Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Hydrostatic Pressure For RTR
Uploaded by
Muthu KumaranOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Hydrostatic Pressure For RTR
Uploaded by
Muthu KumaranCopyright:
Available Formats
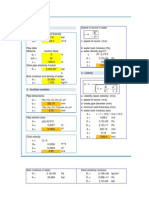
The hydrostatic pressure for RTR (Reinforced Thermosetting Resin) pipes can be calculated using the
following formula:
Hydrostatic Pressure (P) = Density of fluid (ρ) x Gravity (g) x Height of fluid column (h)
Where:
P is the hydrostatic pressure in Pascals (Pa) or pounds per square inch (psi)
ρ is the density of the fluid in kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m^3) or pounds per cubic foot (lb/ft^3)
g is the acceleration due to gravity in meters per second squared (m/s^2) or feet per second squared
(ft/s^2)
h is the height of the fluid column in meters (m) or feet (ft)
For example, if the fluid is water with a density of 1000 kg/m^3 and the height of the fluid column is 20
meters, the hydrostatic pressure at the bottom of the pipe would be:
P = 1000 kg/m^3 x 9.8 m/s^2 x 20 m = 196000 Pa = 196 kPa
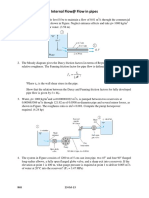
It's important to note that the hydrostatic pressure test is done by filling the pipe with a liquid (usually
water) and pressurizing it to a certain value and hold it for a certain time. The pressure must be higher
than the normal operating pressure and the time must be for a certain time to check for leaks or any
other issues. Additionally, the pressure must be in compliance with the standard specification and the
design of the pipe.
You might also like
- M 388 ContentDocument54 pagesM 388 ContentKOWSHIK 4310No ratings yet
- Water Pressure ConsiderationsDocument18 pagesWater Pressure ConsiderationsEnha EnhaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of AerodynamicsDocument25 pagesFundamentals of AerodynamicsPaul Timothy Hao100% (3)
- 6.mud Hydraulics Fundamentals PDFDocument11 pages6.mud Hydraulics Fundamentals PDFمعلومات ممتعه mohammedNo ratings yet
- Viscous Flow in PipesDocument34 pagesViscous Flow in PipesShinee JayasilanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Tutorial 8C Pumped Piped Systems: Let's Start by Examining The Meaning of Specific Speed of PumpsDocument17 pagesFluid Mechanics Tutorial 8C Pumped Piped Systems: Let's Start by Examining The Meaning of Specific Speed of Pumps12No ratings yet
- Wellbore Hydraulics, Pressure Drop CalculationsDocument85 pagesWellbore Hydraulics, Pressure Drop CalculationsDan Morrell100% (1)
- Water and Slurry HammerDocument48 pagesWater and Slurry Hammeralvarezjgo100% (2)
- Fluid Flow PDFDocument55 pagesFluid Flow PDFHarrrison100% (1)
- PipeFlow PracticeProblemsDocument23 pagesPipeFlow PracticeProblemsFawaz PartoNo ratings yet
- Water Hammer. Examples Tyler - PehmcoDocument12 pagesWater Hammer. Examples Tyler - PehmcoZwingerfeltNo ratings yet
- Fluid Flow Sample Problem-Continuity EquationDocument41 pagesFluid Flow Sample Problem-Continuity EquationJaid Hedriana100% (1)
- Drilling Hydraulics ADocument63 pagesDrilling Hydraulics Asryn89100% (3)
- A Simplified Approach To Water-Hammer AnalysisDocument4 pagesA Simplified Approach To Water-Hammer AnalysisChem.EnggNo ratings yet
- Fluids HW SolutionDocument8 pagesFluids HW SolutionDennis Brown100% (1)
- Anschp 15Document21 pagesAnschp 15Avi Ramirez Cervantes56% (9)
- Texto Vent - Cent y Axiales Cap1-6Document68 pagesTexto Vent - Cent y Axiales Cap1-6baztionNo ratings yet
