Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MCQS Thermal Methods of Analysis MSC 4th
Uploaded by
Photon Online Science Academy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4K views6 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4K views6 pagesMCQS Thermal Methods of Analysis MSC 4th
Uploaded by
Photon Online Science AcademyCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
MCQS Thermal methods of Analysis MSC 4th
Q 1: Thermal analysis is defined as ___________
Option 1:Measurement of concentration of materials as a function of temperature
Option 2: Measurement of solubility of materials as a function of temperature
Option 3: Measurement of physical properties as a function of temperature
Option 3: Measurement of line positions of crystals as a function of temperature
Answer: Option 3
Explanation: Thermal analysis is defined as the measurement of physical and chemical properties
of materials as a function of temperature. In practice, however the term thermal analysis is used
to cover certain specific properties only. These are enthalpy, heat capacity, mass and coefficient
thermal expansion.
Q 2: Which of the following method can be used for the measurement of change in weight of the
oxysalts?
Option 1: Thermoelectric analysis
Option 2: Wagner analysis
Option 3: Stockbarger analysis
Option 3: Thermal analysis
Answer: d
Explanation: Measurement of change in weight of the oxysalts and hydrates can be achieved by
thermal analysis as they decompose on heating, In which we measure the physical and chemical
properties of the materials. Wide range of materials can be studied.
3: What are the two main techniques for thermal analysis?
Option 1: FTG AND DGG
Option 2: MSP AND FCT
Option 3: TGA AND DTA
Option 3: TSA AND DGF
Answer: c
Explanation: The two main thermal analysis techniques are thermogravimetric analysis known as
TGA which measures the change in weight with temperature and Differential thermal analysis
known as DTA which detects changes in heat content.
4: Dilatometry is also known as by which of the following names?
Option 1: TGA
Option 2: DTA
Option 3: DSC
Option 3: TMA
Answer: d
Explanation: A fourth thermal analysis technique is Dilatometry in which the change in linear
dimension of a sample as a function of temperature is recorded. Recently it has acquired a new
name, thermomechanical analysis (TMOPTION 1:.
5: Which of the following statements given below is false?
Option 1: TGA, DTA and DSC are measured using same instrument
Option 2: TGA and DTA can be carried out simultaneously.
Option 3: TGA, DTA and DSC are measured using different instruments.
Option 3: TMA is a recent name of Dilatometry.
Answer: c
Explanation: With modern automatic thermal analysis equipment it I possible to do TGA, DTA
and DSC using the same instrument, with some models, TGA and DTA may be carried out
simultaneously. However, the thermal analysis equipment is necessarily rather complicated and
expensive in order that a wide variety of thermal events and properties may be studied
6: In thermogravimetric analysis, the result obtained appear as a __________
Option 1: Continuous chart
Option 2: Continuous parabola
Option 3: Continuous circular positions
Option 3: Discontinuous chart
Answer: a
Explanation: Thermogravimetric is a technique for measuring the change in weight of a
substance as a function of temperature or time, the result usually appears a continuous chart
record, a schematic, typical, single step decomposition reaction.
7: What is the range of the rate in ◦Cmin-1 required during the heating process in TGA?
Option 1: 1-20
Option 2: 25-50
Option 3: 100-200
Option 3: 150-1000
Answer: a
Explanation: In the process of TGA thermogravimetric technique, the sample usually a few
milligrams in weight, is heated at a constant rate, typically in the range of 1-20 ◦Cmin-1 and a
constant weight Wi, until it begins to decompose at temperature Ti.
8: Under conditions of ______________ heating, decomposition usually take place in
thermogravimetry. Fill up the suitable option from the choices given below.
Option 1: First order
Option 2: Second order
Option 3: Third order
Option 3: Dynamic
Answer: d
Explanation: In thermogravimetric analysis (TGOPTION 1:, decomposition usually take place
under dynamic heating conditions over a range of temperature Ti to Tf and a second constant
weight plateau is then observed above Tf, which corresponds to the weight of the residue Wf.
9: The Ti and Tf temperature depends on which of the following factor?
