Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Midterm Review Quadradics pt1
Uploaded by
Rishamjot KOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Midterm Review Quadradics pt1
Uploaded by
Rishamjot KCopyright:
Available Formats
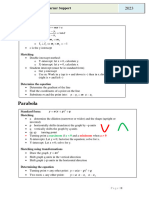
Math 20-1 Chapter 3 Quadratic Functions Review
Key Ideas Description or Example
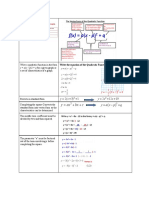
Quadratic Functions Standard Form: f(x) = ax2 + bx + c, a ¹ 0
polynomial of degree two Vertex Form: f(x) = a(x - p)2 + q , a ¹ 0
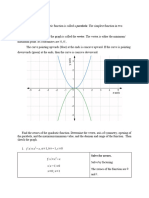
For a quadratic function, the graph is
in the shape of a parabola
Parent Graph is y = x2
Characteristics of a Quadratic • The coordinates of the vertex are at (p, q). Note that the negative
Function from the vertex form of the symbol from (x - p) does not transfer to p.
equation f(x) = 2(x - 3)2 + 4 vertex at (3, 4)
f(x) = a(x - p)2 + q f(x) = 2(x + 3)2 + 4 vertex at (-3, 4)
When p > 0 the graph moves (translated) to the right.
When p < 0 is translated or shifts to the left.
When q > 0 the parabola shifts up.
When q < 0 the parabola shifts down.
• The parameter “a” indicates the direction of opening as well as how
narrow or wide the graph is in relation to the parent graph.
When a > 0 , the graph opens up and the vertex is a minimum
min max
When a < 0, the graph opens downward and the vertex is a
maximum.
When -1 < a < 1, the parabola is wider than the parent graph.
When a > 1 or a < -1, the parabola is narrower than the parent
graph.
• The Axis of Symmetry is an imaginary vertical line through the
vertex that divides the function graph into two symmetrical parts.
The equation for the axis of symmetry is represented by x – p = 0
or x = p
• The domain of a quadratic function is all real numbers
{x | x ÎÂ}.
• The range of a quadratic function depends on the value of the
parameters “a” and “q”.
{
When “a” is positive, y | y ³ q .}
When “a” is negative, { y | y £ q}.
x- and y- intercepts Calculate the x-intercept by replacing y with 0 in either form of the
function equation. ax2 + bx + c = 0 or a(x - p)2 + q = 0.
Calculate the y-intercepts by replacing x with 0 and solving for the
value of y.
You might also like
- Lecture NotesDocument3 pagesLecture NotesJustin Paul TumaliuanNo ratings yet
- Gdtology GDTP Practice Exam 2009 Answers FDocument48 pagesGdtology GDTP Practice Exam 2009 Answers FSandeep Patnala100% (4)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Quadratic FunctionsDocument16 pagesQuadratic FunctionsAbby Lumanglas100% (1)
- A Harmony of The Passion of Christ (NKJV)Document17 pagesA Harmony of The Passion of Christ (NKJV)Kevin L. Morgan100% (1)
- Graphs of Polynomial FunctionsDocument38 pagesGraphs of Polynomial FunctionsEvelyn MaligayaNo ratings yet
- Biblical-Sanctuary - William H. SheaDocument369 pagesBiblical-Sanctuary - William H. SheaErick Jose Rodriguez Jimenez100% (2)
- 02.21.2020 Algebra I Quadraic FunctionsDocument90 pages02.21.2020 Algebra I Quadraic FunctionsNerissa LacsonNo ratings yet
- Graph of Quadratic FunctionsDocument26 pagesGraph of Quadratic FunctionsashNo ratings yet
