Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IPlan DLP Format v.02
Uploaded by
Julie Anne MacuseCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IPlan DLP Format v.02
Uploaded by
Julie Anne MacuseCopyright:
Available Formats
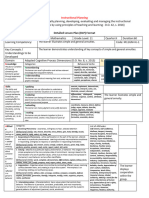
Instructional Planning
(The process of systematically planning, developing, evaluating and managing the instructional
process by using principles of teaching and learning - D.O. 42, s. 2016)
Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format
DLP No.: Learning Area: Grade Level: Quarter: Duration:
Learning Code:
Competency/ies:
(Taken from the Curriculum Guide)
Key Concepts /
Understandings to be
Developed
Domain Adapted Cognitive Process Dimensions (D.O. No. 8, s. 2015) 1. Objectives
Knowledge Categories: Behavioral Verbs:
The fact or condition identify, retrieve, recognize,
Remembering
of knowing duplicate, list, memorize,
The learner can recall information and retrieve relevant
something with repeat, describe, reproduce
knowledge from long-term memory
familiarity gained
Understanding interpret, exemplify, classify,
through experience
The learner can construct meaning from oral, written and summarize, infer, compare,
or association
graphic messages explain, paraphrase, discuss
Skills Applying execute, implement, demonstrate,
The ability and The learner can use information to undertake a dramatize, interpret, solve, use,
capacity acquired procedure in familiar situations or in a new way illustrate, convert, discover
through deliberate, Analyzing differentiate, distinguish, compare,
systematic, and The learner can distinguish between parts and contrast, organize, outline, attribute,
sustained effort to determine how they relate to one another, and to the deconstruct
smoothly and overall structure and purpose
adaptively carryout coordinate, measure, detect, defend,
complex activities or
Evaluating
The learner can make judgments and justify decisions judge, argue, debate, describe,
the ability, coming critique, appraise, evaluate
from one's
knowledge, practice, Creating generate, hypothesize, plan, design,
The learner can put elements together to form a develop, produce, construct,
aptitude, etc., to do
functional whole, create a new product or point of formulate, assemble, devise
something
view
Attitud Categories: List of Attitudes:
1. Receiving Phenomena - Awareness, willingness to hear, selected attention
e Self-esteem, Self-confidence,
Growth in Behavioral Verbs: ask, choose, describe, erect, follow, give, hold, identify, locate, name, Wellness, Respect, Honesty,
feelings or point to, reply, select, sit, Study, use Personal discipline, Perseverance,
emotional 2. Responding to Phenomena - Active participation on the part of the learners. Attends and Sincerity, Patience, Critical thinking,
areas. reacts to a particular phenomenon. Learning outcomes may emphasize compliance in Open-mindedness, Interest,
A settled responding, willingness to respond, or satisfaction in responding (motivation). Courteous, Obedience, Hope,
way of Behavioral Verbs: aid, answer, assist, comply, conform, discuss, greet, help, label, Charity, Fortitude, Resiliency,
thinking perform, practice, present, read, recite, report, select, tell, write Positive vision, Acceptance,
or feeling 3. Valuing - Attaches to a particular object, phenomenon, or behavior. This ranges from simple Determined, Independent ,
about acceptance to the more complex state of commitment. Valuing is based on the Gratitude, Tolerant, Cautious,
someone internalization of a set of specified values, while clues to these values are expressed in the Decisive, Self-Control, Calmness,
or learner's overt behavior and are often identifiable. Responsibility, Accountability,
somethin Industriousness, Industry,
Behavioral Verbs: work, complete, demonstrate, differentiate, explain, follow, form, Cooperation, Optimism,
g, initiate, invite, join, justify, propose, read, report, select, share, study
typically Satisfaction, Persistent, Cheerful,
4. Organization - Organizes values into priorities by contrasting different values, resolving Reliable, Gentle, Appreciation of
