Professional Documents
Culture Documents
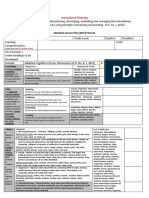
Instructional Planning Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format
Uploaded by
Antonio CaballeroOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Instructional Planning Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format
Uploaded by
Antonio CaballeroCopyright:
Available Formats
*Instructional Planning
(The process of systematically planning, developing, evaluating and managing the instructional
process by using principles of teaching and learning - D.O. 42, s. 2016)
Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format
DLP No.: Learning Area: Grade Level: Quarter: Duration:
Learning Competency/ies:
(Taken from the Curriculum Guide)
Key Concepts /
Understandings to be
Developed
Domain Adapted Cognitive Process Dimensions (D.O. No. 8, s. 2015) 1. Objectives
Knowledge Categories: Behavioral Verbs:
The fact or condition identify, retrieve, recognize,
Remembering
of knowing duplicate, list, memorize,
The learner can recall information and retrieve relevant
something with repeat, describe, reproduce
knowledge from long-term memory
familiarity gained
Understanding interpret, exemplify, classify,
through experience
The learner can construct meaning from oral, written and summarize, infer, compare,
or association
graphic messages explain, paraphrase, discuss
Skills Applying execute, implement, demonstrate,
The ability and The learner can use information to undertake a dramatize, interpret, solve, use,
capacity acquired procedure in familiar situations or in a new way illustrate, convert, discover
through deliberate, Analyzing differentiate, distinguish, compare,
systematic, and The learner can distinguish between parts and contrast, organize, outline, attribute,
sustained effort to determine how they relate to one another, and to the deconstruct
smoothly and overall structure and purpose
adaptively carryout coordinate, measure, detect, defend,
complex activities or
Evaluating
The learner can make judgments and justify decisions judge, argue, debate, describe,
the ability, coming critique, appraise, evaluate
from one's generate, hypothesize, plan, design,
knowledge, practice, Creating
The learner can put elements together to form a develop, produce, construct,
aptitude, etc., to do formulate, assemble, devise
something functional whole, create a new product or point of view
Attitude Categories: List of Attitudes:
Growth in 1. Receiving Phenomena - Awareness, willingness to hear, selected attention Self-esteem, Self-confidence,
feelings or Behavioral Verbs: ask, choose, describe, erect, follow, give, hold, identify, locate, Wellness, Respect, Honesty,
emotional name, point to, reply, select, sit, Study, use Personal discipline, Perseverance,
areas. 2. Responding to Phenomena - Active participation on the part of the learners. Attends Sincerity, Patience, Critical
A settled and reacts to a particular phenomenon. Learning outcomes may emphasize compliance thinking, Open-mindedness,
way of in responding, willingness to respond, or satisfaction in responding (motivation). Interest, Courteous, Obedience,
thinking Behavioral Verbs: aid, answer, assist, comply, conform, discuss, greet, help, label, Hope, Charity, Fortitude,
or feeling perform, practice, present, read, recite, report, select, tell, write Resiliency, Positive vision,
about 3. Valuing - Attaches to a particular object, phenomenon, or behavior. This ranges from Acceptance, Determined,
someone simple acceptance to the more complex state of commitment. Valuing is based on the Independent , Gratitude, Tolerant,
or internalization of a set of specified values, while clues to these values are expressed in Cautious, Decisive, Self-Control,
something the learner's overt behavior and are often identifiable. Calmness, Responsibility,
, typically Accountability, Industriousness,
one that is
Behavioral Verbs: work, complete, demonstrate, differentiate, explain, follow, form, Industry, Cooperation, Optimism,
reflected initiate, invite, join, justify, propose, read, report, select, share, study Satisfaction, Persistent, Cheerful,
in a 4. Organization - Organizes values into priorities by contrasting different values, resolving Reliable, Gentle, Appreciation of
person’s conflicts between them, and creating a unique value system. The emphasis is on one’s culture, Globalism,
