Professional Documents
Culture Documents
sheet (6) ازهر E1
sheet (6) ازهر E1
Uploaded by
magdy kamelOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
sheet (6) ازهر E1
sheet (6) ازهر E1
Uploaded by
magdy kamelCopyright:
Available Formats
Sheet (3)
Tegara English
First year
SECOND TERM
Chapter (6)
Accounting for
purchases
Edited by Dr/ Magdy Kamel
Tel/ 01273949660
1 | Page Dr. Magdy Kamel
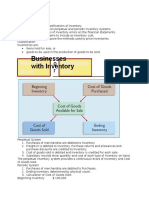
1. merchandising company is an enterprise that buys and sells goods to earn revenue.
Merchandising companies that purchase and sell directly to consumers are called
retailers
Merchandising companies that sell to retailers are known as wholesalers.
The Primary source of revenue is the sales of merchandise
Two categories of expenses for merchandising companies are
(1) Cost of goods sold, (2) Operating expenses
Sales revenue less cost of goods sold is called gross profit.
After gross profit is calculated, operating expenses are deducted to determine net
income ( or loss).
A merchandising company may use either a perpetual or a periodic inventory system in
determining cost of goods sold
(1) perpetual inventory system (2) periodic inventory system
نظام الجرد الدائم او المستمر نظام الجرد الدورى
Maintain detailed records of the
Do not keep detailed records of
cost of each inventory purchase
the goods on hand.
and sale.
Records continuously show
inventory that should be on
hand for every item.
Notes that
Notes that 1. Cost of goods sold determined
1. cost of goods sold is recorded by count at the end of the
with each sale accounting period.
2. Purchases of merchandise are 2. Purchases of merchandise are
debited to Inventory. debited to Purchases.
2 | Page Dr. Magdy Kamel
3 | Page Dr. Magdy Kamel
Under periodic inventory system
Calculation of Cost of Goods Sold:
Purchase xxxx
Less : purchase returns and allowance xx
Purchase discounts xx (xxx)
= Net purchases xxxx
Add: freight in xx__
Cost of goods purchased xxxx
Beginnings inventory xx
(+) Cost of goods purchased xx
= Cost of goods available for sale xx
(-) ending inventory (xx)
= cost of goods sold xxxx
Net sales = sales revenue – sales returns and allowances – sales discounts
So, Sales discounts is a contra revenue accounts
Net purchase = purchase – purchase returns & allowances – purchase discount
4 | Page Dr. Magdy Kamel
Single & multiple income statement
First: single income statement
Second: multiple income statement
5 | Page Dr. Magdy Kamel
True/False
1. Measuring net income for a merchandising company is conceptually the same as for a
service company.
o True False
2. The cost of goods sold is determined only at the end of the accounting period under a
perpetual inventory system.
o True False
3. Under the perpetual inventory system, the purchase of merchandise is recorded with
a debit to the Purchases account.
o True False
4. Sales Discounts is a contra revenue account and has a debit balance.
o True False
5. A customer may receive a sales discount for goods that are damaged or defective.
o True False
6. In a single-step income statement, gross profit and operating income are shown on
the income statement.
o True False
7. In the balance sheet, inventory is reported as a current asset immediately below
accounts receivable.
o True False
8. Income from operations is determined by subtracting other expenses and losses from
gross profit.
o True False
9. Merchandising companies report nonoperating activities in the income statement
immediately after the company’s primary operating activities.
o True False
6 | Page Dr. Magdy Kamel
10. In preparing a worksheet for a merchandising firm, all income statement column
debits represent expenses.
o True False
Multiple Choice
1. Sales Discounts
a. is a contra revenue account.
b. has a normal debit balance.
c. appears on the income statement.
d. all of the above.
2. When a company uses the perpetual method of accounting for inventories the
a. Inventory account does not change until the end of the year.
b. Inventory account is debited when inventory is purchased
and Cost of Goods Sold is debited when inventory is sold.
c. sale of inventory requires a credit to Cost of Goods Sold.
d. acquisition of merchandise requires a debit to Purchases.
3. The recording of a sale requires a
a. credit to a sales account and a debit to an asset account.
b. debit to Cash and a credit to Owner’s Capital.
c. debit to a sales account and credit to an asset account.
d. credit to Sales Revenue and a debit to Sales Discounts.