one that conflicts between them, and creating a unique value system. The emphasis is on
is one’s culture, Globalism,
comparing, relating, and synthesizing values. Compassion, Work Ethics, Creativity,
reflected
in a Behavioral Verbs: adhere, alter, arrange, combine, compare, complete, defend, explain, Entrepreneurial Spirit, Financial
person’s formulate, generalize, identify, integrate, modify, order, organize, prepare, relate, Literacy, Global, Solidarity, Making
behavior synthesize a stand for the good, Voluntariness
5. Internalizing values - (Characterization): Has a value system that controls their behavior. of human act, Appreciation of one’s
The behavior is pervasive, consistent, predictable, and most importantly, characteristic of the rights, Inclusiveness, Thoughtful,
learner. Instructional objectives are concerned with the student's general patterns of Seriousness, Generous, Happiness,
adjustment (personal, social, emotional). Modest, Authority, Hardworking,
Behavioral Verbs: act, discriminate, display, influence, listen, modify, perform, practice, Realistic, Flexible, Considerate,
propose, qualify, question, revise, serve, solve, verify Sympathetic, Frankness
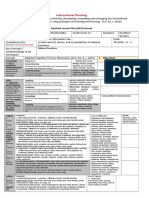
Values Categories: List of Values:
A 1. Receiving Phenomena - Awareness, willingness to hear, selected attention 1. Maka-Diyos
learner's Behavioral Verbs: ask, choose, describe, erect, follow, give, hold, identify, locate, Love of God, Faith, Trusting,
principles name, point to, reply, select, sit, Study, use Spirituality, Inner Peace, Love of
or 2. Responding to Phenomena - Active participation on the part of the learners. Attends truth, Kindness, Humble
standards and reacts to a particular phenomenon. Learning outcomes may emphasize compliance in
of responding, willingness to respond, or satisfaction in responding (motivation).
behavior; Behavioral Verbs: aid, answer, assist, comply, conform, discuss, greet, help, label,
one's 2. Maka-tao
perform, practice, present, read, recite, report, select, tell, write
judgment Concern for Others, Respect for
3. Valuing - Attaches to a particular object, phenomenon, or behavior. This ranges from
of what is human rights, Gender equality,
simple acceptance to the more complex state of commitment. Valuing is based on the
important Family Solidarity, Generosity,
internalization of a set of specified values, while clues to these values are expressed in the
in life. Helping, Oneness
learner's overt behavior and are often identifiable.
Go
Behavioral Verbs: work, complete, demonstrate, differentiate, explain, follow, form,
beyond
initiate, invite, join, justify, propose, read, report, select, share, study
learner’s
4. Organization - Organizes values into priorities by contrasting different values, resolving 3. Makakalikasan
life on
conflicts between them, and creating a unique value system. The emphasis is on Care of the environment, Disaster
earth,
comparing, relating, and synthesizing values. Risk Management, Protection of
include
more Behavioral Verbs: adhere, alter, arrange, combine, compare, complete, defend, the Environment, Responsible
than explain, formulate, generalize, identify, integrate, modify, order, organize, prepare, Consumerism, Cleanliness,
wealth relate, synthesize Orderliness, Saving the
and fame, 5. Internalizing values - (Characterization): Has a value system that controls their ecosystem, Environmental
and would behavior. The behavior is pervasive, consistent, predictable, and most importantly, sustainability
affect the characteristic of the learner. Instructional objectives are concerned with the student's 4. Makabansa
eternal general patterns of adjustment (personal, social, emotional). Peace and order, Heroism and
destiny of Behavioral Verbs: act, discriminate, display, influence, listen, modify, perform, Appreciation of Heroes, National
millions. practice, propose, qualify, question, revise, serve, solve, verify Unity, Civic Consciousness, Social
(Intention responsibility, Harmony,
ally add Patriotism, Productivity
value to
people
everyday.
