Professional Documents
Culture Documents
31 Acid Base Imbalances ABGs II - 230110 - 004938
Uploaded by
JanaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
31 Acid Base Imbalances ABGs II - 230110 - 004938
Uploaded by
JanaCopyright:
Available Formats
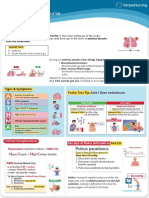
Acid Base Imbalances + ABGs II
Pathophysiology Course
Respiratory Acidosis & Alkalosis - Causes
O2 in CO2 out
Recall the patho & memory tricks
- Carbon Dioxide CO2
- Think “Carbon diACID” since it pushes the body into acidosis.
Hypoventilation (low & slow breathing) = HIGHER CO2
Hyperventilation (fast breathing) = Lower CO2
Over 7.45 pH
Under 7.35 pH Respiratory Acidosis = Low & Slow RR
Sleep apnea
Head trauma “knocked out”
Respiratory Alkalosis = Fast RR Post-operative
Drugs = CNS depressants
Panic Attack • Opioid overdose NCLEX TIP
Key Manifestations • Alcohol intoxication
• Benzodiazepines (Diazepam)
• Low PaCO2 Pneumonia
• Low HCO3 COPD or Asthma attack
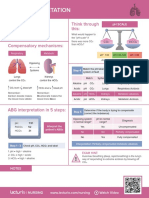
Compensation: Key Manifestations
• Kidneys excrete LESS H+ • Mental Status changes
& reabsorb LESS HCO3 • Elevated PaCO2
• Elevated HCO3
Compensation:
• Kidneys excrete H+ (acid)
& retain HCO3 (base)
Top Missed Exam Question
The nurse expects which client
to be in respiratory acidosis?
MEMORY TRICKS 1. Morphine overdose
2. Panic attack
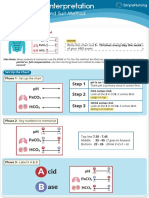
pH
Respiratory ACIDosis Respiratory ALKalosis
3. Sleep apnea
Respiratory ACIDosis
4. COPD
Low & Slow RR Fast RR
5. Asthma attack
6. Alcohol intoxication
alk alk alk
alk-alooosis
CO2
Common NCLEX question
CO2 How does the nurse expect the client to
show compensation for the following
Snoring & Think of a person ABG values?
Ph 7.20, PaO2 82 mm Hg, PaCO2 37 mm
hypoventilation panting like a dog
Hg, HCO3 15 mEq/L
(metabolic acidosis)
sounds like (hyperventilation), 4
5
6 7 8 9
10
1. Decreased respiratory rate
2. Increased respiratory rate
11
“Accccccid-osis”
3
it sounds like
12
2
13 14
0 1
pH
3. Increased renal retention of H+…
“ALK, alk, alk-alosis” Acidotic
7.35 pH
NORMAL pH Alkalotic
4. Decreased renal excretion of HCO3
7.45 pH
You might also like
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Asthma - Pathom, Signs & ComlicationsDocument1 pageAsthma - Pathom, Signs & ComlicationsVishalNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Pneumonia PathophysiologyDocument1 pageRespiratory Pneumonia PathophysiologyTrisha VergaraNo ratings yet
- Visual Chart 1 - Developmental MilestonesDocument1 pageVisual Chart 1 - Developmental MilestonesVishalNo ratings yet
- High Yield Surgery Compatible Version-2Document20 pagesHigh Yield Surgery Compatible Version-2zoozsuhai2No ratings yet
- The Child With Endocrine DysfunctionDocument5 pagesThe Child With Endocrine Dysfunctionhenny1620No ratings yet
- Nursing Exam Cram Sheet For The NCLEX-RN: 1. Test Information 5. ABG ValuesDocument8 pagesNursing Exam Cram Sheet For The NCLEX-RN: 1. Test Information 5. ABG ValuesManuela GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- Nclex PrepDocument2 pagesNclex PrepJeremy HodgesNo ratings yet
- NURS 460 Nursing Licensure Examination Course: Jv7@hawaii - EduDocument5 pagesNURS 460 Nursing Licensure Examination Course: Jv7@hawaii - EduJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- All About NCLEX Exam: Preparation, Sections, Tips for SuccessDocument8 pagesAll About NCLEX Exam: Preparation, Sections, Tips for SuccessNikmatul RizqiNo ratings yet
