Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Alcatel - Optimization 31 40
Uploaded by
Tas KayOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Alcatel - Optimization 31 40
Uploaded by
Tas KayCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
4 Unbalanced power budget problem
Abis trace
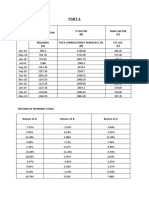
Example of an Abis trace analysis
delta_Path_loss
nb_of samples
AV_MS_PWR
Path_loss_UL
Path_loss_DL
delta_quality
RxQual_UL
RxQual_DL
Frequency
RxLev_UL
RxLev_DL
106 -9 4 . 5 2 -8 7 . 1 9 0.43 0.25 127.55 130.19 -2 . 6 4 0.18 33.03 2066
89 -8 4 . 2 9 -7 5 . 1 7 0.65 0.44 115.32 118.17 -2 . 8 5 0.21 31.03 2001
118 -9 0 . 7 5 -8 3 . 3 6 0.46 0.41 123.22 126.36 -3 . 1 4 0.04 32.46 3193
124 -8 8 . 8 9 -8 5 . 3 0 0.29 0.67 120.48 128.30 -7 . 8 2 -0 . 3 7 31.59 2931
D IS TR IB U TIO N O F U P L IN K Q U A L ITY
F re q u e n c y Q u a l0 Q u a l1 Q u a l2 Q u a l3 Q u a l4 Q u a l5 Q u a l6 Q u a l7 B a d _ Q u a lit y
106 84.75 % 4.07 % 3.68 % 3.19 % 1.36 % 1.50 % 0.92 % 0.53 % 2.95 %
89 81.41 % 1.70 % 2.95 % 3.65 % 6.35 % 2.55 % 1.30 % 0.10 % 3.95 %
118 83.62 % 4.23 % 4.23 % 3.35 % 1.57 % 1.79 % 0.97 % 0.25 % 3.01 %
124 90.79 % 1.06 % 2.18 % 2.35 % 1.77 % 1.30 % 0.48 % 0.07 % 1.84 %
D IS TR IB U TIO N O F D O W N L IN K Q U A L ITY
F re q u e n c y Q u a l0 Q u a l1 Q u a l2 Q u a l3 Q u a l4 Q u a l5 Q u a l6 Q u a l7 B a d _ Q u a lit y
106 90.27 % 3.44 % 2.08 % 1.55 % 0.92 % 1.36 % 0.34 % 0.05 % 1.74 %
89 80.16 % 6.45 % 7.00 % 3.85 % 1.50 % 0.50 % 0.45 % 0.10 % 1.05 %
118 86.78 % 2.72 % 3.95 % 1.82 % 1.41 % 1.13 % 1.19 % 1.00 % 3.32 %
124 77.14 % 4.37 % 5.87 % 5.94 % 3.48 % 1.36 % 0.82 % 1.02 % 3.21 %
1.31
Example of Computation of delta path loss based on Abis measurements
BTS transmitted power , MS transmitted power
combiner loss - ,
measured received DL level - measured received UL level -
DL Path loss UL path loss
delta path loss computed on Abis - dBm
© Alcatel University - 8AS902001485 VH ZZA Ed.02 Page 1.31
1.4 Unbalanced power budget problem
RMS data
Suspecting a TRX hardware problem
Average Path Balance
Average Cell Path Balance
= -0. 9 dB
Fair average Path Balance at Cell level can hide a bad value
for one TRX
1.32
▼ These RMS indicators are provided on RNO tool per TRX, per Cell:
Vector of the Number of Measurement Results per Path Balance band
RMPBV = RMS_PathBalance_sample
Average Path Balance value
RMPBAN = RMS_PathBalance_avg
© Alcatel University - 8AS902001485 VH ZZA Ed.02 Page 1.32
1.4 Unbalanced power budget problem
Typical causes
Antennae or common RF components, TMA (pb common to all
TRXs of the BTS)
TRX RF cables/LNA ... if problem located on only 1 FU
1.33
▼ Every BTS has its proper architecture and the diagnosis must be adapted.
