Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mindmap Bio320 Chapter 4 Protist Protozoa
Uploaded by
nursuraya wahida0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views1 page1) Amoeboids are unicellular organisms that move and engulf food using pseudopodia and reproduce asexually through binary fission. Some pathogens like Entamoeba histolytica cause human dysentery.
2) Foraminiferans are marine organisms that secrete chalky shells with pores and extend cytoplasmic projections to catch prey. Some live on the ocean floor while others are plankton. Dead shells can help identify sedimentary rock layers.
3) Actinopods are marine plankton with long filamentous projections called axopods that help entangle prey. Most have algal endosymbionts and use their ax
Original Description:
MINDMAP BIO320 CHAPTER 4 PROTIST PROTOZOA
Original Title
MINDMAP BIO320 CHAPTER 4 PROTIST PROTOZOA
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) Amoeboids are unicellular organisms that move and engulf food using pseudopodia and reproduce asexually through binary fission. Some pathogens like Entamoeba histolytica cause human dysentery.
2) Foraminiferans are marine organisms that secrete chalky shells with pores and extend cytoplasmic projections to catch prey. Some live on the ocean floor while others are plankton. Dead shells can help identify sedimentary rock layers.
3) Actinopods are marine plankton with long filamentous projections called axopods that help entangle prey. Most have algal endosymbionts and use their ax
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views1 pageMindmap Bio320 Chapter 4 Protist Protozoa
Uploaded by
nursuraya wahida1) Amoeboids are unicellular organisms that move and engulf food using pseudopodia and reproduce asexually through binary fission. Some pathogens like Entamoeba histolytica cause human dysentery.
2) Foraminiferans are marine organisms that secrete chalky shells with pores and extend cytoplasmic projections to catch prey. Some live on the ocean floor while others are plankton. Dead shells can help identify sedimentary rock layers.
3) Actinopods are marine plankton with long filamentous projections called axopods that help entangle prey. Most have algal endosymbionts and use their ax
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
unicellular -soil, freshwater, ocean and parasitic
asymmetric body form and continually change shape
move and engulf food by pseudopodia
Amoeboids Reproduce asexually by binary fission
Entamoeba hystolitica - human dysentery
Acanthamoeba sp. infections in contact lens users
Marine organisms that secretes chalky
many chambered tests with pores,
cytoplasmic projections can be extended to catch prey.
endosymbiotic with unicellular algae
Foraminiferan
live ocean floor, others as plankton. e.g. Globigerina
Dead forams settle on the bottom of the ocean.
markers to help identify sedimentary rock layers
marine plankton organisms
with long, filamentous cytoplasmic projections called axopods
A cluster of microtubules strengthens each axopod.
Prey become entangled in these axopods
Actinopods Most of actinopods e.g. Actinophrys have algal endosymbiont
Axopods increase the surface area - floating
Prey can be phagocytize by the thin layer of cytoplasm
Some known as radiolarians - glassy shells made of silica
Mostly unicellular (a feware colonial)
with spherical or elongated body
CHAPTER 4 - PROTOZOA a single central nucleus, and one/many long,
whiplike flagella.
Move by lashingflexible flagella
Some engulf food by forming pseudopodia like amoeba
Zooflagellates Heterotrophic.Free-living or endosymbionts.
e.g Trichonymphs live in the guts of termites.
(Zoomastigophora)
digest cellulose in the wood the termites eat
can cause disease e.g. Trypanosoma;
causes African sleeping sickness
Read symptoms of African Sleeping Sickness
Diplomonad e.g. Giardia intestinalis causes
backpackers’diarrhea
Unicellular organisms,possess flexible outer
coverage called pellicle
thousand fine, short, hairlike cilia
trichocysts, organelles that discharge
filaments to aid trapping and holding prey.
