Professional Documents
Culture Documents
S223 Env203Geo205 S09 04 Map TimeZone GIS RS
Uploaded by
Malisha Rahman Tonni 1921946042Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
S223 Env203Geo205 S09 04 Map TimeZone GIS RS
Uploaded by
Malisha Rahman Tonni 1921946042Copyright:
Available Formats
ENV 203 / GEOL 205
Elements, Scale, Time Zone,
Geographic Information System,
and Remote Sensing
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Maps are a representation of the Earth's surface.
include certain basic elements that provide the reader with critical information.
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
History
Projections
Elements
Time Zone
GIS and RS
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
History
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
oldest map of the world?
the Imago Mundi
More commonly known as the Babylonian Map of the World
• It is considered the oldest surviving
world map.
• It is currently on display at the British
Museum in London.
• It dates back to between 700 and 500
BC and was found in a town called
Sippar in Iraq.
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Hecataeus 550 BC
Herodotus 440 BC
Eratosthene 1883
Pomponius Melas 43 BC
Han Dynasty 202 BC - 9 AD
Tabula Peutingeriana 13th century
Al-Khwārizmī 15th Century
Al-Idrisi 1154
• The first of the logographers to attempt a serious prose
history and to employ critical method to distinguish myth
from historical fact
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hecataeus_of_Miletus
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Hecataeus 550 BC
Herodotus 440 BC
Eratosthene 1883
Pomponius Melas 43 BC
Han Dynasty 202 BC - 9 AD
Tabula Peutingeriana 13th century
Al-Khwārizmī 15th Century
Al-Idrisi 1154
• A modern depiction of ancient Greek historian
Herodotus' view of the Ecumene (or oecumene), literally
the the known or the inhabited world, in the 5th Century
BC.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Herodotus
• While obviously far from fully accurate it clearly shows
Europe, Africa and Asia.
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Hecataeus 550 BC
Herodotus 440 BC
Eratosthene 276
Pomponius Melas 43 BC
Han Dynasty 202 BC - 9 AD
Tabula Peutingeriana 13th century
Al-Khwārizmī 15th Century
Al-Idrisi 1154
• In his three-volume work Geography, he described and
mapped his entire known world, even dividing the Earth
into five climate zones: two freezing zones around the
poles, two temperate zones, and a zone encompassing
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eratosthenes the equator and the tropics.
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Hecataeus 550 BC
Herodotus 440 BC
Eratosthene 276
Pomponius Melas 43 BC
Han Dynasty 202 BC - 9 AD
Tabula Peutingeriana 13th century
Al-Khwārizmī 15th Century
Al-Idrisi 1154
• Pomponius Mela, who wrote around AD 43, was the
earliest Roman geographer.
• He was born in Tingentera and died c. AD 45.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pomponius_Mela
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Hecataeus 550 BC
Herodotus 440 BC
Eratosthene 276
Pomponius Melas 43 BC
Han Dynasty 202 BC - 9 AD
Tabula Peutingeriana 13th century
Al-Khwārizmī 15th Century
Al-Idrisi 1154
• An early Western Han dynasty silk map found in tomb 3
of Mawangdui, depicting the Kingdom of Changsha and
Kingdom of Nanyue in southern China (note: the south
direction is oriented at the top).
• Cartography existed in China before the Han. Some of
the earliest Han maps ink-penned silk maps
• The general Ma Yuan created the world's first known
raised-relief map from rice in the 1st century.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pomponius_Mela
• Cartographer Zhang Heng was the first to use scales and
grids for maps
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Hecataeus 550 BC
Herodotus 440 BC
Eratosthene 276
Pomponius Melas 43 BC
Han Dynasty 202 BC - 9 AD
Tabula Peutingeriana 13th century
Al-Khwārizmī 15th Century
Al-Idrisi 1154
• 13th-century parchment copy of a possible Roman
original. It covers Europe, North Africa, and parts of Asia,
including the Middle East, Persia, and India.
• According to one hypothesis, the existing map is based
on a document of the 4th or 5th century world map
originally prepared by Agrippa during the reign of the
emperor Augustus (27 BC – AD 14).
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tabula_Peutingeriana • Named after the 16th-century German antiquarian
Konrad Peutinger
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Hecataeus 550 BC
Herodotus 440 BC
Eratosthene 276
Pomponius Melas 43 BC
Han Dynasty 202 BC - 9 AD
Tabula Peutingeriana 13th century
Al-Khwārizmī 15th Century
Al-Idrisi 1154
• Muhammad ibn Musa al-Khwarizmi
• Contributions to mathematics, geography, astronomy,
and cartography established the basis for innovation in
algebra and trigonometry.