- Testing Strategies For The Nclex-Rn Examination: Chapter OneDocument22 pagesTesting Strategies For The Nclex-Rn Examination: Chapter OneShiraishiNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Failure & ARDSDocument1 pageAcute Respiratory Failure & ARDSVishalNo ratings yet
- Visual Chart 2 - Developmental MilestonesDocument1 pageVisual Chart 2 - Developmental MilestonesVishalNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Review GuideDocument3 pagesNCLEX Review GuidefallenangelleNo ratings yet
- Growth Hormone DisordersDocument1 pageGrowth Hormone DisordersVishalNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Balance: Carol Johns, MSN, RNDocument36 pagesAcid Base Balance: Carol Johns, MSN, RNkatrinasdNo ratings yet
- Nclex-Rn CramsheetDocument2 pagesNclex-Rn Cramsheetapi-287105616No ratings yet
- TonsillitisDocument1 pageTonsillitisVishalNo ratings yet
- NCLEXDocument1 pageNCLEXfrank87ali100% (1)
- 35 Nclex QuestionsDocument6 pages35 Nclex Questionsjohnnymyunghee0% (1)
- Basic Chart 1 of 2 - Delopmental MilestonesDocument1 pageBasic Chart 1 of 2 - Delopmental MilestonesVishalNo ratings yet
- Clinical Nursing JudgmentDocument7 pagesClinical Nursing Judgmentapi-502994344No ratings yet
- Ch. 1, Lesson 1: What Is The Next Gen NCLEXDocument4 pagesCh. 1, Lesson 1: What Is The Next Gen NCLEXChantelNo ratings yet
- Improve venous return in client with full leg castDocument39 pagesImprove venous return in client with full leg castDavis WhiteNo ratings yet
- ReMar Nurse University 2020 (VT) Student WorkbookDocument50 pagesReMar Nurse University 2020 (VT) Student WorkbookAnderson AlfredNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal: Nclex-Rn ReviewerDocument34 pagesGastrointestinal: Nclex-Rn ReviewerJohnasse Sebastian NavalNo ratings yet
- 5 Types of QuestionsDocument5 pages5 Types of QuestionsQwequ Gong AnanseNo ratings yet
- Medical Abbreviations Cheat Sheet for NursesDocument2 pagesMedical Abbreviations Cheat Sheet for NursescarlyNo ratings yet
- 8 Essential NCLEX RN ConceptsDocument6 pages8 Essential NCLEX RN ConceptsJot grewalNo ratings yet
- RN Plan StudyDocument13 pagesRN Plan Studywestlake12100% (1)
- Faculty Collaboration in Transitioning To NGN Test Item WritingDocument5 pagesFaculty Collaboration in Transitioning To NGN Test Item WritingCherie BurkeNo ratings yet
- When Can I Register For The NCLEX-RN Exam?Document3 pagesWhen Can I Register For The NCLEX-RN Exam?mimNo ratings yet
- Prioritization LectureDocument6 pagesPrioritization LecturesamNo ratings yet
- Kidney transplant nursing care questionsDocument11 pagesKidney transplant nursing care questionsmonmonNo ratings yet
- Emergent Care Clinic StudyDocument5 pagesEmergent Care Clinic StudyAna Bienne0% (1)
- Immunity 1Document6 pagesImmunity 1Tori RolandNo ratings yet
- My Pledge My NCLEX Success PlanDocument2 pagesMy Pledge My NCLEX Success PlanAnjali Naudiyal100% (1)
- Nclex Question and Rationale Week 1Document8 pagesNclex Question and Rationale Week 1Winnie OkothNo ratings yet
- Ignatavicius Nursing Study Guides and Textbook ChaptersDocument63 pagesIgnatavicius Nursing Study Guides and Textbook ChaptersNursyNurseNo ratings yet
- Hesi Management of A Medical UnitDocument2 pagesHesi Management of A Medical UnitAna Bienne100% (1)
- Nurseslabs Cram SheetDocument17 pagesNurseslabs Cram SheetCris GalendezNo ratings yet
- Mark Klimek Youtube NotesDocument2 pagesMark Klimek Youtube NotesJohn DesirNo ratings yet
