Professional Documents
Culture Documents
14 Cardiovascular System
Uploaded by
Oribello, Athenna Jae W.Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
14 Cardiovascular System
Uploaded by
Oribello, Athenna Jae W.Copyright:
Available Formats
College of Nursing
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
LABORATORY
ACTIVITY # 14
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM:
HEART, BLOOD VESSELS AND BLOOD COMPONENTS
I. OBJECTIVES:
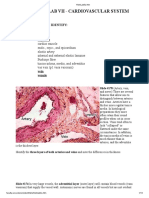
a. To identify the layers that comprises veins, arteries and capillaries
b. To deduce difference between a vein and an artery
c. To identify the major blood vessels in the body
d. To perform the slide method of direct ABO typing and interpret the results completely.
II. MATERIALS
Compound microscope, prepared slide of X-S of vein and artery, charts, Anti-A/B serum, blood
typing slide, sterile lancet, dry alcohol, wet cotton balls, marking pencil, applicator stick.
III. PROCEDURES
Focus the slide containing the X-s of an artery and a vein under LPO and MPO. Identify the
histological layers of each type as to cellular components, cellular arrangement and the presence of other
specific structures in each layer of the artery and vein. Tale note of the distinct differences between the
artery and vein.
For blood grouping: draw a line down the center of a clean glass slide with a marking pencil and
label the upper portion of each slide with A on the left and B on the right. Next, scrub your hands. Clean
the tip of one finger (preferably the ring finger) with cotton moistened with alcohol. Let it dry in the air.
Prick at the side or center of the finger with sterile lancet and wipe off the first ball blood forms. Produce
another drop of blood and place each on the labeled portions of the slide. Then, add a drop of anti-A
serum on the side marked with A and drop an anti-B serum on the slide marked B and mix with clean
application stick. Tilt the slide back and forth, and examine for agglutination over a 2-minute period.
Record.
IV. DRAW AND LABEL
o Gross anatomy of the heart (anterior view)
o Frontal section of the heart (showing inferior chambers and valves)
o The systemic and pulmonary circulations
o Arterial blood supply of the brain
o The fetal circulation
V. QUESTIONS FOR RESEARCH
1. Enumerate the different histological layers common in artery and vein. Describe each layer according
to their arrangement, thickness and composition (tabulate).
Artery and Vein Arrangement Thickness and Composition
Layer of connective tissue that
Tunica adventitia, the outer consists mostly of longitudinally
most layer arranged collagen and elastic
fibers.
The middle layer or tunica Consists mostly of smooth
media muscle.
Arteries will also contain a lot
UC-CON: Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory│The Cardiovascular System | 1
more elastic fibers in
comparison to veins.
Both the smooth muscle and
elastic fibers are arranged in
circular or concentric layers
surrounding the lumen of the
blood vessel.
Lined with a single layer of a
specialized epithelium called the
endothelium, which acts as a
semipermeable barrier.
The subendothelial layer is the
layer beneath the endothelium
The inner layer or tunica intima
and is still part of the tunica
intima.
This layer, which consists of
loose connective tissue and
occasionally smooth muscle as
well.
2. In a tabulated form, differentiate an artery from a vein considering the following aspects:
aspects artery vein
a. Thickness of layers
Tunica media Tunica externa
b. Presence of valves
Pulmonary valve and Aortic
Tricuspid valve and Mitral valve
valve
c. Form of shape when
empty Circular shape Floppy and irregular shape
d. General function
Carry blood away from the heart Convey blood from the tissues
to other organs. back to the heart.
e. Location in the body All parts of the body, except in
Veins can be found in your
the hairs, nails, epidermis,
muscles and along your bones.
cartilages, and cornea.
3. Name the three major branches of the arch of the aorta.
Brachiocephalic (right common carotid and right subclavian), left common carotid artery and left
subclavian artery.
4. Name the subdivisions of the aorta
The aorta can be divided into four subdivisions: the ascending aorta, the aortic arch, the thoracic
(or descending) aorta and the abdominal aorta.
5. What are varicose veins? What are the anatomical structures affected?
Varicose veins are swollen and enlarged veins that usually occur on the legs and feet. They may be
blue or dark purple, and are often lumpy, bulging or twisted in appearance.
UC-CON: Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory│The Cardiovascular System | 2
6. Describe the changes that occur in the arteries and veins as they age.
The most common aging change is increased stiffness of the large arteries, called arteriosclerosis or
hardening of the arteries. On the other hand, the vein physical change among aging populations is
the increase of visible, bulging veins, specifically in the legs.
