Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab Exercise No. 3
Uploaded by
JOHN ISAAC BENITEZ0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesThis document is a laboratory exercise for a General Histology and Embryology course. It provides information about different types of connective tissue, including their structure, function, and microscopic representation. Students are asked to complete a table identifying each type of connective tissue - mucous, mesenchyme, loose areolar, dense regular, dense irregular, reticular, and adipose tissue - and drawing the microscopic representation of each.
Original Description:
asdasdasd
Original Title
Lab-exercise-no.-3 (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document is a laboratory exercise for a General Histology and Embryology course. It provides information about different types of connective tissue, including their structure, function, and microscopic representation. Students are asked to complete a table identifying each type of connective tissue - mucous, mesenchyme, loose areolar, dense regular, dense irregular, reticular, and adipose tissue - and drawing the microscopic representation of each.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesLab Exercise No. 3
Uploaded by
JOHN ISAAC BENITEZThis document is a laboratory exercise for a General Histology and Embryology course. It provides information about different types of connective tissue, including their structure, function, and microscopic representation. Students are asked to complete a table identifying each type of connective tissue - mucous, mesenchyme, loose areolar, dense regular, dense irregular, reticular, and adipose tissue - and drawing the microscopic representation of each.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE – CAVITE
SCHOOL OF DENTAL MEDICINE
General Histology and Embryology
Course Code: DHE1 21
NAME: DATE:
STUDENT NO.:
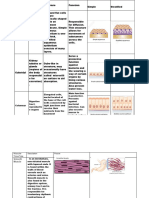
Laboratory Exercise No. 3 – CONNECTIVE TISSUE
I. Complete the table with drawing
CONNECTIVE TISSUE Structure and Function Microscopic representation
(Draw and identify the tissue)
Mucous Connective Tissue The main function of mucous is to keep
the tissue moist for example in respiratory
tract, including the mouth and nose. The
mucosa is composed of one or more layers
of epithelial cells that secrete mucus and
an underlhong lamina propria of loose
connective tissue.
Mesenchyme Connective Tissue It is a type of animal tissue that comprised
loose of cells embedded in a mesh of
proteins and fluid calle extracellular
matrix. It has a large nuclei which later
differentiate to form different cells of
connective tissues.
Loose Areolar Connective Tissue The function of this is binding organs and
their components together providing
elasticity when stretched and it acts as a
support structure for the epithelium. It
consist of Meshwork collagen, Elastic
tissue, and Reticular fibres.
Dense Regular Connective Tissue Dense regular connective tissue is present
in ligaments and tendons. A section of a
tendon in longitudinal plane is illustrated
in which some of the collagen fibers are
stretched and some are relaxed. A tendon
shows that it has a compact, regular, and
parallel arrangement of collagen fibers.
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue The function of dense connective tissue is
to protect the body from mechanical
stress. Dense irregular tissue has fibers
that are not arranged in parallel bundles as
in dense regular tissue.
Reticular Tissue The function of this tissue is to provide
support to the organs, tissue and
individual cells like adipose tissues and
muscles. They are found in series of
branching threads. Reticular fibers present
in the tissue are fragile, and together bond
to foram a meshwork or a fibrous skeleton
(stroma).
Adipose Tissue A small section of a mesentary of the
intestine is illustrated, in which large
accumulations of adipose (fat) cells are
organized into an adipose tissue. Adipose
tissue is fairly uncomplicated, All is
enclosed within a fibrous extracellular
matrix that is very well connected to
blood and lymph vessels.
You might also like
- Life Sciences Grade 10 Revision Material Term 2 - 2023Document28 pagesLife Sciences Grade 10 Revision Material Term 2 - 2023Linati Dawedi100% (1)
- Full Download Ebook PDF Legal and Ethical Issues For Health Professionals 5Th Edition Ebook PDF Docx Kindle Full ChapterDocument22 pagesFull Download Ebook PDF Legal and Ethical Issues For Health Professionals 5Th Edition Ebook PDF Docx Kindle Full Chapternicole.jenkins429100% (34)
- CH1 Path D&R AgamDocument34 pagesCH1 Path D&R Agam062100% (1)
- Tissues & Membranes: The Relationship Between Structure and Function of Epithelial TissuesDocument3 pagesTissues & Membranes: The Relationship Between Structure and Function of Epithelial Tissueskyla columnaNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissues 2Document71 pagesConnective Tissues 2Asma Aijaz100% (1)
- Tissue Gen Bio ReviewerDocument9 pagesTissue Gen Bio ReviewerAlfred CariñoNo ratings yet
- Human TissueDocument47 pagesHuman TissueAngelo Cadenas75% (4)
- AP Module4 Trans DiazDocument18 pagesAP Module4 Trans DiazJohn Rafael DiazNo ratings yet
- HISTOLOGY NOTES by Red (Connective)Document2 pagesHISTOLOGY NOTES by Red (Connective)Edzeal Bruan JrNo ratings yet
- BIOL 1409 - Animal - Tissues - LR - Lab Report 4Document11 pagesBIOL 1409 - Animal - Tissues - LR - Lab Report 4Tonya Oliver100% (1)
- Epithelial Tissue DefinitionDocument6 pagesEpithelial Tissue DefinitionRica NorcioNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument2 pagesConnective Tissueyuri dominxNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: Epithelial TissueDocument19 pagesAnimal Tissues: Epithelial TissueJnana YumnaNo ratings yet
- Definition and Types of Connective Tissue - KenhubDocument19 pagesDefinition and Types of Connective Tissue - Kenhubyigermalamanuel32No ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument31 pagesStructural Organisation in AnimalsVenom Gaming YTNo ratings yet
- Title of The Activity: Connective Tissue Objectives:: Ground SubstanceDocument3 pagesTitle of The Activity: Connective Tissue Objectives:: Ground SubstanceKristine PangahinNo ratings yet
- Tissue of The BodyDocument12 pagesTissue of The BodyJuliet Aira Cabero Quibilan100% (1)
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument61 pagesStructural Organisation in AnimalsGanesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue TypeDocument7 pagesEpithelial Tissue Typevaynegod5No ratings yet
- Awdal College Department of Health: General HistologyDocument24 pagesAwdal College Department of Health: General HistologyAyro Business CenterNo ratings yet
- Nadiyah Farhah Salsabila - Animal TissueDocument2 pagesNadiyah Farhah Salsabila - Animal TissueNadiyah SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Connective TissuesstudDocument53 pagesConnective TissuesstudDanial Sharizul100% (1)
- Tissues - Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesTissues - Anatomy and PhysiologyHan CallejaNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument37 pagesAnimal Tissueshero samilinNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Tissues - ObjectivesDocument7 pagesPlant and Animal Tissues - ObjectivesSyedrijal AkberNo ratings yet
- W4 Tissue Level of OrgDocument13 pagesW4 Tissue Level of OrgWisNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissues (BIOLOGY)Document38 pagesConnective Tissues (BIOLOGY)celestine adleyNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument33 pagesConnective Tissue20227730 PRACHI TOMAR100% (1)
- Lesson 4Document11 pagesLesson 4Semper Ann LawagueyNo ratings yet
- Directions For This Reading ActivityDocument5 pagesDirections For This Reading ActivityMariam RuizNo ratings yet
- Human Body OrganizationDocument11 pagesHuman Body OrganizationCay C. CordovaNo ratings yet
- 1.03 - Evidence of Science and Technology During The Ancient TimesDocument13 pages1.03 - Evidence of Science and Technology During The Ancient Timeselio pascualNo ratings yet
- TISSUEDocument15 pagesTISSUEDhananjay GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Textus ConnectivusDocument43 pagesTextus ConnectivusShafiraNo ratings yet
- Lab 05 Connective Tissue ProperDocument3 pagesLab 05 Connective Tissue ProperSarwar Jafar100% (1)
- Animal and Plant TissuesDocument5 pagesAnimal and Plant TissuesShajara Anglacer AnacanNo ratings yet
- Structural Organization in Animals Animal TissuesDocument3 pagesStructural Organization in Animals Animal TissuesHadiya FatimaNo ratings yet
- Structural OrganizationDocument119 pagesStructural OrganizationAVS CONo ratings yet
- Ix BioDocument4 pagesIx Biokartikvarshney98No ratings yet
- Mc1 Types of Tissues 2 4Document5 pagesMc1 Types of Tissues 2 4Karl Devin CorderoNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in Animals: Animal TissuesDocument34 pagesStructural Organisation in Animals: Animal Tissuesafsas rpNo ratings yet
- 25 4.3 Connective Tissue Supports and ProtectsDocument17 pages25 4.3 Connective Tissue Supports and ProtectsJimmy Jamarolin JacaNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissues: Kashif MajeedDocument30 pagesConnective Tissues: Kashif Majeedarmish junaid100% (1)
- General Biology 2Document18 pagesGeneral Biology 2ayah eliviaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument42 pagesChapter 5 Anatomy and PhysiologyNickythaP.PutriNo ratings yet
- BIO122 - CHAPTER 7 Part 1Document53 pagesBIO122 - CHAPTER 7 Part 1lili100% (1)
- Connective TissueDocument4 pagesConnective Tissueneil100% (1)
- Week 3 Module 3 Organization of The Human Body - Tissue (B)Document21 pagesWeek 3 Module 3 Organization of The Human Body - Tissue (B)Kishie Jeyds LaycoNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 Tissues Animal Tissues: Tissue Is A Cellular Organizational Level Intermediate Between Cells andDocument5 pagesChapter-6 Tissues Animal Tissues: Tissue Is A Cellular Organizational Level Intermediate Between Cells andMonika MehanNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument31 pagesTissuealiyyah aswinanda100% (1)
- A P Topic 5 SummaryDocument9 pagesA P Topic 5 SummaryMax Delvalle100% (1)
- Module3 Bio - Sci.2 GenaralZoologyDocument11 pagesModule3 Bio - Sci.2 GenaralZoologyJahzel JacaNo ratings yet
- Baic Tissues For Introductory Module. Part 1Document9 pagesBaic Tissues For Introductory Module. Part 1abdiNo ratings yet
- Chapter-03 Structural Organisation in Animals: Animal TissueDocument5 pagesChapter-03 Structural Organisation in Animals: Animal TissueAravind Shabu100% (1)
- Chapter-03 Structural Organisation in Animals: Animal TissueDocument5 pagesChapter-03 Structural Organisation in Animals: Animal TissueAravind ShabuNo ratings yet
- Tissues Part 2Document4 pagesTissues Part 2Monika Mehan100% (1)
- Connective Tissue ProperDocument15 pagesConnective Tissue ProperFilkal BasnetNo ratings yet
- Tissue (Notes) (1) 6roDocument4 pagesTissue (Notes) (1) 6romljnura3No ratings yet
- EEU2020 Adfinex HDocument23 pagesEEU2020 Adfinex HZainab Jamal SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document35 pagesLecture 4raja11160No ratings yet
- Thorax Lab QuizDocument30 pagesThorax Lab QuizJOHN ISAAC BENITEZNo ratings yet
- Thorax Lab QuizDocument26 pagesThorax Lab QuizJOHN ISAAC BENITEZNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise No. 2Document4 pagesLab Exercise No. 2JOHN ISAAC BENITEZNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise No. 1Document4 pagesLab Exercise No. 1JOHN ISAAC BENITEZNo ratings yet
- Hypoxemic Respiratory FailureDocument70 pagesHypoxemic Respiratory FailureMohamed Rikarz Ahamed RikarzNo ratings yet
- MoPSE Science Module Volume 1 - FINAL4WEBDocument336 pagesMoPSE Science Module Volume 1 - FINAL4WEBSibusiso Ntomby NkalaNo ratings yet
- PromeristemDocument12 pagesPromeristemRosselle NoyoalNo ratings yet
- Vascular and Non-Vascular PlantsDocument3 pagesVascular and Non-Vascular PlantsLeonardo PigaNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy & Histology of Liver: Prepared By: Anish Dhakal (Aryan) MBBS Student Patan Academy of Health SciencesDocument21 pagesGross Anatomy & Histology of Liver: Prepared By: Anish Dhakal (Aryan) MBBS Student Patan Academy of Health SciencesAjeng TunjungputriNo ratings yet
- BTL-4000 Electrotherapy: User S GuideDocument36 pagesBTL-4000 Electrotherapy: User S GuideGorka Sáenz ÁlvarezNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Biomarkers: Ella Melissa L. Pembimbing: Dr. Dr. Tinny E. H., SPPK (K)Document53 pagesCardiac Biomarkers: Ella Melissa L. Pembimbing: Dr. Dr. Tinny E. H., SPPK (K)hariogieNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Human Sperm and Ovum (With Comparison Chart) - Bio DifferencesDocument1 pageDifference Between Human Sperm and Ovum (With Comparison Chart) - Bio DifferencesAhmediqraNo ratings yet
- Students How 2Document5 pagesStudents How 2Bailey MennemeierNo ratings yet
- B. Pathophysiology A) Schematic Diagram (Book - Based) : Wasting Blood Glucose LevelDocument2 pagesB. Pathophysiology A) Schematic Diagram (Book - Based) : Wasting Blood Glucose LevelCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano50% (2)
- Blood VesselsDocument4 pagesBlood VesselsCrazy StrangerNo ratings yet
- Malaria 2018Document11 pagesMalaria 2018gerges8723No ratings yet
- Guyton Respiration QuestionsDocument23 pagesGuyton Respiration QuestionsAli WalayNo ratings yet
- Bio TestDocument3 pagesBio TestMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia in The Newborn and Infant: M.A. Sperling O. Escobar O. Pinhas-HamielDocument2 pagesHypoglycemia in The Newborn and Infant: M.A. Sperling O. Escobar O. Pinhas-HamielDaniela CioboataNo ratings yet
- Final Draft Completed Ebook ManuscriptDocument40 pagesFinal Draft Completed Ebook ManuscriptVic- iNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System ReviewerDocument5 pagesCardiovascular System ReviewerAnna Sofia ReyesNo ratings yet
- Pathology Important Solved BCQs 5th Semester MBBS + 3rd Semester BDS LUMHSDocument57 pagesPathology Important Solved BCQs 5th Semester MBBS + 3rd Semester BDS LUMHSNaheed Jatoi100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Nursing Transes 2Document13 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Transes 2Louise Torres100% (1)
- Neutrophil Maturity in CancerDocument11 pagesNeutrophil Maturity in Cancerxwxdazhong407No ratings yet
- Gizi Vitamin EDocument97 pagesGizi Vitamin EMaya DasmaselaNo ratings yet
- Behavior Analysis and Learning A Biobehavioral Approach Sixth Edition 6Th Edition Full ChapterDocument41 pagesBehavior Analysis and Learning A Biobehavioral Approach Sixth Edition 6Th Edition Full Chaptercharlie.heiliger836100% (20)
- Pinnularia PresentationDocument10 pagesPinnularia PresentationIjaz Ahmed100% (1)
- The Bone Marrow Niche For Haematopoietic Stem CellsDocument21 pagesThe Bone Marrow Niche For Haematopoietic Stem CellsHitomi-No ratings yet
- Visual-Vestibular Interaction and Treatment of Dizziness: A Case ReportDocument5 pagesVisual-Vestibular Interaction and Treatment of Dizziness: A Case ReportsoumenNo ratings yet
- Clotting Time Macromethod: Utilized Larger Amount of BloodDocument4 pagesClotting Time Macromethod: Utilized Larger Amount of BloodGerly MaglangitNo ratings yet
- Dent Pain Management: Developments inDocument18 pagesDent Pain Management: Developments inCaglarBursaNo ratings yet
- Biology Practical-1Document78 pagesBiology Practical-1Praxeda SiimaNo ratings yet