Ciliates (Ciliophora) Some are sessile, and although motile they prefer
attach to substrate
Ciliates have two kinds of nuclei
asexual process called conjugation
Large group of parasitic
Lack of specific structures e.g. cilia, flagella or pseudopodia
Apicomplexans some produce sporozoits (small infective agents transmitted
to the next host)
Plasmodium which cause malaria
Prepared by: Haji Muzamil Haji Mustaffa, Ph.D
UiTM Cawangan Pahang
You might also like
- This Study Resource Was: Animal-Like ProtozoaDocument1 pageThis Study Resource Was: Animal-Like Protozoaayunna ayunniNo ratings yet
- 2 Protista (15p)Document15 pages2 Protista (15p)Olanrewaju AgodirinNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Protista: Yes or NoDocument17 pagesKingdom Protista: Yes or Nomacybnz100% (1)
- Eukarya: Characteristics Life Cycle Energy Locomotion Practical Application 1 Appearance Evolution DiplomonadsDocument5 pagesEukarya: Characteristics Life Cycle Energy Locomotion Practical Application 1 Appearance Evolution DiplomonadsAdrian HelmNo ratings yet
- Enperiment For Spotting-3Document18 pagesEnperiment For Spotting-3Debayan Bhattacharyya class:- 11-ANo ratings yet
- Phylum CtenophoraDocument2 pagesPhylum Ctenophoraabdulmaliqopeyemi04No ratings yet
- Week 9Document87 pagesWeek 9Louela Jean EspirituNo ratings yet
- Reviewer On EukaryotesDocument6 pagesReviewer On EukaryotesAlaica Joice B. JaboneteNo ratings yet
- General Properties of ProtozoaDocument19 pagesGeneral Properties of ProtozoaYsabella LlanetaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Zoology 10th EditionDocument5 pagesChapter 9 - Zoology 10th EditionmariaNo ratings yet
- BIO 101-Lecture 3-ProtistsDocument32 pagesBIO 101-Lecture 3-ProtistsOwusu GideonNo ratings yet
- Muhamad Naufal Daffa - 2005778 - Assigment Porifera and CoelenterataDocument9 pagesMuhamad Naufal Daffa - 2005778 - Assigment Porifera and CoelenterataMuhammad Naufal DaffaNo ratings yet
- OomycotaDocument37 pagesOomycotaSagar Das ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- PROTISTDocument43 pagesPROTISTnurliyanaaminNo ratings yet
- Annelida Platyhelminthes: Manatad, Joy Joy SDocument3 pagesAnnelida Platyhelminthes: Manatad, Joy Joy SJoy ManatadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: ProtozoaDocument10 pagesChapter 11: ProtozoaDavinci LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 Phylum ProtozoaDocument42 pagesExercise 1 Phylum ProtozoaKaten KyoukotsuNo ratings yet
- Plus 2 PracticalDocument16 pagesPlus 2 Practicaljayantaroy783360No ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: What Is Protista ?Document7 pagesThis Study Resource Was: What Is Protista ?ayunna ayunniNo ratings yet
- Supergroup UnikontaDocument5 pagesSupergroup UnikontaTJ HarrisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Lesson 3 ProtozoaDocument17 pagesChapter 3 Lesson 3 ProtozoaKreizel FajaNo ratings yet
- Protozoans RevDocument5 pagesProtozoans RevLLORITO Cristell Joy M.No ratings yet
- Kelompok 2Document17 pagesKelompok 2roky siagianNo ratings yet
- MicroorganismsDocument6 pagesMicroorganismsAngelika TibayanNo ratings yet
- ProtozoansDocument5 pagesProtozoanskingNo ratings yet
- Kingdom FungiDocument11 pagesKingdom FungiPat FerrerNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Protist: ProtistsDocument1 pageLecture 3 - Protist: ProtistsMariz RaymundoNo ratings yet
- Domain Bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria: Systematics LaboratoryDocument5 pagesDomain Bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria: Systematics LaboratorySIlverNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument23 pagesUntitledsrishtiNo ratings yet
