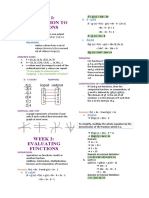
WEEK 1: FUNCTION AND RELATION Composition of Functions
The Composition of function f with g is denoted by f°g(x) and is
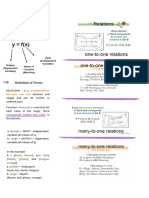
RELATION a set of ordered pairs (x, y).
defined by the equation:
DOMAIN the 1st coordinate in a relation.
(f ° g)(x) = f (g(x))
RANGE the 2nd coordinate in a relation.
Solution:
FUNCTION a relation in which each element of the domain 1. Replace x by g(x)
corresponds to exactly one element of the range. 2. Replace g(x) by the given function.
3. Apply distributive method
How to determine if a graph represents a function or
not? 4. Combine Similar Terms
● VERTICAL LINE TEST A graph represents a function only
WEEK 4: RATIONAL FUNCTION
if no vertical line intersects the graph more than one
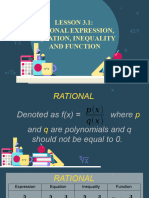
point. Rational Function a function that is a fraction and has the
EVALUATION OF FUNCTION means to substitute a variable with property that both its numerator and denominator are
its given number or expression. polynomials.
Polynomial is an expression consisting of variables and
WEEK 2: OPERATION OF FUNCTION (ADDITION,
coefficients that involves only the operations of addition,
SUBTRACTION, AND MULTIPLICATION) subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer
FUNCTION a relation in which each element of the domain exponents of variables.
corresponds to exactly one element of the range. Rational Expression a ratio of two polynomials, if f is a rational
FOIL Method a technique for distributing two binomials. expression, then f can be written in the form p/q where p and q
are polynomials
Fundamentals Operation on Functions Rational Equation is an equation that contains rational
Formulas:
expression
● Addition/ Sum Function:
Rational Inequality is an inequality that contains rational
expression.
● Subtraction/ Difference Function: Rational Function a function of the form
where p(x) and q(x) are polynomial functions, and q(x) is not a
zero function.
● Multiplication/ Product Function:
Rational Equation, Rational Inequality, and Rational
● Division/ Quotient Functions
Function:
Rational Equation (= sign)
Rational Inequality(<, >, ≥, ≤ sign)
Laws of Exponent
Rational Function
m n m+n
● x ●x =x
● (xm)n = xmn
Solving Rational Equations and Rational Inequality
● (xy)n = xnyn Steps in solving Rational Expression:
1. Determine the LCD of all the denominators
WEEK 3: OPERATION OF FUNCTION (DIVISION 2. Multiply each term of the equation by the LCD.
AND COMPOSITION) 3. Solve the resulting equation.
Steps in Rational Inequalities:
Quotient of Functions
Solution: 1. Determine the LCD of all the denominators
1. Substitute the value of the two functions. 2. Multiply each term of the equation by the LCD.
2. Apply factoring; Cancel out common factors. 3. Solve the resulting equation.
3. Simplify 4. Rearrange the inequality as a single fraction
p(x)/q(x) on the left side and 0 is on the right side.
5. Locate the x-values for which the rational expression
is zero or undefined.
1
� WEEK 5: RATIONAL FUNCTION: INTERCEPTS, WEEK 7: EXPONENTIAL FUNCTION, EQUATION,
ZEROES, AND ASYMPTOTES AND INEQUALITY
INTERCEPTS is a point where the graph of the rational function EXPONENTIAL EXPRESSIONS an expression of the form a. bx−c+d,
intersects the x- or y- axis. where b>0, b≠1
ASYMPTOTE is a line to which the function’s graph draws closer
without touching it. EXPONENTIAL EQUATION an equation involving exponential
HORIZONTAL ASYMPTOTE the horizontal line y=b of the function expressions that can be solved for all x values satisfying the
f if f(x) gets closer to b as x increases or decreases without equation.
bound.
● If n<d the horizontal asymptote is y=0 EXPONENTIAL INEQUALITY an inequality involving exponential
○ r(x) = x/6x2-1 expressions that can be solved for all x values satisfying the
● If n=d the horizontal asymptote is y=a/b, where a is inequality
the leading coefficient of the numerator and b is the
leading coefficient of the denominator.
○ r(x) = 7-4x/5x+1 EXPONENTIAL FUNCTION a function involving exponential
= -4/5 expression showing a relationship between the independent
● If n>d, there is no horizontal asymptote. There is a variable x and dependent variable y or f(X). A function of the
slant/oblique asymptote. form f(x) = bx or y = bx where b > 0, b ≠ 1
4 2
○ r(x) = 2x -1/1-x
VERTICAL ASYMPTOTE the vertical line x=a of a function x if the
graph of f either increases or decreases without bound as the
x-values approach a from the right or left.
EXPONENTIAL FUNCTION: ZEROES, INTERCEPTS,
AND ASYMPTOTES
WEEK 6: INVERSE FUNCTION
INVERSE FUNCTION is a relation reversing the process ● To find the zero of the function, equate it to 0 and
performed by any function f(x). solve for x.
● To find the y-intercept, let x=0 then solve for y.
HORIZONTAL LINE TEST is a convenient method that can ● To find the x-intercept, ley y=0 then solve for x.
determine if the inverse of a function is also a function. If the ● To find the asymptote look for the constant.
horizontal line intersects the graph of a function in all places at
exactly one point, then the given function has an inverse that is
WEEK 8: EXPONENTIAL FUNCTION, EQUATION,
also a function.
AND INEQUALITY
LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS all logarithmic functions can be
VERTICAL LINE TEST is a test used to determine if the given rewritten in exponential form.
graph is a function or not.
COMMON LOGARITHM is any logarithm with base 10.
Steps in solving the inverse of a one-to-one function:
1. Write the function in the form y=f(x) NATURAL LOGARITHM the base of a natural logarithm is the
2. Interchange the x and y variables. special number e.
3. Solve for y in terms of x.
4. Replace y with f-1. y=bx → x=logby (X equals the logarithm of y to the base b)
Formula in converting Celsius to Fahrenheit:
Exponen. Form Log Form
23=8 log28=3
Formula in converting Fahrenheit to Celsius:
52=25 log5(25)=2
32=9 log39=2