Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tissue Reviewer
Uploaded by
Fayena Jose0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views3 pagesTissue Reviewer
Uploaded by
Fayena JoseCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
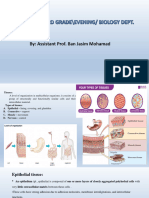
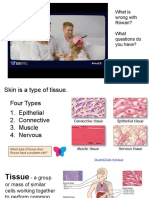
TISSUE 3 TYPES OF EPITHELIUM/SHAPES
1. Squamous (skwā′mŭs) cells are flat or scalelike.
INTRODUCTION
2. Cuboidal (cubelike) cells are cube-shaped—about as
1. Cells are organized in layers or groups to form tissues.
wide as they are tall.
2. Specialized intercellular junctions (tight junctions,
3. Columnar (tall and thin, similar to a column) cells
desmosomes, and gap junctions) connect cells.
tend to be taller than they are wide.
3. The study of tissues is called histology.
4. The four major types of human tissue are epithelial,
EPITHELIAL TISSUES
connective, muscle, and nervous.
1. General characteristics
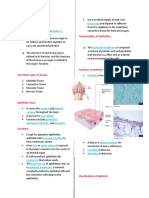
- Epithelial tissue covers all free body surfaces, forms
4 BASIC TYPES OF TISSUE
the inner lining of body cavities, lines hollow organs,
Epithelial tissue: Forms boundaries between different
and is the major tissue of gland
environments, protects, secretes, absorbs, filters
- Epithelial tissue or an epithelium is a sheet of cells that
• Lining of digestive tract organs and other hollow
covers a body surface or lines a body cavity (epithe =
organs
laid on, covering).
• Skin surface (epidermis
b. A basement membrane anchors epithelium to
Connective tissue: Supports, protects, binds other
connective tissue. Epithelial tissue lacks blood vessels,
tissues together
has cells that are tightly packed, and is continuously
• Bones
replaced.
• Tendons
c. It functions in protection, secretion, absorption,
• Fat and other soft padding tissue
excretion, filtration and sensory reception.
Muscle tissue: Contracts to cause movement
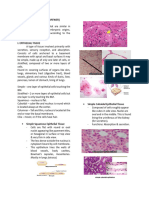
2. Simple squamous epithelium
• Muscles attached to bones (skeletal)
a. This tissue consists of a single layer of thin, flattened
• Muscles of heart (cardiac)
cells through which substances pass easily.
• Muscles of walls of hollow organs (smooth)
b. It functions in the exchange of gases in the lungs and
Nervous tissue: Internal communication
lines blood vessels, lymph vessels, and membranes
• Brain
within the thorax and abdomen.
• Spinal cord
3. Simple cuboidal epithelium
• Nerves
a. This tissue consists of a single layer of cube-shaped
cells
3 MAJOR TYPES OF EPITHELIAL TISSUE
b. It carries on secretion and absorption in the kidneys
1. Simple epithelium consists of a single layer of cells,
and various glands.
with each cell extending from the basement membrane
4. Simple columnar epithelium
to the free surface.
a. This tissue is composed of elongated cells whose
2. Stratified epithelium consists of more than one layer
nuclei are near the basement membrane.
of cells, but only the basal layer attaches the deepest
b. It lines the uterus and digestive tract, where it
layer to the basement membrane.
functions in protection, secretion, and absorption.
3. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium is a special
c. Absorbing cells often possess microvilli. d. This tissue
type of simple epithelium. The prefix pseudo- means
usually contains goblet cells that secrete mucus.
false, so this type of epithelium appears to be stratified
5. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
but is not. It consists of one layer of cells, with all the
a. This tissue appears stratified because the nuclei are at
cells attached to the basement membrane. There
two or more levels.
appear to be two or more layers of cells because some
b. Its cells may have cilia that move mucus over the
of the cells are tall and extend to the free surface,
surface of the tissue.
whereas others are shorter and do not extend to the
c. Its lines tubes of the respiratory system.
free surface.
6. Stratified squamous epithelium
a. This tissue is composed of many layers of cells; the
top layers are flattened.
b. It protects underlying cells from harmful (3) Holocrine glands release cells filled with
environmental effects. secretions.
c. It is the outer layer of the skin and lines the oral
cavity, esophagus, vagina, and anal canal.
