DIVISION OF PAMPANGA
S.T.A.R METHOD. USE OF DECODING IN IMPROVING THE WORDED
PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS IN MATHEMATICS OF GRADE 8
STUDENTS OF STO.ROSARIO HIGH SCHOOL
By
ZALDY R. MENDOZA JR.
Teacher
October 2016
S.T.A.R METHOD. USE OF DECODING IMPROVE THE WORDED PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS 1
� DIVISION OF PAMPANGA
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Title Page………………………………………………………………. 1
Table of Contents …………………………………………………….. 2
Introduction
Review of Related Literature and Studies …………………………. 3
Conceptual Framework………………………………………………..8
Statement of the Problem ………………………………………….....9
Hypothesis ……………………………………………………………..9
Significance of the Study …………………………………………….10
Scope and Limitations ………………………………………………11
Method
Type of Research ………………………………………………….. ..12
Respondents and Sampling Method ……………………………….12
Instruments ………………………………………………………….. 13
Data Collection Procedure and Ethical Considerations ……….. 13
Data Analysis ……………………………………………………….. 14
S.T.A.R METHOD. USE OF DECODING IMPROVE THE WORDED PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS 2
� DIVISION OF PAMPANGA
Introduction and Review of Related Literature and Studies
In the absence of intensive instruction and intervention, students with
mathematics difficulties and disabilities lag significantly behind their peers
(Jitendra et.al., (PAKIKABIT LA RENG GANG AUTHORS) 2013; Sayeski &
Paulsen, 2010). Conservative estimates indicate that 35% to 50% of students
struggle with mathematics knowledge and application skills in general education
classrooms, indicating the presence of mathematics difficulty (Mazzocco, 2007).
Children’s poor performance with mathematical word problems is a trend that
the researcher became aware of very early. This concept is an interest that has
been taken in by those who are involved in Mathematics education. Difficulties
in this category involve children not being able to decode the words used in a
word problem, not comprehending a sentence, not understanding specific
vocabulary and not having confidence or the ability to concentrate when
reading.
The debate stems over what affects students and their ability to be good
problem solvers. Themes found while conducting research which creates a
successful problem solving classroom include 1) word problem comprehension,
S.T.A.R METHOD. USE OF DECODING IMPROVE THE WORDED PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS 3
� DIVISION OF PAMPANGA
2) understanding math vocabulary, 3) translating key words to mathematical
representations, 4) having prior knowledge, 5) confidence in themselves, and 6)
teacher instructional techniques.
According to the learning principle, in order for students to solve problems,
they need to have a conceptual and procedural understanding of the problem. In
addition, confidence and perseverance are qualities necessary to start and finish
when a challenge is given. The students also need to be able to select and
apply mathematical representations. This skill was key to my research because
the students were to identify operation words (decoding) in word problems and
represent them with correct symbols. Students were then not only asked to take
those representations and use reasoning to decide upon an appropriate problem
solving strategy, but to also give a justifiable statement as to their decision. My
last expectation was for students to be able to communicate their findings to
other classmates and myself. In showing their thought process, a connection
was made between different mathematical concepts and how they built upon
one another.
According to the assessment of the researcher during the school year
2016-2107, one of the problems arises in the classroom is the low scores
obtained by the Grade 8 students on test items that requires problem solving
skills. In an attempt to find solution to improve the skills in solving worded
S.T.A.R METHOD. USE OF DECODING IMPROVE THE WORDED PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS 4
� DIVISION OF PAMPANGA
problem and raise the academic performance not only in Mathematics but also
in other subject that requires this kind of skills like Science, the researcher will
take methodical studies on the issues contributing to this weak point.
The researcher used the critical thinking made evaluation to identify problem
that need to address immediately such as the most important, most urgent, most
relevant and most doable among gaps. Collected and recorded results of least
learned in periodical examination in past three school years and results of the
formative and summative assessment of the first quarter are strong evidences
that the problem is really alarming and affects the grades of the learners. The
used of Gap Analysis, area focus, target group and baseline data as tools to
compare on the standard, it is evident that the learners have common problems
and which is actually seen inside the classroom. Out of 154 students of Grade 8
student under my class; 91students still unable to analyze the worded problem
and answer the questions correctly and only 63 students can analyze and
answer worded problem correctly.
If proven successful, the use of decoding could increase the students’
ability to solve problems. The students could also gain confidence at the
academic and emotional levels while working individually and in groups. Their
knowledge of mathematical operation words and problem solving strategies may
give them the confidence to not only attempt, but to solve
S.T.A.R METHOD. USE OF DECODING IMPROVE THE WORDED PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS 5
� DIVISION OF PAMPANGA
mathematical problems they encounter. This newfound knowledge has the
capacity to lead to self-confidence, which is needed in their career as a student
and contributing citizen.
