Overviewیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- Thyroid FinalDocument19 pagesThyroid FinalMariela AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Lecture+18 2021+springDocument21 pagesLecture+18 2021+springWael OsmanNo ratings yet
- 052 - Endocrinology Physiology) Adrenal Gland OverviewDocument2 pages052 - Endocrinology Physiology) Adrenal Gland Overviewیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- Lec 10 - Thyroid Hormone PDFDocument13 pagesLec 10 - Thyroid Hormone PDFrajeshNo ratings yet
- Pancreas Insulin Function AtfDocument3 pagesPancreas Insulin Function Atf2ymyccmvfcNo ratings yet
- 054 - Endocrinology Physiology) Pancreas Insulin FunctionDocument4 pages054 - Endocrinology Physiology) Pancreas Insulin FunctionLily Blossom100% (1)
- 042 - Endocrinology Physiology) Growth HormoneDocument3 pages042 - Endocrinology Physiology) Growth Hormoneیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- The Thyroid GlandDocument74 pagesThe Thyroid GlandAboubakar Moalim Mahad moh'dNo ratings yet
- The Thyroid Gland: Physiology and Pathophysiology: Endocrine Series #6Document16 pagesThe Thyroid Gland: Physiology and Pathophysiology: Endocrine Series #6نذير الشرعبيNo ratings yet
- Antithyroid Drugs by Sejal Khuman Advanced phARMACOLGY 2Document29 pagesAntithyroid Drugs by Sejal Khuman Advanced phARMACOLGY 2Sejal khumanNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland (2015-16)Document49 pagesThyroid Gland (2015-16)Moni RethNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Hormones PPP 10Document19 pagesThyroid Hormones PPP 10Nintendo42No ratings yet
- VND Ms-Powerpoint&rendition 1Document49 pagesVND Ms-Powerpoint&rendition 1Muhammad SamiNo ratings yet
- BIOL1020 NotesDocument40 pagesBIOL1020 NotesChloe BNo ratings yet
- Adrenal RAAS, Vasopressin Lecture 37 PDFDocument9 pagesAdrenal RAAS, Vasopressin Lecture 37 PDFmubashirNo ratings yet
- 10 Diversity of Endocrine System IIDocument23 pages10 Diversity of Endocrine System IIcutethoybaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Physiology and Thyroid Function Testing: Angela M. Leung, Gregory A. BrentDocument16 pagesThyroid Physiology and Thyroid Function Testing: Angela M. Leung, Gregory A. BrentAgustinaNo ratings yet
- Fisiopatologia TiroidesDocument121 pagesFisiopatologia TiroidesSociedad Científica de Estudiantes de Medicina de IcaNo ratings yet
- 8 Hormones of Adrenal GlandDocument27 pages8 Hormones of Adrenal GlandRana AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Not Testable Subject Matter, Just Know Endocrine System Works With Other SystemsDocument23 pagesNot Testable Subject Matter, Just Know Endocrine System Works With Other Systemsjnoah111No ratings yet
- Thyroid CellDocument8 pagesThyroid CellJames Cojab SacalNo ratings yet
- HormonesDocument9 pagesHormonesChandanaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Metabolism UwksDocument54 pagesThyroid Metabolism UwksDaniel VictorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Thyroid Metabolic Hormones FMDocument57 pagesLecture 3 - Thyroid Metabolic Hormones FMHomeground entertainment100% (1)
- Thyroid Gland: Ruswana Anwar, Tono DjuwantonoDocument49 pagesThyroid Gland: Ruswana Anwar, Tono Djuwantonoyuyu tuptupNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Drug: T4 Is Secreted in Excess To T3Document10 pagesEndocrine Drug: T4 Is Secreted in Excess To T3emmanuelNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Thyroid Hormones and Anti Thyroid Drugs For Second Year Medicine StudentsDocument48 pagesPharmacology of Thyroid Hormones and Anti Thyroid Drugs For Second Year Medicine StudentsAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Biochem ThyroidDocument42 pagesBiochem ThyroidHussein QasimNo ratings yet
