Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Water Transportation Processes: Student Tasks
Uploaded by
Atiya MuhammadOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Water Transportation Processes: Student Tasks
Uploaded by
Atiya MuhammadCopyright:
Available Formats
Water transportation processes
Waves and tidal currents transport material in four ways. The dissolved and suspended
load moves with the natural stream flow, while the heavier bed load bounces or rolls
along the floor of the stream.
Student tasks
1. Unscramble the words to identify the ways that water can transport or move material
along.
NTSOOULI ITTOACRN
TANSTOAIL USONSNPEIS
2. Write a sentence to explain each of the four processes.
3. Draw a labelled diagram to illustrate each of the four processes.
4. Look at the image below. Name and explain the transport processes that you think
are present in this coastal environment.
An aerial view of Coastguard Spit, Cape Cod, Massachusetts
Image used courtesy of the National Park Service, U.S. Department of the Interior
http://www.nps.gov/caco/naturescience/cape-cod-ecosystem-monitoring.htm
© www.teachitgeography.co.uk 18702 Page 1 of 3
Water transportation processes
5. Look at the image below. Name and explain the transport processes you think are at
work in this river.
Pont y Pair Bridge, Betws-y-Coed
© Copyright Peter and licensed for reuse under this Creative Commons Licence
http://www.geograph.org.uk/reuse.php?id=2412602
6. Explain the conditions affecting the processes of water transportation. Consider the
different conditions between river and coastal environments.
Extension tasks
7. Draw an annotated sketch of each photograph to show and summarise the water
transport processes at work.
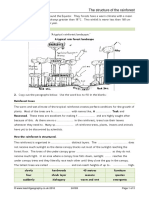
8. Use the diagram on the right, to note the
similarities and differences you can see
between water and wind transportation
processes.
Wind transportation processes
Image used courtesy of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration
http://science.nasa.gov/science-news/science-at-nasa/2002/06dec_dunes
© www.teachitgeography.co.uk 18702 Page 2 of 3
Water transportation processes
Teaching notes
The processes of water transport processes are relevant to studies of any river or coastal
environment. This activity can be used in the classroom as part of a topic study or as
preparation for part of a fieldwork activity. It also provides an opportunity to use and
develop skills.
Suggested answers
1 Unscrambled processes:
SOLUTION TRACTION
SALTATION SUSPENSION
2 Completed table:
Process Explanation of the process
Minerals are dissolved and carried along
SOLUTION
in the flow of the water
SALTATION Pebbles are bounced along the bed
TRACTION Large boulders are rolled along the bed or the river
Finer sands and silt are carried along
SUSPENSION
in the flow of the water
3 Use the following link to a reference diagram to illustrate the four processes.
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/geography/images/riv_004.gif
Photographs (4 & 5) – Students should be able to distinguish between a low energy
coastal and a high energy fluvial environment.
6. Answers should include references to rock types, climate differences, high and
low energy environments e.g. differences between processes in a limestone or
granite areas, during floods, storms, gradient changes, changes in velocity etc.
7 This activity provides an opportunity to encourage pupils to look closely at photos
to apply knowledge from the activity.
8 Saltation and suspension are common processes in both wind and water
transportation. Creep is the equivalent of traction. Solution is not a valid
process for transportation by wind.
© www.teachitgeography.co.uk 18702 Page 3 of 3
You might also like
- Rivers SOWDocument17 pagesRivers SOWGemma Pullan-ThompsonNo ratings yet
- 10 5923 J Ajee 20130306 03Document5 pages10 5923 J Ajee 20130306 03MichaelNo ratings yet
- River Metamorphosis, NeyyarDocument25 pagesRiver Metamorphosis, NeyyarDr.Thrivikramji.K.P.No ratings yet
- Introduction to the Physics of Cohesive Sediment Dynamics in the Marine EnvironmentFrom EverandIntroduction to the Physics of Cohesive Sediment Dynamics in the Marine EnvironmentNo ratings yet