- Nclex RN Sata CompilationDocument10 pagesNclex RN Sata CompilationJanna mae PatriarcaNo ratings yet
- NCLEX NotesDocument34 pagesNCLEX Notesyohans TeferiNo ratings yet
- Answer: CDocument34 pagesAnswer: CLola OladapoNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Study MaterialDocument40 pagesNCLEX Study MaterialChristie GerconNo ratings yet
- Select All That ApplyDocument10 pagesSelect All That ApplyJohnasse Sebastian NavalNo ratings yet
- NCLEX RN Review for Risk ReductionDocument7 pagesNCLEX RN Review for Risk Reductionpaulinatia100% (1)
- Concept Map Et Al 11-04-15Document7 pagesConcept Map Et Al 11-04-15api-353656227No ratings yet
- Global Nursing Pediatrics. Nclex - RNDocument14 pagesGlobal Nursing Pediatrics. Nclex - RNNANANo ratings yet
- NCLEX Categories Study GuideDocument9 pagesNCLEX Categories Study GuideTanya ViarsNo ratings yet
- 02 NursingInterviewPrepGuide NurseWellVersedDocument7 pages02 NursingInterviewPrepGuide NurseWellVersedOceanNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base NclexDocument4 pagesAcid-Base NclexDilNo ratings yet
- Head To Toe AssessmentDocument13 pagesHead To Toe AssessmentVino MaghirangNo ratings yet
- FUNDAMENTALS OF NURSING PRACTICE TESTBANKDocument5 pagesFUNDAMENTALS OF NURSING PRACTICE TESTBANKsuperrhengc0% (1)
- Medical Surgical ATI Review Flashcards - QuizletDocument27 pagesMedical Surgical ATI Review Flashcards - QuizletNursyNurseNo ratings yet
- Completed Concept MapDocument4 pagesCompleted Concept Mapapi-607361848No ratings yet
- MK YellowBookDocument35 pagesMK YellowBookJazzy Kathlene Dumable100% (1)
- Saunders Study PlanDocument1 pageSaunders Study PlanLudmilla MartinsNo ratings yet
- 13 Ways To PASS NCLEXDocument2 pages13 Ways To PASS NCLEXwilyam888No ratings yet
- 3SM ABG InterpretationDocument2 pages3SM ABG InterpretationJanaNo ratings yet
- PCA Pump Vs FentanylDocument1 pagePCA Pump Vs FentanylJanaNo ratings yet
- 1 3 Step ABG Interpretation - 2 - 230110 - 004531Document2 pages1 3 Step ABG Interpretation - 2 - 230110 - 004531JanaNo ratings yet
- Nursing - CS - Take A Manual Blood PressureDocument1 pageNursing - CS - Take A Manual Blood PressureJanaNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS Blood-Transfusion-ChecklistDocument1 pageNursing CS Blood-Transfusion-ChecklistJanaNo ratings yet
- Transfusion Checklist: Pre BloodDocument1 pageTransfusion Checklist: Pre BloodJanaNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS ABG-InterpretationDocument1 pageNursing CS ABG-InterpretationJanaNo ratings yet
- Nursing - CS - Normal Aging of The Renal SystemDocument1 pageNursing - CS - Normal Aging of The Renal SystemJanaNo ratings yet
- Cece's Reviewer 1Document111 pagesCece's Reviewer 1Jana100% (1)
- Unit 7 Cardiac (S)Document78 pagesUnit 7 Cardiac (S)Cheyenne SchimpfNo ratings yet
- Hypokalemia and Anesthetic Implications ReviewDocument23 pagesHypokalemia and Anesthetic Implications ReviewRidski D. MiruNo ratings yet
- Book Review: Thoracic Imaging: Pulmonary and Cardiovascular Radiology, 2nd Ed. by W. Richard Webb and Charles R. HigginsDocument1 pageBook Review: Thoracic Imaging: Pulmonary and Cardiovascular Radiology, 2nd Ed. by W. Richard Webb and Charles R. HigginsDr Apoorva ReddyNo ratings yet
- Pathology Question BankDocument10 pagesPathology Question BankSana UsmaniNo ratings yet
- Respiration Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesRespiration Lecture Notesamrutha mohandasNo ratings yet