- Topic3.3 Physiology Thyroid HormoneDocument7 pagesTopic3.3 Physiology Thyroid HormoneRen AlvNo ratings yet
- 051 Endocrinology Physiology Adrenal Medulla CatecholaminesDocument4 pages051 Endocrinology Physiology Adrenal Medulla Catecholaminesیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland - Normal FunctionDocument34 pagesThyroid Gland - Normal FunctionjabirNo ratings yet
- SAQ 2nd Week (Thyroid Gland)Document15 pagesSAQ 2nd Week (Thyroid Gland)Josephine BediakoNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System - Part 2 - Lecturer Notes-1Document19 pagesThe Endocrine System - Part 2 - Lecturer Notes-1DemilhNo ratings yet
- Pheromones, AutacoidsDocument64 pagesPheromones, Autacoidskelvinmaina9993No ratings yet
- Functions of Growth HormoneDocument19 pagesFunctions of Growth HormoneRezaul RazibNo ratings yet
- Bs Acc 2019 08 005Document54 pagesBs Acc 2019 08 005Angieda SoepartoNo ratings yet
- Nihms 165350Document15 pagesNihms 165350Il InNo ratings yet
- EN2 - HypothyroidismDocument17 pagesEN2 - Hypothyroidismsbobine.imsNo ratings yet
- THYROID GLAND ModuleDocument8 pagesTHYROID GLAND ModuleBJ BermasNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology: Cell Surface ReceptorsDocument25 pagesEndocrinology: Cell Surface ReceptorsSulistyawati 'tyawati'No ratings yet
- Metabolic Endocrinology (Week-2)Document8 pagesMetabolic Endocrinology (Week-2)wasimsafdarNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Keempat (Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands)Document38 pagesKuliah Keempat (Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands)kiki rawitriNo ratings yet
- Thyroid and Antityr DrugsDocument23 pagesThyroid and Antityr Drugsmsmobile shNo ratings yet
- Accorroni Et AlDocument17 pagesAccorroni Et Alp.sepulveda.fiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physiology: ThyroidDocument49 pagesEndocrine Physiology: ThyroidriaNo ratings yet
- Learning JournalDocument82 pagesLearning JournalAnnapurna RavelNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Hormone Transporters Functional and Cinical AplicationsDocument13 pagesThyroid Hormone Transporters Functional and Cinical AplicationsIván LazcanoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument6 pagesEndocrine System NotesHannah Grace CorveraNo ratings yet
- Chemical Co - OrdinationDocument21 pagesChemical Co - OrdinationManinder KaurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Biomolecules Worksheet Answers Set 4Document9 pagesChapter 14 Biomolecules Worksheet Answers Set 4kyomuhendobright4No ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland Gonadocorticoids AtfDocument2 pagesAdrenal Gland Gonadocorticoids Atf2ymyccmvfcNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Pharmacology of Endocrine System: Thyroid Hormone& Anti-Thyroid DrugsDocument8 pagesPharmacology: Pharmacology of Endocrine System: Thyroid Hormone& Anti-Thyroid DrugsRaj Nemala Raj NemalaNo ratings yet
- Biomedic Ii Cardiovascular System: Department of Biochemistry. Faculty of Medicine, UNHAS Rosdiana NatzirDocument55 pagesBiomedic Ii Cardiovascular System: Department of Biochemistry. Faculty of Medicine, UNHAS Rosdiana NatzirZurezki Yuana YafieNo ratings yet
- HHS Public Access: Unraveling The Complex Interplay Between T Cell Metabolism and FunctionDocument33 pagesHHS Public Access: Unraveling The Complex Interplay Between T Cell Metabolism and Functionro111111No ratings yet