4. Which of the following would not be considered an operating expense?
a. Cost of goods sold b. Rent expense
c. Freight-out d. Office expense
5. Which of the following is reported on both a multiple-step and a single-step income
statement?
a. Gross profit b. Income from operations
c. Other revenues and gains d. Net sales
7 | Page Dr. Magdy Kamel
Inventories
There are three methods of recording purchases & sales under different prices.
1) First In First Out FIFO اللى اشتريته فى االول يتباع فى االول
2) Last In First Out LIFO اللى اشتريته فى االخر يتباع فى االول
3) Weighted Average Method
4. Specific identification طريقة التحديد
Example
Ahmed Company uses the Periodic Inventory System, the following transactions show
beginning inventory & purchases of Product No.M25 for the month of July.
1 July Beginning Inventory, 3,000 Units, Cost 5 Each ……….. 15,000
6 July Purchases, 5,000 Units, Cost 6 Each ………….…………… 30,000
17 July Purchases, 6,000 Units, Cost 7 Each …………….……….. 42,000
23 July Purchases, 4,000 Units, Cost 8 Each ……………………….. 32,000
26 July Purchases, 2,000 Units, Cost 9 Each ……………………….. 18,000
137,000
A physical count indicates 4,000 units in inventory at the end of July.
Required
a) determine both the cost of goods sold & ending inventory, using the following
methods and determine the gross profit under each cases if the sale price is $10
1) FIFO Method 2) LIFO Method 3) Average cost Method
Solution
Data
total unit = 3,000 + 5,000 + 6,000 + 4,000 +2,000 = 20,000 units
Ending inventory = 4,000 units
Total Units Sold (COGS) = 20,000 – 4,000 = 16,000 Units
Sales revenues = 16,000 units × $10 = $160,000
1) FIFO Method الوارد اوال يباع اوال
1. Cost Of Goods Sold = 3,000 × 5 = 15,000
+ 5,000 × 6 = 30,000
8 | Page Dr. Magdy Kamel
+ 6,000 × 7 = 42,000
+ 2,000 × 8 = 16,000 103,000 Cost Of Goods Sold
2. Ending Inventory = 2,000 × 8 = 16,000
+ 2,000 × 9 = 18,000 34,000 Ending Inventory
3. Gross profit = sales revenue – COGS = 160,000 – 103,000 = 57,000
2) LIFO Method الوارد اخيرا يباع اوال
1. Cost Of Goods Sold = 2,000 × 9 = 18,000
+ 4,000 × 8 = 32,000
+ 6,000 × 7 = 42,000
+ 4,000 × 6 = 24,000 116,000 COGS
2. Ending Inventory = (1,000 ×6) + (3,000 × 5) = 21,000
3. Gross profit = sales revenue – COGS = 160,000 – 116,000 = 44,000
3) Average Cost Method المتوسط
total cost 137000
Average Cost = total units = 20000 = 6.85 per Unit
1) Cost Of Goods Sold = 16,000 × 6.85 = 109,600
2) Ending Inventory = 4,000 × 6.85 = 27,400
3. Gross profit = sales revenue – COGS = 160,000 – 109,600 = 50,400
9 | Page Dr. Magdy Kamel
Comments
Case (1)
If the purchase price is going up (increase) using FIFO method will increase the net income
Because the cost of goods sold under FIFO is low
While using LIFO will decrease the net income because the cost of goods sold is high
FIFO method استخدم طريقه ال,لو سعر شراء البضاعة بيزداد فى السوق
الن البضاعه المباعه اول المده سعرها قليل وبالتالى هتدينى اكبر ربح للشركه باقل تكلفه
والعكس صحيح Net income بيزيد COGS ملحوظه كل لما يقل ال
If the purchase price is going down ( decrease) using LIFO method will increase the net
income because the cost of goods sold is low
while using FIFO will decrease the net income because the cost of goods sold is high
LIFO method استخدم طريقه ال,لما سعر شراء البضاعة بيقل فى السوق
الن البضاعه المباعه اخر المده سعرها قليل وبالتالى هتدينى اكبر ربح للشركه باقل تكلفه
والعكس صحيح Net income بيزيد COGS ملحوظه كل لما يقل ال
10 | Page Dr. Magdy Kamel
You might also like
- Dps Custodial Terms and Conditions June2022 v28Document7 pagesDps Custodial Terms and Conditions June2022 v28Arasu Chess0% (1)
- MERCHANDISINGDocument21 pagesMERCHANDISINGlorraine85% (13)
- Accounting For Governmental & Nonprofit Entities Chapter 2 SolutionsDocument9 pagesAccounting For Governmental & Nonprofit Entities Chapter 2 SolutionsJeannie Bopes Carter100% (4)