© Alcatel University - 8AS902001485 VH ZZA Ed.02 Page 1.33
1 TYPICAL RADIO PROBLEMS
1.5 TCH Congestion problem
1.34
© Alcatel University - 8AS 90200 1485VH ZZA Ed.02
Theoretical presentation
Coverage problem
Interference problem
Unbalanced power budget problem
TCH Congestion problem
Deducing the right team for intervention
Exercises
© Alcatel University - 8AS902001485 VH ZZA Ed.02 Page 1.34
1.5 TCH Congestion problem
Definition and symptoms
Definition: TCH Congestion
TCH Congestion rate (TCH Assignment Phase) is too high (more
than 2%)
Rule: try to meet the offered traffic (asked by users) by providing the
right number of resources (TRX extension)
Symptoms:
Customers complain about ‘Network busy’
OMC QoS indicators
High “TCH Congestion rate”
Low “incoming Intra/Inter BSC HO success rate” (no TCH available)
High “Directed Retry rate” if activated
A interface indicator: “BSS Congestion failure in OC”
High rate of Assignment Failure messages, No radio resource
available
1.35
© Alcatel University - 8AS902001485 VH ZZA Ed.02 Page 1.35
1.5 TCH Congestion problem
Examination and typical causes
Examination: TCH Congestion
On a per cell basis examination, check the evolution of the TCH
Congestion rate.
Typical causes:
Special events:
Foreseeable: football match, important meeting
Activate some TRXs already installed (and use Synthesized
FH)
Add special moving BTSs
Not foreseeable: car crash on the highway
1.36
▼ Cells on wheel operational by several operators around the world for special events coverage & capacity
IRMA (SFR) connected to Caen’s BSC.
Orange coverage / Football WC 1998 for Paris « Stade de France »:
Specific cells covering Paris Stadium. During games, only small capacity (using joker frequencies).
During breaks, some TRX off cells around are turned off, and frequencies are reused for stadium cells.
© Alcatel University - 8AS902001485 VH ZZA Ed.02 Page 1.36
1.5 TCH Congestion problem
Typical causes (1/2)
Daily periodic problems
At peak hour, the cell is not correctly dimensioned.
Annex 1
Estimate the offered traffic:
– At OMC-R level: Traffic in Erlang/(1- TCH Congestion
rate)
Use the B-Erlang law to estimate the number of TCHs
required for a 2% blocking rate, thus the target configuration
Add TRXs to reach the new target configuration and find ‘joker
frequencies’ and / or implement concentric cells.
1.37
▼ Warning: “offered traffic” is not the capacity delivered by the system but the traffic asked by the users.
© Alcatel University - 8AS902001485 VH ZZA Ed.02 Page 1.37
1.5 TCH Congestion problem
Typical causes (2/2)
Daily periodic problems
At peak hour, the cell is not correctly dimensioned.
Use specific densification features
– Half Rate
– Forced Directed Retry
– Traffic handover
– Fast Traffic handover
– Candidate Cell Evaluation (FREEFACTOR /
LOADFACTOR)
1.38
▼ Half rate may not only mean “SW” solution. Need of G2 BSC/TC, Evolium TRE or G2 DRFU.
© Alcatel University - 8AS902001485 VH ZZA Ed.02 Page 1.38
1 TYPICAL RADIO PROBLEMS
1.6 Deducing the right team for intervention
1.39
© Alcatel University - 8AS 90200 1485VH ZZA Ed.02
Theoretical presentation
Coverage problem
Interference problem
Unbalanced power budget problem
TCH Congestion problem
Deducing the right team for intervention
Exercises
© Alcatel University - 8AS902001485 VH ZZA Ed.02 Page 1.39
1.6 Deducing the right team for intervention
Process
QOS team Drive test team
Problem characterization RFT team - Interferences
- Coverage (indoor)
- Power budget
QOS alarm on the network, Make assumption causes - Congestion (TCH, SDCCH)
on a BSC or some cells - BSS problem
END
DHCP No Investig problem ? No Recurrent problem ?
- Indicators (% call drop)
- Field measurements/planning Yes Yes
- Subscriber complains
Yes Planning/BSS causes
No
Correction
Check the tuning of default radio parameters
action
Planning team
Standard parameters ?
Maintenance team
Dimensionning team
Consult the config. db No Yes Choose an (other) classical algo
On purpose Yes Identify the tunable parameters
Cell corrected ?
No
Neighbor cell ?
Impact simulation of a
NOK Impact estimation parameter modification
Check ? With QOS ? System problem ? No N times No Simulation OK ?