7. Stratified cuboidal epithelium 5.3 CONNECTIVE TISSUES
a. This tissue is composed of two or three layers of 1. General characteristics
cube-shaped cells. a. Connective tissue connects, supports, protects,
b. It lines the larger ducts of the mammary glands, provides frameworks, fills spaces, stores fat, produces
sweat glands, salivary glands, and pancreas. blood cells, protects against infection, and helps repair
c. It functions in protection. damaged tissues.
8. Stratified columnar epithelium b. Connective tissue cells usually have considerable
a. The top layer of cells in this tissue contains elongated extracellular matrix between them.
columns. Cube-shaped cells make up the bottom layers. c. This extracellular matrix consists of fibers, a ground
b. It is in part of the male urethra and ductus deferens, substance, and fluid.
and parts of the pharynx. 2. Major cell types
c. This tissue functions in protection and secretion. a. Fibroblasts produce collagenous and elastic fibers.
9. Transitional epithelium b. Macrophages are phagocytes.
a. This tissue is specialized to become distended. c. Mast cells release heparin and histamine.
b. It lines the urinary bladder, ureters, and superior 3. Connective tissue fibers
urethra. a. Collagenous fibers are composed of collagen and
c. It helps prevent the contents of the urinary have great tensile strength.
passageways from diffusing out. b. Elastic fibers are composed of elastin and are elastic.
10. Glandular epithelium c. Reticular fibers are fi ne collagenous fibers.
a. Glandular epithelium is composed of cells specialized 4. Categories of connective tissues
to secrete substances. a. Connective tissue proper includes loose connective
b. A gland consists of one or more cells. tissue (areolar, adipose, reticular) and dense connective
(1) Exocrine glands secrete into ducts. tissue (dense regular, dense irregular, elastic).
(2) Endocrine glands secrete into tissue fluid or b. Specialized connective tissues include cartilage, bone,
blood. and blood.
c. Exocrine glands are classified according to the 5. Areolar tissue
organization of their cells. a. Areolar tissue forms thin membranes between organs
(1) Simple glands have ducts that do not branch and binds them.
before reaching the secretory portion. b. It is beneath the skin and between muscles.
(2) Compound glands have ducts that branch 6. Adipose tissue
repeatedly before the secretory portion. a. Adipose tissue is a specialized form of connective
(3) Tubular glands consist of simple epithelium- tissue that stores fat, cushions, and insulates.
lined tubes. b. It is found beneath the skin; in certain abdominal
(4) Alveolar glands consist of saclike dilations membranes; and around the kidneys, heart, and various
connected to the surface by narrowed ducts joints.
d. Exocrine glands are classified according to the 7. Reticular tissue
composition of their secretions. a. Reticular connective tissue largely consists of thin,
(1) Merocrine glands secrete watery fluids branched collagenous fibers.
without loss of cytoplasm. Most secretory cells b. It supports the walls of the liver, spleen, and
are merocrine. lymphatic organs.
(a) Serous cells secrete watery fluid 8. Dense regular connective tissue
with a high enzyme content. Dense regular connective tissue is largely composed of
(b) Mucous cells secrete mucus. strong, collagenous fibers that bind structures as parts
(2) Apocrine glands lose portions of their cells of tendons and ligaments.
during secretion. 9. Dense irregular connective tissue
Dense irregular connective tissue has thicker, randomly 2. Synovial membranes are composed of connective
distributed collagenous fibers and is found in the tissue only, and line joints.
dermis.
10. Elastic connective tissue
Elastic connective tissue is mainly composed of elastic 5.5 MUSCLE TISSUES
fibers and imparts an elastic quality to the walls of 1. General characteristics
certain hollow internal organs such as the lungs and a. Muscle tissue contracts, moving structures attached
blood vessels. to it.
11. Cartilage b. Three types are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle
a. Cartilage provides a supportive framework for various tissues.
structures. 2. Skeletal muscle tissue
b. Its extracellular matrix is composed of fi bers and a a. Muscles containing this tissue usually attach to bones
gel-like ground substance. and are controlled by conscious effort.
c. It lacks a direct blood supply and is slow to heal. b. Muscle cells are long and threadlike, containing
d. Most cartilaginous structures are enclosed in a several nuclei, with alternating light and dark cross-
perichondrium, which contains blood vessels. markings (striations).
e. Major types are hyaline cartilage, elastic cartilage, c. Muscle cells contract when stimulated by nerve
and fibrocartilage. impulses, then immediately relax when they are no
f. Cartilage is at the ends of various bones; in the ear; in longer stimulated.
the larynx; and in the pads between the bones of the 3. Smooth muscle tissue
spinal column, pelvic girdle, and knees. a. This tissue of spindle-shaped cells, each with one
12. Bone nucleus, is in the walls of hollow internal organs.
a. The extracellular matrix of bone contains mineral b. Usually it is involuntarily controlled.
salts and collagen. 4. Cardiac muscle tissue
b. Its cells usually form concentric circles around central a. This tissue is found only in the heart.
canals. Canaliculi connect the cells. b. Striated cells, each with a single nucleus, are joined
c. It is an active tissue that heals rapidly. by intercalated discs and form branched networks.