7. What is the hepatic portal vein?
A blood vessel that carries blood to the liver from the intestines, spleen, pancreas, and gallbladder.
8. Explain how do material exchange between a fetus and a mother take place.
The exchange of these substances between the mother and fetus occurs through the placenta.
The placenta is a temporary organ that begins to form from the trophoblast layer of cells shortly
after implantation. The placenta continues to develop and grow to meet the needs of the growing fetus. A
fully developed placenta is made up of a large mass of blood vessels from both the mother and fetus. The
maternal and fetal vessels are close together but separated by tiny spaces. This allows the mother’s and
fetus’s blood to exchange substances across their capillary walls without the blood actually mixing.
9. Explain the danger of giving a person a mismatched blood.
If a patient receives a blood type that is incompatible, antibodies that the patient already has in his or her
blood will attack the donor red blood cells and destroy them. This could cause fever, chills, chest or back
pain, bleeding, increased heart rate, shortness of breath, rapid drop in blood pressure, and/or kidney
damage. This is called an acute hemolytic reaction. A delayed hemolytic reaction can also occur, which is
generally less severe or even asymptomatic, but there will still be destruction of blood cells.
10. If Harry’s blood type is B, his plasma is likely to contain what kind of antibodies?
His plasma is likely to contain anti-A antibodies.
Total score: ______________
Lomioan, Heinrich L. BSN 1-J Viduya, Beth
Student’s Name Yr & Sec Date Clinical Instructor
UC-CON: Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory│The Cardiovascular System | 3
You might also like
- Nursing Diagnoses For PT With Altered Level of ConsciousnessDocument5 pagesNursing Diagnoses For PT With Altered Level of Consciousnessmikaela_pascua95% (40)
- CH 18 Blood VesselsDocument30 pagesCH 18 Blood VesselsprocellogirlNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For High Acuity Nursing 7th Edition WagnerDocument25 pagesSolution Manual For High Acuity Nursing 7th Edition WagnerJamesThomasngec100% (31)
- Chapter 4 Tissue - The Living FabricDocument23 pagesChapter 4 Tissue - The Living FabricMariaNo ratings yet
- 'Aliah's Cardiovascular SystemDocument45 pages'Aliah's Cardiovascular SystemLuqman Al-Bashir FauziNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Cardiovascular System-t22-HDocument22 pagesHistology of The Cardiovascular System-t22-HSekry EyaNo ratings yet
- Tissues in the Human BodyDocument35 pagesTissues in the Human Bodyraja11160No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Histology Layers and StructuresDocument4 pagesCardiovascular Histology Layers and StructuresJason Anthony SupenaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System-SsDocument56 pagesCirculatory System-SsSofia TyasniNo ratings yet
- Introtohistology LukegarbettDocument4 pagesIntrotohistology Lukegarbettapi-340693501No ratings yet
- Circulatory System AnatomyDocument9 pagesCirculatory System AnatomyJovelou MihangosNo ratings yet
- SGD 13 Nabira & Amirah - Compressed-1Document11 pagesSGD 13 Nabira & Amirah - Compressed-1Maulidatul HusnaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 21 Blood Vessels and Circulatory Doran Mls 1 FDocument12 pagesAnaphy Chapter 21 Blood Vessels and Circulatory Doran Mls 1 FayenaNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Circulatory SystemDocument24 pagesHistology of The Circulatory SystemFatima Zehra YusefNo ratings yet
- Tissues Respiratory Circulatory Immune SystemDocument6 pagesTissues Respiratory Circulatory Immune SystemHarold BunnydotNo ratings yet
- Hhis 211 - Week 9 - Lecture - The Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesHhis 211 - Week 9 - Lecture - The Circulatory Systemkyle LuNo ratings yet
- Histology Lab Vii - Cardiovascular System: Be Able To Identify: Arteriole Artery CapillaryDocument14 pagesHistology Lab Vii - Cardiovascular System: Be Able To Identify: Arteriole Artery CapillaryddnnnNo ratings yet