)
2. Content
3. Learning Resources
4. Procedures
4.1 Introductory Activity (____ minutes). This part introduces the lesson Curriculum
content. Although at times optional, it is usually included to serve as a warm- Contextualization
up activity to give the learners zest for the incoming lesson and an idea about
Localization:
what it to follow. One principle in learning is that learning occurs when it is
Consider/include here
conducted in a pleasurable and comfortable atmosphere.
the appropriate Local
Heritage Themes:
4.2 Activity/Strategy (____ minutes). This is an interactive strategy to A. Annual Rites,
elicit learner’s prior learning experience. It serves as a springboard for new Festivals, and
learning. It illustrates the principle that learning starts where the learners are. Rituals
Carefully structured activities such as individual or group reflective exercises, (Historical/Religiou
group discussion, self-or group assessment, dyadic or triadic interactions, s Festivals, Local
puzzles, simulations or role-play, cybernetics exercise, gallery walk and the like Cultural Festivals,
may be created. Clear instructions should be considered in this part of the Local
lesson. Delicacies/Products
4.3 Analysis (____ minutes). Essential questions are included to serve as a Festivals, Rituals,
guide for the teacher in clarifying key understandings about the topic at hand. Wedding Ritual,
Critical points are organized to structure the discussions allowing the learners Palihi Ritual, Burial
to maximize interactions and sharing of ideas and opinions about expected Ritual,
issues. Affective questions are included to elicit the feelings of the learners B Literary Anthologies
about the activity or the topic. The last questions or points taken should lead Written In Local
the learners to understand the new concepts or skills that are to be presented Language (BALITAW,
in the next part of the lesson. BALAK, Folktales/
4.4 Abstraction (____ minutes). This outlines the key concepts, important Short Stories, Local
skills that should be enhanced, and the proper attitude that should be Heroes
emphasized. This is organized as a lecturette that summarizes the learning C. Historical Events,
emphasized from the activity, analysis and new inputs in this part of the Enduring Values,
lesson. Indigenous Materials,
Indigenous Cultural
4.5 Application (____ minutes). This part is structured to ensure the Communities/Indigen
commitment of the learners to do something to apply their new learning in ous People,
their own environment. Indigenous Games
D. Topography, Flora/
Fauna (Falls,
Mountains, River,
4.6 Assessment (___ minutes). For the Teacher to: a) Assess whether Cave, Trees, Flower,
learning objectives have been met for a specified duration, b) Remediate Fauna
E. Food & Local
and/or enrich with appropriate strategies as needed, and c) Evaluate whether products
learning intentions and success criteria have been met. (Reminder: Formative G. Role Model Family
Assessment may be given before, during, or after the lesson). Choose any
from the Assessment Methods below:
Assessment Method Possible Activities
a) Observation Investigation, Role
(Formal and informal observations of learners’ performance or behaviors are Play, Oral
recorded, based on assessment criteria) Presentation, Dance,
Musical Performance,
Skill Demonstration,
Group Activity (e.g.
Choral Reading),
Debate, Motor &
Psychomotor Games,
Simulation Activities,
Science Experiment
b) Talking to Learners / Conferencing Hands-on Math
(Teachers talk to and question learners about their learning to gain insights on Activities, Written
their understanding and to progress and clarify their thinking) Work and Essay,
Picture Analysis,
Comic Strip, Panel
Discussion, Interview,
Think-Pair-Share,
Reading
c) Analysis of Learners’ Products Worksheets for all
(Teachers judge the quality of products produced by learners according to subjects, Essay,
agreed criteria) Concept
Maps/Graphic
Organizer, Project,
Model, Artwork,
Multi-media
Presentation, Product
made in technical-
vocational subjects
d) Tests Skill Performance
(Teachers set tests or quizzes to determine learners’ ability to demonstrate Test, Open-Ended
mastery of a skill or knowledge of content) Question, Practicum,
Pen and Paper Test,
Pre and Post Test,
Diagnostic Test, Oral
Test, Quiz
4.7 Assignment (____ minutes). Fill-in below any of the four purposes:
Reinforcing / strengthening the day’s lesson
Enriching / inspiring the day’s lesson
Enhancing / improving the day’s lesson
Preparing for the new lesson
4.8 Concluding Activity (____ minutes).
This is usually a brief but affective closing activity such as a strong quotation, a short song, an anecdote,
parable or a letter that inspires the learners to do something to practice their new learning.