13. Blood c. Cardiac muscle tissue is involuntarily controlled
a. Blood is composed of cells suspended in fluid.
b. Blood cells are formed by special tissue in the hollow 5.6 NERVOUS TISSUES
parts of certain bones. 1. Nervous tissue is in the brain, spinal cord, and
peripheral nerves.
5.4 TYPES OF MEMBRANES 2. Neurons
1. Epithelial membranes a. Neurons sense changes and respond by transmitting
a. Serous membranes nerve impulses to other neurons or to muscles or
(1) Serous membranes line body cavities that do glands.
not open to the outside. b. They coordinate, regulate, and integrate body
(2) They are composed of epithelium and loose activities.
connective tissue. 3. Neuroglia
(3) Cells of serous membranes secrete watery a. Some of these cells bind and support nervous tissue.
serous fluid that lubricates membrane surfaces. b. Others carry on phagocytosis.
b. Mucous membranes c. Still others connect neurons to blood vessels.
(1) Mucous membranes line cavities and tubes d. Some are involved in cell-to-cell communication
opening to the outside of the body.
(2) They are composed of epithelium and loose
connective tissue.
(3) Cells of mucous membranes secrete mucus.
c. The cutaneous membrane is the external body
covering commonly called skin.
You might also like
- Anatomy - TissuesDocument43 pagesAnatomy - TissuesGleceree Filomeno100% (1)
- Ch05 Answer Key-TissuesDocument10 pagesCh05 Answer Key-TissuesGaveen CoatesNo ratings yet
- Tissue of The BodyDocument12 pagesTissue of The BodyJuliet Aira Cabero Quibilan100% (1)
- Chapter 2- Jnu Techniques in Cell and Molecular Biology - 複本Document40 pagesChapter 2- Jnu Techniques in Cell and Molecular Biology - 複本Wai Kwong ChiuNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- StainigDocument38 pagesStainigyuppie_raj2175No ratings yet
- Deulin e A Et Al Mechanics and Physics of Precise Vacuum MecDocument244 pagesDeulin e A Et Al Mechanics and Physics of Precise Vacuum MecHien TranNo ratings yet
- Types of Tissues: Lesson 02Document33 pagesTypes of Tissues: Lesson 02DASH100% (2)
- Chapter 4 TissuesDocument10 pagesChapter 4 TissuesAl-Shuaib Astami Son100% (1)
- Chapter 4 - Tissues Glands and MembranesDocument49 pagesChapter 4 - Tissues Glands and MembranesNess G. Mamasabulod100% (1)
- Tissues: Tissue: A Tissue Is A Collection of Cells Having Similar Origin, Structure, and FunctionDocument13 pagesTissues: Tissue: A Tissue Is A Collection of Cells Having Similar Origin, Structure, and FunctionnagahushanamNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Day 1 LessonDocument143 pagesWeek 1 Day 1 LessonTRIXIE CYRAH MIRANDA SALAVIANo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Tissue - The Living FabricDocument23 pagesChapter 4 Tissue - The Living FabricMariaNo ratings yet
- 03-Epithelial TissuesDocument9 pages03-Epithelial TissuesRehab OmerNo ratings yet
- BIOL111 Lab 3 TissuesDocument13 pagesBIOL111 Lab 3 TissuesdonnaNo ratings yet
- Common Characteristics of Most Types of Epithelial Tissue AreDocument2 pagesCommon Characteristics of Most Types of Epithelial Tissue AreGwen Llanes AmbronaNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument6 pagesTissuesyes noNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY TissuesDocument7 pagesANAPHY TissuesClarence MallariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document10 pagesChapter 4jenf7481No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ANAPHY NOTESDocument13 pagesChapter 4 ANAPHY NOTESShannelle SinciocoNo ratings yet
- 7 Structural Organisation in Animals - Notes - SampleDocument2 pages7 Structural Organisation in Animals - Notes - SampleManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 5 TISSUES GANDocument7 pagesActivity No. 5 TISSUES GANTORRES, EFRAIM MATTHEW S.No ratings yet
- CH 7Document9 pagesCH 7Ruchika Kumari, VIII-A, 3956100% (1)