- G9 Math Q1 - Week 6 - Quadratic Functions and Its GraphDocument27 pagesG9 Math Q1 - Week 6 - Quadratic Functions and Its GraphMechael ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Accenture Informatica Interview Question AnswersDocument3 pagesAccenture Informatica Interview Question AnswersSweta Singh100% (2)
- PC Functions RationalDocument11 pagesPC Functions RationalHector R.No ratings yet
- Mini Project ReportDocument19 pagesMini Project Reportashim01100% (1)
- 1000 Most Common English Phrases PREVIEWDocument7 pages1000 Most Common English Phrases PREVIEWFelipe Santiago100% (1)
- Language Documentation Annotated BibliographyDocument77 pagesLanguage Documentation Annotated BibliographyStephen N SelfNo ratings yet
- Vijeo Citect User Guide PDFDocument1,389 pagesVijeo Citect User Guide PDFalejososo100% (1)
- Quadratic Functions Concept ReviewDocument3 pagesQuadratic Functions Concept ReviewdaanjansenluoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Quadratic FunctionsDocument44 pagesChapter 5 - Quadratic FunctionsashNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus 11 WorkbookDocument44 pagesPre-Calculus 11 Workbooklogicalbase3498No ratings yet
- GR 12 - Maths - Winter Revision Document - 2023-1Document47 pagesGR 12 - Maths - Winter Revision Document - 2023-1vanessamahlatse81No ratings yet
- Session 8 Trigonometric FunctionsDocument7 pagesSession 8 Trigonometric Functionswmayeza11No ratings yet
- Mathematics GR 12 Learner Support - Inverse FunctionsDocument9 pagesMathematics GR 12 Learner Support - Inverse Functionsdonz69914No ratings yet
- Function 1Document12 pagesFunction 1tahosin jusiNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Graphs 1Document23 pagesQuadratic Graphs 1Alicia HaughtonNo ratings yet
- Graphs For Quadratic FunctionsDocument14 pagesGraphs For Quadratic Functionschelsea correaNo ratings yet
- 3 Functions Part 2Document22 pages3 Functions Part 2Rabbin CaracasNo ratings yet
- Graphing Quadratic Functions: y Ax + BX + CDocument14 pagesGraphing Quadratic Functions: y Ax + BX + CMegan Dolan FenneuffNo ratings yet
- Pre - Calculus 12 Workbook SolutionsDocument3 pagesPre - Calculus 12 Workbook Solutionsanchet.isabelNo ratings yet
- Math q2 1Document6 pagesMath q2 1Sheryl Mae EmanelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document18 pagesChapter 1sidrajaffri72No ratings yet
- Session 9 FunctionDocument7 pagesSession 9 Functionzlmulaudzi42No ratings yet
- Graphs of Quadratic FunctionsDocument3 pagesGraphs of Quadratic FunctionsYumeko SNo ratings yet
- Formulas and Properties 9th GradeDocument4 pagesFormulas and Properties 9th Gradedgjdf hgjhdgNo ratings yet
- AmathDocument9 pagesAmathAnnette ChiangNo ratings yet
- PC Graph QuadsDocument20 pagesPC Graph QuadsHector R.No ratings yet
- FUNCTIONS - Linear, Quadratics and CubicDocument4 pagesFUNCTIONS - Linear, Quadratics and CubicTito AgooNo ratings yet
- Graphs, Linear Equations, and FunctionsDocument46 pagesGraphs, Linear Equations, and FunctionsAmit BhararaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE AMaths 0606 4037 SB Quick Revision GuideDocument7 pagesIGCSE AMaths 0606 4037 SB Quick Revision GuideNITAKSH jain NJNo ratings yet