• In addition to his best-known works, he revised
Ptolemy's Geography, listing the longitudes and latitudes
of various cities and localities.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Muhammad_ibn_Musa_al-Khwarizmi • Earliest extant map of the Nile, in al-Khwārazmī’s Kitāb
ṣūrat al- arḍ
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Hecataeus 550 BC
Herodotus 440 BC
Eratosthene 276
Pomponius Melas 43 BC
Han Dynasty 202 BC - 9 AD
Tabula Peutingeriana 13th century
Al-Khwārizmī 15th Century
Al-Idrisi 1154
• Muhammad al-Idrisi
• Al-Idrisi's world map from 'Alî ibn Hasan al-Hûfî al-
Qâsimî's 1456 copy. According to the French National
Library.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Muhammad_al-Idrisi
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Projections
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Cartographers (map
makers) have developed
different ways of projecting
our three-dimensional
world onto a flat map, and
each approach is called a
map projection.
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
preserve
worse for maps
shapes but
conformal that show larger
areas are
areas
distorted
Compass
Areas are directions cannot
equal-area preserved but be shown
projections shape is correctly, should
distorted not be used for
navigation
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
MAP Projections
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nJ5r4HJMrfo
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Projections
Goode
Cylindrical
Robinson
Conical
Planar
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Projections
Goode
Cylindrical
Robinson
Conical
Planar shape distortion problem
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Projections
Goode
Cylindrical
Robinson
Conical
high-latitude distortion increases to such
Planar an extent that the poles cannot be shown
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Projections
Goode
Cylindrical
Robinson
Conical • robinson projections are not equivalent
• the amount of area distortion is generally
Planar low within about 45° of the equator.
• shapes are distorted.
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Projections
Goode
Cylindrical
Robinson
Conical
only show areas within a single, complete
Planar hemisphere
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Projections
Goode
Cylindrical
Robinson
Conical
distortion increases away from this point, only
Planar one full hemisphere can be shown
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Projection Distortion
Understand distortions
• Gedymin faces
• Tissot’s indicatrix
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
AuthaGraph Projection
• AuthaGraph World Map is
proportionally perfect.
• It folds it into a three-
dimensional globe.
• Japanese architect Hajime
Narukawa invented this
projection in 1999
• Equally dividing a spherical
surface into 96 triangles.
• Considers the Earth a
tetrahedrons
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YsQtLASlDKE
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Elements
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
• Frame Line and
Neat Line
• Inset
• Data Source
• Title and Subtitle
• Legend
• Scale
• Orientation/North
Line
• Latitude and
Longitude
• Labels
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
• Frame Line and Frame Line Encloses all other map
Neat Line elements.
• Inset
Neat Line Is used to crop (limit
the extent of) the
• Data Source
mapped area.
• Title and Subtitle
Frame Line
• Legend
• Scale Neat Line
• Orientation/North
Line
• Latitude and
Longitude
• Labels
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
• Frame Line and
A smaller map included within the
Neat Line
context of a larger map
• Inset • Used to show the primary mapped
area in relation to a larger, more
• Data Source recognizable area (a locator map).
• Used to enlarge important or
• Title and Subtitle congested areas (a zoom, or blow-up
map).
• Legend
• Scale
• Orientation/North
Line
• Latitude and
Longitude
• Labels
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
• Frame Line and
Allows the map user to determine
Neat Line
where thematic data were obtained.
• Inset
• Data Source
• Title and Subtitle
• Legend
• Scale
• Orientation/North
Line
• Latitude and
Longitude
• Labels
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
• Frame Line and
The title and subtitle tell the map user
Neat Line
what the map is about.
• Inset
• Data Source
• Title and Subtitle
• Legend
• Scale
• Orientation/North
Line
• Latitude and
Longitude
• Labels
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
• Frame Line and
The legend defines the symbols found
Neat Line
on a map.
