Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Alcatel Optimization 251 260
Uploaded by
Tas KayCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Alcatel Optimization 251 260
Uploaded by
Tas KayCopyright:
Available Formats
4.
2 Examples and Exercises
Example 1: Optimization of Handover Algorithms (1/4)
Search for best tuning of HO parameters to decrease
call drop
Call drop
HO/Call
1.251
© Alcatel University - 8AS902001485 VH ZZA Ed.02 Page 1.251
4.2 Examples and Exercises
Example 1: Optimization of Handover Algorithms (2/4)
Main Objective: make the HO algorithm as efficient as
possible
Minimize call drop rate
trigger HO soon enough
toward the “best” neighbor
while keeping a good speech quality
avoid HO due to quality: “too late”
avoid having HO/call rate too high
1.252
© Alcatel University - 8AS902001485 VH ZZA Ed.02 Page 1.252
4.2 Examples and Exercises
Example 1: Optimization of Handover Algorithms (3/4)
Method
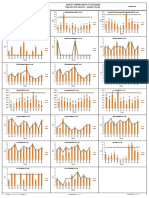
Collect Abis trace chart
Search for HO level to avoid quality
lower than 4 (or even 3)
sufficient number of “bad quality”
< R x Q u a l _ D L > = f(A V _ R x L e v_ D L ) < R x Q u a l_ U L > = f(A V _ R x L e v_ U L )
7 7
6 6
samples 5
3
5
2 2
low standard deviation 1
0
1
N b_sam ples N b_ sa m ple s
problem when HO already 600
400
200
1000
800
600
400
200
activated 0
2
S ta n d a rd D e vi a ti o n
3
0
S ta n d a rd D e vi a ti o n
1 .5
2
1
1
0 .5
0 0
Then tune according to QoS indicators (OMC-R) by repetitive process
A_PBGT_HO/A_LEV_HO/A_QUAL_HO
L_RXLEV_UL_H, L_RXLEV_DL_H, L_RXLEV_UL_P,
L_RXLEV_DL_P
OK as soon as HO success rate stabilized
1.253
▼ Never forget that Abis information takes into account the traffic distribution in the cell. Any parameter tuning done after
an Abis study has to be checked periodically as the distribution in the cell can change from one week to another.
▼ Use the pivot table function (Excel) to build this graph.
RxQUAL
RxQUAL
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
© Alcatel University - 8AS902001485 VH ZZA Ed.02 Page 1.253
4.2 Examples and Exercises
Example 1: Optimization of Handover Algorithms (4/4)
neighboring relationship cleanup
Remove useless relationships (A interface statistics, PM
Type 180)
Remove the common BCCH/BSIC couple
Add new relationships when a new site is created
Finally, check the main QoS indicators
Call drop rate
HO failure rate
HO/call rate
1.254
© Alcatel University - 8AS902001485 VH ZZA Ed.02 Page 1.254
4.2 Examples and Exercises
Example 1: training exercise
According to the Abis results and some parameters already set,
tune qualitatively the sliding averaging windows:
A_QUAL_HO
A_LEV_HO
Level at RxQual=3 -80dBm -96dBm -90dBm
Time allowed:
L_RXLEV_DL_H -85dBm -90dBm -90dBm
5 minutes
A_QUAL_HO 6 6 ?
A_LEV_HO ? ? 4
1.255
© Alcatel University - 8AS902001485 VH ZZA Ed.02 Page 1.255
4.2 Examples and Exercises
Example 2: Optimization of Power Control Algorithms (1/2)
Optimization of Downlink Power Control
Decrease of downlink interference
Risks of delay of HO (without fast power control)
Optimization of Uplink Power Control
Decrease of Uplink interference
MS battery saving
Risks of delay of HO (without fast power control)
1.256
© Alcatel University - 8AS902001485 VH ZZA Ed.02 Page 1.256
4.2 Examples and Exercises
Example 2: Optimization of Power Control Algorithms (2/2)
The main tuning problem is the interaction with handover, which
can slow down HO decision, and debase call drop rate
Power control threshold must be within HO ones
Dynamic step size must be activated if possible
1.257
▼ In the example below, a dynamic MS PC is activated. The MS power changes are really reactive and control the UL
level between -80 and -90dBm. In this example, the HO threshold is -98 dBm.