- Retirement Saver Terms and ConditionsDocument44 pagesRetirement Saver Terms and ConditionsColinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 InventoryDocument12 pagesChapter 1 InventoryDaniel AssefsNo ratings yet
- Strategic Business Analysis - Course Outline, Content, Topics Etc.Document3 pagesStrategic Business Analysis - Course Outline, Content, Topics Etc.Joyce Anne Garduque100% (2)
- Chapter - 1-Accounting For InventoriesDocument40 pagesChapter - 1-Accounting For InventoriesWonde Biru100% (2)
- Quick Company Acquired A Piece of Equipment in Year 1Document1 pageQuick Company Acquired A Piece of Equipment in Year 1Taimour HassanNo ratings yet
- IFA-I ch-3 Investories NewDocument59 pagesIFA-I ch-3 Investories Newhasenabdi30No ratings yet
- Bis Second Term Sheet 1Document11 pagesBis Second Term Sheet 1magdy kamelNo ratings yet
- Abm Fabm1 Airs LM q4-m14Document12 pagesAbm Fabm1 Airs LM q4-m14Rudyna MarzanNo ratings yet
- CH 04Document61 pagesCH 04natiman090909No ratings yet
- PPAcct II InventoryDocument9 pagesPPAcct II InventoryNigussie BerhanuNo ratings yet
- Bis Sheet 3Document11 pagesBis Sheet 3magdy kamelNo ratings yet
- Module 9 Accounting For A Merchandiser Dec 2021 (20231122130953)Document34 pagesModule 9 Accounting For A Merchandiser Dec 2021 (20231122130953)Antonette LaurioNo ratings yet
- INVENTORYDocument21 pagesINVENTORYFiruzaNo ratings yet
- Far Eastern University-Diliman: Department of Accounts and BusinessDocument8 pagesFar Eastern University-Diliman: Department of Accounts and BusinessJohn Paul PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- CH 05Document99 pagesCH 05Reinch Closs100% (1)
- Inventory ManagementDocument22 pagesInventory Managementpgp39150No ratings yet
- Accounting ChapterDocument13 pagesAccounting ChapterMamaru SewalemNo ratings yet
- Perpetual and Periodic Inventory System 1Document45 pagesPerpetual and Periodic Inventory System 1Kathleen SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Acc II Chapter 1 - InventoryDocument11 pagesFundamentals of Acc II Chapter 1 - Inventoryceerbe tubeNo ratings yet
- Summary After MidDocument40 pagesSummary After Midmc2hin9No ratings yet
- Module 5Document16 pagesModule 5Ma Leah TañezaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Inventory and Biological AssetsDocument19 pagesModule 4 Inventory and Biological AssetsAndrea Miles VasquezNo ratings yet
- Inventories and Cost of Goods SoldDocument38 pagesInventories and Cost of Goods Soldakram ouk100% (1)
- Week 006 007 Types of Business According To ActivitiesDocument62 pagesWeek 006 007 Types of Business According To ActivitiesKatherine Jane GeronaNo ratings yet
- Saint Mary's University: Chapter FiveDocument63 pagesSaint Mary's University: Chapter FivehenockNo ratings yet
- Inventory EstimationDocument4 pagesInventory EstimationShy Ng0% (1)
- Types of Business According To Activities: Prepared By: Prof. Jonah C. PardilloDocument60 pagesTypes of Business According To Activities: Prepared By: Prof. Jonah C. PardilloShaneil MatulaNo ratings yet
- Act512 - Assignment Chapter - 06Document9 pagesAct512 - Assignment Chapter - 06Rafin MahmudNo ratings yet
- Acctg. Ed 1 - Module 10 Accounting Cycle of A Merchandising BusinessDocument35 pagesAcctg. Ed 1 - Module 10 Accounting Cycle of A Merchandising BusinessChen Hao100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Accounting For Merchandising OperationsDocument10 pagesChapter 3 Accounting For Merchandising OperationsSKY StationeryNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Merchandising OperationsDocument32 pagesAccounting For Merchandising OperationsAllen CarlNo ratings yet
- Inventory LastDocument27 pagesInventory LastNigus AyeleNo ratings yet
