0% found this document useful (0 votes)
933 views1 pageMathematical Foundation of Computer Science
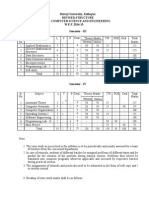
This document outlines the mathematical foundations covered in three units for a computer science course. Unit 1 covers binary relations, equivalence relations, orderings, functions, induction, and recursion. Unit 2 introduces mathematical logic including statements, connectives, truth tables, and validity. Unit 3 discusses Boolean algebra topics such as lattices, duality, Boolean functions, and normal forms.
Uploaded by
Simranjeet SinghCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
933 views1 pageMathematical Foundation of Computer Science
This document outlines the mathematical foundations covered in three units for a computer science course. Unit 1 covers binary relations, equivalence relations, orderings, functions, induction, and recursion. Unit 2 introduces mathematical logic including statements, connectives, truth tables, and validity. Unit 3 discusses Boolean algebra topics such as lattices, duality, Boolean functions, and normal forms.
Uploaded by
Simranjeet SinghCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd