Professional Documents
Culture Documents
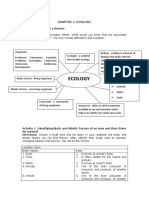
Ecology
Uploaded by
Ninia Dabu Lobo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views16 pagesscience
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentscience
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views16 pagesEcology
Uploaded by
Ninia Dabu Loboscience
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
Introducing
© 2004 Plano ISD, Plano, TX
Ecology
Is the branch of Biology that
studies the interrelationships of
organisms with their environment.
oikos home
logos study
© 2004 Plano ISD, Plano, TX
Ecosystem
includes all abiotic and biotic factors in
one particular environment
Biotic Factors Abiotic Factors
the living parts of the nonliving parts
an ecosystem of an ecosystem
© 2004 Plano ISD, Plano, TX
Bio
Biotic Factors
Producers or autotrophs- those
that can produce their own food.
Example: Plants
Consumers or heterotrophs- those
that consume autotrophs or eat
other heterotrophs.
Example: Animals/Insects
© 2004 Plano ISD, Plano, TX
Examples of Biotic
Factors
© 2004 Plano ISD, Plano, TX
Consumers- are type of organism that
feeds from the producers and/or another
consumer.
1. Herbivores- are kind of consumer that
eats only the producers.
2. Carnivores- are types of organisms
known as the “meat eaters”.
3. Omnivores- consumers whose primary
food source are the plants and other
animals.
© 2004 Plano ISD, Plano, TX
Decomposers- Consumers that obtains
their nourishment by feeding on dead
plants and animals.
1. Scavengers- primary source of food
are the bodies of animals.
2. Detritivores- eat the bodies that are
already decaying.
3. Saprotrophs- feed themselves by
absorbing nutrients from the decaying
organisms thereby speeding the
decomposition process.
© 2004 Plano ISD, Plano, TX
A
Abiotic Factors
Are nonliving factors may be energy
and materials that living things need
in order to live. It includes soil,
water, air and sunlight.
© 2004 Plano ISD, Plano, TX
Examples of Abiotic
Factors
© 2004 Plano ISD, Plano, TX
ACTIVITY: Identify the biotic and the abiotic
factors of the ecosystem.
Oxygen Soil Insect Fungi
Rock Wind Human Tree
Sun Hydrogen Moth
Precipitation Algae Fire
Water Snow Bacteria Grass
Amoeba Rabbit
© 2004 Plano ISD, Plano, TX
Ecological Relationships
It pertains to the interaction between or
among two different species of organisms.
Predation is when one organism benefits
from killing another organism.
predator- the organism that harm.
prey- the organism being harmed.
(eaten)
© 2004 Plano ISD, Plano, TX
Competition is when two organisms are
trying to get the same resources, whether
it's food, water, or sunlight.
Intraspecific- competition within the same
organisms.
Interspecific- competition among two
different organisms.
© 2004 Plano ISD, Plano, TX
Mutualism: is often referred to as the
“perfect relationships” wherein both
organisms benefit from each other.
© 2004 Plano ISD, Plano, TX
Commensalism: One organism
benefits while the other is
unaffected.
© 2004 Plano ISD, Plano, TX
Parasitism: One organism benefits
(parasite), while the other is harmed
(host).
Ectoparasite- found outside the body of
the host.
Endoparasite- found inside the body of
the host.
© 2004 Plano ISD, Plano, TX
Based on the table; create pairs of organisms in
a rice field community that exhibit interactions
then, identify their ecological relationship.