- Accounting For InventoriesDocument29 pagesAccounting For InventoriesLakachew GetasewNo ratings yet
- Merchandising Accounting: Youtube Channel Link (Also Subscribe) Because I Need Your FeedbackDocument27 pagesMerchandising Accounting: Youtube Channel Link (Also Subscribe) Because I Need Your FeedbackBharti PahujaNo ratings yet
- 9Document10 pages9Maria G. BernardinoNo ratings yet
- Inventory ManagementDocument23 pagesInventory ManagementSrujana GantaNo ratings yet
- Operating Cycle of A Merchandising BusinessDocument10 pagesOperating Cycle of A Merchandising BusinessJanelle FortesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Accounting For Merchandising OperationsDocument15 pagesChapter 5 Accounting For Merchandising OperationsSantun Pi TOen100% (2)
- Lectures 5, 6Document10 pagesLectures 5, 6Lolita IsakhanyanNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document51 pagesCH 6anjo hosmerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Handout 2013Document24 pagesChapter 3 Handout 2013samita2721No ratings yet
- P2 - New Ch2Document10 pagesP2 - New Ch2mulugetaNo ratings yet
- Week4 Handout WORKEDDocument14 pagesWeek4 Handout WORKEDLecia Lebby CNo ratings yet
- Handout For Principles of Accounting II PDFDocument42 pagesHandout For Principles of Accounting II PDFhelen haileselassieNo ratings yet
- True or False: Accounting 205 - Quiz 1Document3 pagesTrue or False: Accounting 205 - Quiz 1CHENGNo ratings yet
- Bahan Ajar PersediaanDocument17 pagesBahan Ajar PersediaanKIKY FAUZIYYAH NUR ANNISANo ratings yet
- One of The Largest Current Assets InventoryDocument15 pagesOne of The Largest Current Assets InventorySaadat ShaikhNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document51 pagesCH 6Ella ApeloNo ratings yet
- Mir For L 4 Year 2Document14 pagesMir For L 4 Year 2tinsaeniguse6No ratings yet
- Main Inv RecDocument21 pagesMain Inv Receliyas mohammedNo ratings yet
- Far Notes - Accounting Cycle of Merchandising BusinessDocument15 pagesFar Notes - Accounting Cycle of Merchandising BusinessVan MateoNo ratings yet
- Tugas Summary Bab 6Document11 pagesTugas Summary Bab 6Meirna LarasatiNo ratings yet
- Practice Quiz 07 - ACTG240 - Q2202122Document11 pagesPractice Quiz 07 - ACTG240 - Q2202122Đinh Ngọc Minh ChâuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Inventorie Ifa 4 NewDocument62 pagesChapter 4 Inventorie Ifa 4 NewNigussie BerhanuNo ratings yet
- FOA II HandoutDocument67 pagesFOA II HandoutGirma NageoNo ratings yet
- Prin Acct Final ChapterDocument14 pagesPrin Acct Final ChapterGizachew NadewNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Income Statement and Statement of Comrehensive IncomeDocument20 pages1.3 Income Statement and Statement of Comrehensive IncomeRula Abu NuwarNo ratings yet
- BA991 Activity Guide Chapter 3Document12 pagesBA991 Activity Guide Chapter 3vanessaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and Management 2: Statement of Comprehensive IncomeDocument9 pagesFundamentals of Accountancy, Business and Management 2: Statement of Comprehensive IncomeBea allyssa CanapiNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On: Accounting For Merchandising OperationDocument26 pagesA Presentation On: Accounting For Merchandising OperationKayesCjNo ratings yet
- FABM1 - LAS - 9 - Nature of Transaction of A Mdsg. BusDocument8 pagesFABM1 - LAS - 9 - Nature of Transaction of A Mdsg. BusVenus Ariate100% (1)
- Management Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandManagement Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- sheet 5 E1 ازهرDocument9 pagessheet 5 E1 ازهرmagdy kamelNo ratings yet
- Sheet 4 E1 ازهرDocument13 pagesSheet 4 E1 ازهرmagdy kamelNo ratings yet