• Inset
• Data Source
• Title and Subtitle
• Legend
• Scale
• Orientation/North
Line
• Latitude and
Longitude
• Labels
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
• Frame Line and
Neat Line
• Inset
• Data Source
• Title and Subtitle
• Legend
• Scale
• Orientation/North
Line
• Latitude and
Longitude
• Labels
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
• Frame Line and
Neat Line
• Inset
• Data Source
• Title and Subtitle
• Legend
• Scale
• Orientation/North
Line
• Latitude and
Longitude
• Labels
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
• Frame Line and
Indicates the amount of reduction that
Neat Line
has taken place on a map, or allows the
map user to measure distances.
• Inset
• Representative Fraction (RF) 1:24,000
• Data Source
• Title and Subtitle
• Legend • Verbal Scale (VS) 1 Inch to 1 Mile)
• Scale
• Orientation/North • Graphical Scale (GS) / Bar Scale (BS)
Line
• Latitude and
Longitude
• Labels
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
• Frame Line and
Neat Line RF to Graphical Scale
• Inset
RF 1 : 100,000
• Data Source
• Title and Subtitle
GS ?
we know, 100 cm = 1 m
• Legend
1
so, 1 cm = m
• Scale 100
again, 1000 m = 1 km
• Orientation/North 1
so, 1 m = km
Line 1000
1 1
• Latitude and thus, 1 cm = x km
Longitude 100 1000
1
so, 1 cm = km
• Labels 100000
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
• Frame Line and
Neat Line RF to Graphical Scale
• Inset
RF 1 : 100,000
• Data Source
• Title and Subtitle
GS ?
• Legend 1
so, 1 cm = km
100000
• Scale
100000
• Orientation/North 1 cm ≈ km
100000
Line
1 cm ≈ 1 km
• Latitude and
Longitude 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
• Labels
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
• Frame Line and
Neat Line RF to Graphical Scale
• Inset
RF 1 : 100,000
• Data Source
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
GS
• Title and Subtitle
• Legend
• Scale
• Orientation/North
Line EXAMPLE
Mr. Jabbar is preparing a map and was
• Latitude and provided an RF value for the working
Longitude area as 1:200,000 by his client. Draw a
graphical scale for Mr. Jabbar.
• Labels
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
• Frame Line and
Neat Line The indication of North on a map. It can
be indicated by…
• Inset
• North Arrow
• Data Source
• Graticule/Grid Lines/Lat. & Long.
• Title and Subtitle
• Legend
• Scale
• Orientation/North
Line
• Latitude and
Longitude
• Labels
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
• Frame Line and
Represents Grid lines with different
Neat Line
types of projection. It can be
represented as;
• Inset
• Degree, Minutes and Seconds.
• Data Source
• Degree Decimal
• Title and Subtitle
• Legend
• Scale
• Orientation/North
Line
• Latitude and
Longitude
• Labels
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
• Frame Line and Latitude and longitude, coordinate
Neat Line system by means of which the position or
location of any place on Earth’s surface can
• Inset be determined and described.
• Data Source
• Title and Subtitle
• Legend
• Scale
• Orientation/North
Line
• Latitude and
Longitude
• Labels
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
• Frame Line and Latitude and longitude, coordinate
Neat Line system by means of which the position or
location of any place on Earth’s surface can
• Inset be determined and described.
• Data Source
• Title and Subtitle
• Legend
• Scale
• Orientation/North
Line
• Latitude and
Longitude
• Labels
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Longitude (shown as a vertical line) is the angular Latitude (shown as a horizontal line) is the angular
distance, in degrees, minutes, and seconds, of a point east distance, in degrees, minutes, and seconds of a point
or west of the Prime (Greenwich) Meridian. Lines of north or south of the Equator. Lines of latitude are often
longitude are often referred to as meridians. referred to as parallels
North-South Run in direction East-West
Meridians Known as Parallels
East or west from prime North or south from
Measure distance
meridian equator
Equator Farthest apart Parallel to one another
At the poles Meet each other Never
The Equator Cross at Right angle The Prime Meridian
Equal in length lenght Get shorter towards poles
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
• Frame Line and
the craft of placing text on a map in
Neat Line
relation to the map symbols, together
representing features and properties of
• Inset the real world.
• Data Source • Alphanumerical way of marking a
spot on a map
• Title and Subtitle • Font size should be taken into
account.
• Legend • Water bodies should be written in
Italics.
• Scale
• Hierarchy of places should be
reflected by text size.
