Professional Documents
Culture Documents
F3 Phy Buke
Uploaded by
BUKENYA BEEE-2026Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
F3 Phy Buke
Uploaded by
BUKENYA BEEE-2026Copyright:
Available Formats
535/2
PHYSICS
Paper 2
Nov. / Dec. 2022
2 1/4
hours
KAWAALA HIGH SCHOOL
END OF YEAR 2022
PHYSICS.
Paper
2B
2 hours 15 minutes
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:
Attempt any five questions.
Mathematical tables, slide and non-programmable electronic calculators maybe used.
These values of physical quantities may be useful to you.
Acceleration due gravity, g = 10m s -2
Speed of light = 108m s -1
Density of water = 1000kg m -3
© 2022 kawaala high school physics department Turn Over
1. (a) What is meant by uniform acceleration.
(b) A body of mass 60 kg starts moving with a velocity of 15 m s -1 and accelerates uniformly at
after 7 s. -2
(i) Draw a velocity-time graph for the motion.
(ii) Calculate the momentum of the body during the eighth second.
(iii) Calculate the retarding force.
(c)
Object
18 N 6N Figure 4
Two forces of 18 N and 6 N act in opposite directions on an object of mass 3 kg as shown in
figure 4. Calculate the acceleration of the body.
2. (a) Define the following terms:
(i) atomic number.
(ii) mass number.
(iii) isotopes.
(b) A radioactive nucleus decays by emission of alpha particles.
(i) What are alpha particles?
(ii) What changes occur in mass number and atomic number when the alpha particle is
emitted?
(iii) State any three differences between alpha particles and beta particles.
(c) The table shows the count rates of a certain radioactive material.
Count rate (s -1) 6400 5380 3810 2700 1910 1350
Time (min) 0 1 3 4 7 9
Plot a graph and use it to find the half-life of the material.
3. (a) A radioactive nuclide decays by emission of two alpha particles and two beta
particles to a nuclide Y.
(i) What is meant by a radioactive nuclide?
(ii) Give three differences between alpha and beta particles.
(iii) State the atomic number and mass number of Y.
(b) What precautions would have to be taken when handling radioactive materials?
(c) A certain mass of a radioactive material contains 2.7 x 10 24 radioactive atoms. How
many atoms will have decayed after 3200 years if the half-life of the material is 1600
years?
(d) Explain briefly one industrial application of radioactivity.
4 (a) Define each of the following terms as applied to wave motion;
(i) wave front. (ii)
wavelength.
(b) The wavelength of a radio wave is 10 m. Calculate
(i) the frequency.
(ii) the period of the wave.
(c) Why does sound travel faster in solids than in gases?
(d) (i) Explain why an open pipe is preferred to a closed pipe when used in producing
different notes.
(ii) The frequency of the third harmonic in a closed pipe is 280 Hz. Find the length of the
air column in the pipe.
5. (a) Give the differences between transverse and longitudinal waves.
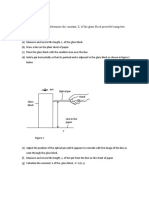
(b) Two identical sources are made to produce circular waves in a ripple tank.
(i) Explain with the aid of a diagram, how interference fringes may be obtained.
(ii) What happens when the distance between the sources is reduced?
(c) A vibrator of frequency 50 Hz produces circular waves in a ripple tank. If the distance
between consecutive crests is 3 cm, what is the speed of the waves?
(d) (i) Explain why echoes are not heard in a small room.
(ii) Describe a simple echo method of determining the speed of sound in air.