- تلخيص لغة تانيه 20233Document4 pagesتلخيص لغة تانيه 20233magdy kamelNo ratings yet
- Sales RevenueDocument1 pageSales Revenuemagdy kamelNo ratings yet
- تلخيص سنه اولىDocument1 pageتلخيص سنه اولىmagdy kamelNo ratings yet
- ch (14) جامعه الازهرDocument26 pagesch (14) جامعه الازهرmagdy kamelNo ratings yet
- Alison Krauss CompanyDocument3 pagesAlison Krauss Companymagdy kamelNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Sheet (5) Part (2) Chapter (3) Costing and Control of Materials and LaborDocument11 pagesCost Accounting Sheet (5) Part (2) Chapter (3) Costing and Control of Materials and Labormagdy kamelNo ratings yet
- Sheet (8) Intermediate Accounting: InventoriesDocument12 pagesSheet (8) Intermediate Accounting: Inventoriesmagdy kamelNo ratings yet
- Girum Tsega PerfectDocument13 pagesGirum Tsega PerfectMesi YE GINo ratings yet
- Implied Equity Risk Premium of Morrocon Stock ExchangeDocument4 pagesImplied Equity Risk Premium of Morrocon Stock Exchangeحبا عرفانNo ratings yet
- OFS7.Special OFS Messages-R08.02Document18 pagesOFS7.Special OFS Messages-R08.02nana yaw100% (1)
- Tax Invoice/Bill of Supply/Cash Memo: (Original For Recipient)Document3 pagesTax Invoice/Bill of Supply/Cash Memo: (Original For Recipient)Harshawardhan PatilNo ratings yet
- Cynthia Riley Depo 1-15-2013 HighlightedDocument110 pagesCynthia Riley Depo 1-15-2013 Highlightedmmeindl100% (1)
- What Does The DFL of 3 Times Imply?Document7 pagesWhat Does The DFL of 3 Times Imply?Sushil ShresthaNo ratings yet
- The Structure of Financial MarketsDocument7 pagesThe Structure of Financial MarketsVũ Thị Thu HiếuNo ratings yet
- Cash Management Techniques: Presented byDocument12 pagesCash Management Techniques: Presented byShivkarVishalNo ratings yet
- FINS 3616 Tutorial Questions-Week 3Document5 pagesFINS 3616 Tutorial Questions-Week 3Alex WuNo ratings yet
- CV - Fiorela KostareDocument3 pagesCV - Fiorela KostareEmianNo ratings yet
- New Chapter 17 - Cash FlowDocument17 pagesNew Chapter 17 - Cash FlowCheyenne Dawhitegurl GuillNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06 - AnswerDocument11 pagesChapter 06 - Answerveil clarizeNo ratings yet
- Harvard Kennedy School EE StudentsDocument26 pagesHarvard Kennedy School EE StudentsKhishigdelger Dulamdorj0% (1)
- SDDocument1 pageSDJPNo ratings yet
- Trade and Cash Discount NotesDocument3 pagesTrade and Cash Discount NotesAyushNo ratings yet
- BullseyeDocument40 pagesBullseyeMatthew100% (1)
- Facility AgreementDocument52 pagesFacility AgreementIlyes JerbiNo ratings yet
- Kimsis Fiori AppsDocument37 pagesKimsis Fiori AppsPrashant KumarNo ratings yet
- Toronto Parks, Forestry & Recreation 2016 BudgetDocument97 pagesToronto Parks, Forestry & Recreation 2016 BudgetT.O. Nature & DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions, Markets, & Money, 10 Edition: Power Point Slides ForDocument56 pagesFinancial Institutions, Markets, & Money, 10 Edition: Power Point Slides Forsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Financial SectorsDocument19 pagesFinancial SectorsSamrat Singh100% (1)
- Bina Goat Farming Business Plan CompleteDocument26 pagesBina Goat Farming Business Plan Completebina khatiwadaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial Management (History, Nature and Significance of Finance)Document41 pagesIntroduction To Financial Management (History, Nature and Significance of Finance)Ronan PermejoNo ratings yet
- Reviewed QUESTIONNAIRE ON THE FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT BEHAVIOR AND FINANCIAL WELLDocument3 pagesReviewed QUESTIONNAIRE ON THE FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT BEHAVIOR AND FINANCIAL WELLJenalyn Miranda Cayanan - Marayag100% (1)
- FINWIN Capital LTDDocument9 pagesFINWIN Capital LTDDhrubajyoti PatraNo ratings yet