• Orientation/North
Line
• Latitude and
Longitude
• Labels
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Convert 15o 10’ 05””
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Longitude / Latitude
1 degree = 60 minute 1 Minute = 60 seconds
15o 10’ 05” = 15 + (10 / 60) + (5 / (60 * 60))
= 15 + (10 / 60) + (5 / 3600)
= 15 + 0.1667 + 0.001389
= 15.168089
= 15.168 Degree Decimal
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Time Zone
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Greenwitch Mean Time
• The Royal observatory, Greenwich, is the home of the
prime meridian of the world. Longitude 0hr 0min 0sec.
• GMT- Solar time (time measured by Earth's rotation
relative to the Sun) at the 0 degree longitude (Prime
Meridian)
• UTC (Coordinated universal time)
• Replaced GMT in 1972 as the time standard
• Time Zones- region on Earth that use the same local
time/ standard time
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Understanding Time Zones
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-j-SWKtWEcU
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
1 complete rotation = 1 day
Calculating Time
1 complete rotation = 360o
Thus, 1 day = 360o
Thus, 24 hours = 360o
360o
Now 1 hour = = 15o
24
So, 60 mins = 15o
15o
Thus, 1 mins = = 0.25 mins
60
• Earth moves West to East
60
Or, 1o = = 4 mins • It takes 24 hrs to complete the spin
15
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
EXAMPLE
Abdul Hayer shaheb traveled 110o from his house to
visit his aunt at Fatikchari. Mr Hayer lives at lauchara
next to the sorbohara lake. How far is the lake from
Fatikchari?
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
GIS and RS
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Geographic Information System (GIS)
GIS is a system of hardware and software used for storage,
retrieval, mapping, and analysis of geographic data.
• A map connected to a database
Information System
• GIS is a spatial decision support system.
• A GIS is a computerized tool for solving geographic problems.
• GIS Combines Physical/Spatial Data and Attribute Data.
• Physical Data Road, Area, Building, Lake, etc.
• Attribute Data Width, Population, # of Plot Boundary, Depth, etc.
Geographic Position
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Point
Attributes
Point Line Polygon
• Area in Acre • Road type • Name
• Village • Length • Population
Line
Features
• Union • Width • Population Density
• Upazila • Surface quality • Number of village
• District • Soil type • Number of ward
• Country • Height • Number of school
• Capacity • Existence of Tunnel • Number of cyclone
• Year of establishment forestry shelter
• Number of room • Presence of • Number of tubewell
Polygon • Building type unauthorized structure • Length of protection
• Number of tubewell • Year of Establishment embankment
• Number of toilet • Year of • Total Area in acre
repair/maintenance • Water body in acre
• Disaster affected • Forest area in acre,
• Number of Bridges etc.
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Vector Data Model Raster Data Model
Data Representation
Raster and Vector are two methods
of
representing geographic data in GIS
GPS (Global Positioning System)
GPS is a to show exact position on Earth
anytime, in any weather, anywhere. • A spatial data model that uses a • A data model that uses points
grid and cells to represent the and their x-, y- coordinates to
The three parts of GPS are spatial variation of a feature. construct spatial features.
• Satellite • The vector data model is based • The raster data model is a widely
• Receiver on the assumption that the used method of storing
• Software earth's surface is composed of geographic data.
The accuracy of data & discrete objects such as trees,
rivers, lakes, etc. ...
information depends on the
quality or the error levels of • The vector data model • The model most commonly
the device. represents real-world features as takes the form of a grid-like
points, lines, and polygons structure that holds values at
whose boundaries are defined by regularly spaced intervals over
x,y coordinate pairs. the extent of the raster.
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Data Representation
Raster and Vector are two methods
of
representing geographic data in GIS
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Remote Sensing (RS)
GIS is a system of hardware and software used for storage,
retrieval, mapping, and analysis of geographic data.
• acquiring information about an object
• without entering in contact with it
• by sensing and recording reflected or emitted energy and processing,
analyzing, and applying that information.
Progress of Remote Sensing
1609 1859 1862 1890 1908 1947
Invention of the First Aerial US Army Baloon Corp Kite photography, First photos from an Space
telescope Photographer (Nadar) Pegion Camera, etc Airplane
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
GIS RS
• allows people to see the world in a different • educe the need for manual labor
way by mapping the position and quantity of by automating manual, repetitive
things, storage and retrieval tasks
Advantage • mapping the density of people and objects • automating tasks increases
• mapping any changes that occur. accuracy and efficiency
• find out what is happening inside a specific area • freeing up human workers to focus
or nearby to a specific area. on higher-value activities.