Snake Tree Orchid Rat Mosquito
Carabao Sparrow Farmer Weeds Rice
plant
Competition Predation Commensalism Mutualism Parasitism
© 2004 Plano ISD, Plano, TX
You might also like
- Sci7 Studytnotes Jan. 16,2023-Science7Document4 pagesSci7 Studytnotes Jan. 16,2023-Science7lucky laguraNo ratings yet
- Ecological ConceptsDocument16 pagesEcological ConceptsMary Ylane LeeNo ratings yet
- Department of Polymer Engineering: Environmental, Health and Safety EngineeringDocument23 pagesDepartment of Polymer Engineering: Environmental, Health and Safety EngineeringNumanNo ratings yet
- Principles and Concept of EcosystemDocument16 pagesPrinciples and Concept of EcosystemJay Bianca Abera Alistado100% (1)
- Ecology IDocument8 pagesEcology IAiman AfzalNo ratings yet
- Modules 3 & 4 2019Document14 pagesModules 3 & 4 2019ChamsNo ratings yet
- Our Environment (Prashant Kirad)Document10 pagesOur Environment (Prashant Kirad)abupendariNo ratings yet
- Lesson Proper For Week 2 GEE1Document3 pagesLesson Proper For Week 2 GEE1Russel Kent PaduaNo ratings yet
- Envi SciDocument23 pagesEnvi SciJeanelle Ledesma MarabutNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document5 pagesLesson 2angelina cajuraoNo ratings yet
- Module 2-Ge Elect PesDocument10 pagesModule 2-Ge Elect PesDivine Grace CincoNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgBP07BkcIXuk5zstOTtL8uMudksr-3BVthEdBaEtwC7h3zhWOIGAhz6Tgky32x - DZ1ulKaW94SEP5KNNxyf1qBJ Ab47hRrCtgmWp-SpmLQnZoaMsPDk9ReBXmNBKciE EMMl7r3O EF1wDocument42 pagesACFrOgBP07BkcIXuk5zstOTtL8uMudksr-3BVthEdBaEtwC7h3zhWOIGAhz6Tgky32x - DZ1ulKaW94SEP5KNNxyf1qBJ Ab47hRrCtgmWp-SpmLQnZoaMsPDk9ReBXmNBKciE EMMl7r3O EF1wKate Zairah ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes (TB)Document8 pagesBiology Notes (TB)ChamsNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument86 pagesEcosystemvishalNo ratings yet
- Ecology of LifeDocument10 pagesEcology of LifePaul Jeremy MendozaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 - Biotic Components of An EcosystemDocument3 pagesLesson 9 - Biotic Components of An EcosystemAbegail HernandezNo ratings yet
- Geography & Environmental Studies: Submitted byDocument10 pagesGeography & Environmental Studies: Submitted byMD. ASHIKUR RAHMANNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Community InteractionDocument95 pages3.0 Community InteractionAT4-11 HUMSS 2 CEDRICK ILAONo ratings yet
- Module 1.1 Ecosystem ConceptsDocument27 pagesModule 1.1 Ecosystem ConceptsFrizza LynNo ratings yet
- Week004 The EcosystemDocument6 pagesWeek004 The EcosystemEthan RosarioNo ratings yet
- Interactions: Environment and OrganismsDocument33 pagesInteractions: Environment and OrganismsAngelica MartinNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Ge10Document13 pagesReviewer in Ge10Rej AgustinNo ratings yet
- Biotic and AbioticDocument14 pagesBiotic and AbioticSummer PerezNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Chapter 4Document13 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 4EeJun LeeNo ratings yet
- Project Report On EcosystemDocument15 pagesProject Report On EcosystemAditya GoenkaNo ratings yet
- EnviEng MRII 0894 PDFDocument47 pagesEnviEng MRII 0894 PDFDaniel MalapitanNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Ecology Claass 1Document51 pagesPresentation On Ecology Claass 1Soumyajit NandiNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Environmental ScienceDocument9 pagesReviewer For Environmental ScienceZaldy CruzNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument9 pagesEcosystemLeo JacobNo ratings yet
- Insect Ecology AssignmentDocument22 pagesInsect Ecology AssignmentSarita Anjum MuniaNo ratings yet