- ITM401S Unit 3.7.4 Exponential and Logarithmic CurvesDocument3 pagesITM401S Unit 3.7.4 Exponential and Logarithmic CurvesEfraim KasinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, 12 Curve Tracing and EnvelopeDocument37 pagesChapter 11, 12 Curve Tracing and EnvelopeNitish PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Unit 18 - Curved Graphs - DerivativeDocument5 pagesUnit 18 - Curved Graphs - DerivativeRaffaella LaxaldeNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument38 pagesReportEdward Raymund CuizonNo ratings yet
- Matrices and VectorsDocument18 pagesMatrices and Vectorsramlal18ramNo ratings yet
- displaystyle F (X) Ax (2) +BX+CF (X) Ax +BX+C Aa BB CC A/neq 0a 0Document4 pagesdisplaystyle F (X) Ax (2) +BX+CF (X) Ax +BX+C Aa BB CC A/neq 0a 0Kezhia ShaneNo ratings yet
- Graphing QuadraticsDocument19 pagesGraphing QuadraticsMaclharenn TiquiNo ratings yet
- 11.1 ParabolasDocument15 pages11.1 ParabolasAnalyn ErederosNo ratings yet
- Sketching Graphs - GCSE Maths - Steps, Examples & WorksheetDocument25 pagesSketching Graphs - GCSE Maths - Steps, Examples & Worksheetsyl.sylvia000No ratings yet
- Graphing Quadratic Function 1Document3 pagesGraphing Quadratic Function 1Tristan Ryan Gagni TingsonNo ratings yet
- Math1414 Polynomial FunctionsDocument10 pagesMath1414 Polynomial FunctionsRichel BannisterNo ratings yet
- 11.1 ParabolasDocument14 pages11.1 Parabolasalfred naveaNo ratings yet
- Polynomial Functions of Higher DegreeDocument10 pagesPolynomial Functions of Higher DegreedoocsNo ratings yet
- Graphs of Quadratic FunctionsDocument3 pagesGraphs of Quadratic FunctionsYumeko SNo ratings yet
- 2-5 Rational FunctionsDocument36 pages2-5 Rational Functions5xh7k2stm7No ratings yet
- Graph of Cubic Functions and Reciprocal FunctionsDocument53 pagesGraph of Cubic Functions and Reciprocal FunctionsMark Vincent DoriaNo ratings yet
- Rational Function NoteDocument63 pagesRational Function NoteMark Francis HernandezNo ratings yet
- Graphs Revision Sheet FinalDocument27 pagesGraphs Revision Sheet FinalLuumuno PeaceNo ratings yet
- Mathematics-Functions and FinanceDocument100 pagesMathematics-Functions and Financeblessedbusisiwe153No ratings yet
- Shapes of The GraphsDocument6 pagesShapes of The GraphsTazeen FatimaNo ratings yet
- FunctionDocument35 pagesFunctionDae DayNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus Conic Section Q1 - Week 4: HyperbolaDocument23 pagesPre-Calculus Conic Section Q1 - Week 4: HyperbolaNelsonNelsonNo ratings yet
- Student BK Alg2-Sect11 1Document68 pagesStudent BK Alg2-Sect11 1Xiaoxu MaNo ratings yet
- A, B, and C Are Real Numbers and A and B Are: C. by Quadratic FormulaDocument2 pagesA, B, and C Are Real Numbers and A and B Are: C. by Quadratic FormulaLean Amara VillarNo ratings yet
- A, B, and C Are Real Numbers and A and B Are: C. by Quadratic FormulaDocument2 pagesA, B, and C Are Real Numbers and A and B Are: C. by Quadratic FormulaLean Amara VillarNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICSDocument2 pagesMATHEMATICSLean Amara VillarNo ratings yet
- Asymptotes of Rational FunctionsDocument19 pagesAsymptotes of Rational FunctionsKen AguilaNo ratings yet
- Example 11 Chapter 2 Sketching Quadratics PDFDocument5 pagesExample 11 Chapter 2 Sketching Quadratics PDFTanaka HlupoNo ratings yet
- Cubic FunctionDocument19 pagesCubic Functionjoshua balansagNo ratings yet