• its technical nature may portray results as being • fairly expensive method of
more reliable than they actually are and the analysis.
errors • requires a special kind of training
Disadvantage
• the assumptions can be hidden to analyze the images
• leading to a lack of questioning into the results . • expensive to analyze repetitive
photographs
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
Thank You
North South University ENV203 / GEO205 (JWR)
You might also like
- The Fayum Landscape: Ten Thousand Years of Archaeology, Texts, and Traditions in EgyptFrom EverandThe Fayum Landscape: Ten Thousand Years of Archaeology, Texts, and Traditions in EgyptNo ratings yet
- Archaeological Theory - : Classical Beginnings, Antiquarian Yearnings, and Scientific GlimmersDocument48 pagesArchaeological Theory - : Classical Beginnings, Antiquarian Yearnings, and Scientific GlimmersJefff YasdasdasdadNo ratings yet
- Bible World History Timeline - 504-254BCDocument2 pagesBible World History Timeline - 504-254BCSagitonette DadapNo ratings yet
- Proto OghamDocument49 pagesProto OghamM.d. PejrhardssonNo ratings yet
- Kouros, Kouroi, Kore, KoraiDocument18 pagesKouros, Kouroi, Kore, Koraikritisk kulturNo ratings yet
- (1855) The Life and Travels of Herodotus (Volume 1)Document400 pages(1855) The Life and Travels of Herodotus (Volume 1)Herbert Hillary Booker 2ndNo ratings yet
- (Bloomsbury Egyptology) Susan Tower Hollis - Five Egyptian Goddesses_ Their Possible Beginnings, Actions, and Relationships in the Third Millennium BCE-Bloomsbury Academic (2019)Document233 pages(Bloomsbury Egyptology) Susan Tower Hollis - Five Egyptian Goddesses_ Their Possible Beginnings, Actions, and Relationships in the Third Millennium BCE-Bloomsbury Academic (2019)גיא שפיראNo ratings yet
- Reflections of Osiris, Lives From Ancient EgyptDocument193 pagesReflections of Osiris, Lives From Ancient Egyptbasupriyaguha100% (1)
- A Genetic History of The Near East From An aDNA Time Course Sampling Eight Points in The Past 4,000 YearsDocument9 pagesA Genetic History of The Near East From An aDNA Time Course Sampling Eight Points in The Past 4,000 YearsJohn MuñozNo ratings yet
- سميراميسDocument626 pagesسميراميسAtheer Ahmad100% (1)
- A History of AnatoliaDocument71 pagesA History of AnatoliaA. Rod PaoliniNo ratings yet
- An Alternative History For The AlphabetDocument26 pagesAn Alternative History For The AlphabetRichter, JoannesNo ratings yet
- Emmet Sweeney - The Pyramid AgeDocument192 pagesEmmet Sweeney - The Pyramid AgeARCHEOMACEDONIA100% (1)
- (Ebook) - Piri Reis Map - Proof of Ancient Advanced Civilisation PDFDocument8 pages(Ebook) - Piri Reis Map - Proof of Ancient Advanced Civilisation PDFGiDantasNo ratings yet
- (LU) ANDERSON, J.K., (1954) - A Topographical and Historical Study of AchaeaDocument22 pages(LU) ANDERSON, J.K., (1954) - A Topographical and Historical Study of AchaeaJulian BrouetNo ratings yet
- A Genetic History of the Near East from aDNA Samples Over 4,000 YearsDocument9 pagesA Genetic History of the Near East from aDNA Samples Over 4,000 YearsRICHARD BLANDININo ratings yet
- Download The Greeks History Culture And Society 2Nd Internat Edition Ian Morris full chapterDocument67 pagesDownload The Greeks History Culture And Society 2Nd Internat Edition Ian Morris full chaptercharles.stewart250100% (2)
- British School at Athens The Annual of The British School at AthensDocument48 pagesBritish School at Athens The Annual of The British School at AthensrybrybNo ratings yet
- Chinese Origin Story Pan Gu and The Egg of The WorldDocument31 pagesChinese Origin Story Pan Gu and The Egg of The WorldKenneth Anrie MoralNo ratings yet