- Cardiac BiomarkersDocument35 pagesCardiac BiomarkersArya Khan Arya KhanNo ratings yet
- AQA Biology Cell Biology GraspIT GCSE - Re-Usable WorksheetDocument4 pagesAQA Biology Cell Biology GraspIT GCSE - Re-Usable Worksheetmaaa7No ratings yet
- Archives of Biochemistry and BiophysicsDocument10 pagesArchives of Biochemistry and BiophysicsJuanNo ratings yet
- S7 - Q2 - Week 4aDocument7 pagesS7 - Q2 - Week 4agazelle grapes S. RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Gynecology 8Th Edition David M Gershenson MD Full ChapterDocument67 pagesComprehensive Gynecology 8Th Edition David M Gershenson MD Full Chapterinez.garcia238100% (3)
- Metabolic Integration in The Fed and Starve States: Endocrine Module - Med 7524 (Biochemistry)Document61 pagesMetabolic Integration in The Fed and Starve States: Endocrine Module - Med 7524 (Biochemistry)Rohith KumarNo ratings yet
- Ib NeurohistochemistryDocument44 pagesIb NeurohistochemistryAkua Konama AttakoraNo ratings yet
- G11 Bio WS5 Cell TypesDocument1 pageG11 Bio WS5 Cell TypesArlance Sandra Marie MedinaNo ratings yet
- Academic VerbsDocument43 pagesAcademic VerbsKojo Yeboah EnchillNo ratings yet
- US6015716 - BET in LiposomesDocument13 pagesUS6015716 - BET in LiposomesDholakiaNo ratings yet
- Gen. Bio 1 Q 1 - Week 4 Module 4Document24 pagesGen. Bio 1 Q 1 - Week 4 Module 4Gyeon Dae-HoNo ratings yet
- L7 - MeiosisDocument38 pagesL7 - MeiosisAl-Arqam OmarNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Bio 2 NotesDocument26 pagesEdexcel Bio 2 NotesHusain Khuzema80% (5)
- Vitamin D Analogues A Possible Therapeutic Option in COVID-19Document12 pagesVitamin D Analogues A Possible Therapeutic Option in COVID-19Mariana Concepción Parra GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Module 3Document7 pagesGen Bio Module 3Jann Ranniel PanlilioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - PlateletsDocument6 pagesLesson 1 - PlateletsMary Leigh JocsonNo ratings yet
- All Questions of Life Science III +2021Document147 pagesAll Questions of Life Science III +2021lashqarghanaiymNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lecture: Bachelor of Science in Medical Laboratory ScienceDocument10 pagesBiochemistry Lecture: Bachelor of Science in Medical Laboratory ScienceDCRUZNo ratings yet
- 2.7 Dna Replication Transcription and Translation 4Document168 pages2.7 Dna Replication Transcription and Translation 4Senam DzakpasuNo ratings yet
- AlzheimersDocument127 pagesAlzheimersshanes100% (1)
- Pathophysiology ExamDocument17 pagesPathophysiology ExammarcoNo ratings yet
- Complex Intracellular Structures in ProkaryotesDocument375 pagesComplex Intracellular Structures in Prokaryotesuriel francoNo ratings yet
- Biolistrik: DR - Susy OliviaDocument97 pagesBiolistrik: DR - Susy OliviaHartomas BumiharjoNo ratings yet
- Physiology lab: Faculty of Medical laboratory since Patch 7 ليعامسإ دمحم اللهدبع مكوخأ صيخلتDocument32 pagesPhysiology lab: Faculty of Medical laboratory since Patch 7 ليعامسإ دمحم اللهدبع مكوخأ صيخلتmohammedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NeurophysiologyDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Neurophysiologyvenkata ramakrishnaiahNo ratings yet
- Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews: Erkki RuoslahtiDocument10 pagesAdvanced Drug Delivery Reviews: Erkki RuoslahtiacbgdvNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles: Name - PeriodDocument9 pagesChapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles: Name - PeriodmynameNo ratings yet