Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Solubility Data Assignment
Uploaded by
Tracy NewKirkOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Solubility Data Assignment
Uploaded by
Tracy NewKirkCopyright:
Available Formats
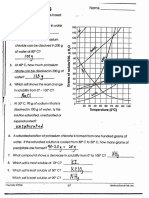
Solubility Data for Sugar
160
Solubility (g/100 g H2O)
140
130
120
110
100
90
80
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110
Temperature (°C)
Analysis
1. A student conducted an experiment on the solubility of a sugar in water. The graph shows her results.
Which inference can logically be made from the data?
a) The solubility of sugar increases with temperature
b) The solubility of sugar decreases with temperature
c) The temperature increases as sugar is added to the solution
d) The solution must be heated to 50 °C before any sugar dissolves
2. Using the graph, which of the following is the most logical prediction for the solubility of sugar at
temperatures above 50°C?
a) The solubility will be constant
b) The solubility will increase
c) The solubility will decrease
d) The solubility will be zero
3. Which of the following is true of the solution at 10°C as compared to the solution at 40°C?
a) The solution is more concentrated at 40°C
b) The solution is more concentrated at 10°C
c) The solution is saturated at 40°C
d) The sugar is not dissolving at either temperature
4. Using the graph, determine the point at which the solution becomes saturated. Explain what saturated is,
and what evidence you see that the solution is saturated.
5. Explain what you would expect to see if the temperature was increased to 110°C?
6. Draw a diagram showing the solute and solvent particle ratios at 10°C and at 60°C
7. What is the Independent Variable? Dependent Variable?
You might also like
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Molecular Mass Determination Using Boiling Point and Freezing Point LabDocument4 pagesMolecular Mass Determination Using Boiling Point and Freezing Point LabDan TranNo ratings yet
- Solubility Lab-Student-GuideDocument2 pagesSolubility Lab-Student-Guideitz tyreezyNo ratings yet
- G4 Chem BoilingDocument5 pagesG4 Chem BoilingNashwaAlinsangaoNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Ismatterarounduspure 01Document6 pages09 Science Ismatterarounduspure 01sureshabcdNo ratings yet
- Solubility Curves, Solutions & Molarity Answer KeysDocument5 pagesSolubility Curves, Solutions & Molarity Answer KeysABCD100% (1)
- Unit 6 Test Review ChemDocument5 pagesUnit 6 Test Review Chemapi-483662721No ratings yet
- Reading A Solubility CurveDocument4 pagesReading A Solubility CurveMar GomezNo ratings yet
- Solubility CurvesDocument37 pagesSolubility Curvesapi-298247873100% (1)
- CHP 6 IX - CHMDocument3 pagesCHP 6 IX - CHMAdvent SolutionsNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument18 pagesSolutionsShantanu Gontia100% (1)
- Lab Report Experiment 2Document7 pagesLab Report Experiment 2Nurin Nazifa100% (2)
- Solubility Curve WorksheetDocument5 pagesSolubility Curve WorksheetJammellia WilliamsNo ratings yet
- 3210 06 07 SolubilityDocument3 pages3210 06 07 SolubilityKenneth WevoyaNo ratings yet
- WS SolubilityChartDocument2 pagesWS SolubilityChartMuhammad_Syaki_1428No ratings yet
- Lab SolubilityDocument3 pagesLab SolubilityKenneth WevoyaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Temperature On SolubilityDocument8 pagesEffect of Temperature On SolubilityMuzahid KhatryNo ratings yet
- L-4 9AM2 13 JulyDocument22 pagesL-4 9AM2 13 JulyEshu JainNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Experiment 3 (Student)Document3 pagesLab Manual Experiment 3 (Student)214297No ratings yet
- Table1.1 Types of Dispersed SystemsDocument7 pagesTable1.1 Types of Dispersed SystemsIsabella Gamulo LabatosNo ratings yet
- Experiment #1 / Unit 10 Solubility Curve of Potassium NitrateDocument2 pagesExperiment #1 / Unit 10 Solubility Curve of Potassium Nitrateapi-368121935100% (1)
- Solubility Curve Practice Problems Worksheet 1Document3 pagesSolubility Curve Practice Problems Worksheet 1judith cueNo ratings yet
- Boiling Point ElevationDocument6 pagesBoiling Point ElevationJohn Gil Peñas OdsinadaNo ratings yet
- Solubility Curve Practice Problems Worksheet 1Document2 pagesSolubility Curve Practice Problems Worksheet 1MobiNo ratings yet
- Solubility Curve Practice Problems Worksheet 1Document2 pagesSolubility Curve Practice Problems Worksheet 1Unexpected TheoryNo ratings yet
- LAB REPORT - Effect of Temperature On Solubility of A SaltDocument5 pagesLAB REPORT - Effect of Temperature On Solubility of A SaltOlivia RidleyNo ratings yet
- WRDTHDSHFJEJEVEJEIDocument21 pagesWRDTHDSHFJEJEVEJEIAshleyNo ratings yet
- Solubility and TemperatureDocument4 pagesSolubility and Temperaturehenry bhoneNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Solubility Curve WorksheetDocument2 pagesKami Export - Solubility Curve WorksheetdddsdsNo ratings yet
- Mixtures and Their Separations: TOPIC: Solubility of Solids in WaterDocument15 pagesMixtures and Their Separations: TOPIC: Solubility of Solids in WaterNicaliaNo ratings yet