- Ian Morris, Barry B. Powell - The Greeks - History, Culture, and Society-Pearson (2013)Document582 pagesIan Morris, Barry B. Powell - The Greeks - History, Culture, and Society-Pearson (2013)Theo Nash100% (5)
- Central Bicol State University of Agriculture: Republic of The Philippines San Jose, Pili, Camarines Sur 4418Document6 pagesCentral Bicol State University of Agriculture: Republic of The Philippines San Jose, Pili, Camarines Sur 4418joshua quijanoNo ratings yet
- Bargas TIMELINE PDFDocument20 pagesBargas TIMELINE PDFBargas, Mia Kazandra Loren L.100% (2)
- Agata RC HidesDocument3 pagesAgata RC HidesIAalejandro IGioNo ratings yet
- Vikrama & Tribedy N&N PDFDocument16 pagesVikrama & Tribedy N&N PDFElora TribedyNo ratings yet
- Ian Shaw (Editor) - The Oxford History of Ancient Egypt - Oxford University Press, USA (2000)Document550 pagesIan Shaw (Editor) - The Oxford History of Ancient Egypt - Oxford University Press, USA (2000)Jose Carlos de la Fuente Leon100% (4)
- Birth of CivilizationDocument10 pagesBirth of CivilizationDipenSomaniNo ratings yet
- 2016 IJHS From Balkh To Baghdad Vol51 - 4 - 2016 - Art14Document12 pages2016 IJHS From Balkh To Baghdad Vol51 - 4 - 2016 - Art14wujastykNo ratings yet
- ANCIENT EGYPT - The Pyramid Texts in The Tomb of Pharaoh Wenis, Unis or UnasDocument48 pagesANCIENT EGYPT - The Pyramid Texts in The Tomb of Pharaoh Wenis, Unis or UnasCarlie GreenNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lession 4Document5 pagesModule 1 Lession 4Nica EllyzaNo ratings yet
- Tradition or Innovation The Ugaritic EgyDocument10 pagesTradition or Innovation The Ugaritic EgyRenato De Carvalho FerreiraNo ratings yet
- UgaritDocument6 pagesUgaritusama87t100% (2)
- Handout wk2Document15 pagesHandout wk2api-493307654No ratings yet
- Begley ArikameduReconsidered 1983Document22 pagesBegley ArikameduReconsidered 1983Sadhish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bronze Age: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument24 pagesBronze Age: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaZerotheoryNo ratings yet
- 1 KroppDocument18 pages1 KroppJose manuelNo ratings yet
- Pace, ART 102, Week 6, Etruscan, Roman Arch. & SculpDocument36 pagesPace, ART 102, Week 6, Etruscan, Roman Arch. & SculpJason ByrdNo ratings yet
- Ancient events and people timelineDocument15 pagesAncient events and people timelineJowayne HudsonNo ratings yet
- The 100 Most Influential Books Ever WrittenDocument7 pagesThe 100 Most Influential Books Ever Writtendevendrameher50% (2)
- The Catalogue of The Ships in Homer's Iliad - R. Hope SimpsonDocument198 pagesThe Catalogue of The Ships in Homer's Iliad - R. Hope SimpsonJavier Martinez EspuñaNo ratings yet
- Timeline Ordering ActivityDocument3 pagesTimeline Ordering ActivityTasnim MbarkiNo ratings yet
- Judah in The Neo-Babylonian PeriodDocument34 pagesJudah in The Neo-Babylonian PeriodJustin SingletonNo ratings yet
- On The Origin of The Iberomaurusians (Upper Palaeolithic - North Africa) - A New Hypothesis (Journal of Human Evolution, Vol. 14, Issue 4) (1985)Document5 pagesOn The Origin of The Iberomaurusians (Upper Palaeolithic - North Africa) - A New Hypothesis (Journal of Human Evolution, Vol. 14, Issue 4) (1985)johnkalespi100% (1)
- A Short History of The Thyroid Gland PDFDocument4 pagesA Short History of The Thyroid Gland PDFsmartjohnsmith10No ratings yet
- Human Burial HistoryDocument18 pagesHuman Burial HistoryStutiBindlishNo ratings yet
- Cultural Sequence of Bet Dwarka Island Based On Thermoluminescence DatingDocument6 pagesCultural Sequence of Bet Dwarka Island Based On Thermoluminescence Datingनटराज नचिकेताNo ratings yet