RxLev_UL
- RxLev_UL
MS_PwrLevel
© Alcatel University - 8AS902001485 VH ZZA Ed.02 Page 1.257
4.2 Examples and Exercises
Example 2: Training Exercise
Explain qualitatively the impacts of some parameter changes
What happens if:
we increase POW_INC_FACTOR?
we increase MAX_POW_INC?
We increase A_LEV_PC?
Time allowed:
5 minutes
1.258
© Alcatel University - 8AS902001485 VH ZZA Ed.02 Page 1.258
4.2 Examples and Exercises
Example 3: Traffic Load Sharing (1/12)
Used to unload cell with too high traffic, without HW extension
Trade-off between traffic sharing/radio quality
Different algorithm
Fast Traffic Handover: Cause 28
Traffic Handover: Cause 23 and 12 with DELTA_HO_MARGIN(0,n)
Static (couple of cells): HO_MARGIN, LINK_FACTOR
On a local traffic basis:
Load_Factor/Free_Factor
Forced Directed Retry
1.259
© Alcatel University - 8AS902001485 VH ZZA Ed.02 Page 1.259
4.2 Examples and Exercises
Example 3: Traffic Load Sharing (2/12)
Fast Traffic HO
Useful in case of sudden traffic peaks as the process
response is instantaneous (no averaging window)
The principle is to force handover towards neighbor cells
which have lower traffic when a request is queued in the
serving cell.
Interaction with Forced DR due to the use of same
thresholds
Optimization method (repetitive process)
Tunes L_RXLEV_NCELL_DR(n), FREElevel_DR(n)
Applies new values, checks traffic peaks, QoS
indicators
1.260
© Alcatel University - 8AS902001485 VH ZZA Ed.02 Page 1.260
You might also like
- HUD Settlement Statement - 221-1993Document4 pagesHUD Settlement Statement - 221-1993Paul GombergNo ratings yet
- SEAFARERSDocument29 pagesSEAFARERSJohanna Arnaez100% (1)
- Harmony XAC Pendant Control Stations: CatalogDocument62 pagesHarmony XAC Pendant Control Stations: CatalogMarcosNo ratings yet
- 7 Anéis: Egberto Gismonti Adaptação Daniel Murray 76Document8 pages7 Anéis: Egberto Gismonti Adaptação Daniel Murray 76Gustavo Mendes100% (1)
- Esp32 Cam V1.6 PDFDocument1 pageEsp32 Cam V1.6 PDFBuzatu Giani100% (1)
- Bocik Nocturno No.3Document1 pageBocik Nocturno No.3Miloš Sládečka100% (1)
- Proyeccion de Cubierta: Oficio BARDocument1 pageProyeccion de Cubierta: Oficio BARBruce JimenezNo ratings yet
- Law On Other Business Transactions 20181Document365 pagesLaw On Other Business Transactions 20181Leonel King0% (1)
- "Disaster Readiness and Risk Reduction": Test 2 True or FalseDocument2 pages"Disaster Readiness and Risk Reduction": Test 2 True or FalseMiki AntonNo ratings yet
- IATF Objective Data Analysis - Quality - Example2 PDFDocument2 pagesIATF Objective Data Analysis - Quality - Example2 PDFSachin RamdurgNo ratings yet
- Cisco VoipDocument37 pagesCisco VoipLino Vargas0% (1)
- Student Report Card ManagementDocument38 pagesStudent Report Card ManagementKannan Thangaraju41% (17)
- Crowdstrike Incident Response InfographicDocument1 pageCrowdstrike Incident Response Infographicshekhar'No ratings yet
- Programa de Mejora Continua: Metodología Incrementa Lean Six SigmaDocument70 pagesPrograma de Mejora Continua: Metodología Incrementa Lean Six SigmaROCIO RoSALYN EGOAVIL CONDORNo ratings yet
- Ghost In a Flower OST Guitar TabDocument3 pagesGhost In a Flower OST Guitar TabGarbriella FongNo ratings yet
- KPI Student Satisfaction and Engagement SurveyDocument4 pagesKPI Student Satisfaction and Engagement SurveyMoataz DeiabNo ratings yet
- No. of Provincial Constituency: 2 No. of House of Representative Constituency: 1Document1 pageNo. of Provincial Constituency: 2 No. of House of Representative Constituency: 1Bijay Aryan DhakalNo ratings yet
- LC RS25 9 Open BA 705157ADocument8 pagesLC RS25 9 Open BA 705157APaulo César C SNo ratings yet