“The mathematical language that we use (symbols, pictures, words, and
numbers) is sometimes unique (only used by mathematicians) or is taken from
everyday language and turned into something else (i.e. table)” (Kotsopoulos,
2007, p. 302). Sometimes students are quick to only look at the numbers and
then put operation symbols between them in one-step problems. These students
are rushing into finding a calculation (Lee, 2007). Hegarty, Mayer, and Monk
(1995) performed a study at the college level on the different types of reading
errors made by two types of problem solvers—successful and unsuccessful.
They found that unsuccessful problem solvers had more difficulties than
successful problem solvers in translating the word problem to mathematical
representations because they were more focused on the numbers than on
informative words within the problem. Learning how to find these key words in a
word problem is a key ingredient to being a successful problem solver and must
be modeled within the classroom.
The model of education typical of 20th century classrooms was effective
for that era of human history, but the ‘knowledge society’ we now live in
requires new thinking about what constitutes effective and engaging teaching
and learning. Teachers are now faced with the challenge that “former
S.T.A.R METHOD. USE OF DECODING IMPROVE THE WORDED PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS 6
� DIVISION OF PAMPANGA
conceptions of knowledge, minds and learning no longer serve a world where
what we know is less important that what we are able to do with knowledge in
different contexts.”( Friesen, 2013).
This study concerns whether or not decoding has any effect on word
problem solving, primarily being able to select a strategy from the given
information. The topic becomes the priority of the researcher because
mathematics educators have consistently struggle with students and word
problem solving instruction. Furthermore, this research will investigate the
effects of decoding word problems on students’ abilities to determine what
problem solving strategy to use to solve a word problem. The literature
reviewreflects the key components of this research—reading, comprehension,
translation, instructional methods, problem solving steps and strategies,
confidence, and prior mathematical knowledge.
The study may reiterate what Fuentes (1988) and Maikos-Diegnan (2000)
believe to be important in problem solving, which is reading and vocabulary.
S.T.A.R METHOD. USE OF DECODING IMPROVE THE WORDED PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS 7
� DIVISION OF PAMPANGA
Conceptual Framework
Independent Variable Dependent Variable
Students’ Worded
S.T.A.R. Method Problem Solving
Skills
Figure 1. Research Paradigm
The above figure shows the paradigm of the study, it covers the
independent and dependent variables. The independent variable include the use
of decoding which is the S.T.A.R. Method and the dependent variable is the
Students’ Worded Problem Solving Skills. S.T.A.R. Method involves:
S— Search the word problem.
T— Translate the words into an equation in picture form
A— Answer the problem
R— Review the problem.
The categories of the types of questions pertained to the follow areas: 1)
decoding, 2) choosing a problem solving strategy, 3) justifying a problem solving
strategy, 4) setting up the problem, or 5) justifying their answer.
S.T.A.R METHOD. USE OF DECODING IMPROVE THE WORDED PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS 8
� DIVISION OF PAMPANGA
Statement of the Problem
The ultimate aim of this study is to determine the effectiveness of
S.T.A.R. Method as a decoding process to improve the worded problem solving
skills of Grade 8 students in Mathematics of Sto. Rosario High School, S.Y.
2016-2017.
Specifically, it seeks answer to the following questions:
1. What is the level of skills in analyzing and solving worded problem of
Grade 8 students in Mathematics before the exposure to STAR
method?
2. What is the level of skills in analyzing and solving worded problem of
Grade 8 students in Mathematics after the exposure to STAR Method?
3. Is there a significant difference on the level of skills in analyzing and
solving worded problem of Grade 8 students in Mathematics before
and after the exposure to STAR Method?
Hypothesis
This study is guided by the hypothesis:
1. There is no significant difference on the level of skills in analyzing and solving
worded problem of Grade 8 students in Mathematics before and after the
exposure to STAR Method.
S.T.A.R METHOD. USE OF DECODING IMPROVE THE WORDED PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS 9
� DIVISION OF PAMPANGA
Significance of the Study
This study will be essential and important in the field of Mathematics
education. It will show the effects of the new proposed technique in teaching
worded problem in Mathematics in uplifting the proficiency level of the students.
Findings and results of this study will ultimately benefit the following:
Students. They are the primordial beneficiaries as respondents of this
study. The knowledge and experiences gained may use by the students to
motivate themselves to strive harder in their studies. Moreover, this will serve as
motivation to uplift their performance in Mathematics.
Teachers. The result of the study may serve as a guide to remind teachers
on their role in providing intervention such as decoding in solving worded
problem to improve their performance in Mathematics and other related
subjects. They will be able to formulate, help and facilitate improvements in
solving worded problems.
School Administrators. The findings of the study will be beneficial to the
administrators in managing their respective institution and serve as an
opportune venue to encourage teachers to teach with dedication in meeting the
needs of the students.
Community. The study will also be important to the community as a
whole, because quality students will be an asset of the society in towards
nation-building.
S.T.A.R METHOD. USE OF DECODING IMPROVE THE WORDED PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS 10
� DIVISION OF PAMPANGA
Future Researchers. The researcher ultimately believes that the results of this
study will help the future researchers to conduct an in-depth study or similar
subject using other variables.