- A 'Macedonian Bronze' Juglet From Zagora, Andros - Stavros A. PaspalasDocument13 pagesA 'Macedonian Bronze' Juglet From Zagora, Andros - Stavros A. PaspalasSonjce Marceva100% (1)
- New Era University: Historical Anteceden Ts Description Imag e TimeDocument6 pagesNew Era University: Historical Anteceden Ts Description Imag e TimeJefford ObañaNo ratings yet
- Further,: Steven EDocument18 pagesFurther,: Steven EAra JavierNo ratings yet
- Zpe 204 Tribulato-OlivieriDocument9 pagesZpe 204 Tribulato-OlivieriKanemotoNo ratings yet
- Tombs at TocraDocument3 pagesTombs at TocraLaith EddwyliNo ratings yet
- Eretria A Town in Greece Wiki 1 21 2017Document7 pagesEretria A Town in Greece Wiki 1 21 2017seeallconcernNo ratings yet
- Archaeology in Georgia 1980-1990Document9 pagesArchaeology in Georgia 1980-1990Onur GüvenNo ratings yet
- ANCIENT EGYPT: KEYS TO HIEROGLYPHSDocument6 pagesANCIENT EGYPT: KEYS TO HIEROGLYPHSgabisaenaNo ratings yet
- Drakospita ArcheoastronomiaDocument6 pagesDrakospita ArcheoastronomiaAlessandro MazzucchelliNo ratings yet
- The Tragic End of The Bronze Age (The Screenplay)Document69 pagesThe Tragic End of The Bronze Age (The Screenplay)Tom Slattery60% (5)
- 'Archaic Greece and The Veda' by N. KazanasDocument27 pages'Archaic Greece and The Veda' by N. KazanasSrini KalyanaramanNo ratings yet
- Brill Journal of The Economic and Social History of The OrientDocument58 pagesBrill Journal of The Economic and Social History of The OrientAdriana BernalNo ratings yet
- Greek Egyptian Relations in NaukratisDocument12 pagesGreek Egyptian Relations in Naukratisyunyao ChenNo ratings yet
- 2 The Prehistoric PeriodDocument10 pages2 The Prehistoric PeriodPetraNo ratings yet
- BD's High Population & Fertile LandDocument108 pagesBD's High Population & Fertile LandMalisha Rahman Tonni 1921946042No ratings yet
- MalishaRahmanTonni QuestionForQuiz-2Document2 pagesMalishaRahmanTonni QuestionForQuiz-2Malisha Rahman Tonni 1921946042No ratings yet
- Earth Spheres Structure DynamicsDocument46 pagesEarth Spheres Structure DynamicsMalisha Rahman Tonni 1921946042No ratings yet
- NSU Env-203 Assignment on Mobility TheoryDocument2 pagesNSU Env-203 Assignment on Mobility TheoryMalisha Rahman Tonni 1921946042No ratings yet
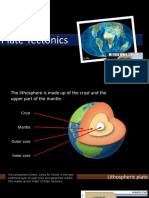
- S223 Env203Geo205 S09 06 Plate TecctonicsDocument66 pagesS223 Env203Geo205 S09 06 Plate TecctonicsMalisha Rahman Tonni 1921946042No ratings yet
- S223 Env203Geo205 S09 02 Continents CountriesDocument13 pagesS223 Env203Geo205 S09 02 Continents CountriesMalisha Rahman Tonni 1921946042No ratings yet
- S223 Env203Geo205 S09 03 Theme Concepts ElementsDocument49 pagesS223 Env203Geo205 S09 03 Theme Concepts ElementsMalisha Rahman Tonni 1921946042No ratings yet
- Parent/Guardian Consent Form For Industrial Internship / Training / Visit / OthersDocument1 pageParent/Guardian Consent Form For Industrial Internship / Training / Visit / OthersMalisha Rahman Tonni 1921946042No ratings yet
- CSE498R/EEE498R/ETE 498R: Student Learning and Outcome Achievement FormDocument1 pageCSE498R/EEE498R/ETE 498R: Student Learning and Outcome Achievement FormMalisha Rahman Tonni 1921946042No ratings yet
- 1112 Weather Forecast Powerpoint TemplateDocument5 pages1112 Weather Forecast Powerpoint TemplateMalisha Rahman Tonni 1921946042No ratings yet
- Vector Prod Basics PDFDocument11 pagesVector Prod Basics PDFMalisha Rahman Tonni 1921946042No ratings yet
- CSE498R/EEE498R/ETE 498R: Exit Viva QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesCSE498R/EEE498R/ETE 498R: Exit Viva QuestionnaireMalisha Rahman Tonni 1921946042No ratings yet