5. Remarks Indicate below special cases including but not limited to continuation of lesson plan to the following day in case of re-teaching or lack of time,
transfer of lesson to the following day, in cases of class suspension, etc.
6. Reflections Reflect on your teaching and assess yourself as a teacher. Think about your student’s progress this week. What works? What else needs to be
done to help the students learn? Identify what help your instructional supervisors can provide for you so when you meet them, you can ask them
relevant questions. Indicate below whichever is/are appropriate.
A. No. of learners who
earned 80% in the
evaluation.
B. No. of learners who
require additional
activities for
remediation.
C. Did the remedial
lessons work? No.
of learners who
have caught up
with the lesson.
D. No. of learners who
continue to require
remediation.
E. Which of my
learning strategies
worked well? Why
did these work?
F. What difficulties did
I encounter which
my principal or
supervisor can help
me solve?
G. What innovation or
localized materials
did I use/discover
which I wish to
share with other
teachers?
Prepared by:
Name: School:
Position/Designation: Division:
Contact Number: Email address:
Bibliography
Appendices: (attach all materials that will be used)
1. Activity Sheet …
2. Formative Assessment …
3. Answer Key …
4. Handouts …
5. PowerPoint Presentation …
6. Others
You might also like
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningJesson AlbaranNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningRendyNo ratings yet
- IplanDocument4 pagesIplanJeraldine RepolloNo ratings yet
- IPlan DLP Format English-VersionDocument5 pagesIPlan DLP Format English-VersionDina ArcenalNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument3 pagesInstructional Planning Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatAntonio CaballeroNo ratings yet
- OC 13 Identifies Strategies Used by Each Speaker To Convey Hisher Ideas EffectivelyDocument4 pagesOC 13 Identifies Strategies Used by Each Speaker To Convey Hisher Ideas EffectivelyZeen Dee100% (1)
- 10.3.3 DLP RetuyaDocument4 pages10.3.3 DLP RetuyaGlad Norman LimoconNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningAnonymous HJlXukJrNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningJeraldine RepolloNo ratings yet
- DLP - Iplan Template From The Region - Sir ElnarDocument4 pagesDLP - Iplan Template From The Region - Sir ElnarRhona Liza CanobasNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningRemedios Enad CataoNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning DLP FormatDocument5 pagesInstructional Planning DLP FormatAlvin Cuandot100% (1)
- OC 12 The Learner Distinguishes The Types of SpeechDocument4 pagesOC 12 The Learner Distinguishes The Types of SpeechZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- OC 11 The Learner Distinguishes The Types of SpeechDocument4 pagesOC 11 The Learner Distinguishes The Types of SpeechZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- OC 11.1 Ascertains The Verbal and Nonverbal Cues That Each Speaker Uses To Achieve His Her PurposeDocument4 pagesOC 11.1 Ascertains The Verbal and Nonverbal Cues That Each Speaker Uses To Achieve His Her PurposeZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- C1 - Joey Jabonet-W4-Dlp1-3Document5 pagesC1 - Joey Jabonet-W4-Dlp1-3ludabelle19No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningEdgar Jr. SenarloNo ratings yet
- M11GM Ia 1Document5 pagesM11GM Ia 1Dan Albert Abes67% (3)
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningReynalyn HernandezNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningPapellero Villamor GlendaNo ratings yet
- M11GM IIc 1Document6 pagesM11GM IIc 1Hordan Jay SalleNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning for Exponential EquationsDocument7 pagesInstructional Planning for Exponential EquationsLionelNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning: Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument4 pagesInstructional Planning: Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatReynalyn HernandezNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningBlessila LopezNo ratings yet