Scope and Limitations
The respondents of this study will be the two sections of Grade 8 in Sto.
Rosario High School. The study will be delimited on the use of S.T.A.R. Method
(Decoding) in improving the worded problem solving skills of Grade 8 students
in Mathematics of Sto. Rosario High School, Minalin, Pampanga, S.Y. 2016-
2017.
S.T.A.R METHOD. USE OF DECODING IMPROVE THE WORDED PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS 11
� DIVISION OF PAMPANGA
Type of Research
The researcher will use the quasi-experimental design in which the researcher
will use an experimental group and control group as part of the study. As stated
by Baker, Shinn, and Briers (2007), it is designed to conceptualize the study and
its specific aims or purposes.
The researchers will use comparative study to show facts about comparing the
capability of the Grade 8 students in terms of understanding concepts and
improving skills in solving worded problem. This will further investigate the
effects of Decoding in improving the worded problem solving skills of Grade 8
students in Mathematics.
Respondents and Sampling Method
The 103 Grade 8 students of Sto. Rosario High School, Minalin,
Pampanga, S.Y. 2016-2017 will be the respondents of this study, likewise, total
enumeration will be employed in this study.
Provide table of the respondents
S.T.A.R METHOD. USE OF DECODING IMPROVE THE WORDED PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS 12
� DIVISION OF PAMPANGA
Instrument
A teacher made pre-test and post test will be used by the researcher as
instrument of this study. The test will undergo content validation in order to
make sure that right questions will be given to the respondents. Experts in
Mathematics will be asked to validate the test.
Data Collection Procedure and Ethical Consideration
Upon the approval of the action research proposal, the teacher will
administer the pre-test on the two participating group. The researcher will teach
Mathematics lessons in different technique, control group (Group B) will not be
exposed to the intervention while the experimental group (Group A) using the
S.T.A.R. Method Decoding as intervention.
S.T.A.R METHOD. USE OF DECODING IMPROVE THE WORDED PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS 13
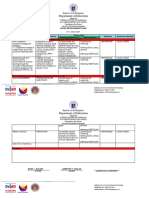
� Activities Target Period Data Needed
1. Submission of AR Proposal
October 2016 AR Proposal
2. Collection of data (before
the conduct of the study) November 2016 Pre-test
3.The conduct of the research November 2016 – DLL, Decoding
activity. January 2017 intervention
4.Collection of data (after the
January 2017 Posttest
conduct of the study)
5.Treatment and
Interpretation of data.
2nd week February 2017 AR Manuscript
6.Submission of AR to the
Division Office for approval.
S.T.A.R METHOD. USE OF DECODING IMPROVE THE WORDED PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS 14
� DIVISION OF PAMPANGA
The researcher will keep in mind the ethical considerations for this study,
such as the experiences of the participants during study. The researcher will
refrain from making judgments or comments that may have affected the
confidence or perceptions of the participants. The researcher will consider the
potential impact of his or her research on those affected.
Data Analysis
To determine the effectiveness of S.T.A.R. Method (Decoding) in
improving the worded problem solving skills of Grade 8 students in
Mathematics, t-test analysis will be employed in this study.
The pretest scores of the selected control and experimental groups will be
compared using independent t test. Moreover, if the pretest scores are normally
S.T.A.R METHOD. USE OF DECODING IMPROVE THE WORDED PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS 15
�distributed, a variance ratio test will be performed to determine whether t test for
groups with equal or unequal variance will be used.
If the pretest scores of the two randomly selected groups turn out to be
significantly different, another group of pupils/students will have to be selected
and the pretest scores will again be compared. The final control and
experimental groups should be comparable at baseline in terms of S.T.A.R.
Method (Decoding).
After the intervention, the posttest scores will also be compared following
the same procedures mentioned for the pretest scores.
DIVISION OF PAMPANGA
P-values less than 0.05 will be considered statistically significant.
Statistical computations will be performed using Stata.
S.T.A.R METHOD. USE OF DECODING IMPROVE THE WORDED PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS 16
� DIVISION OF PAMPANGA
S.T.A.R METHOD. USE OF DECODING IMPROVE THE WORDED PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS xvii
� DIVISION OF PAMPANGA
S.T.A.R METHOD. USE OF DECODING IMPROVE THE WORDED PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS 1
� DIVISION OF PAMPANGA
S.T.A.R METHOD. USE OF DECODING IMPROVE THE WORDED PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS 1
� DIVISION OF PAMPANGA
S.T.A.R METHOD. USE OF DECODING IMPROVE THE WORDED PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS 2
� DIVISION OF PAMPANGA
S.T.A.R METHOD. USE OF DECODING IMPROVE THE WORDED PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS 3
� DIVISION OF PAMPANGA
S.T.A.R METHOD. USE OF DECODING IMPROVE THE WORDED PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS 4
� DIVISION OF PAMPANGA
1 space
S.T.A.R METHOD. USE OF DECODING IMPROVE THE WORDED PROBLEM SOLVING SKILLS 5