Option 1: Cooling rate
Option 2: Mechanical property of the material
Option 3: Thermal expansion coefficient
Option 3: Atmosphere above the sample
Answer: d
Explanation: Initial and final temperature Ti, Tf depends on variables such as heating rate, the
nature of the solid (e.g. its particle size) and the atmosphere above the sample. The effect of the
atmosphere can be dramatic.
10: What is the temperature required for the decomposition of CaCO3 in degree Celsius?
Option 1: 200
Option 2: 500
Option 3: 900
Option 3: 1200
Answer: b
Explanation: The decomposition in the thermogravimetric analysis of CaCO3 is completed in
vacuum at ~500◦C but in CO2 at one atmosphere pressure, decomposition does not even
commence until above 900◦C. Ti, Tf pertain to the particular experimental conditions, therefore
and do not necessarily represent equilibrium decomposition temperatures.
11: Which of the following option is appropriate for the TGA and DTA?
Option 1: TGA and DTA measures only weight
Option 2: TGA measures only weight while DTA measures other effects
Option 3: TGA and DTA measures only temperature
Option 3: TGA measures only temperature while DTA measures other effects
Answer: b
Explanation: DTA is more versatile than TGA, TGA detects effects which involve weight
changes only. DTA also detects such effects in addition, detects other effects such as
polymorphic transitions, which do not involve changes in weight.
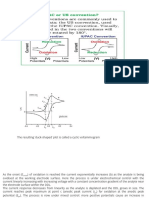
12: In the schematic DTA sequence having reversible and irreversible changes, starting with the
hydrated material, which of the following steps occurs first on heating?
Option 1: Esterification
Option 2: Methylation
Option 3: Rehydration
Option 3: Dehydration
Answer: d
Explanation: During the DTA, differential thermal analysis sequence having reversible and
irreversible changes when started with hydrated material, dehydration is the first step that occurs
on heating and appears as an endotherm On cooling, the melt crystallizes and the polymeric
change also occur, exothermically on cooling but rehydration does not occur.
13: On studying the reversible process during DTA which of the following is observed on both
heating and cooling?
Option 1: Esterification
Option 2: Hysteresis
Option 3: Methylation
Option 3: Carboxylation
Answer: b
Explanation: On both heating and cooling during the studies of reversible processes in DTA,
differential thermal analysis, it is common to observe hysteresis, for instance, the exotherm that
appears on cooling may be displaced to occur at a lower temperature than the corresponding
endotherm which appears on heating.
14: Which one of the following options is not true for hysteresis?
Option 1: It depends on the nature of the material
Option 2: It depends on the structural change involved
Option 3: It doesn’t depend on the experimental conditions
Option 3: It doesn’t depend on the concentration of the electrode
Answer: c
Explanation: Hysteresis depends not only on the nature of the material and the structural changes
involved such as difficult transitions involving, for example, the breaking of string bonds are
likely to exhibit much hysteresis but also on the experimental conditions such as the rates of
heating and cooling.
15: In the application of DTA and DSC which of the following parameters is measured for the
glasses?
Option 1: Concentration of the glass
Option 2: Solubility of the glass
Option 3: Cooling temperature
Option 3: Transition temperature
Answer: d
Explanation: In the application of DTA and DSC for glass the transition temperature Tg is
measured. This appears not as a clear peak but rather as a broad anomaly in the baseline of the
DTA curve, and it represents the temperature at which the glass transforms from a rigid solid to a
supercooled, albeit very viscous, liquid.
16: DTA can be used for which of the following process?
Option 1: Line positions of the crystals
Option 2: Mechanical properties of the crystals
Option 3: Phase diagrams
Option 3: Catalytic properties of enzymes
Answer: c
Explanation: Differential thermal analysis is a powerful method for the determination of phase
diagram, especially when used in conjunction with other techniques such as X-ray diffraction for
the identification of the crystalline phases present.
17: For the decomposition of the anhydrous calcium oxalate, which of the following steps occur?
Option 1: Intermediates, transition state, product
Option 2: Intermediates, anhydrous oxalate, calcium oxysalts
Option 3: Intermediates, aqueous hydrates, calcium hydroxides
Option 3: Intermediates, anhydrous calcium oxalate, calcium carbonate
Answer: d
Explanation: In the multistage decomposition processes, TG either alone or in conjunction with
DTA may be used to separate and determine the individual steps. A known example is the
decomposition of the anhydrous calcium oxalate where the decomposition occurs in three steps,
intermediates, anhydrous calcium oxalate, and calcium carbonate.