- CH 15 (Our Environment)Document10 pagesCH 15 (Our Environment)Rajvir tradaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Ecology TasksDocument7 pagesChapter 1 - Ecology TasksAngelica PacquingNo ratings yet
- Environment GGDocument291 pagesEnvironment GGNijam NagoorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document34 pagesChapter 3Belsty Wale KibretNo ratings yet
- GRADE 7 - SCIENCE Q3 Wk2 ModuleDocument6 pagesGRADE 7 - SCIENCE Q3 Wk2 Modulejovan amihanNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Ecological SystemDocument1 pageCharacteristics of Ecological SystemJudyAnIntongQuiroyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Part 1 Plant EcologyDocument57 pagesLecture 6 Part 1 Plant EcologyChala KelbessaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 EnviDocument8 pagesModule 1 EnviJimuel LadaoNo ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument46 pagesUnit IIAnonymous fbUJwFVPNo ratings yet
- Environment Paloma BSPDocument17 pagesEnvironment Paloma BSPJosh Sebastian LabraNo ratings yet
- Science of EcologyDocument2 pagesScience of Ecologyhomamunfat100% (1)
- ECOLOGYDocument34 pagesECOLOGYRachelle MamarilNo ratings yet
- EcologyDocument31 pagesEcologyVinisha KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Ecology DiscussionDocument31 pagesEcology DiscussionAl Marjorie Abrasaldo TatingNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Ecosystem Learning OutcomesDocument5 pagesLesson 4 Ecosystem Learning OutcomesMelberlaine SalvadorNo ratings yet
- SZL202 Topic One Components of An EcosystemDocument5 pagesSZL202 Topic One Components of An Ecosystemmarubegeoffrey41No ratings yet
- Interactions in EcosystemsDocument42 pagesInteractions in EcosystemsJeanelle AlbertNo ratings yet
- Food ChainDocument7 pagesFood ChainAiman AfzalNo ratings yet
- EnSci Reviewer #1 - Ecosystem ReviewerDocument2 pagesEnSci Reviewer #1 - Ecosystem ReviewerJohn PaulNo ratings yet
- Booklet 4.1Document18 pagesBooklet 4.1Seo Young YOONNo ratings yet
- PLNG Bwu PnyaDocument8 pagesPLNG Bwu Pnya1931989No ratings yet
- Insects and The Biotic EnvironmentDocument4 pagesInsects and The Biotic Environmentirfan khanNo ratings yet
- Terrestrial Ecology Notes1Document130 pagesTerrestrial Ecology Notes1api-265611555No ratings yet
- Ecology RevDocument46 pagesEcology RevrivaNo ratings yet
- Unit I Environment, Ecosystems and BiodiversityDocument24 pagesUnit I Environment, Ecosystems and BiodiversitydeepaNo ratings yet
- EVS Unit-1bDocument42 pagesEVS Unit-1bAkshay GoyalNo ratings yet
- Food ChainsDocument7 pagesFood ChainsAbhijitNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Definition PDFDocument2 pagesEcosystem Definition PDFJonas TenederoNo ratings yet
- q1 ST 2 Gr.4 Math With TosDocument3 pagesq1 ST 2 Gr.4 Math With TosNinia Dabu LoboNo ratings yet
- Second Periodical Test English IiiDocument5 pagesSecond Periodical Test English IiiNinia Dabu LoboNo ratings yet
- Algebraic ExpressionDocument23 pagesAlgebraic ExpressionNinia Dabu LoboNo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument20 pagesCell TheoryNinia Dabu LoboNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living ThingsDocument22 pagesCharacteristics of Living ThingsNinia Dabu LoboNo ratings yet
- DLL - Daily WK 1 Day 1 A NewDocument4 pagesDLL - Daily WK 1 Day 1 A NewNinia Dabu LoboNo ratings yet
- DLL - Daily WK 1 Day 1 B NewDocument3 pagesDLL - Daily WK 1 Day 1 B NewNinia Dabu LoboNo ratings yet
- DLL - MTB 1 - Q1 - W1Document6 pagesDLL - MTB 1 - Q1 - W1Ninia Dabu LoboNo ratings yet
- DLL Mathematics 1 q1 w1Document6 pagesDLL Mathematics 1 q1 w1Ninia Dabu LoboNo ratings yet