- Chapter End Questions (Pg.31) : Short ResponseDocument2 pagesChapter End Questions (Pg.31) : Short Responsekzy1234No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S002216941200368X MainDocument14 pages1 s2.0 S002216941200368X MainÁlvarez AndrésNo ratings yet
- Modeling Sediment Transport in Coral Reef EnvironmentsDocument7 pagesModeling Sediment Transport in Coral Reef EnvironmentsJnr FiavaaiNo ratings yet
- PAPER Portoroz w97Document13 pagesPAPER Portoroz w97Harshvardhan Hemant SamvatsarNo ratings yet
- Cohesive Sediments in Open Channels: Erosion, Transport and DepositionFrom EverandCohesive Sediments in Open Channels: Erosion, Transport and DepositionNo ratings yet
- Three-Dimensional Numerical Modelling of The FlushingDocument9 pagesThree-Dimensional Numerical Modelling of The Flushing074BCE174 Suman Rana MagarNo ratings yet
- Numerical Modelling of Reservoir Sedimentation For Sustainable Storage Capacity A Geospatial ApproachDocument8 pagesNumerical Modelling of Reservoir Sedimentation For Sustainable Storage Capacity A Geospatial Approachwcsac2022No ratings yet
- Lesson 8: Currents: Standards AddressedDocument9 pagesLesson 8: Currents: Standards AddressedKarla PereyraNo ratings yet
- Sedimentological Parameterization of Shallow-MarinDocument19 pagesSedimentological Parameterization of Shallow-MarinDoan Hong ThangNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Water Ess Powerpoint 2021Document95 pagesTopic 4 Water Ess Powerpoint 2021zihan yuanNo ratings yet
- Modelling Erosion, Sediment Transport and Sediment Yield - UNESCO PDFDocument263 pagesModelling Erosion, Sediment Transport and Sediment Yield - UNESCO PDFGuilherme FiorotNo ratings yet
- 2 Depositional Environments As Interpreted From Primary Sedimentary and Stratigraphic SequencesDocument158 pages2 Depositional Environments As Interpreted From Primary Sedimentary and Stratigraphic SequencesTefy Soñadora AustralNo ratings yet
- Krause-Mapping Australias WaterbodiesDocument28 pagesKrause-Mapping Australias WaterbodiesZigmārs RendenieksNo ratings yet
- Metamorphism and Massive Sulphide Generation in Oceanic CrustDocument12 pagesMetamorphism and Massive Sulphide Generation in Oceanic CrustDody AlfayedNo ratings yet
- Modelling Cohesive Sediment Transport in Rivers: Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering February 2011Document11 pagesModelling Cohesive Sediment Transport in Rivers: Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering February 2011agussantoso_stNo ratings yet
- Sum 12Document10 pagesSum 12suman_154521055No ratings yet
- Research Article Experimental Study On Capillary Water Migration Characteristics of Tailings With Different Particle SizesDocument12 pagesResearch Article Experimental Study On Capillary Water Migration Characteristics of Tailings With Different Particle SizesEmanuel RicardoNo ratings yet
- 10 11648 J Cse 20200402 11Document16 pages10 11648 J Cse 20200402 11ebagalan2022No ratings yet
- Water On Earth LPDocument12 pagesWater On Earth LPapi-261388349No ratings yet
- The Tide-Dominated Han River Delta, Korea: Geomorphology, Sedimentology, and Stratigraphic ArchitectureFrom EverandThe Tide-Dominated Han River Delta, Korea: Geomorphology, Sedimentology, and Stratigraphic ArchitectureNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Module Assessment AnswersDocument5 pagesHydrology Module Assessment AnswersVENUS B. FLORESNo ratings yet
- Freshwater Ecosystems and BiodiversityDocument13 pagesFreshwater Ecosystems and Biodiversityhaneefak034No ratings yet
- The Effect of Groynes On Rivers PDFDocument58 pagesThe Effect of Groynes On Rivers PDFSeun QuadriNo ratings yet
- Fu 1Document35 pagesFu 1dgdfgdfNo ratings yet
- Experiments With Weathering, Erosion and Deposition For The Earth Science Regents CourseDocument10 pagesExperiments With Weathering, Erosion and Deposition For The Earth Science Regents CourseLembert CasinilloNo ratings yet
- Circulation Patterns in a Reef LagoonDocument28 pagesCirculation Patterns in a Reef LagoonAzhafiz AbdullahNo ratings yet
- How To Write ProposalDocument25 pagesHow To Write ProposalsolomonNo ratings yet
- The Basin-Wide Two-Dimensional Model of Sediment Production and Transportation For Estuary Sediment SimulationDocument11 pagesThe Basin-Wide Two-Dimensional Model of Sediment Production and Transportation For Estuary Sediment SimulationdequanzhouNo ratings yet