- LipnCott Summary SmallerDocument21 pagesLipnCott Summary SmallerAdil Yousaf0% (1)
- Lung Adenocarcinoma With Solitary MetastDocument88 pagesLung Adenocarcinoma With Solitary MetastMikmik bay BayNo ratings yet
- ESTUDiO-JAMA-METABOLICA Jun 2020Document11 pagesESTUDiO-JAMA-METABOLICA Jun 2020José M. Del PinoNo ratings yet
- Giles A1Document27 pagesGiles A1Jem Rhod CamenseNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Hydroxide: Acid-Base Balance Overview of Acids and Bases DescriptionDocument15 pagesHydrogen Hydroxide: Acid-Base Balance Overview of Acids and Bases DescriptionElisha WorworNo ratings yet
- Sarawak Handbook of Medical Emergencies, 3rd EdDocument410 pagesSarawak Handbook of Medical Emergencies, 3rd EdKelvin SuNo ratings yet
- Pakya ECG BasicsDocument5 pagesPakya ECG BasicsFrederick CokroNo ratings yet
- Farmakoterapi DispilidemiaDocument33 pagesFarmakoterapi DispilidemiavivinNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument3 pagesLymphatic Systempierre TritzNo ratings yet
- Clinical Cardiology - September 1996 - Stewart - Systemic Side Effects of Topical Beta Adrenergic BlockersDocument7 pagesClinical Cardiology - September 1996 - Stewart - Systemic Side Effects of Topical Beta Adrenergic BlockersamanabduwahabNo ratings yet
- B. Pale Skin C. Difficulty Concentrating D. Shivering 1547. Which Is The Most Suitable Site For Assessing Edema? A. Foot/Ankle B. ClavicleDocument58 pagesB. Pale Skin C. Difficulty Concentrating D. Shivering 1547. Which Is The Most Suitable Site For Assessing Edema? A. Foot/Ankle B. ClavicleS.d HussainiNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 (Prelims) - Lesson 2Document18 pagesNCM 109 (Prelims) - Lesson 2nianNo ratings yet
- Scalamogna Et Al. 2022 - CRM - IsAR-CALC-2 DesignDocument6 pagesScalamogna Et Al. 2022 - CRM - IsAR-CALC-2 DesignPraveenVeeraNo ratings yet
- History and Physical Examination: S4.M24.Case - Ms. KominskyDocument3 pagesHistory and Physical Examination: S4.M24.Case - Ms. KominskyFarah FildzahNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disorders - AuriculotherapyDocument3 pagesCardiovascular Disorders - AuriculotherapyCarissa Nichols100% (2)
- Med Surg Report Sheet Night Shift FINAL2Document2 pagesMed Surg Report Sheet Night Shift FINAL2Cindy Ann100% (1)
- BLS Manual 2020Document162 pagesBLS Manual 2020james rukenya87% (118)
- Splitup Syllabus For Class Xi Science 2020-21Document10 pagesSplitup Syllabus For Class Xi Science 2020-21Neha NNo ratings yet
- Medicina 58 01115 v2Document21 pagesMedicina 58 01115 v2silmanuryanzila2705No ratings yet
- 14 Cardiovascular SystemDocument3 pages14 Cardiovascular SystemOribello, Athenna Jae W.No ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On Blood and Blood Forming AgentsDocument29 pagesDrugs Acting On Blood and Blood Forming AgentsSri RamNo ratings yet
- Benign Paroxysmal Positional VertigoDocument12 pagesBenign Paroxysmal Positional VertigoErnesto Trinidad Jr RNNo ratings yet
- 06 2016 Biomedical Instrumentation - Blood Pressure MeasurementDocument27 pages06 2016 Biomedical Instrumentation - Blood Pressure Measurementviki mikiNo ratings yet
- FormatDocument3 pagesFormatchiragNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia Considerations in Neurological Emergencies (2021)Document14 pagesAnesthesia Considerations in Neurological Emergencies (2021)Allan HongNo ratings yet