behavior comparing, relating, and synthesizing values. Compassion, Work Ethics,
Behavioral Verbs: adhere, alter, arrange, combine, compare, complete, defend, Creativity, Entrepreneurial Spirit,
explain, formulate, generalize, identify, integrate, modify, order, organize, prepare, Financial Literacy, Global,
relate, synthesize Solidarity, Making a stand for the
5. Internalizing values - (Characterization): Has a value system that controls their good, Voluntariness of human act,
behavior. The behavior is pervasive, consistent, predictable, and most importantly, Appreciation of one’s rights,
characteristic of the learner. Instructional objectives are concerned with the student's Inclusiveness, Thoughtful,
general patterns of adjustment (personal, social, emotional). Seriousness, Generous, Happiness,
Behavioral Verbs: act, discriminate, display, influence, listen, modify, perform, Modest, Authority, Hardworking,
practice, propose, qualify, question, revise, serve, solve, verify Realistic, Flexible, Considerate,
Sympathetic, Frankness
Values Categories: List of Values:
A 1. Receiving Phenomena - Awareness, willingness to hear, selected attention 1. Maka-Diyos
learner's Behavioral Verbs: ask, choose, describe, erect, follow, give, hold, identify, locate, Love of God, Faith, Trusting,
principles name, point to, reply, select, sit, Study, use Spirituality, Inner Peace, Love of
or 2. Responding to Phenomena - Active participation on the part of the learners. Attends truth, Kindness, Humble
standards and reacts to a particular phenomenon. Learning outcomes may emphasize compliance in 2. Maka-tao
of responding, willingness to respond, or satisfaction in responding (motivation). Concern for Others, Respect for
behavior; Behavioral Verbs: aid, answer, assist, comply, conform, discuss, greet, help, label, human rights, Gender equality,
one's perform, practice, present, read, recite, report, select, tell, write Family Solidarity, Generosity,
judgment 3. Valuing - Attaches to a particular object, phenomenon, or behavior. This ranges from Helping, Oneness
of what is simple acceptance to the more complex state of commitment. Valuing is based on the 3. Makakalikasan
important internalization of a set of specified values, while clues to these values are expressed in the Care of the environment, Disaster
in life. learner's overt behavior and are often identifiable. Risk Management, Protection of
Go the Environment, Responsible
beyond Behavioral Verbs: work, complete, demonstrate, differentiate, explain, follow, form, Consumerism, Cleanliness,
learner’s initiate, invite, join, justify, propose, read, report, select, share, study Orderliness, Saving the ecosystem,
life on 4. Organization - Organizes values into priorities by contrasting different values, resolving Environmental sustainability
earth, conflicts between them, and creating a unique value system. The emphasis is on 4. Makabansa
include comparing, relating, and synthesizing values. Peace and order, Heroism and
more than Appreciation of Heroes, National
Behavioral Verbs: adhere, alter, arrange, combine, compare, complete, defend,
wealth Unity, Civic Consciousness, Social
explain, formulate, generalize, identify, integrate, modify, order, organize, prepare,
and fame, responsibility, Harmony,
relate, synthesize
and would Patriotism,
5. Internalizing values - (Characterization): Has a value system that controls their behavior.
affect the Productivity
The behavior is pervasive, consistent, predictable, and most importantly, characteristic of
eternal
the learner. Instructional objectives are concerned with the student's general patterns of
destiny of
adjustment (personal, social, emotional).
millions.
Intention Behavioral Verbs: act, discriminate, display, influence, listen, modify, perform,
ally practice, propose, qualify, question, revise, serve, solve, verify
adding
value to
people
everyday.
2. Content
3. Learning Resources
4. Procedures
4.1 Introductory Activity ( 5 minutes). This part introduces the lesson Curriculum
content. Although at times optional, it is usually included to serve as a Contextualization
warm-up activity to give the learners zest for the incoming lesson and an
Localization:
idea about what it to follow. One principle in learning is that learning occurs
Consider/include here the
when it is conducted in a pleasurable and comfortable atmosphere.