- No Objection Certificate (NOC) : Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering (ECE)Document1 pageNo Objection Certificate (NOC) : Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering (ECE)Malisha Rahman Tonni 1921946042No ratings yet
- ICSE Geo Graphy Voyage Solutions Class 9 Chapter 2 Geographic Grid Latitudes and LongitudesDocument20 pagesICSE Geo Graphy Voyage Solutions Class 9 Chapter 2 Geographic Grid Latitudes and LongitudesSamyaNo ratings yet
- 4890 1 13116 1 10 20160107Document20 pages4890 1 13116 1 10 20160107Ana Kathrin TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Earth Navigation ConceptsDocument245 pagesEarth Navigation ConceptsCharles Jzenicho NollanNo ratings yet
- QIBLATIMEDocument444 pagesQIBLATIMEasifali.qadriNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLesson Planapi-354866005No ratings yet
- Matlab Netcdf GuideDocument12 pagesMatlab Netcdf GuideRyedho SlhiversNo ratings yet
- Locating Places with Latitudes and LongitudesDocument11 pagesLocating Places with Latitudes and LongitudesHannah VipunamNo ratings yet
- Deriving The Curve of Quickest DescentDocument23 pagesDeriving The Curve of Quickest DescentvishveshwarNo ratings yet
- Lat/Long ExplainedDocument4 pagesLat/Long Explainedhooty_OWLNo ratings yet
- Dps-T2-Revision-Simple Machines & Mapping The World - Ans KeyDocument4 pagesDps-T2-Revision-Simple Machines & Mapping The World - Ans KeySUHANEERIYANo ratings yet
- CartoDocument6 pagesCartoBeltran KathNo ratings yet
- Earth Coverage by Satellites in Circular Orbit: Alan R. WashburnDocument18 pagesEarth Coverage by Satellites in Circular Orbit: Alan R. Washburnart paglaNo ratings yet
- AST - Cat 048 - Appendix ADocument15 pagesAST - Cat 048 - Appendix AViorelNo ratings yet
- Proof of Earth's Shape and SizeDocument32 pagesProof of Earth's Shape and Sizejoshua.brussell82% (11)
- Automatic Flight Control Systems - Latest DevelopmentsDocument215 pagesAutomatic Flight Control Systems - Latest DevelopmentsMatevž BrojanNo ratings yet
- Marine Chart Work (D.a.moore)Document114 pagesMarine Chart Work (D.a.moore)Pawan Kumar75% (4)
- Science 7 LAS Q4Document50 pagesScience 7 LAS Q4Gil Anne Marie100% (2)
- Latitude and Longhitude Learning PacketsDocument1 pageLatitude and Longhitude Learning PacketsJolens VelasquezNo ratings yet
- B.A. (Hons.) Geography Syllabus CBCS Choice Based Credit SystemDocument15 pagesB.A. (Hons.) Geography Syllabus CBCS Choice Based Credit Systemmoives pointNo ratings yet
- Jyotish - Surya Siddhanta and Siddhanta Siromani - Bhaktisiddhanta - 1890Document796 pagesJyotish - Surya Siddhanta and Siddhanta Siromani - Bhaktisiddhanta - 1890Saiprasad Nitw100% (1)
- Practical Astronomy and Geodesy, NarrienDocument470 pagesPractical Astronomy and Geodesy, Narrienandresmejia68No ratings yet
- OYO LBsDocument18 pagesOYO LBsdavNo ratings yet
- 1 - How Geographers View The WorldDocument4 pages1 - How Geographers View The WorldWilliam HoltNo ratings yet
- Longitude Latitude and EquatorDocument14 pagesLongitude Latitude and EquatorLorie Ann RatunilNo ratings yet
- The Dear NoteDocument2 pagesThe Dear NoteZhordiqueuserNo ratings yet
- 373 07 2Document143 pages373 07 2fpttmmNo ratings yet
- Nautical AstronomyDocument11 pagesNautical AstronomyPolaris BridgemanNo ratings yet
- ECQB 090 ACG PPL A.de - enDocument73 pagesECQB 090 ACG PPL A.de - enmitNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Distance and Direction PDFDocument9 pagesMeasurement of Distance and Direction PDFShoaib hossain100% (1)
- Latitude Pre-Test - Answer Key PDFDocument5 pagesLatitude Pre-Test - Answer Key PDFIrene MartinNo ratings yet