- 48 Practice Problems For CH 17Document9 pages48 Practice Problems For CH 17Hasantha PereraNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties ReviewerDocument1 pageColligative Properties ReviewerRugi Vicente RubiNo ratings yet
- Experiment ManualDocument29 pagesExperiment ManualSamiksha SinghNo ratings yet
- Bell Ringer: - What Does Being "Saturated" Mean?Document9 pagesBell Ringer: - What Does Being "Saturated" Mean?PualeilehuaNo ratings yet
- Solutions Practice-17Document2 pagesSolutions Practice-17api-368121935No ratings yet
- Mohamed El Sayed - Titration Lab ReportDocument7 pagesMohamed El Sayed - Titration Lab ReportoklolsubNo ratings yet
- gr10 Chem Revision Sheet MCQ Questions CH 16 T.MariamDocument5 pagesgr10 Chem Revision Sheet MCQ Questions CH 16 T.Mariamهخه •No ratings yet
- Defense Paper FormatDocument14 pagesDefense Paper Format23-1-01249No ratings yet
- Effects of Temperature On SolubilityDocument5 pagesEffects of Temperature On Solubilityvinsmoke1No ratings yet
- Exp 5 Physical ChemistryDocument8 pagesExp 5 Physical ChemistryHuiling GohNo ratings yet
- Solubility and Solubility CurveDocument39 pagesSolubility and Solubility CurveSymon Alonzo VersozaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document20 pagesExperiment 1ApipMNNo ratings yet
- Collin, Chem Lab Report 3Document3 pagesCollin, Chem Lab Report 3Juan EstradaNo ratings yet
- Solubility and Temperature: Answer KeyDocument4 pagesSolubility and Temperature: Answer KeyHannah SeokNo ratings yet
- Yoddha24 DPP 1to7 - LiquidSolutionDocument19 pagesYoddha24 DPP 1to7 - LiquidSolutionKunalNo ratings yet
- Solutions Homework - 2 (R2)Document17 pagesSolutions Homework - 2 (R2)A KNo ratings yet
- Beer Lambert ExDocument11 pagesBeer Lambert ExHarsh DesaiNo ratings yet
- CH 13 Review 2013Document14 pagesCH 13 Review 2013FariaFaruqChoaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7: Investigating The Change of Volume in The Change of Temperature (Document2 pagesExperiment 7: Investigating The Change of Volume in The Change of Temperature (EDWIN SIMBARASHE MASUNUNGURENo ratings yet
- Solubility PracticalDocument1 pageSolubility PracticalChrisaundria LuceroNo ratings yet
- MRT MDocument8 pagesMRT MSrijan JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Honors Chemistry Solubility Lab 35Document7 pagesHonors Chemistry Solubility Lab 35alyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4Document3 pagesExperiment 4Jepoy Nisperos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Experiment 17 Colligative PropertiesDocument4 pagesExperiment 17 Colligative PropertiesLILYNo ratings yet
- (2S) States & Solubility LabDocument2 pages(2S) States & Solubility LabAndrew HeffnerNo ratings yet
- Sci Rep SampleDocument11 pagesSci Rep SampleJhun Rey MoralesNo ratings yet
- Changing The Rate of A Reaction (Part I)Document2 pagesChanging The Rate of A Reaction (Part I)Shahid Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Titration of Vinegar-1reDocument4 pagesTitration of Vinegar-1reCandice ChuaNo ratings yet
- Phychem Exp 1Document5 pagesPhychem Exp 1Alyssa OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Chem ActivityDocument6 pagesChem ActivityYuri MonkeyNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane and Cell Transport WebquestDocument6 pagesCell Membrane and Cell Transport WebquestTracy NewKirkNo ratings yet
- Chemical Elements ProjectDocument3 pagesChemical Elements ProjectTracy NewKirkNo ratings yet
- Element Poster ProjectDocument1 pageElement Poster ProjectTracy NewKirkNo ratings yet
- States of Matter WebquestDocument2 pagesStates of Matter WebquestTracy NewKirkNo ratings yet
- TranscriptDocument9 pagesTranscriptTracy NewKirkNo ratings yet
- Tiny Volcano LabDocument2 pagesTiny Volcano LabTracy NewKirkNo ratings yet
- The Rock Cycle NOTESDocument22 pagesThe Rock Cycle NOTESTracy NewKirkNo ratings yet
- Convergent Plate Boundaries Guided NotesDocument2 pagesConvergent Plate Boundaries Guided NotesTracy NewKirkNo ratings yet
- DivergentPlateBoundary NOTESDocument10 pagesDivergentPlateBoundary NOTESTracy NewKirkNo ratings yet
- Convergent Plate Boundaries NOTESDocument15 pagesConvergent Plate Boundaries NOTESTracy NewKirkNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA NOTESDocument16 pagesDNA and RNA NOTESTracy NewKirkNo ratings yet
- Divergent Plate Boundaries Guided NotesDocument1 pageDivergent Plate Boundaries Guided NotesTracy NewKirkNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates: Protein: Protein: Protein: Lipids (Fat) : Lipids (Fat) : Lipids (Fat)Document3 pagesCarbohydrates: Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates: Protein: Protein: Protein: Lipids (Fat) : Lipids (Fat) : Lipids (Fat)Tracy NewKirkNo ratings yet
- Volcano ProjectDocument2 pagesVolcano ProjectTracy NewKirkNo ratings yet
- Lesson - Atoms, Ions & IsotopesDocument1 pageLesson - Atoms, Ions & IsotopesTracy NewKirkNo ratings yet
- Calculating Weight and Mass: Weight (N) Mass (KG) X Acceleration Due To Gravity (M/sDocument1 pageCalculating Weight and Mass: Weight (N) Mass (KG) X Acceleration Due To Gravity (M/sTracy NewKirkNo ratings yet
- Transform Plate Boundaries Guided NotesDocument1 pageTransform Plate Boundaries Guided NotesTracy NewKirkNo ratings yet