appropriate Local
4.2 Activity/Strategy ( 15 minutes). This is an interactive strategy to Heritage Themes:
elicit learner’s prior learning experience. It serves as a springboard for new A. Annual Rites, Festivals,
learning. It illustrates the principle that learning starts where the learners and Rituals
are. Carefully structured activities such as individual or group reflective (Historical/Religious
exercises, group discussion, sel f-or group assessment, dyadic or triadic Festivals, Local Cultural
interactions, puzzles, simulations or role-play, cybernetics exercise, gallery Festivals, Local
walk and the like may be created. Clear instructions should be considered in Delicacies/Products
this part of the lesson. Festivals, Rituals,
4.3 Analysis ( 5 minutes). Essential questions are included to serve as a Wedding Ritual, Palihi
guide for the teacher in clarifying key understandings about the topic at Ritual, Burial Ritual,
hand. Critical points are organized to structure the discussions allowing the B Literary Anthologies
learners to maximize interactions and sharing of ideas and opinions about Written In Local
expected issues. Affective questions are included to elicit the feelings of the Language (BALITAW,
learners about the activity or the topic. The last questions or points taken BALAK, Folktales/ Short
should lead the learners to understand the new concepts or skills that are to Stories, Local Heroes
be presented in the next part of the lesson. C. Historical Events,
4.4 Abstraction ( 30 minutes). This outlines the key concepts, important Enduring Values,
Indigenous Materials,
skills that should be enhanced, and the proper attitude that should be
emphasized. This is organized as a lecturette that summarizes the learning Indigenous Cultural
Communities/Indigenous
emphasized from the activity, analysis and new inputs in this part of the
lesson. People, Indigenous
Games
4.5 Application ( 30 minutes). This part is structured to ensure the D. Topography, Flora/
commitment of the learners to do something to apply their new learning in Fauna (Falls, Mountains,
their own environment. River, Cave, Trees,
4.6 Assessment ( 20 minutes). For the Teacher to: a) Assess whether Flower, Fauna
learning objectives have been met for a specified duration, b) Remediate E. Food & Local products
and/or enrich with appropriate strategies as needed, and c) Evaluate G. Role Model Family
whether learning intentions and success criteria have been met. (Reminder:
Formative Assessment may be given before, during, or after the lesson).
Choose any from the Assessment Methods below:
Assessment Method Possible Activities
a) Observation Investigation, Role Play,
(Formal and informal observations of learners’ performance or behaviors Oral Presentation,
are recorded, based on assessment criteria) Dance, Musical
Performance, Skill
Demonstration, Group
Activity (e.g. Choral
Reading), Debate, Motor
& Psychomotor Games,
Simulation Activities,
Science Experiment
b) Talking to Learners / Conferencing Hands-on Math Activities,
(Teachers talk to and question learners about their learning to gain insights Written Work and Essay,
on their understanding and to progress and clarify their thinking) Picture Analysis, Comic
Strip, Panel Discussion,
Interview, Think-Pair-
Share, Reading
c) Analysis of Learners’ Products Worksheets for all
(Teachers judge the quality of products produced by learners according to subjects, Essay, Concept
agreed criteria) Maps/Graphic Organizer,
Project, Model, Artwork,
Multi-media
Presentation, Product
made in technical-
vocational subjects
d) Tests Skill Performance Test,
(Teachers set tests or quizzes to determine learners’ ability to demonstrate Open-Ended Question,
mastery of a skill or knowledge of content) Practicum, Pen and
Paper Test, Pre and Post
Test, Diagnostic Test,
Oral Test, Quiz
4.7 Assignment ( 5 minutes). Fill-in below any of the four purposes:
Reinforcing / strengthening the day’s lesson
Enriching / inspiring the day’s lesson
Enhancing / improving the day’s lesson
Preparing for the new lesson
4.8 Concluding Activity (5 minutes). -
This is usually a brief but affective closing activity such as a strong quotation, a short song, an anecdote,
parable or a letter that inspires the learners to do something to practice their new learning.
5. Remarks
6. Reflections
A. No. of learners who
earned 80% in the
evaluation.
B. No. of learners who
require additional
activities for
remediation.
C. Did the remedial
lessons work? No.
of learners who
have caught up
with the lesson.
D. No. of learners who
continue to require
remediation.
E. Which of my
learning strategies
worked well? Why
did these work?
F. What difficulties did
I encounter which
my principal or
supervisor can help
me solve?
G. What innovation or
localized materials
did I use/discover
which I wish to
share with other
teachers?