Yes =N Yes
OK
Standard setting ? Call expert Parameters modification
Database updating
END
DHCP
- Microcell, multiband - Hopping
- Concentric - Marketing
1.40
© Alcatel University - 8AS902001485 VH ZZA Ed.02 Page 1.40
You might also like
- Math Practice Simplified: Decimals & Percents (Book H): Practicing the Concepts of Decimals and PercentagesFrom EverandMath Practice Simplified: Decimals & Percents (Book H): Practicing the Concepts of Decimals and PercentagesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Gambia QCELL ROUND 2 234G Cluster4 DT Optimization ReportDocument50 pagesGambia QCELL ROUND 2 234G Cluster4 DT Optimization Reportleandre vanieNo ratings yet
- Labor 1Document1 pageLabor 1Putra NovariNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios ForoDocument56 pagesEjercicios ForoLaura HernandezNo ratings yet
- Big Data Analysis Assig.2Document5 pagesBig Data Analysis Assig.2gerrydenis20No ratings yet
- % Var. COLCAP: Limite Inferior Limite Superio RDocument79 pages% Var. COLCAP: Limite Inferior Limite Superio RMonicaNo ratings yet
- Parte InferencialDocument46 pagesParte InferencialLeidy Tatiana MartinezNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledrositaNo ratings yet
- WorkingDocument4 pagesWorkingKhawaja HamzaNo ratings yet
- Statistical POwerDocument35 pagesStatistical POwerWawex DavisNo ratings yet
- Tasas - TerminadoDocument8 pagesTasas - TerminadojeanNo ratings yet
- Return Saham Bulan A B C rA-rA RB-RBDocument8 pagesReturn Saham Bulan A B C rA-rA RB-RBCitra ParwatiNo ratings yet
- Confiabilidad EjerciciosDocument10 pagesConfiabilidad EjerciciosGely CruzNo ratings yet
- MCRSDocument9 pagesMCRSMercedes Isla VertizNo ratings yet
- 6055 TwoDocument2 pages6055 Twoapi-3699305No ratings yet
- Kinetics 9 TH ProblemDocument4 pagesKinetics 9 TH ProblempepechuyhrNo ratings yet
- Description Interest Rate Remaining Term Current Principal BalanceDocument23 pagesDescription Interest Rate Remaining Term Current Principal BalanceShubhangi JainNo ratings yet
- Public 33 Utility SummaryDocument1 pagePublic 33 Utility Summaryfarhan121921No ratings yet
- Chart Title: Valor de KDocument9 pagesChart Title: Valor de KNatalia BordaNo ratings yet
- Ey CaDocument5 pagesEy CaTrường Vĩ HuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Individual-Excercise Profile ORIGINALDocument39 pagesIndividual-Excercise Profile ORIGINALSilvestre GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Mean and Standard Deviation SolutionDocument4 pagesMean and Standard Deviation SolutionC.E.O AnnieNo ratings yet
- Examples 9-3 and 9-4 - ProbabilityDocument22 pagesExamples 9-3 and 9-4 - ProbabilityFernando WuNo ratings yet
- Correlation-and-P I GDocument11 pagesCorrelation-and-P I GCamiloArenasBonillaNo ratings yet
- Monroe County Board of Elections: Absentee StatisticsDocument1 pageMonroe County Board of Elections: Absentee StatisticsNews 8 WROCNo ratings yet
- Determinacion de Portafolio OptimoDocument8 pagesDeterminacion de Portafolio OptimoDanie RomaniNo ratings yet
- TABLE: Modal Participating Mass Ratios Case Mode Period UX UY UZ Sum UX Sum UY Sum UZDocument2 pagesTABLE: Modal Participating Mass Ratios Case Mode Period UX UY UZ Sum UX Sum UY Sum UZsowmith16No ratings yet
- Book 3Document2 pagesBook 3sowmith16No ratings yet
- Tamiz A.S.T.M. % Acumulado Retenido Pasante Abertura (MM) Peso Retenido Gr. % Peso RetenidoDocument3 pagesTamiz A.S.T.M. % Acumulado Retenido Pasante Abertura (MM) Peso Retenido Gr. % Peso RetenidofrankNo ratings yet
- Tamiz A.S.T.M. % Acumulado Retenido Pasante Abertura (MM) Peso Retenido Gr. % Peso RetenidoDocument3 pagesTamiz A.S.T.M. % Acumulado Retenido Pasante Abertura (MM) Peso Retenido Gr. % Peso RetenidofrankNo ratings yet
- Diskusi2 Statistik EkonomiDocument1 pageDiskusi2 Statistik Ekonomitjut firsa pirrazaNo ratings yet
- Summer Project DataDocument22 pagesSummer Project Datayashaswisharma68No ratings yet
- Dileep Stats2Document10 pagesDileep Stats2Vanad KuthialaNo ratings yet