18: A rapid TGA method is used for which of the following process?
Option 1: Decomposition of polymers exothermally
Option 2: Decomposition of enzymes exothermally
Option 3: Decomposition of crystals endothermally
Option 3: Decomposition of reactions isothermally
Answer: d
Explanation: An accurate and rapid TGA method is to study the decomposition of reactions
isothermally, the TGA furnace is arranged at a pre-set temperature and the sample introduced
directly at this temperature. After allowing 2 to 3 minutes for the sample with time can be
followed. The process may be repeated at other temperatures and the results analyzed to
determine reaction mechanisms, etc.
19. Which of the following parameters can be used, using the DSC and DTA cells?
Option 1: Catalytic properties of enzyme
Option 2: Elasticity of crystals
Option 3: Enthalpy of substances
Option 3: Line positions of phases
Answer: c
Explanation: With DSC cells or with DTA cells that have been designed for a calorimetric
response such measurements may be made rather more accurately and in addition the heat
capacity of substances or phases may be measured as a function of temperature.
20: Differential Scanning Calorimeters (DSOPTION 3: measure temperatures and heat flows
associated with thermal transitions in a material.
21: Thermo-mechanical Analysis (TMOPTION 1:
A technique in which a deformation of the sample under non-oscillating stress is monitored
against time or temperature while the temperature of the sample, in a specified atmosphere, is
programmed. The stress may be compression, tension, flexure or torsion
22. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMOPTION 1:
A technique in which the sample's kinetic properties are analyzed by measuring the strain or
stress that is generated as a result of strain or stress, varies (oscillate) with time, applied to the
sample.
23: Differential Thermal Analysis (DTOPTION 1:
A technique in which the difference in temperature between the sample and a reference material
is monitored against time or temperature while the temperature of the sample, in a specified
atmosphere, is programmed.
You might also like
- Analytical Chemistry McqsDocument5 pagesAnalytical Chemistry McqsAll For U100% (3)
- MCQ Test On Gas ChromatographyDocument9 pagesMCQ Test On Gas ChromatographyHd Ns0% (2)
- Question and Answers: 500+ Chromatography MCQ and Answer With Free PDFDocument11 pagesQuestion and Answers: 500+ Chromatography MCQ and Answer With Free PDFياسمين مفتكرNo ratings yet
- MCQ ChromatographyDocument13 pagesMCQ ChromatographyReecha Madan100% (4)
- HPLC - GCDocument28 pagesHPLC - GCTayyaba Sadaq100% (1)
- Flame Photometry Topic McqsDocument9 pagesFlame Photometry Topic McqsAli Hamza Sajid Ali Hamza Sajid100% (5)
- MCQs Nuclear Analytical Techniques MSC 4THDocument11 pagesMCQs Nuclear Analytical Techniques MSC 4THPhoton Online Science Academy100% (1)
- Analytical Chemistry Quiz 2Document12 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Quiz 2Lokesh Bhoi100% (1)
- Spectroscopy (MCQ) - : YogeshDocument16 pagesSpectroscopy (MCQ) - : YogeshYUGI SINGH100% (1)
- Unit2 A Final MCQS Data-1Document19 pagesUnit2 A Final MCQS Data-1Rohit Ghere50% (2)
- Mcqs - Biochemistry - HPLC - PFMSG ForumDocument4 pagesMcqs - Biochemistry - HPLC - PFMSG ForumArslan Bashir67% (3)