- B101 Assessment2lec Navales1bDocument2 pagesB101 Assessment2lec Navales1bEdzel NavalesNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument6 pagesBiologySuraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Cnidaria 2Document27 pagesCnidaria 2Pratyush BasnetNo ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument4 pagesAsexual ReproductionBounce AtomNo ratings yet
- Annelida 1Document36 pagesAnnelida 1Hescel An ButacNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide Invertebrates PDFDocument61 pagesPractical Guide Invertebrates PDFMOUSTAFA ALEMAMNo ratings yet
- LOPEZC - Biology NotesDocument11 pagesLOPEZC - Biology Notescasey lNo ratings yet
- BotanyDocument25 pagesBotanynaagin12300No ratings yet
- Cnidaria: Body Cavity Known As The CoelenteronDocument21 pagesCnidaria: Body Cavity Known As The CoelenteronLakshya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Day 2Document15 pagesDay 2saifali986254No ratings yet
- Nonchordatesb CoelomatesDocument5 pagesNonchordatesb CoelomatesKrishna JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Phylum GnathostomulidaDocument1 pagePhylum GnathostomulidaMahmood Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Gen Boi 2Document5 pagesGen Boi 2yvet garciaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Biological Classfication NotesDocument5 pagesCH 2 Biological Classfication NotesJiya GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Protists Review WSDocument4 pagesProtists Review WSIZ - 12JR 1013186 Lincoln Alexander SSNo ratings yet
- Phaeophyta: Stypopodium TurbinariaDocument13 pagesPhaeophyta: Stypopodium TurbinariabetriaceNo ratings yet
- Ctenophora RevisedDocument9 pagesCtenophora RevisedLuisa San SebastianNo ratings yet
- Phylum Platyhelminthes: Class TrematodaDocument8 pagesPhylum Platyhelminthes: Class TrematodaKaten KyoukotsuNo ratings yet
- 3rd Lects KINGDOM PROTISTA CombineDocument94 pages3rd Lects KINGDOM PROTISTA CombinenoreenasyikinNo ratings yet
- General Characteristics of Major Phyla in The AnimalDocument33 pagesGeneral Characteristics of Major Phyla in The AnimalSiddharth SirvaiyaNo ratings yet
- Biological ClassificationDocument5 pagesBiological Classificationsivarigil0610No ratings yet
- 422 - Topic 1Document7 pages422 - Topic 1Elaine PaguioNo ratings yet
- Biological Classification (Edustudy Point)Document8 pagesBiological Classification (Edustudy Point)canyouguess18No ratings yet
- Animal TaxonomyDocument3 pagesAnimal TaxonomyJudy Flores100% (1)
- Filum Protozoa Dan PoriferaDocument5 pagesFilum Protozoa Dan PoriferaDidik PrasetyaNo ratings yet
- 28.2B Class AnthozoaDocument1 page28.2B Class AnthozoaOwolabi DavidNo ratings yet
- Amoeba PrefinalsDocument5 pagesAmoeba PrefinalsKervy Jay AgraviadorNo ratings yet
- Protista: The First EukaryotesDocument102 pagesProtista: The First EukaryoteshannNo ratings yet
- Camp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- Aloe Vera and PineappleDocument10 pagesAloe Vera and Pineapplenursuraya wahidaNo ratings yet
- Mindmap Bio320 Chapter 3 BacteriaDocument1 pageMindmap Bio320 Chapter 3 Bacterianursuraya wahidaNo ratings yet
- Basic Calibration of UV/ Visible SpectrophotometerDocument5 pagesBasic Calibration of UV/ Visible SpectrophotometerMeta Zahro KurniaNo ratings yet
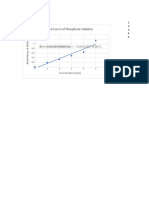
- Standard CurveDocument2 pagesStandard Curvenursuraya wahidaNo ratings yet
- Mindmap Bio320 Chapter 1 ClassificationDocument1 pageMindmap Bio320 Chapter 1 Classificationnursuraya wahidaNo ratings yet
- Aloe Vera and BlueberryDocument15 pagesAloe Vera and Blueberrynursuraya wahidaNo ratings yet
- Aloe Vera and GrapeDocument10 pagesAloe Vera and Grapenursuraya wahidaNo ratings yet
- Aloe Vera With LemongrassDocument9 pagesAloe Vera With Lemongrassnursuraya wahidaNo ratings yet
- Aloe Vera, Fruit and VegetableDocument11 pagesAloe Vera, Fruit and Vegetablenursuraya wahidaNo ratings yet