- Problem A RioDocument9 pagesProblem A RioKoe Chien ThongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Process and Process Variables 2 Fall22Document24 pagesChapter 3 Process and Process Variables 2 Fall22iB13eNo ratings yet
- Solution#1Document5 pagesSolution#1Exel Dua CincinNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Hydraulic Analysis Lec 6Document30 pagesPipeline Hydraulic Analysis Lec 6Kokab AzazNo ratings yet
- 5 6224290721604569803Document4 pages5 6224290721604569803manayagamaryjoy9No ratings yet
- Fisika Terapan, Fluids 2006Document8 pagesFisika Terapan, Fluids 2006N_ie89No ratings yet
- PE-hydraulic Design of Liquid or Water Piping SystemDocument16 pagesPE-hydraulic Design of Liquid or Water Piping SystemmujeebscribdNo ratings yet
- Vdocuments - MX Solucionario Capitulo 15 Paul e TippensDocument21 pagesVdocuments - MX Solucionario Capitulo 15 Paul e TippensElizabeth Sanchez0% (2)
- Fluid Mech. Chapter10 - UploadedDocument25 pagesFluid Mech. Chapter10 - UploadedBryan ChooiNo ratings yet
- Compressible Gas FlowDocument7 pagesCompressible Gas FlowAl KappNo ratings yet
- Manometer PressureDocument4 pagesManometer PressureLos BastardosNo ratings yet
- FE Fluids Review 2013Document31 pagesFE Fluids Review 2013Mahmoud HelmyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Measurement of PressureDocument9 pagesChapter 2: Measurement of PressurenursyahzananiNo ratings yet
- Rigonan A-1 HydraulicsDocument13 pagesRigonan A-1 HydraulicsFrancis Angelo RigonanNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Sheet 5 Energy ADocument19 pagesHydraulics Sheet 5 Energy AMohamed H AliNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Mass Energy Eq ProbsDocument6 pagesFluid Mechanics Mass Energy Eq ProbsDÈènvêËr 빛 사랑No ratings yet
- Ejercicios IDocument6 pagesEjercicios IFlavio Mayta LauraNo ratings yet
- Pressure Loss Major LossDocument2 pagesPressure Loss Major Lossvictor.sNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - Chapter 1 - Flow in PipesDocument13 pagesFluid Mechanics - Chapter 1 - Flow in PipesHazzim HamdanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - jan2015.PDF (Fluid Mech)Document4 pagesTutorial 3 - jan2015.PDF (Fluid Mech)pijechadNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument16 pagesPDFŘïśhåbh ÇhåţúŕvëđîNo ratings yet
- CHE 324 Fluid and Particle Processes: AssignmentDocument2 pagesCHE 324 Fluid and Particle Processes: Assignmentrizanda93No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Worksheet 2Document8 pagesFluid Mechanics Worksheet 2anon_293092329No ratings yet
- FLuid Mechs ExercisesDocument8 pagesFLuid Mechs ExercisesMark Andrew TabucanonNo ratings yet
- Fisica Solo Ejemplos Chapter 15. FLUIDS: DensityDocument8 pagesFisica Solo Ejemplos Chapter 15. FLUIDS: DensityEdvin CastilloNo ratings yet
- Exp 4 Gas AbsorptionDocument18 pagesExp 4 Gas AbsorptionakuNo ratings yet
- FM Sol Chap03-001Document34 pagesFM Sol Chap03-001scs1720No ratings yet
- AnnieDocument6 pagesAnnieAnnie Glorina LumauigNo ratings yet
- DCC30122 - Fluids MechanicsDocument9 pagesDCC30122 - Fluids MechanicsHadif NuqmanNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Flujo CriticoDocument4 pagesEjercicios Flujo Criticoedgar leonNo ratings yet
- Internal FlowDocument41 pagesInternal FlowTusanita MapuolaNo ratings yet
- Fluids Tutorial 2Document1 pageFluids Tutorial 2tzonerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21. Hydraulics: by Brian BomanDocument10 pagesChapter 21. Hydraulics: by Brian BomanLao ZhuNo ratings yet
- SolveDocument11 pagesSolveShamanAcolyteNo ratings yet
- Mebc CH 1 Questions of GtuDocument3 pagesMebc CH 1 Questions of GtuDeep Khunt100% (1)