- Gas Chromatography-1Document6 pagesGas Chromatography-1muhammadNo ratings yet
- LO14 Nanoscience MCQDocument5 pagesLO14 Nanoscience MCQpew75% (4)
- Instrumentation Final ExamDocument6 pagesInstrumentation Final ExamHabtamu Molla100% (2)
- Analytical Instrumentation Questions and Answers - Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocument3 pagesAnalytical Instrumentation Questions and Answers - Atomic Absorption SpectrosMikaila Denise LoanzonNo ratings yet
- MCQ CharacterizationDocument18 pagesMCQ CharacterizationAmjed AL-KAHTEEB100% (2)
- MCQ Test-4, Unit 2, Engg - Chemistry, 2020-21Document10 pagesMCQ Test-4, Unit 2, Engg - Chemistry, 2020-21Dr. N. P. Tripathi100% (1)
- I - Colloidal Dispersion MCQ BankDocument19 pagesI - Colloidal Dispersion MCQ BankKishor Sarode100% (1)
- MCQs Suface Tension & Interficial TensionDocument15 pagesMCQs Suface Tension & Interficial Tensionmukul sidhqueNo ratings yet
- Chromatography QuizDocument38 pagesChromatography QuizKhadeeja Mohamed100% (1)
- Multiple Choice Questions For Fluorescence SpectrosDocument3 pagesMultiple Choice Questions For Fluorescence SpectrosArpit Bhargava82% (17)
- MCQ-Unit-1 - Water Technology-1Document36 pagesMCQ-Unit-1 - Water Technology-1Rohit Ghere100% (3)
- Test - Molecular Spectroscopy - 30 Questions MCQ TestDocument15 pagesTest - Molecular Spectroscopy - 30 Questions MCQ Testsatish100% (1)
- Advanced Analytical Quiz 5Document2 pagesAdvanced Analytical Quiz 5Kemikage Peter87% (15)
- Multiple Choice Questions SURFACE CHEMISTRYDocument12 pagesMultiple Choice Questions SURFACE CHEMISTRYMahrishiShukla50% (2)
- MCQ Ch3 Nano Science Fermi EnergyDocument17 pagesMCQ Ch3 Nano Science Fermi EnergyJamilur Rahman0% (2)
- Question Bank On Ir Spectroscopy-MatDocument10 pagesQuestion Bank On Ir Spectroscopy-MatRohan Sharma33% (3)
- Nanotechnology MCQ'sDocument10 pagesNanotechnology MCQ'sKomal fatima100% (2)
- MCQ in ChromatograpgyDocument25 pagesMCQ in ChromatograpgyDeepak Pradhan62% (63)
- BP 401T MCQ Unit3 by Dr. Parjanya ShuklaDocument28 pagesBP 401T MCQ Unit3 by Dr. Parjanya ShuklaVikash Kushwaha100% (2)
- Mcqs - BiochemistryDocument3 pagesMcqs - Biochemistrynagendra_rdNo ratings yet
- UV/VIS Quiz 2 and AnswersDocument2 pagesUV/VIS Quiz 2 and Answerslebogang80% (15)
- Instrumental Methods of Chemical Analysis 1Document9 pagesInstrumental Methods of Chemical Analysis 1uvir iitm100% (1)
- Model Question of Unit 4 PharmacognosyDocument5 pagesModel Question of Unit 4 Pharmacognosysadia parveen100% (3)
- MCQDocument14 pagesMCQشمس صبيح عبد الرحيم100% (1)
- Advanced Chromatographic TechniquesDocument9 pagesAdvanced Chromatographic Techniquesmsabubakar100% (1)
- Semester Iv Physical Pharmaceutics Ii (BP403TP) Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument52 pagesSemester Iv Physical Pharmaceutics Ii (BP403TP) Multiple Choice Questionsvaibhavi mali75% (4)
- MCQ - SE Volumetric AnaDocument8 pagesMCQ - SE Volumetric Anaismaeel24775% (8)
- Physical Chemistry MCQS Question BankDocument5 pagesPhysical Chemistry MCQS Question BankMUHAMMAD JUNAID0% (2)
- B.sc. First Year Physical Chemistry Mcqs Question BankDocument24 pagesB.sc. First Year Physical Chemistry Mcqs Question BankMUHAMMAD JUNAID100% (3)
- MCQ On ElectrophoresisDocument2 pagesMCQ On ElectrophoresisHunzala100% (3)