- Currency Options Pricing Under Mean Reverting VolatilityDocument20 pagesCurrency Options Pricing Under Mean Reverting Volatilitymichael odiemboNo ratings yet
- Cortec CV Table 2.5 CageDocument1 pageCortec CV Table 2.5 CageFernando Ledesma SolaecheNo ratings yet
- Week 3 OLA Dashboard From July 17-July 23 2023Document21 pagesWeek 3 OLA Dashboard From July 17-July 23 2023yimerNo ratings yet
- Practica - Excel - XLSX Filename - UTF-8''Practica Excel-1Document9 pagesPractica - Excel - XLSX Filename - UTF-8''Practica Excel-1Henry Arias SolizNo ratings yet
- Blackjack Excel Zen vs. Omega ComparisonDocument2 pagesBlackjack Excel Zen vs. Omega ComparisonKarthik S. IyerNo ratings yet
- Data Epid InfoDocument53 pagesData Epid Infodina kardinaNo ratings yet
- Price and Return Data For Walmart (WMT) and Target (TGT)Document8 pagesPrice and Return Data For Walmart (WMT) and Target (TGT)Raja17No ratings yet
- Taller de PortafolioDocument18 pagesTaller de PortafolioEdi CostaNo ratings yet
- Ho Lee ModelDocument2 pagesHo Lee Modelkkstarrr2No ratings yet
- ESTADSTICADocument28 pagesESTADSTICALeidy dayana Mejia castroNo ratings yet
- Semana 2 ForoDocument26 pagesSemana 2 ForoLaura HernandezNo ratings yet
- ExcelDocument16 pagesExcelcoooleNo ratings yet
- 20 Statistics DataAnalysis ExpResultsINTaPRESDocument16 pages20 Statistics DataAnalysis ExpResultsINTaPRESrasha assafNo ratings yet
- ExamplesCh33 24jan2017Document21 pagesExamplesCh33 24jan2017Haidar IsmailNo ratings yet
- Soal No 2Document3 pagesSoal No 2priya teguhNo ratings yet
- Sintaxis de FrecuenciaDocument13 pagesSintaxis de FrecuenciaLupe SalgadoNo ratings yet
- Description of The Data: Ratio Desorbe DDocument5 pagesDescription of The Data: Ratio Desorbe DPritish DasNo ratings yet
- Investment Management ProjectDocument12 pagesInvestment Management ProjectArchana ChapatwalaNo ratings yet
- Comprador TaxasDocument4 pagesComprador TaxasRenan MartinelliNo ratings yet
- Kurva S TGL 8Document1 pageKurva S TGL 8FahriNo ratings yet
- Auto-C Liquicolor: Design VerificationDocument9 pagesAuto-C Liquicolor: Design VerificationclaudiaNo ratings yet
- Des AgueDocument19 pagesDes AgueRIOS CAHUACHI JoseNo ratings yet
- CourseworkDocument3 pagesCourseworkKhawaja HamzaNo ratings yet
- Dependent Indep1 Indep2 Indep3: No. of Variables No. of ObservationsDocument14 pagesDependent Indep1 Indep2 Indep3: No. of Variables No. of Observationscontact7809No ratings yet
- 5 3-QaDocument10 pages5 3-QaRehaan ShahNo ratings yet
- Formula para Calcular El Caudal en Tuberias de Desague: Norma Iso 0.10Document19 pagesFormula para Calcular El Caudal en Tuberias de Desague: Norma Iso 0.10HUMBERTO CARRASCONo ratings yet
- Forecasting Question SheetDocument35 pagesForecasting Question SheetShahzar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Alcatel Optimization 261 270Document10 pagesAlcatel Optimization 261 270Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Alcatel Optimization 251 260Document10 pagesAlcatel Optimization 251 260Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Alcatel Optimization 211 220Document10 pagesAlcatel Optimization 211 220Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Alcatel Optimization 281 290Document10 pagesAlcatel Optimization 281 290Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Alcatel Optimization 271 280Document10 pagesAlcatel Optimization 271 280Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Alcatel Optimization 241 250Document10 pagesAlcatel Optimization 241 250Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Siemens MAC15 4Document4 pagesSiemens MAC15 4Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Alcatel - Optimization 21 30Document10 pagesAlcatel - Optimization 21 30Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Alcatel - Optimization 1 10Document10 pagesAlcatel - Optimization 1 10Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Siemens MAC15NDocument4 pagesSiemens MAC15NTas KayNo ratings yet
- Ak Automatic RohtakDocument1 pageAk Automatic RohtakMark SmithNo ratings yet
- Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis: Guan Jie, Li Ying-Shun, Lu Mai-XiDocument5 pagesJournal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis: Guan Jie, Li Ying-Shun, Lu Mai-XiPaulo SantosNo ratings yet
- Grandstream Gxp1620 1625 DatasheetDocument2 pagesGrandstream Gxp1620 1625 DatasheetJanaki RamanNo ratings yet
- GaN Doherty Amplifier For LTE Micro Cell and Active Antenna System ApplicationsDocument4 pagesGaN Doherty Amplifier For LTE Micro Cell and Active Antenna System ApplicationsStephen MeyerNo ratings yet
- EiS EXpress Reporting Concurrent Manager - White PaperDocument8 pagesEiS EXpress Reporting Concurrent Manager - White PaperRickNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD Electrical Tips Tricks 0618 No2.Docx v2Document5 pagesAutoCAD Electrical Tips Tricks 0618 No2.Docx v2scribdhas2006No ratings yet
- Documentation. HiPath 3000 - 5000 HiPath 3000 Manager C. Communication For The Open Minded. Administrator Documentation A31003-H3580-M101!7!76A9Document283 pagesDocumentation. HiPath 3000 - 5000 HiPath 3000 Manager C. Communication For The Open Minded. Administrator Documentation A31003-H3580-M101!7!76A919237543No ratings yet
- AdrielDocument3 pagesAdrielalylanuzaNo ratings yet
- How To Get A Client A Day With Facebook GroupsDocument6 pagesHow To Get A Client A Day With Facebook Groupscentenojohn.businessNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Sensor Based Traffic Light SystemDocument5 pagesDesign and Development of Sensor Based Traffic Light SystemAyan BiswasNo ratings yet
- Sanmati Engineering College Brochure PDFDocument22 pagesSanmati Engineering College Brochure PDFMES Sanmati Group Adv. Vaishali Jain EducationNo ratings yet
- BIOBASE Fume Hood FH (A) Series User Manual 202007Document37 pagesBIOBASE Fume Hood FH (A) Series User Manual 202007vmpazvNo ratings yet
- 2021 Threat Hunting ReportDocument20 pages2021 Threat Hunting Reportmiss miseryNo ratings yet
- Iso 11119-4-2016Document48 pagesIso 11119-4-2016MaciekNo ratings yet
- Mcqs in Computer Science 5nbsped 9789351342496 - CompressDocument487 pagesMcqs in Computer Science 5nbsped 9789351342496 - CompressAsimullah, M.Phil. Scholar Department of Computer Science, UoPNo ratings yet
- Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash SystemDocument1 pageBitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash SystemjoeyNo ratings yet
- ICF 9 1st SummativeDocument2 pagesICF 9 1st Summativeallan tomasNo ratings yet
- Domestic Data Entry OperatorDocument283 pagesDomestic Data Entry OperatorVilciaDanFlorisNo ratings yet
- Efficia CMSeries Masimo IFUDocument87 pagesEfficia CMSeries Masimo IFUVincent MicallefNo ratings yet
- Proportional Hydraulic Bank: Electrical SpecificationsDocument1 pageProportional Hydraulic Bank: Electrical SpecificationsJaime Basquez PaccoNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering QBDocument6 pagesSoftware Engineering QBKarthick ThiyaguNo ratings yet
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 Security Hardening en USDocument110 pagesRed Hat Enterprise Linux 8 Security Hardening en USMD Showeb Arif SiddiquieNo ratings yet
- Zip 33iDocument43 pagesZip 33iJulio GuarnizNo ratings yet
- Mba Om Course OutlineDocument6 pagesMba Om Course OutlinealeNo ratings yet
- Bm2009i003468348 PDFDocument8 pagesBm2009i003468348 PDFRahulNo ratings yet
- Alarm Monitoring System Overview - Connection DiagramDocument61 pagesAlarm Monitoring System Overview - Connection DiagramDalmatius GonsalvesNo ratings yet
- in The AVR, Looping Action With The "BRNE Target" Instruction Is LimitedDocument3 pagesin The AVR, Looping Action With The "BRNE Target" Instruction Is LimitedMushahid Hussain NomeeNo ratings yet
- IDK-1112R-45SVA1E: User ManualDocument41 pagesIDK-1112R-45SVA1E: User Manualamit281276No ratings yet
- Pessimism and Optimism in Timing Analysis - by ANKIT MAHAJAN - MediumDocument4 pagesPessimism and Optimism in Timing Analysis - by ANKIT MAHAJAN - MediumRAZNo ratings yet
- H590 User Manual V3 WITHOUT SpotifyDocument20 pagesH590 User Manual V3 WITHOUT Spotifys.serdaryilmazNo ratings yet