- Histology of The CvsDocument25 pagesHistology of The CvsroqibniniolaNo ratings yet
- Activity 7 OrgansDocument9 pagesActivity 7 OrgansKEILAH ENCILAYNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Reviewer Tissue and Integumentary SystemDocument7 pagesAnaphy Reviewer Tissue and Integumentary System10. Briol AlvinNo ratings yet
- Histology Notes 2Document13 pagesHistology Notes 2Lukas BüchlerNo ratings yet
- Act 14Document9 pagesAct 14ETHELHYN JHANE MACOBNo ratings yet
- Histology II: January 2006Document67 pagesHistology II: January 2006natnael belayNo ratings yet
- Blood Vessels, AnatomyDocument20 pagesBlood Vessels, AnatomyAbu BakarNo ratings yet
- Histology LecDocument258 pagesHistology LecBan JMNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System (Lecture 1)Document55 pagesCardiovascular System (Lecture 1)Ranime A. FatouhNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 TissuesDocument6 pagesLesson 2 TissuesRodefe AmitNo ratings yet
- ANPH111 Tissue TypesDocument13 pagesANPH111 Tissue Typeselio pascualNo ratings yet
- Outline ReportingDocument4 pagesOutline Reportingmooshee06No ratings yet
- Anatomia y Fisiologuia General Libro-901-950Document50 pagesAnatomia y Fisiologuia General Libro-901-950Felipe Aguirre CórdovaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument32 pagesAnaphy Reviewerpatientsafety100% (1)
- Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesCirculatory SystemJennie WatanabeNo ratings yet
- Histology of Heart and Vessels - ANAT3888 - 2023Document41 pagesHistology of Heart and Vessels - ANAT3888 - 2023RachaelNo ratings yet
- Tissue, Glands, and Membranes Epithelial TissueDocument5 pagesTissue, Glands, and Membranes Epithelial TissueMoises MontalboNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pagesCardiovascular SystemMax DelvalleNo ratings yet
- ANIMAL TISSUES AND ORGAN SYSTEMSDocument7 pagesANIMAL TISSUES AND ORGAN SYSTEMSKenneth Rodriguez HerminadoNo ratings yet
- EAC-Cavite Connective Tissue Lab ExerciseDocument3 pagesEAC-Cavite Connective Tissue Lab ExerciseJOHN ISAAC BENITEZNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant TissuesDocument5 pagesAnimal and Plant TissuesShajara Anglacer AnacanNo ratings yet
- Blood Vascular SystemDocument3 pagesBlood Vascular SystemddnnnNo ratings yet
- Blood Vascular SystemDocument3 pagesBlood Vascular SystemJnn DstNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue: Location of EpitheliumDocument3 pagesEpithelial Tissue: Location of EpitheliumVanyVillegasNo ratings yet
- 7. Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument31 pages7. Structural Organisation in AnimalsVenom Gaming YTNo ratings yet
- 3 Types of Epithelium and Connective TissueDocument3 pages3 Types of Epithelium and Connective TissueFayena JoseNo ratings yet
- Exercise 13 Urinary SystemDocument7 pagesExercise 13 Urinary SystemJovelou MihangosNo ratings yet
- Lec Activity4 Tissues PDFDocument6 pagesLec Activity4 Tissues PDFYda Maxine PalmaNo ratings yet
- BIOL111 Lab 3 TissuesDocument13 pagesBIOL111 Lab 3 TissuesdonnaNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues ExplainedDocument9 pagesAnimal Tissues ExplainedAlfred CariñoNo ratings yet
- Prep Bio FT 2122 Ello XidDocument17 pagesPrep Bio FT 2122 Ello XidSMAXICLouis Bintang AlexisNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Cardiovascular System#Document36 pagesHistology of The Cardiovascular System#DonaldNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument31 pagesHistology of The Cardiovascular Systemirakozehugue14No ratings yet
- Cardiac Layers: Collage of Medicine Anatomy and Histology Department DR - Hameda A.GahziDocument8 pagesCardiac Layers: Collage of Medicine Anatomy and Histology Department DR - Hameda A.GahziJnn DstNo ratings yet
- HUMAN TISSUE PRESENTATIONDocument47 pagesHUMAN TISSUE PRESENTATIONAngelo Cadenas75% (4)
- Assignment AnaphyDocument7 pagesAssignment Anaphyysa.antonio12No ratings yet
- Histology of Vascular System 2017: Agnes NemeskériDocument36 pagesHistology of Vascular System 2017: Agnes NemeskériJanice SanNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissues & SystemsDocument14 pagesConnective Tissues & SystemsJohn Rick OrineNo ratings yet