Prepared by:
Name: School:
Position/Designation: Division:
Contact Number: Email address:
Bibliography:
Appendices:
You might also like
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningJesson AlbaranNo ratings yet
- Learning StylesDocument12 pagesLearning StylesSafaa Mohamed0% (1)
- Writing Verb List 40Document2 pagesWriting Verb List 40Alvin Jay GarciaNo ratings yet
- Writing Rubric: Reflective EssayDocument1 pageWriting Rubric: Reflective EssayJanus Van AsNo ratings yet
- The Elements - LearnerDocument48 pagesThe Elements - LearnerJellie Felonia CapinoNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency and VariabilityDocument2 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency and VariabilitynesumaNo ratings yet
- Sequence SignalsDocument28 pagesSequence SignalsCHAERA x BLACKPINKNo ratings yet
- Classroom Rules ExerciseDocument4 pagesClassroom Rules Exerciseapi-445508958No ratings yet
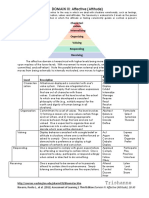
- Trishanne: DOMAIN III: Affective (Attitude)Document2 pagesTrishanne: DOMAIN III: Affective (Attitude)ᜆ᜔ᜇᜒᜐ᜔ᜑ᜔ ᜀᜈ᜔No ratings yet
- Personality Development & Soft SkillsDocument4 pagesPersonality Development & Soft SkillsRizwan MohammedNo ratings yet
- THEORY OF MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCESpptDocument30 pagesTHEORY OF MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCESpptZenda Marie Facinal SabinayNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus For Principles of Teaching and Learning in Healthcare Science PTL 301Document3 pagesCourse Syllabus For Principles of Teaching and Learning in Healthcare Science PTL 301beaNo ratings yet
- Global and Multicultural LiteracyDocument46 pagesGlobal and Multicultural Literacyangeli camilleNo ratings yet
- Emotions Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesEmotions Lesson Planapi-632882470No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanningDocument29 pagesLesson PlanningRuffa Mae Libo-onNo ratings yet
- Study of Values - Role PlayDocument13 pagesStudy of Values - Role PlayApakElBuheiriGetbNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal Defense Form: Group No. Final Score Final Grade ResearchersDocument3 pagesResearch Proposal Defense Form: Group No. Final Score Final Grade ResearchersKat MirallesNo ratings yet
- Realism: By: Julia and JhonamieDocument32 pagesRealism: By: Julia and JhonamieRuth LarraquelNo ratings yet
- Declamation Speech Evaluation CriteriaDocument1 pageDeclamation Speech Evaluation CriteriaAiken MarceloNo ratings yet
- Develop Your Personality in 40 CharactersDocument24 pagesDevelop Your Personality in 40 CharactersNidhi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Thesis StatementDocument15 pagesThesis StatementJos50% (2)
- Module 1 Metacognition and Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument54 pagesModule 1 Metacognition and Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesBrixylle AnneNo ratings yet
- Thesis Statements-Practice PDFDocument2 pagesThesis Statements-Practice PDFArmando GutierresNo ratings yet
- Process in Developing and Using RubricsDocument81 pagesProcess in Developing and Using RubricsLeri Cerenado AliliranNo ratings yet
- Multicultural Teaching Benefits All StudentsDocument9 pagesMulticultural Teaching Benefits All StudentsIlene Dawn AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Theories On Teaching ReadingDocument3 pagesTheories On Teaching ReadingPrince MendozaNo ratings yet
- Student Peer Evaluation RatingsDocument3 pagesStudent Peer Evaluation Ratingsjackson_ricquelNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Orientation On PeerEducation - 1Document36 pagesModule 1 - Orientation On PeerEducation - 1Jymaer GeromoNo ratings yet
- Observation Checklist 2016 1Document1 pageObservation Checklist 2016 1api-318797785100% (1)
- Dare To Say No-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesDare To Say No-WPS OfficeJerlyn Rose FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Active Passive VoiceDocument26 pagesActive Passive VoiceAman BeriwalNo ratings yet
- Dumaguete City National High School Senior High School Learning Module Weeks 7-8 Modules 7-8 Personal DevelopmentDocument7 pagesDumaguete City National High School Senior High School Learning Module Weeks 7-8 Modules 7-8 Personal DevelopmentClareen June DagoyNo ratings yet