END
You might also like
- GCE Physics Mock Exam SolutionsDocument8 pagesGCE Physics Mock Exam SolutionsBaninla NerusNo ratings yet
- AQA - GCSE Separate Science - Higher - Physics - Paper 1 - 2023 PredictionsDocument26 pagesAQA - GCSE Separate Science - Higher - Physics - Paper 1 - 2023 PredictionsooooNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 2 Uneb Question BankDocument116 pagesPhysics Paper 2 Uneb Question BankOnen-can Hendry Nyeko100% (1)
- ICSE Phy Specimen PaperDocument7 pagesICSE Phy Specimen Paperansh KNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 - 1993Document5 pagesPhysics 1 - 1993Alhamdu Mussa SogoleNo ratings yet
- ALL QB's PDFDocument36 pagesALL QB's PDFanimesh0gargNo ratings yet
- Physics Science 1Document7 pagesPhysics Science 1BarunMondalNo ratings yet
- Physics PDFDocument5 pagesPhysics PDFHabibu IsmailNo ratings yet
- Physics "O"Level Seminar 535 at Seeta High School Green Campus 6 JUL 2019Document7 pagesPhysics "O"Level Seminar 535 at Seeta High School Green Campus 6 JUL 2019Daniel MarkNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 9 Physics Exam Paper with Questions on Light, Motion, Sound and MagnetismDocument5 pagesICSE Class 9 Physics Exam Paper with Questions on Light, Motion, Sound and MagnetismStudy in an easy wayNo ratings yet
- ICSE Physics Gold Series Sample PaperDocument16 pagesICSE Physics Gold Series Sample PaperArijit Das GuptaNo ratings yet
- Uce Physics Paper Two 3Document7 pagesUce Physics Paper Two 3Okiror GeorgeNo ratings yet
- PHY 2 TOSA- 2023Document12 pagesPHY 2 TOSA- 2023sam2jbegNo ratings yet
- 131 - Physics 2Document4 pages131 - Physics 2nassorussi9No ratings yet
- Sample Paper On Physics Grade 10Document3 pagesSample Paper On Physics Grade 10aadesh_mahatoNo ratings yet
- Exam18 ICSE Physics Sample PaperDocument11 pagesExam18 ICSE Physics Sample Paperfahad alamNo ratings yet
- S4 Physics P2Document5 pagesS4 Physics P2ivalryder3No ratings yet
- 131 - Physics 1Document4 pages131 - Physics 1nassorussi9No ratings yet
- Physics Question-01 Choose The Correct AnswersDocument3 pagesPhysics Question-01 Choose The Correct Answersbapasito969No ratings yet
- CL 9 - Final Assessment 2020-2021 PhysicsDocument2 pagesCL 9 - Final Assessment 2020-2021 PhysicsKrish JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 - F6 - 2017Document6 pagesPhysics 1 - F6 - 2017sam2jbegNo ratings yet
- ICSE Board Class X Physics Gold Series Sample Paper - 4: Time: 1 Hrs Total Marks: 80 General InstructionsDocument16 pagesICSE Board Class X Physics Gold Series Sample Paper - 4: Time: 1 Hrs Total Marks: 80 General InstructionsArijit Das GuptaNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 2 July 2017 Mock ExamDocument6 pagesPhysics Paper 2 July 2017 Mock Examcyber secNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Physics Sample Paper 6Document5 pagesICSE Class 10 Physics Sample Paper 6OverRush AmareshNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Physics Previous Year Question Paper 2018Document10 pagesICSE Class 10 Physics Previous Year Question Paper 2018Niyati AgarwalNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Physics Previous Year Question Paper 2017Document6 pagesICSE Class 10 Physics Previous Year Question Paper 2017Niyati AgarwalNo ratings yet
- s.4 Physics p2 Mock 2Document7 pagess.4 Physics p2 Mock 2amootiNo ratings yet
- GR 9 ICSE Final Exam Question Paper PhysicsDocument4 pagesGR 9 ICSE Final Exam Question Paper PhysicsanjalimenonNo ratings yet
- Null 10Document5 pagesNull 10nassorussi9No ratings yet
- Class 9 Science Preboard Exam GuideDocument1 pageClass 9 Science Preboard Exam GuidemathelearnNo ratings yet
- Class 9 PhysicsDocument3 pagesClass 9 PhysicsGreatAkbar1No ratings yet
- ICSE Physics Sample Paper - Class X Gold Series Exam 5Document15 pagesICSE Physics Sample Paper - Class X Gold Series Exam 5Arijit Das GuptaNo ratings yet
- Merryland High School (Physics) PDFDocument3 pagesMerryland High School (Physics) PDFVictor LusibaNo ratings yet
- Sample Class Ix Question Paper See 2022Document4 pagesSample Class Ix Question Paper See 2022Mayank SharmaNo ratings yet
- Physics Complete SyllabusDocument4 pagesPhysics Complete SyllabusSamridhi JainNo ratings yet
- St Peter Claver Form Six Physics Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesSt Peter Claver Form Six Physics Exam QuestionsCharles GhatiNo ratings yet