- Cot 3-Prepare AppetizersDocument5 pagesCot 3-Prepare AppetizersIvy Rosell Buayaban100% (3)
- Nail Care Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesNail Care Lesson PlanMa. Crissa Aboyme100% (1)
- Instructional Planning: Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument7 pagesInstructional Planning: Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatRed Zye UbayNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningEllorin RANo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningdanNo ratings yet
- ABM - BM11BS IIa 11Document6 pagesABM - BM11BS IIa 11Junard AsentistaNo ratings yet
- OC 12.1 Comprehends Various Kinds of Oral TextsDocument4 pagesOC 12.1 Comprehends Various Kinds of Oral TextsZeen Dee100% (1)
- Solving exponential equationsDocument7 pagesSolving exponential equationsJeger JbTattoo BaguioNo ratings yet
- M11 GM-Ic-1Document5 pagesM11 GM-Ic-1Dan Albert AbesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningJulia Maria LoviteNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm 1Document7 pagesOral Comm 1Theresa B.No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningRed Zye UbayNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Various Models of CommunicationDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Various Models of CommunicationZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningRed Zye UbayNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- Per Dev Week 2Document4 pagesPer Dev Week 2Andrey DyNo ratings yet
- DLP FBS 1Document5 pagesDLP FBS 1Christine Rose Villanueva VargasNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: The Characteristics Quantitative ResearchDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: The Characteristics Quantitative ResearchHanelen DadaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Evaluates The Effectiveness of An Oral Communication Activity EN11/12OC-Ibe-14Document4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Evaluates The Effectiveness of An Oral Communication Activity EN11/12OC-Ibe-14Zeen DeeNo ratings yet
- CS - RS12 Id e 2Document8 pagesCS - RS12 Id e 2Josua GarciaNo ratings yet
- OC 21 Types of Communicative StrategiesDocument7 pagesOC 21 Types of Communicative StrategiesZeen Dee0% (1)
- Instructional Planning (iPlan) Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument4 pagesInstructional Planning (iPlan) Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatNathalie Yvonne AliserNo ratings yet
- 10.2.4 DLP GealonDocument4 pages10.2.4 DLP GealonGlad Norman LimoconNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningSuzetteBragaSamuela100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument10 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningReynalyn HernandezNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningRed Zye UbayNo ratings yet
- Sample DLP 5 Organization and ManagementDocument5 pagesSample DLP 5 Organization and ManagementAileen I Reyes50% (2)
- OC 10 Watches and Listens To Sample Oral Communication ActivitiesDocument4 pagesOC 10 Watches and Listens To Sample Oral Communication ActivitiesZeen Dee86% (7)
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningEllorin RANo ratings yet
- DLP 51Document6 pagesDLP 51Maricris Galman SalamatNo ratings yet
- M11GM IIc 2Document6 pagesM11GM IIc 2Hordan Jay SalleNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning: Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument6 pagesInstructional Planning: Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatAndrey DyNo ratings yet
- Mohammed Farhan - Safety OfficerDocument3 pagesMohammed Farhan - Safety OfficerAlok SinghNo ratings yet
- HISTORY OF INDIAN POLICE FROM ANCIENT TO MODERN TIMESDocument5 pagesHISTORY OF INDIAN POLICE FROM ANCIENT TO MODERN TIMESaslamNo ratings yet