- Wilfordetal 2004Document7 pagesWilfordetal 2004Raveen SinghNo ratings yet
- Peter Robins PaperDocument7 pagesPeter Robins PaperArief Danial RahmanNo ratings yet
- Environmental Degradation A Review On The PotentiaDocument8 pagesEnvironmental Degradation A Review On The PotentiaRaynaldiNo ratings yet
- Choi 2015Document7 pagesChoi 2015Ahmad IhyasolihinNo ratings yet
- Sediment TransportDocument346 pagesSediment TransportAnwar AdemNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Water Cycle Connecting Earth Systems WCAGDocument4 pagesEarth Science Water Cycle Connecting Earth Systems WCAGMercy CatogNo ratings yet
- School of Engineering Colegio de DagupanDocument10 pagesSchool of Engineering Colegio de Dagupanjek vinNo ratings yet
- Sediment Transport Mechanics and Bed Formation ProcessesDocument6 pagesSediment Transport Mechanics and Bed Formation ProcessesselahNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Thesis TopicsDocument8 pagesHydrology Thesis TopicsPaySomeoneToWritePaperSingapore100% (1)
- Motion in The Ocean: Ocean Currents Lesson PlanDocument17 pagesMotion in The Ocean: Ocean Currents Lesson PlanNaga Nagendra100% (1)
- Geosciences: Distinguishing Between Deep-Water Sediment Facies: Turbidites, Contourites and HemipelagitesDocument43 pagesGeosciences: Distinguishing Between Deep-Water Sediment Facies: Turbidites, Contourites and HemipelagitesUgik GeoNo ratings yet
- Methods For Medium-Term Prediction of The Net Sediment Transport by WavesDocument13 pagesMethods For Medium-Term Prediction of The Net Sediment Transport by WavesLazaros NtoanidisNo ratings yet
- ABEN70a LR02 Briones Rachel DDocument5 pagesABEN70a LR02 Briones Rachel DRACHEL BRIONESNo ratings yet
- Tracking Historical Storm Records From High-Barrier Lagoon Deposits On The Southeastern Coast of Hainan IslandDocument15 pagesTracking Historical Storm Records From High-Barrier Lagoon Deposits On The Southeastern Coast of Hainan IslandJorge ZamoranoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Guide in Earth and Life Science: (S11/ES-If-14)Document7 pagesLesson Guide in Earth and Life Science: (S11/ES-If-14)MariaYsaDaganNo ratings yet
- Evacuation of Sediments From ReservoirsDocument280 pagesEvacuation of Sediments From Reservoirsjoaoaugusto79No ratings yet
- Coastal Education & Research Foundation, Inc. Journal of Coastal ResearchDocument13 pagesCoastal Education & Research Foundation, Inc. Journal of Coastal ResearchJnr FiavaaiNo ratings yet
- Hilgerson Hal 1Document12 pagesHilgerson Hal 1Riyo RiyoNo ratings yet
- 1-s2.0-S0309170809001870-mainDocument13 pages1-s2.0-S0309170809001870-mainAvinash SajwanNo ratings yet
- Modeling Oceanic Transport of Floating Marine DebrisDocument26 pagesModeling Oceanic Transport of Floating Marine DebrisRikiJooNo ratings yet
- Week 1 of Empowerment TechnologiesDocument4 pagesWeek 1 of Empowerment TechnologiesJohnKierCorbitaNo ratings yet
- Ocean Modelling: John C. Warner, Brandy Armstrong, Ruoying He, Joseph B. ZambonDocument15 pagesOcean Modelling: John C. Warner, Brandy Armstrong, Ruoying He, Joseph B. Zambonjorge godoyNo ratings yet
- Modelling Coastal Sediment Transport For Harbour Planning: Selected Case StudiesDocument25 pagesModelling Coastal Sediment Transport For Harbour Planning: Selected Case StudiesMonika KshNo ratings yet
- 3 Curriculum Guides Mathematics 10.09.13Document264 pages3 Curriculum Guides Mathematics 10.09.13Atiya MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Tropical rainforest soil and humus layersDocument2 pagesTropical rainforest soil and humus layersAtiya MuhammadNo ratings yet
- 2pGdbdCDEembrwoAFLaohg - Virtual Learning Environments VLE - JiscDocument2 pages2pGdbdCDEembrwoAFLaohg - Virtual Learning Environments VLE - JiscAtiya MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Questions: Rivers HexbusterDocument3 pagesQuestions: Rivers HexbusterAtiya MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Arrange The Cards in The Correct Order: Freeze Thaw WeatheringDocument3 pagesArrange The Cards in The Correct Order: Freeze Thaw WeatheringAtiya MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Student Tasks: The Structure of The RainforestDocument3 pagesStudent Tasks: The Structure of The RainforestAtiya MuhammadNo ratings yet