- Radio TroubleshootingDocument14 pagesRadio TroubleshootingrolandNo ratings yet
- NokiaVsApple 10.12.23Document31 pagesNokiaVsApple 10.12.23Florian MuellerNo ratings yet
- Rencana Tata Letak Rumah 2 LantaiDocument1 pageRencana Tata Letak Rumah 2 LantaiAgus SuryadiNo ratings yet
- Nokia: W D W IDocument41 pagesNokia: W D W IFlorian Mueller50% (2)
- Solving A System of Equations Algebraically - Comparison Method - Substitution Method - Elimination MethodDocument11 pagesSolving A System of Equations Algebraically - Comparison Method - Substitution Method - Elimination MethodAtif SaeedNo ratings yet
- 24 The 7-Stroke RollDocument1 page24 The 7-Stroke RolljyidouNo ratings yet
- Snímka Obrazovky 2023-09-02 o 23.19.09Document1 pageSnímka Obrazovky 2023-09-02 o 23.19.09Kokt KorNo ratings yet
- Harmony XK, XD Controllers For Hoisting Applications: CatalogDocument50 pagesHarmony XK, XD Controllers For Hoisting Applications: CatalogMauro MiguelNo ratings yet
- This Land: Lion KingDocument2 pagesThis Land: Lion KingmiromarkoNo ratings yet
- Botoneras ScneiderDocument43 pagesBotoneras ScneiderSalvador MurilloNo ratings yet
- n-up-pdf_720988310-1-5042314579284066427-50-93 (2)Document3 pagesn-up-pdf_720988310-1-5042314579284066427-50-93 (2)thiagomateowaos12No ratings yet
- Contesting Democracy Political Ideas in Twentieth-... - (Contents)Document2 pagesContesting Democracy Political Ideas in Twentieth-... - (Contents)Натали ШуляковаNo ratings yet
- Shab e QadarDocument1 pageShab e QadarMuhammad KHalidNo ratings yet
- Nokia: W D W IDocument34 pagesNokia: W D W IFlorian Mueller100% (1)
- Kneutzer, Caprice 6Document1 pageKneutzer, Caprice 6Çağatay TaşbilekNo ratings yet
- Standard guitar tuning 90 degreesDocument2 pagesStandard guitar tuning 90 degreesAndrew StainberhNo ratings yet
- As Primeiras LevadasDocument2 pagesAs Primeiras LevadasJoabe OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Pci204h - Pci Power - Mp3000Document1 pagePci204h - Pci Power - Mp3000AdeniltonNo ratings yet
- Canon in HellDocument2 pagesCanon in Hell郑男No ratings yet
- Estudios de Cuerdas Al Aire para ContrabajoDocument1 pageEstudios de Cuerdas Al Aire para ContrabajoSantiagoNo ratings yet
- IATF Objective Data Analysis - Quality - Example2Document2 pagesIATF Objective Data Analysis - Quality - Example2Sachin RamdurgNo ratings yet
- IELTS Free Practice Test Answer SheetDocument6 pagesIELTS Free Practice Test Answer SheetKim MedairosNo ratings yet
- Flat 05.8.2021 (E0 E1) OkDocument12 pagesFlat 05.8.2021 (E0 E1) OkZeody YoeuyNo ratings yet
- Left Alone TabsDocument8 pagesLeft Alone TabsbruheNo ratings yet
- Vote Ki Sharai HaisyatDocument8 pagesVote Ki Sharai HaisyatZikr Ur Rehman SukkurviNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Sixteenth Notes Eighth Notes Music RhythmDocument1 pageLesson 8 Sixteenth Notes Eighth Notes Music RhythmjyidouNo ratings yet
- Team Performance Indicator: Orientación OrientaciónDocument1 pageTeam Performance Indicator: Orientación OrientaciónCristhian GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Recursos 11 PDFDocument1 pageRecursos 11 PDFCristhian GutierrezNo ratings yet
- ContentDocument12 pagesContentKamila sharminNo ratings yet
- Tokyopop Board 11x17Document1 pageTokyopop Board 11x17Dan AnderssonNo ratings yet
- Assembly Instructions for Steel Ties and TurnoutsDocument35 pagesAssembly Instructions for Steel Ties and Turnoutshiginito1410No ratings yet
- Foundation Plan: LegendDocument1 pageFoundation Plan: LegendVince GarciaNo ratings yet