- Instrumentation QuestionsDocument36 pagesInstrumentation QuestionsMarlon Peteros100% (1)
- UV-VIS Organic Spectroscopy MCQDocument20 pagesUV-VIS Organic Spectroscopy MCQShunmugasundaram Arunachalam100% (2)
- Unit IV MCQ'SDocument9 pagesUnit IV MCQ'STejas Katkar100% (1)
- IMA MCQsDocument18 pagesIMA MCQsPCOP Pharmacy100% (1)
- Poc 2 MCQDocument20 pagesPoc 2 MCQj setty81% (26)
- P.P MCQ 1&2 PDFDocument4 pagesP.P MCQ 1&2 PDFAhan Bhaskar100% (2)
- MCQs of PolymersDocument5 pagesMCQs of PolymersKifayat Ullah100% (2)
- Question Papernnswer Key of NanotechnologyDocument21 pagesQuestion Papernnswer Key of Nanotechnologyrumman100% (1)
- All MCQS First YearDocument85 pagesAll MCQS First YearNazimEhsanMalik25% (4)
- 1H NMR Spectroscopy in Organic Chemistry - MCQDocument18 pages1H NMR Spectroscopy in Organic Chemistry - MCQShunmugasundaram ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Engineering MCQDocument20 pagesPharmaceutical Engineering MCQSanjy Kumar83% (6)
- MM 302 X Ray Mcqs Test Combined - 1 4Document16 pagesMM 302 X Ray Mcqs Test Combined - 1 4د.حاتممرقه100% (6)
- INSTRU I (Spectroscopy 1) (65 Items)Document7 pagesINSTRU I (Spectroscopy 1) (65 Items)Mark Ryan Tripole100% (1)
- Aaaaahhhhh I Don't Know If You Have AnyDocument32 pagesAaaaahhhhh I Don't Know If You Have AnyTom VloggerNo ratings yet
- Thermo GravimetricDocument21 pagesThermo GravimetricBhupendra TomarNo ratings yet
- Thermal PropertiesDocument20 pagesThermal PropertiesMONIRUZZAMAN MONIRNo ratings yet
- Differential Thermal Analysis (Dta)Document15 pagesDifferential Thermal Analysis (Dta)DanielNo ratings yet
- MSC I Sem - BRP - Lect 8Document20 pagesMSC I Sem - BRP - Lect 8Nutan GautamNo ratings yet
- Differential Scanning CalorimetryDocument6 pagesDifferential Scanning CalorimetrySurender MalikNo ratings yet
- MCQS of Inorganic BS6THDocument12 pagesMCQS of Inorganic BS6THPhoton Online Science AcademyNo ratings yet
- Physical CHM MCQS For MSCDocument15 pagesPhysical CHM MCQS For MSCPhoton Online Science AcademyNo ratings yet
- MSC 2 Mcqs Analytical Chemistry MSC 2ndDocument20 pagesMSC 2 Mcqs Analytical Chemistry MSC 2ndPhoton Online Science AcademyNo ratings yet
- Mcqs Inorganic Bs 2ndDocument18 pagesMcqs Inorganic Bs 2ndPhoton Online Science Academy100% (1)
- MCQS Special TopicsDocument18 pagesMCQS Special TopicsPhoton Online Science AcademyNo ratings yet
- MCQs Nuclear Analytical Techniques MSC 4THDocument11 pagesMCQs Nuclear Analytical Techniques MSC 4THPhoton Online Science Academy100% (1)
- Cyclic VoltaDocument3 pagesCyclic VoltaPhoton Online Science AcademyNo ratings yet
- MCQS Introduction To Statistical Theory MSC 4THDocument19 pagesMCQS Introduction To Statistical Theory MSC 4THPhoton Online Science AcademyNo ratings yet
- Debye-Huckel Limiting Law Debye-Huckle Theory of Activity CoefficientsDocument5 pagesDebye-Huckel Limiting Law Debye-Huckle Theory of Activity CoefficientsPhoton Online Science AcademyNo ratings yet
- Mcqs Electrochemistry: Chemistry by Saad AnwarDocument5 pagesMcqs Electrochemistry: Chemistry by Saad AnwarPhoton Online Science Academy0% (1)