- Animal TissueDocument14 pagesAnimal TissueSagar GavasNo ratings yet
- Histology Lec 1 & 2Document22 pagesHistology Lec 1 & 2Asma Ghazy100% (1)
- AnaPhyLec Midterms TissueDocument4 pagesAnaPhyLec Midterms TissueSoul YuNo ratings yet
- Simple Epithelium-Found in Areas That Require Stratified Epithelium - More Than One Layer of CellsDocument4 pagesSimple Epithelium-Found in Areas That Require Stratified Epithelium - More Than One Layer of CellsDimple Lexiry Gloria100% (1)
- Ikramullah RN BSN MPH: Tissues Types and FunctionsDocument62 pagesIkramullah RN BSN MPH: Tissues Types and FunctionsIkram UllahNo ratings yet
- Histology: (1) - Epithelial TissueDocument8 pagesHistology: (1) - Epithelial TissueDTM FHKNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument31 pagesTissuealiyyah aswinanda100% (1)
- Chapter-03 Structural Organisation in Animals: Animal TissueDocument5 pagesChapter-03 Structural Organisation in Animals: Animal TissueAravind ShabuNo ratings yet
- Chapter-03 Structural Organisation in Animals: Animal TissueDocument5 pagesChapter-03 Structural Organisation in Animals: Animal TissueAravind Shabu100% (1)
- Week 2 The Tissues MembranesDocument60 pagesWeek 2 The Tissues MembranesJeqtopher RoaNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument5 pagesEpithelial TissueMiss KilmoryNo ratings yet
- Tissues - Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesTissues - Anatomy and PhysiologyHan CallejaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Tissues ReviewerDocument9 pagesAnaphy Tissues ReviewerleyluuuuuhNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument22 pagesTissueRuhul Qudus NaimNo ratings yet
- Gen Zoo Animal TissuesDocument84 pagesGen Zoo Animal TissuesDale Gil JuliaNo ratings yet
- Tissues, Glands and Membranes: A. FunctionsDocument4 pagesTissues, Glands and Membranes: A. FunctionsRyan Cadorna FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument32 pagesAnaphy Reviewerpatientsafety100% (1)
- Anaphy - Tissue - Part 1Document5 pagesAnaphy - Tissue - Part 1Aileen DemaguilaNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument75 pagesAnimal TissuesFaithlyn Riche YocorNo ratings yet
- Histology LecDocument258 pagesHistology LecBan JMNo ratings yet
- Tissues: By: Ruth Abigail C. Valdez BSN, RNDocument62 pagesTissues: By: Ruth Abigail C. Valdez BSN, RNrJNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy Chap4 Tissues TransesDocument4 pagesAnaPhy Chap4 Tissues TransesSophia Margarette CawalingNo ratings yet
- Tissue Level ReviewerDocument9 pagesTissue Level ReviewerChloe Mikaela MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Histology ReviewerDocument11 pagesHistology ReviewerMaryell Denize LandichoNo ratings yet
- CH 099 TissuesDocument55 pagesCH 099 Tissuesalyssa bananNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument16 pagesHistologyJeong song parkNo ratings yet
- CH 7 - Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument8 pagesCH 7 - Structural Organisation in AnimalsLaxmiNo ratings yet
- Histology Presentation PDFDocument67 pagesHistology Presentation PDFAbd ElNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Reviewer Tissue and Integumentary SystemDocument7 pagesAnaphy Reviewer Tissue and Integumentary System10. Briol AlvinNo ratings yet
- Structural Organization in Animals - NotesDocument11 pagesStructural Organization in Animals - NotesAlfiya ShereefNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument11 pagesTissuesReyni DeysNo ratings yet
- Introtohistology LukegarbettDocument4 pagesIntrotohistology Lukegarbettapi-340693501No ratings yet
- Types of Tissue 13.01.2016Document18 pagesTypes of Tissue 13.01.2016Christian MontesNo ratings yet
- Histology 2018 1Document38 pagesHistology 2018 1Marvin Ndashimye100% (1)
- General Biology 2Document18 pagesGeneral Biology 2ayah eliviaNo ratings yet