- D.1.07.01 SHPPro DataSheetDocument2 pagesD.1.07.01 SHPPro DataSheetspaul297No ratings yet
- PaciênciaDocument3 pagesPaciênciaandrels89No ratings yet
- TraumereiDocument1 pageTraumereiLisa AzevedoNo ratings yet
- PDF Buho Papercraft - CompressDocument5 pagesPDF Buho Papercraft - CompressRepuestos CuencaNo ratings yet
- MPC Aug 18Document8 pagesMPC Aug 18Kunal SinhaNo ratings yet
- Single Stroke FrasesDocument2 pagesSingle Stroke FrasesRuan Pablo BateraNo ratings yet
- Muddula KakiDocument14 pagesMuddula KakiFruit reaNo ratings yet
- Physics Booklet2 2017Document31 pagesPhysics Booklet2 2017Anas OsamaNo ratings yet
- Instructions: - Mathematics - Iit Jee - Test 1 (July 11, 2010) - Real Numbers - Maximum Marks 20 - Time 20 MinutesDocument5 pagesInstructions: - Mathematics - Iit Jee - Test 1 (July 11, 2010) - Real Numbers - Maximum Marks 20 - Time 20 MinutesRajat KaliaNo ratings yet
- Second Floor Fourth FloorDocument1 pageSecond Floor Fourth FloorAbhishek SoniNo ratings yet
- Prof Ghafoor Ahmed - by Khurram BadrDocument192 pagesProf Ghafoor Ahmed - by Khurram BadrDr FaiyazNo ratings yet
- Infinitely Better: Automation Tools and SolutionsDocument16 pagesInfinitely Better: Automation Tools and Solutionsnine starNo ratings yet
- About Us: (Co. No. 202101009545 (1409844-K) )Document2 pagesAbout Us: (Co. No. 202101009545 (1409844-K) )DamonChongNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Dumper2Document11 pagesDynamic Dumper2Dorivaldo Sebasti�o Gomes 20190511No ratings yet
- Alcatel Optimization 261 270Document10 pagesAlcatel Optimization 261 270Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Alcatel Optimization 271 280Document10 pagesAlcatel Optimization 271 280Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Alcatel Optimization 231 240Document10 pagesAlcatel Optimization 231 240Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Alcatel Optimization 251 260Document10 pagesAlcatel Optimization 251 260Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Alcatel Optimization 291 300Document10 pagesAlcatel Optimization 291 300Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Alcatel Optimization 211 220Document10 pagesAlcatel Optimization 211 220Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Alcatel Optimization 241 250Document10 pagesAlcatel Optimization 241 250Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Alcatel Optimization 281 290Document10 pagesAlcatel Optimization 281 290Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Alcatel Optimization 271 280Document10 pagesAlcatel Optimization 271 280Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Alcatel Optimization 261 270Document10 pagesAlcatel Optimization 261 270Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Alcatel Optimization 211 220Document10 pagesAlcatel Optimization 211 220Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Alcatel - Optimization 11 20Document10 pagesAlcatel - Optimization 11 20Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Alcatel Optimization 281 290Document10 pagesAlcatel Optimization 281 290Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Alcatel Optimization 241 250Document10 pagesAlcatel Optimization 241 250Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Alcatel Optimization 241 250Document10 pagesAlcatel Optimization 241 250Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Alcatel - Optimization 21 30Document10 pagesAlcatel - Optimization 21 30Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Alcatel - Optimization 1 10Document10 pagesAlcatel - Optimization 1 10Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Siemens MAC15 4Document4 pagesSiemens MAC15 4Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Alcatel - Optimization 31 40Document10 pagesAlcatel - Optimization 31 40Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Alcatel - Optimization 41 50Document10 pagesAlcatel - Optimization 41 50Tas KayNo ratings yet