- Rate of Reaction 2 MSDocument5 pagesRate of Reaction 2 MSPhoton Online Science AcademyNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction 1 MSDocument7 pagesRate of Reaction 1 MSPhoton Online Science AcademyNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Computer Aided Analysis and Design ofDocument7 pagesComparison of Computer Aided Analysis and Design ofPacha Khan KhogyaniNo ratings yet
- Dose Calc - Practice ProblemsDocument3 pagesDose Calc - Practice Problemsapi-484630324No ratings yet
- CPED and MatSci PDFDocument3 pagesCPED and MatSci PDFonyxNo ratings yet
- ISU - Ilagan Module Foundation EngineeringDocument7 pagesISU - Ilagan Module Foundation EngineeringRanie boy CabanillaNo ratings yet
- Article 3 (2019) - Wang, Jing, Et Al.Document12 pagesArticle 3 (2019) - Wang, Jing, Et Al.Doom RefugeNo ratings yet
- Fluid Flow in PipesDocument29 pagesFluid Flow in PipesitzGeekInside90% (20)
- GS16 Gas Valve: With On-Board DriverDocument4 pagesGS16 Gas Valve: With On-Board DriverProcurement PardisanNo ratings yet
- Norma MAT2004Document12 pagesNorma MAT2004Marcelo Carvalho100% (1)
- What Do You WhatDocument22 pagesWhat Do You WhatSaikat SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Copper and Its AlloysDocument6 pagesCopper and Its AlloysNaidra AbarquezNo ratings yet
- Tinuvin 928: Technical Data SheetDocument3 pagesTinuvin 928: Technical Data SheetCarlotta C.No ratings yet
- Mass Flow Vs Volumetric Flow MetersDocument5 pagesMass Flow Vs Volumetric Flow MetersMostafa Ahmed ZeinNo ratings yet
- PierDocument4 pagesPierAtulkumar ManchalwarNo ratings yet
- 420118-Hydraulic Pump SettimaDocument9 pages420118-Hydraulic Pump SettimaAndreyOsyaninNo ratings yet
- Metal Forming & Machining (MF F313) : BITS PilaniDocument54 pagesMetal Forming & Machining (MF F313) : BITS PilaniNavkar MehtaNo ratings yet
- heat-exchangers-TEMA TYPEDocument12 pagesheat-exchangers-TEMA TYPEvaibhavNo ratings yet
- Heavy Weight DrillPipeDocument10 pagesHeavy Weight DrillPipeAPERARLTATORRESNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectrometers Coupled To Thermal AnalysisDocument24 pagesFourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectrometers Coupled To Thermal Analysisc_passerino6572No ratings yet
- Grade3 3rd Q-ScienceDocument5 pagesGrade3 3rd Q-Scienceflower.power11233986No ratings yet
- Solution DPP Nitesh Devnani.Document19 pagesSolution DPP Nitesh Devnani.YUKTESH YuBoNo ratings yet
- MECHANICAL CONCEPTS TestDocument19 pagesMECHANICAL CONCEPTS TestBob DehnkeNo ratings yet
- Nex Flow: Frigid-X Panel CoolerDocument17 pagesNex Flow: Frigid-X Panel CoolerrehanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 7.2 Rate of ReactionDocument3 pagesWorksheet 7.2 Rate of Reactionsavage hunterNo ratings yet
- Three Types of Clouds - Elementary WorksheetsDocument2 pagesThree Types of Clouds - Elementary Worksheetssixhotpeppers100% (18)
- Climate ZonesDocument2 pagesClimate Zonesapi-308047560No ratings yet
- Sediment Lab ReportDocument5 pagesSediment Lab ReportMihails Aleksejevs100% (1)
- Hoja Técnica Mpa 4020 Ba AntiedimentanteDocument2 pagesHoja Técnica Mpa 4020 Ba AntiedimentanteBryan GavilanezNo ratings yet
- Labsheet DJJ30113 Heat Treatment PDFDocument3 pagesLabsheet DJJ30113 Heat Treatment PDFkarim100% (1)
- Blaine Number - Average Particle SizeDocument2 pagesBlaine Number - Average Particle Sizedondo1004No ratings yet
- In Memoriam Frank LeslieDocument17 pagesIn Memoriam Frank Leslieac.diogo487No ratings yet