- Sanjeevni PhysicsDocument4 pagesSanjeevni PhysicsInfinyNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Physics ICSEDocument3 pagesPaper 1 Physics ICSEAkash KaleNo ratings yet
- Alhoda International School: PhysicsDocument5 pagesAlhoda International School: PhysicsWhats Going On ??No ratings yet
- Chemistry EM IMPDocument53 pagesChemistry EM IMPdharmishthakaneriya4No ratings yet
- 2017-18 ICSE Class 10 Physics SQPDocument5 pages2017-18 ICSE Class 10 Physics SQPBharati GulajkarNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science SA 2 Question PaperDocument16 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science SA 2 Question Paperipankaj2u@gmail0% (2)
- Physics Questions Vol-Ii Bernard PDF PDFDocument2 pagesPhysics Questions Vol-Ii Bernard PDF PDFSilva scary svNo ratings yet
- Iit/Aiims 2020-Screeningcum Scholarship Exam: Date: 00 October 2018Document11 pagesIit/Aiims 2020-Screeningcum Scholarship Exam: Date: 00 October 2018LukewarmNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes For Secondary Education of UgandaDocument11 pagesPhysics Notes For Secondary Education of UgandaMukiibi DuncanNo ratings yet
- PHY-2Document6 pagesPHY-2kakajumaNo ratings yet
- ICSE-Class-10-Physics-Previous-Year-Question-Paper-2013Document7 pagesICSE-Class-10-Physics-Previous-Year-Question-Paper-2013Retoja SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Physics Test (Sayan)Document5 pagesPhysics Test (Sayan)sayanchatterjee098No ratings yet
- Physics 9 Icse Question Paper 2Document5 pagesPhysics 9 Icse Question Paper 2Nimmi Nims0% (1)
- Pawar Public School, Bhandup Class Subject Exam Marks Date Duration No. of Printed Pages X Physics Prelim 2 40 01.02.2022 1 Hours 5Document4 pagesPawar Public School, Bhandup Class Subject Exam Marks Date Duration No. of Printed Pages X Physics Prelim 2 40 01.02.2022 1 Hours 5kim loveNo ratings yet
- Pre-Board Test PhysicsDocument2 pagesPre-Board Test PhysicsGhulam FaridNo ratings yet
- 1st-1st Sem-2022qDocument24 pages1st-1st Sem-2022qAnshuman BanikNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper on Solid State and Nano-Physics (1748Document3 pagesPhysics Paper on Solid State and Nano-Physics (1748Shubhamm RohillaNo ratings yet
- End of Term 1 2023 Phy S.4Document5 pagesEnd of Term 1 2023 Phy S.4DENIS AKOLNo ratings yet
- ICSE X Physics 2018 PDFDocument6 pagesICSE X Physics 2018 PDFKinjal Mazumder100% (1)
- 2021 780 Mock Paper2 QuestionsDocument6 pages2021 780 Mock Paper2 QuestionsVerla MfeerNo ratings yet
- 06 Nuclear PhysicsDocument4 pages06 Nuclear PhysicsFrank MalengaNo ratings yet
- ICSE Board Class IX Physics Gold Series Sample Paper - 4: Time: 2 Hrs Total Marks: 80 General InstructionsDocument5 pagesICSE Board Class IX Physics Gold Series Sample Paper - 4: Time: 2 Hrs Total Marks: 80 General InstructionsnitikanehiNo ratings yet
- Physics ICSE Class X - Sample paperDocument8 pagesPhysics ICSE Class X - Sample paperApaNo ratings yet
- Procurement and TenderingDocument68 pagesProcurement and TenderingBUKENYA BEEE-2026No ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Glass BlockDocument3 pagesExperiment 4 Glass BlockBUKENYA BEEE-2026No ratings yet
- Project Team BuildingDocument46 pagesProject Team BuildingBUKENYA BEEE-2026No ratings yet
- HALIDDocument23 pagesHALIDBUKENYA BEEE-2026No ratings yet
- Donor Funded Project RequirementDocument8 pagesDonor Funded Project RequirementBUKENYA BEEE-2026100% (1)
- MathsDocument13 pagesMathsBUKENYA BEEE-2026No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument4 pagesAssignmentBUKENYA BEEE-2026No ratings yet
- Project Communication and ManagementDocument6 pagesProject Communication and ManagementBUKENYA BEEE-2026No ratings yet
- BukenyaDocument78 pagesBukenyaBUKENYA BEEE-2026No ratings yet
- ReportDocument43 pagesReportBUKENYA BEEE-2026No ratings yet
- InternshipDocument46 pagesInternshipBUKENYA BEEE-2026No ratings yet
- F5 Applied MathDocument6 pagesF5 Applied MathBUKENYA BEEE-2026No ratings yet
- Power SupplyDocument51 pagesPower SupplyBUKENYA BEEE-2026No ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument2 pagesMathematicsBUKENYA BEEE-2026No ratings yet
- Lecture Two Substation InstallationsDocument7 pagesLecture Two Substation InstallationsBUKENYA BEEE-2026No ratings yet
- Lecture 11 Electrification of Commercial InstallationDocument7 pagesLecture 11 Electrification of Commercial InstallationBUKENYA BEEE-2026No ratings yet