- ABC Poem - Capa ModelDocument4 pagesABC Poem - Capa ModelRishamjot KNo ratings yet
- Chase Problems SolutionsDocument4 pagesChase Problems SolutionsRishamjot KNo ratings yet
- Returning Grade 12 2023-24 Expression of InterestDocument1 pageReturning Grade 12 2023-24 Expression of InterestRishamjot KNo ratings yet
- Midterm Review Quadradtics pt2Document1 pageMidterm Review Quadradtics pt2Rishamjot KNo ratings yet
- Rational Expressions Questions & AnswersDocument3 pagesRational Expressions Questions & AnswersRishamjot KNo ratings yet
- GE 5-8 StudentDocument95 pagesGE 5-8 StudentbyuuharNo ratings yet
- Pronoun & Types of Pronoun: What Is Pronoun? The Word Which Is Used in Place of A Noun Is CalledDocument5 pagesPronoun & Types of Pronoun: What Is Pronoun? The Word Which Is Used in Place of A Noun Is CalledgregoryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document77 pagesChapter 3HassnainNo ratings yet
- Superbook Family Discussion Guide A-Giant-AdventureDocument2 pagesSuperbook Family Discussion Guide A-Giant-AdventureElisha CortezNo ratings yet
- Verba Hispanica 22Document248 pagesVerba Hispanica 22JelicaVeljovicNo ratings yet
- Scolnicov PDFDocument9 pagesScolnicov PDFEduardo CharpenelNo ratings yet
- Periodic Test in 1ST To 4TH Epp 5Document80 pagesPeriodic Test in 1ST To 4TH Epp 5MARILU M. RAYMUNDONo ratings yet
- 28 October Holy Protection of Our Lady Theotokos: Festal Hymns - Matins & Divine LiturgyDocument8 pages28 October Holy Protection of Our Lady Theotokos: Festal Hymns - Matins & Divine LiturgyMarguerite PaizisNo ratings yet
- The Sign of The CrossDocument2 pagesThe Sign of The CrossikonographicsNo ratings yet
- DX DiagDocument38 pagesDX DiagTokugawa ArakkunNo ratings yet
- DLL Kinder w7Document6 pagesDLL Kinder w7Mel Rose Cabrera100% (1)
- Ubuntu InstallDocument7 pagesUbuntu InstallWhisky MiloNo ratings yet
- The Project Gutenberg Ebook of Colloquies of ErasmusDocument415 pagesThe Project Gutenberg Ebook of Colloquies of ErasmusJuan RulfoNo ratings yet
- FS Industrie (PDF - Io)Document42 pagesFS Industrie (PDF - Io)don dadaNo ratings yet
- PP Lesson KCDocument9 pagesPP Lesson KCapi-636859912No ratings yet
- (Studies in Phenomenology and Existential Philosophy) Michel Henry, Kathleen McLaughlin - Marx - A Philosophy of Human Reality-Indiana University Press (1983)Document348 pages(Studies in Phenomenology and Existential Philosophy) Michel Henry, Kathleen McLaughlin - Marx - A Philosophy of Human Reality-Indiana University Press (1983)DIEGO ALVARO RETAMOZO CASTILLONo ratings yet
- Lab 17: TACACS+ Device AdministrationDocument12 pagesLab 17: TACACS+ Device AdministrationJosel ArevaloNo ratings yet
- R911338914 - 03mm Ilovepdf Compressed PDFDocument316 pagesR911338914 - 03mm Ilovepdf Compressed PDFScada IgnitionNo ratings yet
- Interpolation TechniquesDocument17 pagesInterpolation TechniquesSantiago SarmientoNo ratings yet
- SOAL UTS Bhs Inggris EksekutifDocument2 pagesSOAL UTS Bhs Inggris EksekutifHabiburrahmanNo ratings yet
- Clark & PaivioDocument62 pagesClark & PaivioGeléias Artesanais Fraga Delfino & KunzNo ratings yet
- Sas Inggris Kelas 4 22-23Document4 pagesSas Inggris Kelas 4 22-23Fitria Hardiyanti100% (1)