- 3 Ways Webinar - WorkbookDocument6 pages3 Ways Webinar - WorkbookAtiya MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Soils Blockbuster Questions: © WWW - Teachitgeography.co - Uk 2012 18616 Page 1 of 1Document1 pageSoils Blockbuster Questions: © WWW - Teachitgeography.co - Uk 2012 18616 Page 1 of 1Atiya MuhammadNo ratings yet
- 00 F 96 FDocument6 pages00 F 96 FAtiya MuhammadNo ratings yet
- How To Record Your Screen and Create Engaging ScreencastsDocument11 pagesHow To Record Your Screen and Create Engaging ScreencastsAtiya MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Rites of Acceptance For Altar Servers PDFDocument3 pagesRites of Acceptance For Altar Servers PDFJohn Carl Aparicio100% (1)
- Packaging Materials and Handling Technique: Dr. Ranjeet SinghDocument48 pagesPackaging Materials and Handling Technique: Dr. Ranjeet Singharon demagiba100% (1)
- Understanding and Quantifying Mountain TourismDocument84 pagesUnderstanding and Quantifying Mountain TourismfloridNo ratings yet
- Blackmer Pump Parts ListDocument2 pagesBlackmer Pump Parts ListFelipe Ignacio PaillavilNo ratings yet
- What Is The Kingdom of GodDocument10 pagesWhat Is The Kingdom of GodSunil ChelladuraiNo ratings yet
- Audit Keselamatan Jalan Pada Jalan Yogyakarta-Purworejo KM 35-40, Kulon Progo, YogyakartaDocument10 pagesAudit Keselamatan Jalan Pada Jalan Yogyakarta-Purworejo KM 35-40, Kulon Progo, YogyakartaSawaluddin SawalNo ratings yet
- DM3xxx Accessory List LeafletDocument2 pagesDM3xxx Accessory List LeafletAdvantec SrlNo ratings yet
- Siemens 810dDocument13 pagesSiemens 810dAdo ŠehićNo ratings yet
- Vitamin and Mineral Contents of Gongronema Latifolium LeavesDocument3 pagesVitamin and Mineral Contents of Gongronema Latifolium LeavesFrida Febriani IsnanisafitriNo ratings yet
- dSPACE CLP1104 Manual 201663013420Document172 pagesdSPACE CLP1104 Manual 201663013420meghraj01No ratings yet
- Worthy - Elevation WorshipDocument1 pageWorthy - Elevation WorshipSabine J.100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan Boyle's LawDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan Boyle's LawTeacher Derick Daet86% (7)
- Monthly Fire Extinguisher Inspection ChecklistDocument2 pagesMonthly Fire Extinguisher Inspection ChecklistisaacbombayNo ratings yet
- Melese Hotel ST ReportDocument74 pagesMelese Hotel ST ReportKidist MollaNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Science - Summer 2011 - The Universe Is CreativeDocument84 pages21st Century Science - Summer 2011 - The Universe Is CreativeMatthew EhretNo ratings yet
- The Affinity Laws of Centrifugal PumpsDocument5 pagesThe Affinity Laws of Centrifugal Pumpssba98No ratings yet
- Airway Management in The Critically Ill: ReviewDocument9 pagesAirway Management in The Critically Ill: ReviewQuarmina HesseNo ratings yet
- Altivar ATV61HU55N4 CatalogueDocument4 pagesAltivar ATV61HU55N4 CatalogueEugen Marius BadescuNo ratings yet
- Aam April 2023Document198 pagesAam April 2023Adhitya DewantaraNo ratings yet
- CFD Answer KeyDocument12 pagesCFD Answer KeyRaahini IzanaNo ratings yet
- Line Pack Presentation - Dec 2018Document7 pagesLine Pack Presentation - Dec 2018Goran JakupovićNo ratings yet
- Solvent Extraction: Please Submit Question 4 For MarkingDocument3 pagesSolvent Extraction: Please Submit Question 4 For MarkingThembi Matebula100% (1)
- Water Spray Nozzle: Fire Fighting Equipment Data SheetDocument7 pagesWater Spray Nozzle: Fire Fighting Equipment Data SheetJosef MadronaNo ratings yet
- 2024 Drik Panchang Telugu Calendar v1.0.1Document25 pages2024 Drik Panchang Telugu Calendar v1.0.1Sreekara GsNo ratings yet
- Determine PH by PH Indicator and Universal IndicatorDocument3 pagesDetermine PH by PH Indicator and Universal IndicatorhaleelNo ratings yet
- 88 Dean StreetDocument36 pages88 Dean StreetPatrick BatyNo ratings yet
- ct62010 2013Document165 pagesct62010 2013Amit Poddar100% (2)
- Caelus TT - Caelus Product TrainingDocument93 pagesCaelus TT - Caelus Product TrainingYader Daniel Ortiz CerdaNo ratings yet
- Roland Berger Hot Trends InconstructionDocument24 pagesRoland Berger Hot Trends InconstructionJavier ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Revision 2 Pages Grammar Drills 106078Document3 pagesRevision 2 Pages Grammar Drills 106078Ligia Dragomir100% (1)