- Siemens MAC15NDocument4 pagesSiemens MAC15NTas KayNo ratings yet
- RNYM02-1120A-12Document2 pagesRNYM02-1120A-12bastian silvaNo ratings yet
- Numbers and Codes: Richard Earl Mathematical Institute University of OxfordDocument15 pagesNumbers and Codes: Richard Earl Mathematical Institute University of OxfordCSP EDUNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 The Post Office: Grammar: Omission of Relative PronounsDocument5 pagesUnit 9 The Post Office: Grammar: Omission of Relative PronounsTrung Lê TríNo ratings yet
- A Day With Maria Becerra (1) - 2Document2 pagesA Day With Maria Becerra (1) - 2FelipeNo ratings yet
- L-Ascorbic AcidDocument3 pagesL-Ascorbic AcidJemNo ratings yet
- The Best Chicken Quesadillas - Mel's Kitchen Cafe 4Document1 pageThe Best Chicken Quesadillas - Mel's Kitchen Cafe 4Yun LiuNo ratings yet
- Creo Simulate Components for Stress and Strain QuantitiesDocument1 pageCreo Simulate Components for Stress and Strain QuantitiesSebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- KETRACO Clarifies Technical Queries for 400kV Transmission ProjectDocument5 pagesKETRACO Clarifies Technical Queries for 400kV Transmission Projectahmadove1No ratings yet
- Ang Kin BalletDocument16 pagesAng Kin BalletJane JNo ratings yet
- Topics in English SyntaxDocument131 pagesTopics in English SyntaxPro GamerNo ratings yet
- Ch. 8 - Managing Project Quality Flashcards by Brian Weldon - BrainscapeDocument8 pagesCh. 8 - Managing Project Quality Flashcards by Brian Weldon - BrainscapeKay MendozaNo ratings yet
- Coa - Resolution No. 2017-023 Dtd.12.21.2017 - Intosai Sai Qms Cert.Document2 pagesCoa - Resolution No. 2017-023 Dtd.12.21.2017 - Intosai Sai Qms Cert.Anie Guiling-Hadji GaffarNo ratings yet
- Behaviour of Rectangular Travelling Wave (Unit Step Function at Transition Points-Typical CasesDocument1 pageBehaviour of Rectangular Travelling Wave (Unit Step Function at Transition Points-Typical CasesAngela VaughnNo ratings yet
- Principles of Synthetic BiologyDocument21 pagesPrinciples of Synthetic BiologyOpale PapaleNo ratings yet
- Revista Mexicana de Ciencias Forestales Vol. 9 (49Document32 pagesRevista Mexicana de Ciencias Forestales Vol. 9 (49dacsilNo ratings yet
- Nick Bradbeer Thesis Master v11 Corrections REDACTEDDocument276 pagesNick Bradbeer Thesis Master v11 Corrections REDACTEDbatra_763079313No ratings yet
- Creating and Using Virtual DPUsDocument20 pagesCreating and Using Virtual DPUsDeepak Gupta100% (1)
- A Case Study On Strategies To Deal With The Impacts of COVID-19 Pandemic in The Food and Beverage IndustryDocument13 pagesA Case Study On Strategies To Deal With The Impacts of COVID-19 Pandemic in The Food and Beverage IndustryPeyman KazemianhaddadiNo ratings yet
- How Computer Viruses Work and How to Prevent InfectionDocument4 pagesHow Computer Viruses Work and How to Prevent InfectionVishal guptaNo ratings yet
- Spark Plug ReadingDocument7 pagesSpark Plug ReadingCostas GeorgatosNo ratings yet
- ARIA JumpChainDocument52 pagesARIA JumpChainDorothy FeelyNo ratings yet
- BE InstallGuide RooftopSeries12R ZXDocument80 pagesBE InstallGuide RooftopSeries12R ZXAlexandreau del FierroNo ratings yet
- T TableDocument7 pagesT TableMaguz GurniwaNo ratings yet
- PK 7Document45 pagesPK 7Hernan MansillaNo ratings yet