- Periodic Exam in Music 7Document2 pagesPeriodic Exam in Music 7Ninia Dabu LoboNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-MicrosDocument31 pagesLesson 1-MicrosNinia Dabu LoboNo ratings yet
- Aquamarine Map 2 Rules - Apex Predators - A4Document2 pagesAquamarine Map 2 Rules - Apex Predators - A4Luiz HenriqueNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - MolluscaDocument9 pagesLab 2 - MolluscaCherry Mae AdlawonNo ratings yet
- BSC Agriculture 3 Sem Fundamentals of Insect Morphology and Systematics 72553 May 2019Document2 pagesBSC Agriculture 3 Sem Fundamentals of Insect Morphology and Systematics 72553 May 2019Navneet KumarNo ratings yet
- Embryonic Development of ChickenDocument33 pagesEmbryonic Development of ChickenArsh RizviNo ratings yet
- Annelida 1Document36 pagesAnnelida 1Hescel An ButacNo ratings yet
- Intestinal FlukesDocument24 pagesIntestinal Flukesroy mata88% (8)
- Taxonomy NotesDocument5 pagesTaxonomy NotesEllah Iracielli TevesNo ratings yet
- Animal Riddles 1 EasyDocument3 pagesAnimal Riddles 1 EasyCarolyna BakaraNo ratings yet
- 2022 - Bi Pemahaman Tahun 5Document14 pages2022 - Bi Pemahaman Tahun 5Alif AsyrafNo ratings yet
- Raise Organic Chicken: Select Healthy StocksDocument12 pagesRaise Organic Chicken: Select Healthy StocksFarah Jamaica Villegas100% (1)
- The Livestock Production & ManagementDocument237 pagesThe Livestock Production & ManagementtrukuniNo ratings yet
- Baseline Assessment Memorandum - Grade 4 - English HL - Miss Du Toit - 2023Document2 pagesBaseline Assessment Memorandum - Grade 4 - English HL - Miss Du Toit - 2023Renaldi Du ToitNo ratings yet
- Artificial SelectionDocument2 pagesArtificial SelectionJuan Carlos RebolledoNo ratings yet
- Austin Zoo Intern CurriculumDocument3 pagesAustin Zoo Intern Curriculumapi-300514002No ratings yet
- Sept - 2019 - HR - Final - Medres - Natural History Notes PDFDocument62 pagesSept - 2019 - HR - Final - Medres - Natural History Notes PDFhilaryy13No ratings yet
- Morfometri, Pemijahan, Dan Indeks Kematangan GonadDocument10 pagesMorfometri, Pemijahan, Dan Indeks Kematangan GonadOki PratamaNo ratings yet
- IQ Test and GKDocument48 pagesIQ Test and GKNakhreli KuriNo ratings yet
- Common Yukon Birds: Wildlife ViewingDocument21 pagesCommon Yukon Birds: Wildlife Viewingoorhan41No ratings yet
- Imrad Bio 2 #2Document2 pagesImrad Bio 2 #2pia tyNo ratings yet
- Hele Quiz #2 Hele Quiz #2Document2 pagesHele Quiz #2 Hele Quiz #2Roxanne Dhale Culos VinluanNo ratings yet
- Quail FarmingDocument9 pagesQuail FarmingOlaegbeRotimiNo ratings yet
- Biology Jeopardy - AnimalsDocument27 pagesBiology Jeopardy - AnimalsCggNo ratings yet
- Inherited - Vs - Aquired - Traits - PPT EditedDocument37 pagesInherited - Vs - Aquired - Traits - PPT EditedNerwin UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Joshua James S. Rodriguez Bsa - 1A Animal Science 101 Mrs. Hercily Abiera Agustin Module 2 - Anatomy and Physiology IDocument4 pagesJoshua James S. Rodriguez Bsa - 1A Animal Science 101 Mrs. Hercily Abiera Agustin Module 2 - Anatomy and Physiology IJoshua James Sanguenza RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 30 African Malawi Cichlids PDFDocument2 pages30 African Malawi Cichlids PDFshachoujosephNo ratings yet
- Mel GibsonDocument4 pagesMel Gibsonelle-et-luiNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom - Worksheet 3Document1 pageAnimal Kingdom - Worksheet 3ultbngNo ratings yet
- GR 9 Term 1 2019 Ns TrackerDocument20 pagesGR 9 Term 1 2019 Ns TrackerSnqobileNo ratings yet
- Kids Ant FactsDocument3 pagesKids Ant Factsaditya patelNo ratings yet
- Periodical Test Q2 Science 4 Melc BasedDocument6 pagesPeriodical Test Q2 Science 4 Melc BasedRia RiaNo ratings yet