- Saint Dominic College of Batanes, Inc.: Republic of The Philippines Commission On Higher EducationDocument6 pagesSaint Dominic College of Batanes, Inc.: Republic of The Philippines Commission On Higher EducationEliseo Acedo PamaNo ratings yet
- Six stages of intercultural sensitivityDocument1 pageSix stages of intercultural sensitivityHero DiasNo ratings yet
- Learning Target and Assessment Methods MatchDocument2 pagesLearning Target and Assessment Methods MatchEdgar HinotanNo ratings yet
- Pilipino Values PerspectiveDocument26 pagesPilipino Values PerspectiveErwin Y. CabaronNo ratings yet
- Multiple Intelligences PowerpointDocument11 pagesMultiple Intelligences Powerpointapi-324379360No ratings yet
- Guidelines For Preparation and Presentation of SeminarDocument2 pagesGuidelines For Preparation and Presentation of SeminarVenkitaraj K PNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Perspective Gestalt Psychology: Rejoice A. SuarezDocument13 pagesCognitive Perspective Gestalt Psychology: Rejoice A. SuarezJoy AgustinNo ratings yet
- Learning StylesDocument22 pagesLearning StylesShailini GestosaniNo ratings yet
- Education 5.0 & Flipped ClassroomDocument10 pagesEducation 5.0 & Flipped ClassroommonikaNo ratings yet
- Simulation Performance RubricDocument2 pagesSimulation Performance Rubricapi-278832381No ratings yet
- Importance of PECS traitsDocument5 pagesImportance of PECS traitsJane Delano EstiponaNo ratings yet
- Rubrics in Individual Work - Reflection PapersDocument2 pagesRubrics in Individual Work - Reflection PapersMaria Theresa Deluna Macairan100% (1)
- Grammar Translation MethodDocument12 pagesGrammar Translation MethodDani AltamiraNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Template 4 PlacematDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Template 4 Placematapi-283858120No ratings yet
- Interview RubricDocument2 pagesInterview RubricAsehi DanskNo ratings yet
- Authentic, AlternativeDocument16 pagesAuthentic, AlternativeMharkzy LancxeNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet (SHS) Contemporary Arts From The Philippines and The RegionsDocument6 pagesLearning Activity Sheet (SHS) Contemporary Arts From The Philippines and The RegionsEricka VerchezNo ratings yet
- Institute of Teacher Education Chess Piece and Numeral DiceDocument54 pagesInstitute of Teacher Education Chess Piece and Numeral DiceArtlie Antonio GarciaNo ratings yet
- HGP Module 2 Q1Document18 pagesHGP Module 2 Q1Lorena RomeroNo ratings yet
- Body Image and Self Esteem: PPT By: CJ LaoDocument18 pagesBody Image and Self Esteem: PPT By: CJ LaoPaul Adrian AvecillaNo ratings yet
- Identify Interests, Strengths, and Aptitudes Through AssessmentDocument1 pageIdentify Interests, Strengths, and Aptitudes Through AssessmentElizabeth Perez RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 20 Differentiated Instruction Strategies and ExamplesDocument19 pages20 Differentiated Instruction Strategies and ExamplesBlessa ParagasNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Part 1Document21 pagesEvaluation Part 1saravanamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Personal Development MODULE 2Document8 pagesPersonal Development MODULE 2Christy ParinasanNo ratings yet
- IPlan DLP Format English-VersionDocument5 pagesIPlan DLP Format English-VersionDina ArcenalNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningRemedios Enad CataoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningRendyNo ratings yet
- IplanDocument4 pagesIplanJeraldine RepolloNo ratings yet
- Authority Request Form For Unofficial Travel Abroad: Schools Division OfficeDocument3 pagesAuthority Request Form For Unofficial Travel Abroad: Schools Division OfficeNyliram CariagaNo ratings yet
- CSC Resolution No. 1500088 Sworn Statement of Assets FormDocument4 pagesCSC Resolution No. 1500088 Sworn Statement of Assets Formwyclef_chin100% (6)
- Diagnostic Exam in TLE 9 Agricultural Crop Production Based On CGDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Exam in TLE 9 Agricultural Crop Production Based On CGAntonio Caballero91% (22)
- Postion Description FormDocument2 pagesPostion Description FormAnn OdrapalacNo ratings yet
- Personal Data SheetDocument4 pagesPersonal Data SheetLeonil Estaño100% (7)
- Diagnostic Exam in TLE 9 Agricultural Crop Production Based On CGDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Exam in TLE 9 Agricultural Crop Production Based On CGAntonio Caballero91% (22)
- Agri-Crop Grade 10 LMDocument184 pagesAgri-Crop Grade 10 LMharry timbol100% (5)