- Themes and Characters of Joseph AndrewsDocument3 pagesThemes and Characters of Joseph Andrewsdanearjabbar1990No ratings yet
- Jess 407Document12 pagesJess 407PracKillerNo ratings yet
- Chaucer: Echaucer Chaucer in The Twenty-First Century The Wife of Bath'S TaleDocument13 pagesChaucer: Echaucer Chaucer in The Twenty-First Century The Wife of Bath'S Taleneha rahmanNo ratings yet
- BTC OPW WS4 Consolidate Moatgate Completed Structure TableDocument6 pagesBTC OPW WS4 Consolidate Moatgate Completed Structure Tablechiar tern yeapNo ratings yet
- Debating Tips and StrategiesDocument13 pagesDebating Tips and StrategiesDacien NguyeenNo ratings yet
- Blameful Rightdoing and Blameless Wrongdoing. Torbjörn TännsjöDocument12 pagesBlameful Rightdoing and Blameless Wrongdoing. Torbjörn TännsjöALBERT ORLANDO CORTES RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Kailash Chandra Difficult Words CompilationDocument23 pagesKailash Chandra Difficult Words Compilationashish.bhargava156No ratings yet
- ID Perjanjian Perkawinan Sebagai Sarana Perlindungan Hukum Bagi para Pihak Dalam PeDocument26 pagesID Perjanjian Perkawinan Sebagai Sarana Perlindungan Hukum Bagi para Pihak Dalam PeEvelyn Larissa Florentia WijayaNo ratings yet
- Titan, by Jean Paul Friedrich RichterDocument228 pagesTitan, by Jean Paul Friedrich RichterMauro TrindadeNo ratings yet
- CSE Reviewer Part 4Document8 pagesCSE Reviewer Part 4AsukinNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Health Professions: Drexel E-Repository and Archive (iDEA)Document4 pagesCollege of Nursing and Health Professions: Drexel E-Repository and Archive (iDEA)Ghie DomingoNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 Materi-EM101-M01-The Foundation of Business 2Document48 pagesWEEK 1 Materi-EM101-M01-The Foundation of Business 2ddhani299No ratings yet
- Syllabus of The Sarawak Civil Service Six (6) Shared ValuesDocument10 pagesSyllabus of The Sarawak Civil Service Six (6) Shared ValuesNBHNo ratings yet
- Confidential OB Exam AnswersDocument9 pagesConfidential OB Exam AnswersSyedNo ratings yet
- Ethics Code Guidance Professional AccountantsDocument13 pagesEthics Code Guidance Professional AccountantsAisa TriNo ratings yet
- 25 etiquette rules everyone should knowDocument4 pages25 etiquette rules everyone should knowigoginNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of Consent-JonaDocument1 pageAffidavit of Consent-Jonajude thaddeus estoquiaNo ratings yet
- Paradine V Jane - (1646) 82 ER 897Document2 pagesParadine V Jane - (1646) 82 ER 897TimishaNo ratings yet
- Group-1: This Study Resource WasDocument5 pagesGroup-1: This Study Resource WasKAUSHIK KUMAR PATRO100% (1)
- Q5: Based On The Scenario, These Are The Roles and Responsibilities That Needs To Be Done Within SC Company in Health and Safety Management SystemDocument2 pagesQ5: Based On The Scenario, These Are The Roles and Responsibilities That Needs To Be Done Within SC Company in Health and Safety Management SystemMohamed saidNo ratings yet
- Vipassana Meditation: Incomplete Forms Will Not Be Accepted. Please Fill Up All FieldsDocument2 pagesVipassana Meditation: Incomplete Forms Will Not Be Accepted. Please Fill Up All FieldsDark loverNo ratings yet
- "Umeed": Implemented by The Jammu & Kashmir State Rural Livelihoods SocietyDocument3 pages"Umeed": Implemented by The Jammu & Kashmir State Rural Livelihoods SocietyChetan RandhawaNo ratings yet
- 41-Article Text-213-1-10-20210202Document19 pages41-Article Text-213-1-10-20210202a1011201060No ratings yet
- Kim Basinger Vs MLP Oral AgreementDocument31 pagesKim Basinger Vs MLP Oral AgreementrafiqNo ratings yet
- English Activity JClass-12Document9 pagesEnglish Activity JClass-12raulpradeep362No ratings yet
- 2397 883X Article p319Document14 pages2397 883X Article p319Hà Quốc HuyNo ratings yet
- GST 112 Mock ExamsDocument6 pagesGST 112 Mock ExamsOtaru kehindeNo ratings yet
- Pingala UvacaDocument3 pagesPingala UvacaAniket DubeyNo ratings yet