- Module3 Bio - Sci.2 GenaralZoologyDocument11 pagesModule3 Bio - Sci.2 GenaralZoologyJahzel JacaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Levels of Organization in Animal ComplexityDocument61 pagesLecture 2 Levels of Organization in Animal ComplexityLouella Artates100% (1)
- MC 1 Midterm Notes (Anatomy and Physiology)Document14 pagesMC 1 Midterm Notes (Anatomy and Physiology)Aiza CereighneNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument12 pagesAnatomy & PhysiologyTyrNo ratings yet
- General Biology R Q3Document16 pagesGeneral Biology R Q3Maysheil GalarceNo ratings yet
- DANAHER CORP /DE/ 10-K (Annual Reports) 2009-02-25Document332 pagesDANAHER CORP /DE/ 10-K (Annual Reports) 2009-02-25http://secwatch.comNo ratings yet
- DAFTAR PUSTAKA FixDocument3 pagesDAFTAR PUSTAKA FixRegina YunitaNo ratings yet
- Cheek and Onion Peel Exp Xlass 9Document9 pagesCheek and Onion Peel Exp Xlass 9Rakshit YadavNo ratings yet
- Digital Holography MicrosDocument27 pagesDigital Holography MicrosRimple Poonia Dabas100% (1)
- Histochemistry: Historical Development and Current Use in PathologyDocument10 pagesHistochemistry: Historical Development and Current Use in PathologyiuventasNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles 2Document10 pagesCell Organelles 2Hardik tyagiNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Worksheet-PrintDocument2 pagesCell Organelles Worksheet-PrintmuraliMu0% (1)
- Tawoon Medical BrochureDocument10 pagesTawoon Medical Brochuremichael_schindl6525No ratings yet
- Botanical Society of AmericaDocument12 pagesBotanical Society of AmericaAndrew ButcherNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Biotechniques (Staining)Document13 pagesLesson Plan in Biotechniques (Staining)Ronel Pasalo Medina BatanganNo ratings yet
- Bacteria STQ3Document2 pagesBacteria STQ3LIM WEI KIAN HCINo ratings yet
- 7.1 Life Is CellularDocument4 pages7.1 Life Is CellularSafa-99No ratings yet
- Nis Elements enDocument20 pagesNis Elements enRaquel RochaNo ratings yet
- Lesson-3-Prokaryotes-and-Eukaryotes CellsDocument14 pagesLesson-3-Prokaryotes-and-Eukaryotes CellsKivo ZoshikoroNo ratings yet
- Auerbach M.S., Carrado K.a., Dutta P.K. Handbook of Layered Materials (CRC, 2004) (ISBN 0824753496) (659s)Document659 pagesAuerbach M.S., Carrado K.a., Dutta P.K. Handbook of Layered Materials (CRC, 2004) (ISBN 0824753496) (659s)Young Jun ChoNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesCell Parts Lesson PlanHeesung LeeNo ratings yet
- Understandings, Applications and Skills (This Is What You Maybe Assessed On)Document10 pagesUnderstandings, Applications and Skills (This Is What You Maybe Assessed On)beaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology The Human Experience 1st Edition Foster Test BankDocument16 pagesMicrobiology The Human Experience 1st Edition Foster Test Bankdavidnelsonseyjdmpoaz100% (13)
- Lecture 9 - 13.01.2023Document33 pagesLecture 9 - 13.01.2023Adnan Mohammad Adnan HailatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cell Structure and TaxoniomyDocument59 pagesChapter 3 Cell Structure and Taxoniomyjade jaymeNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument2 pagesEpithelial TissueEliannyNo ratings yet
- Environment MicrobiologyDocument16 pagesEnvironment Microbiologymohamed ishaqNo ratings yet
- The Application of Cellulose Acetate Replication Sheets in Enamel Wear InvestigationsDocument10 pagesThe Application of Cellulose Acetate Replication Sheets in Enamel Wear InvestigationsKara WhiteNo ratings yet
- DPP-03 - Cell The Unit of LifeDocument3 pagesDPP-03 - Cell The Unit of LifeSiazzzNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Microbiology BP303TDocument1 pagePharmaceutical Microbiology BP303TAdityaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Microscopic ImagingDocument15 pagesFundamentals of Microscopic ImagingTanzeer KaurNo ratings yet