- K to 12 Agri-Crop Curriculum GuideDocument7 pagesK to 12 Agri-Crop Curriculum GuideAntonio CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification in TLE 9 - Agricultural Crop Production Based On CGDocument3 pagesTable of Specification in TLE 9 - Agricultural Crop Production Based On CGAntonio Caballero90% (20)
- Module 1. Basic Concepts in Horticulture PDFDocument18 pagesModule 1. Basic Concepts in Horticulture PDFagnes rodriguez100% (1)
- MELC TLE 9 Agri-Crop ProductionDocument2 pagesMELC TLE 9 Agri-Crop ProductionAntonio Caballero87% (54)
- MELC-TLE 9 Agri-Crop Production-SimplifiedDocument2 pagesMELC-TLE 9 Agri-Crop Production-SimplifiedAntonio Caballero86% (14)
- Consumer BehaviourDocument16 pagesConsumer BehaviourRiya Agrawal100% (1)
- Beyond Tests Alternatives in AssessmentDocument4 pagesBeyond Tests Alternatives in AssessmentYamith J. FandiñoNo ratings yet
- Feedback and ReportingDocument3 pagesFeedback and ReportingMeilani HartonoNo ratings yet
- Guidelines (AFA)Document6 pagesGuidelines (AFA)Noraz CompanyNo ratings yet
- Orientational Mindoro National High School Summative TestDocument1 pageOrientational Mindoro National High School Summative TestErica RayosNo ratings yet
- CSTP 2 Copp 3Document11 pagesCSTP 2 Copp 3api-482447147No ratings yet
- The Kakinada ExperimentDocument2 pagesThe Kakinada ExperimentRatish NathNo ratings yet
- Multitasking: Evolutionary Skill or Cognitive MythDocument15 pagesMultitasking: Evolutionary Skill or Cognitive Mythakhilesh sahooNo ratings yet
- Script For PresentationDocument5 pagesScript For PresentationSamuel LimNo ratings yet
- Clinical behavior analysis and RFT: Conceptualizing psychopathology and its treatmentDocument28 pagesClinical behavior analysis and RFT: Conceptualizing psychopathology and its treatmentAnne de AndradeNo ratings yet
- Quality Circle Presention - 1Document26 pagesQuality Circle Presention - 1Atta Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Research improves lives & advances societyDocument2 pagesResearch improves lives & advances societyKaye SarmientoNo ratings yet
- The Psychological Effects and Symbolism of ColorsDocument76 pagesThe Psychological Effects and Symbolism of ColorscourtneyNo ratings yet
- Masculinitate Vs FeminitateDocument3 pagesMasculinitate Vs FeminitateCOSMINNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Concept, Trends, Problems, and IssuesDocument22 pagesSeminar On Concept, Trends, Problems, and IssuesAKHILA PKNo ratings yet
- Thai 2016Document9 pagesThai 2016Dika DivinityNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Learning With Multiple-Choice Questions: Nurse Education in PracticeDocument6 pagesAssessment of Learning With Multiple-Choice Questions: Nurse Education in PracticelarasatiNo ratings yet
- Summary Organizational CultureDocument3 pagesSummary Organizational CultureWeStan LegendsNo ratings yet
- Papaliahd14 PPT Ch16 AccessibleDocument38 pagesPapaliahd14 PPT Ch16 Accessiblejesacap9No ratings yet
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument6 pagesReview of Related LiteratureLara Mae GayetaNo ratings yet
- Speech and Theater Arts Semi To FinalDocument14 pagesSpeech and Theater Arts Semi To FinalGeralyn Pelayo Alburo100% (3)
- How Can A Deontological Decision Lead To Moral Behavior?Document13 pagesHow Can A Deontological Decision Lead To Moral Behavior?Tony BlairNo ratings yet
- NCM 100 1D G12 - Madeleine Leininger - Theory of Diversity and UniversalityDocument27 pagesNCM 100 1D G12 - Madeleine Leininger - Theory of Diversity and UniversalityEve Försvunnen100% (1)
- Communication Student From Iqra UniversityDocument19 pagesCommunication Student From Iqra UniversityZarmeen SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Harvard Business Case Analysis MethodDocument2 pagesHarvard Business Case Analysis Methodabbey89No ratings yet
- The Gillette Company: Dry Idea Advertising (B) : Integrated Marketing CommunicationDocument4 pagesThe Gillette Company: Dry Idea Advertising (B) : Integrated Marketing CommunicationShachin ShibiNo ratings yet
- Field Study - CristalDocument55 pagesField Study - Cristaljenee kasumi aino nariesNo ratings yet
- Services Marketing StrategiesDocument4 pagesServices Marketing StrategiesprasadkulkarnigitNo ratings yet
- Employee Engagement Definition and ModelDocument3 pagesEmployee Engagement Definition and ModelJamie YingNo ratings yet
- Types of SeminarsDocument2 pagesTypes of SeminarsLois Malit100% (5)