- Histoloji NotlarıDocument4 pagesHistoloji NotlarıisuhaserkeklerNo ratings yet
- Cvs BdsDocument142 pagesCvs BdsDr Dhiren Kumar PandaNo ratings yet
- Histo Spotting SlidesDocument31 pagesHisto Spotting Slidessrushtip191No ratings yet
- Excitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesFrom EverandExcitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesNo ratings yet
- Coding Packet Guide with CPT and ICD-10 CodesDocument7 pagesCoding Packet Guide with CPT and ICD-10 CodeskebNo ratings yet
- Askep Emboli Paru - Edema Paru - Cor PulmonalDocument63 pagesAskep Emboli Paru - Edema Paru - Cor PulmonalDhevy Sa'PhuttRyyNo ratings yet
- Q&A Pharmacology - 2Document15 pagesQ&A Pharmacology - 2Filipino Nurses Central100% (3)
- Fundamentals of Nursing'09Document9 pagesFundamentals of Nursing'09Faiza100% (2)
- Aged Care QuestionsDocument9 pagesAged Care QuestionsElie RizkNo ratings yet
- MRCPCH - Important Skin DiseasesDocument42 pagesMRCPCH - Important Skin DiseasesarjumandNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Management of Patients With Enterocutaneous Fistulas: Practice and ProgressionDocument12 pagesNutritional Management of Patients With Enterocutaneous Fistulas: Practice and ProgressionKevin Howser T. ViNo ratings yet
- Chief Complaint FormatDocument3 pagesChief Complaint Formatkazniels100% (1)
- 15 - CCLS - PharmacologyDocument32 pages15 - CCLS - PharmacologyVENKATESH RAMSALINo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Geriatric AssessmentDocument87 pagesComprehensive Geriatric AssessmentNurrahmanita AzizaNo ratings yet
- BradiaritmiaDocument12 pagesBradiaritmiaYolita Satya Gitya UtamiNo ratings yet
- Bowel Training Guide for Constipation, Diarrhea and IrregularityDocument2 pagesBowel Training Guide for Constipation, Diarrhea and Irregularitydickie.gdrNo ratings yet
- New Recommendations According To 2022 ILCOR CoSTDocument1 pageNew Recommendations According To 2022 ILCOR CoSTMineTagraNo ratings yet
- BPHDocument20 pagesBPHHerly KakaNo ratings yet
- Viridiana Gonzalez - Conspiracy Theory EssayDocument4 pagesViridiana Gonzalez - Conspiracy Theory Essayapi-595456909No ratings yet
- Allen's Test (Wikipedia)Document2 pagesAllen's Test (Wikipedia)Anonymous LnWIBo1GNo ratings yet
- Malignant Disease of The JawsDocument26 pagesMalignant Disease of The JawsRawda NajjarNo ratings yet
- Nocardia: Gram-Positive Bacteria Found in SoilDocument3 pagesNocardia: Gram-Positive Bacteria Found in Soilsujithas0% (1)
- Or DR Nclex FormsDocument6 pagesOr DR Nclex FormsClarence MangíoNo ratings yet
- CLM PresentationDocument13 pagesCLM PresentationHSC UNITEDNo ratings yet
- Editing Exercise: Improving Grammar, Punctuation and FormalityDocument3 pagesEditing Exercise: Improving Grammar, Punctuation and FormalityMaiElGebaliNo ratings yet
- Reumatoid KELOMPOK 8Document11 pagesReumatoid KELOMPOK 8Ida FarizaNo ratings yet
- About Critical Care Nursing PDFDocument3 pagesAbout Critical Care Nursing PDFKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- X. Comprehensive Pathophysiology and Management of Ovarian CancerDocument3 pagesX. Comprehensive Pathophysiology and Management of Ovarian CancerlieselannjacobNo ratings yet
- Teknik Cuci Tangan BedahDocument8 pagesTeknik Cuci Tangan BedahRegia Verent MNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Pemberian Air Rebusan Daun Sirsak (Annona Muricata) Terhadap Penurunan Kadar Glukosa Darah Pada Mencit Diabetes MellitusDocument1 pagePengaruh Pemberian Air Rebusan Daun Sirsak (Annona Muricata) Terhadap Penurunan Kadar Glukosa Darah Pada Mencit Diabetes MellitusAgus StyawanNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Quarantine and Isolation GuidelinesDocument10 pagesCOVID-19 Quarantine and Isolation GuidelinesFraulein LiNo ratings yet
- ChecklistDocument14 pagesChecklistYooleen SanchezNo ratings yet
- Contact Lenses For Keratoconus: Moodi Kupperman B.SC SoflexDocument22 pagesContact Lenses For Keratoconus: Moodi Kupperman B.SC SoflexAndreea CristeaNo ratings yet