- KYAMBOGO UNIVERSITY ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION DESIGNDocument11 pagesKYAMBOGO UNIVERSITY ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION DESIGNBUKENYA BEEE-2026100% (1)
- F3 Phy MusaDocument4 pagesF3 Phy MusaBUKENYA BEEE-2026No ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Estimation and CostingDocument14 pagesLecture 8 Estimation and CostingBUKENYA BEEE-2026No ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Bills of QuantitiesDocument7 pagesLecture 9 Bills of QuantitiesBUKENYA BEEE-2026No ratings yet
- F3 Phy 1Document12 pagesF3 Phy 1BUKENYA BEEE-2026No ratings yet
- Formation of The Heavy ElementsDocument43 pagesFormation of The Heavy ElementsLevi Lico PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem U-3 and 4Document77 pagesOrganic Chem U-3 and 4sinte beyuNo ratings yet
- 05 - Half-Life & Radioisotope DatingDocument19 pages05 - Half-Life & Radioisotope DatingNawraa AldaifNo ratings yet
- Block 5 Acids and BasesDocument34 pagesBlock 5 Acids and BasesCheng FuNo ratings yet
- June 2018 QP - Paper 1 Edexcel Chemistry As-LevelDocument24 pagesJune 2018 QP - Paper 1 Edexcel Chemistry As-LevelMohammad ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- Final Exam CHEM 5581 - Quantum Chemistry Fall 2015 Due Monday, December 14, 2015, Before 5 P.MDocument9 pagesFinal Exam CHEM 5581 - Quantum Chemistry Fall 2015 Due Monday, December 14, 2015, Before 5 P.MnaveenNo ratings yet
- IGCSE 2.1 2.3 Atomic Structure 2021 4 PDFDocument18 pagesIGCSE 2.1 2.3 Atomic Structure 2021 4 PDFAlexis RJNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 Periodic Table Theory PDFDocument36 pagesChap 1 Periodic Table Theory PDFHari Babu100% (1)
- Rotational and Vibrational Spectroscopy: Lecture Date: January 30, 2008Document61 pagesRotational and Vibrational Spectroscopy: Lecture Date: January 30, 2008mohammedabubakrNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document19 pagesModule 3Ratay EvelynNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document28 pagesCH 1Umme Abdullah100% (1)
- DC Pandey Optics and Modern Physics (Crackjee - Xyz) PDFDocument559 pagesDC Pandey Optics and Modern Physics (Crackjee - Xyz) PDFYASH PRANESH75% (4)
- Introduction to Chemistry EssentialsDocument46 pagesIntroduction to Chemistry EssentialsSam LoveNo ratings yet
- 02 MineralsDocument33 pages02 MineralsAce CardenoNo ratings yet
- Avetissian H. K. - Relativistic Nonlinear Electrodynamics - Interaction of Charged Particles With Strong and Super Strong Laser Fields (2006)Document341 pagesAvetissian H. K. - Relativistic Nonlinear Electrodynamics - Interaction of Charged Particles With Strong and Super Strong Laser Fields (2006)alex3197No ratings yet
- New LightDocument46 pagesNew LightRavi Kiran KoduriNo ratings yet
- Solucionario Capitulo 23 Paul e TippensDocument22 pagesSolucionario Capitulo 23 Paul e TippensAxel Gutiérrez VillaNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential Energy and Electric Potential WorksheetDocument2 pagesElectric Potential Energy and Electric Potential WorksheetMero MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Oxidation States of Transition MetalsDocument7 pagesOxidation States of Transition MetalsMannevaram AbhinavareddiNo ratings yet
- 12 Strand DNA Morphogenetic Engineering Via Holofractal Morphogenetic Reprogramming of Genetic InformationDocument14 pages12 Strand DNA Morphogenetic Engineering Via Holofractal Morphogenetic Reprogramming of Genetic InformationJNo ratings yet
- Aits 2324 FT Vi Jeem TD OfflineDocument16 pagesAits 2324 FT Vi Jeem TD OfflinebhagirathNo ratings yet
- Olsen 1986Document13 pagesOlsen 1986AlexNo ratings yet
- ZeroDocument18 pagesZeroSherlcok HolmesNo ratings yet
- PS - Q1 - Week 1bDocument10 pagesPS - Q1 - Week 1bShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- The Electron Configuration and Oxidation States of Transition MetalsDocument40 pagesThe Electron Configuration and Oxidation States of Transition Metalsizz isalahNo ratings yet
- Specimen 2016 QP - Paper 4 CIE Physics IGCSEDocument18 pagesSpecimen 2016 QP - Paper 4 CIE Physics IGCSEsrikanth subramaniamNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends: Metallic CharacterDocument9 pagesPeriodic Trends: Metallic CharacterJhana Kate FalculanNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 15 A Level Physics WB MSDocument4 pagesChapter - 15 A Level Physics WB MSmichelle winataNo ratings yet
- Pcqa Finals All LessonDocument38 pagesPcqa Finals All LessonLazaro, Javen Andrie A.No ratings yet