- Aloe Vera and MelonDocument7 pagesAloe Vera and Melonnursuraya wahidaNo ratings yet
- American BreakfastDocument4 pagesAmerican BreakfastHamilton Valenzuela ChipongianNo ratings yet
- The Indian Mining Sector: Effects On The Environment & FDI InflowsDocument10 pagesThe Indian Mining Sector: Effects On The Environment & FDI InflowsMehul MandanakaNo ratings yet
- 3200AMMe - Part 4Document207 pages3200AMMe - Part 4Tanja Kesic100% (1)
- tGr12OM CheResoBookU78910Document110 pagestGr12OM CheResoBookU78910Jamunanantha PranavanNo ratings yet
- L27/38S Project Guide - Power Plant: Four-Stroke GensetDocument392 pagesL27/38S Project Guide - Power Plant: Four-Stroke GensetAaron Chan100% (1)
- Tesla Coil ProjectDocument8 pagesTesla Coil ProjectShivam singhNo ratings yet
- Eldritch HighDocument39 pagesEldritch Highteam_moNo ratings yet
- NCP Orif Right Femur Post OpDocument2 pagesNCP Orif Right Femur Post OpCen Janber CabrillosNo ratings yet
- Tugas Dikumpulkan Pada Hari Sabtu, 11 April 2020. Apabila Email Bermasalah Dapat Mengirimkan Via WA PribadiDocument4 pagesTugas Dikumpulkan Pada Hari Sabtu, 11 April 2020. Apabila Email Bermasalah Dapat Mengirimkan Via WA PribadiFebry SugiantaraNo ratings yet
- FemDocument4 pagesFemAditya SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2022 Audi e Tron 22Document318 pages2022 Audi e Tron 22Alejandro Alberto Robalino MendezNo ratings yet
- Proefschrift T. Steenstra - tcm24-268767Document181 pagesProefschrift T. Steenstra - tcm24-268767SLAMET PAMBUDINo ratings yet
- ZF-FreedomLine TransmissionDocument21 pagesZF-FreedomLine TransmissionHerbert M. Zayco100% (1)
- Why Are Solids Are Floating On My Secondary Clarifier - Biological Waste TreatmDocument6 pagesWhy Are Solids Are Floating On My Secondary Clarifier - Biological Waste TreatmIsaac FernándezNo ratings yet
- GROSS Mystery of UFOs A PreludeDocument309 pagesGROSS Mystery of UFOs A PreludeTommaso MonteleoneNo ratings yet
- JKJKJDocument3 pagesJKJKJjosecarlosvjNo ratings yet
- Bulacan Agricultural State College: Lesson Plan in Science 4 Life Cycle of Humans, Animals and PlantsDocument6 pagesBulacan Agricultural State College: Lesson Plan in Science 4 Life Cycle of Humans, Animals and PlantsHarmonica PellazarNo ratings yet
- 300 PSI CTS (MP-1115) Operation Manual Rev1.3Document18 pages300 PSI CTS (MP-1115) Operation Manual Rev1.3Juan Manuel VizosoNo ratings yet
- Napoleonic WargamingDocument13 pagesNapoleonic WargamingandyNo ratings yet
- Amnaya Sutra (English)Document458 pagesAmnaya Sutra (English)Assam Bhakti SagarNo ratings yet
- Indor Lighting DesignDocument33 pagesIndor Lighting DesignRajesh MalikNo ratings yet
- BC-6000 Installation Guide V7.0 enDocument111 pagesBC-6000 Installation Guide V7.0 enmentule88No ratings yet
- Tree Growth CharacteristicsDocument9 pagesTree Growth CharacteristicsMunganNo ratings yet
- Honeycomb Kevlar 49 (Hexcel)Document3 pagesHoneycomb Kevlar 49 (Hexcel)Julia GarciaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Retrofitting Existing Combined Heat and Power Plant With Polygeneration of Biomethane PDFDocument16 pagesImpact of Retrofitting Existing Combined Heat and Power Plant With Polygeneration of Biomethane PDFAwais Salman0% (1)
- Cisco 2500 Series RoutersDocument16 pagesCisco 2500 Series RoutersJull Quintero DazaNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Events Guide May 30 2012 FINAL PDFDocument118 pagesSustainable Events Guide May 30 2012 FINAL PDFInter 4DMNo ratings yet
- Fig. 4 Phasor Diagram of P.TDocument31 pagesFig. 4 Phasor Diagram of P.Tdon aNo ratings yet
- Industrial Artificial Intelligence For Industry 4.0-Based Manufacturing SystemsDocument5 pagesIndustrial Artificial Intelligence For Industry 4.0-Based Manufacturing SystemsMuhammad HaziqNo ratings yet
- Bomba MixerDocument2 pagesBomba MixerBinelli79No ratings yet