Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Content Question Preparation Part2-Optic+answer
Uploaded by
ruukiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Content Question Preparation Part2-Optic+answer
Uploaded by
ruukiCopyright:
Available Formats
Content Preparation Exercise –G8 Part 2 (Optic)
MIRROR
1. A concave mirror with radius 40 cm formed a real image with 4 cm We are
Negative
high and 30 cm in front of the mirror.
a. What is the object distance?
b. What is the magnification?
c. What is the object height?
d. State 2 image characteristics!
a. 60 cm
b. ½
c. 8cm
d. Magnified, real, inverted
2. Now do the same as number before but the mirror is changed into convex mirror
in case of convex mirror, it is impossible to create real image, so it should be virtual ( di =
-30cm) and the radius also negative (-40cm)
a. 1/f =1/di +1/do
-1/20 = -1/30 +1/do
(-3+2) /60 =1/do
do = -60cm which is impossible to happened, because object cannot be negative,
so.. skip this question
3. If I have a concave mirror with focal length 60 cm. Where should I put the object to
produce an inverted and real image which size three times bigger!
1/f = 1/x + 1/3x
1/60 = 4/3x
X = 80cm
4. In front of large concave mirror with 12m radius, stand two person, the first person, Arya
stands 8m in front of lens, while the other one, Adi, stands 16m In front of lens.
Find the distance between Arya’s image and Adi’s image!
Arya: 1/ 6= 1/8+1/di
di =24 cm
Adi: 1/6 = 1/16 +1/di
(8-3)/48 = 1/di
di= 9,6 m
Distance between image : 24 – 9,6 = 14,4 m
LENS
5. Calculate where the object must be placed in front of convex lens with focal length 20
cm to form a real image 100 cm from the lens!
25cm
6. A candle is placed 10 cm in front of a Convex LENS(RALAT) with radius 8 cm, the
image characteristic formed will be inverted, real, enlarge
7. A virtual image with size one third of the object was formed by concave lens with power
of lens -20 D(diopter). What is the object distance?
P = -20D, so f = -5cm
A virtual image with size one third of the object, so if do = x, di = -x/3
1/-5 = 1/x + 1/-x/3
-1/5 = 1/x - 3/x
-1/5 = -2/x
X = 10 cm
Optical Instrument
1. A boy uses eye glasses with power of lens -2,0 D.
a. Determine whether the boy is myopia (nearsightedness) or hyperopic
(farsightedness)! myopia
b. Calculate the focal length of the eyeglasses? P = 100/f, f = -50cm
c. Calculate the far point of the boy? 50 cm
2. A boy with myopia eyes has far point in the amount of 200 cm. If he wants to see objects
at distant (very far away) what is the focal length and power of lens he must use?
-200cm , -0,5 D
3. A man with hyperopic eyes has near point in the amount of 50 cm. If he wants to read a
book at 25 cm what is the focal length and power of lens he must use so a focus image
will formed in his retina? 50cm , +2 D
di is -50 cm( in eye glasses, all image is upright so it iw always virtual/negative)
1/f = -1/ 50+1/25
f= 50cm
P= 100/50 = +2D
4. The closest distance for Budi’s father to read a book is 60 cm. If he wants to read the
books at 30 cm, what type of lens he must use and what is the power of the lens?
di is -60 cm( in eye glasses, all image is upright so it iw always virtual/negative)
1/f = -1/ 60+1/30
1/f = 1/60
F=60cm
ANALYSIS QUESTION
1. Example of eyes defect
A boy with near point in the amount of 25 cm
and far point in the amount of 40 cm.
a. What is the name of this eye defect?
Myopia
b. Can he see a clear object at (i) 10
cm, (ii) 30 cm, (iii) 50 cm?
No, yes, no
c. If he wants to see objects at distant
(very far away) what is the focal length and power of lens he must use so a
focus image will formed in his retina?
f = 40 cm, P = -2,5 D
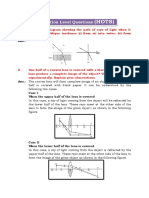
2. A student sits at the classroom. First he looks to the sky outside the window and
after that he looks down to draws it in his notebook. In the process the shape of his
lens is changed as shown in the picture below:
Look at the sky Look at the book
Explain what the eye muscle do in this process, and its effect to the image position!
Eye muscle will push the cornea and eye lens to make it thicker, change the focal length of
eye lens and focus the lens to retina.
You might also like
- CBSE Test Paper-04 Class - 12 Physics (Ray Optics and Optical Instruments)Document7 pagesCBSE Test Paper-04 Class - 12 Physics (Ray Optics and Optical Instruments)kumarisimon2No ratings yet
- Physics: Practice Worksheet (HHW)Document4 pagesPhysics: Practice Worksheet (HHW)Anil BhattNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Light Class 10Document8 pagesChemistry Light Class 10Sangithaa RaghuNo ratings yet
- Class - 10 - Light - NumericalsDocument6 pagesClass - 10 - Light - Numericalsray100% (2)
- Light WorksheetDocument1 pageLight WorksheetKanishka ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Physics worksheet on lens and mirror imagesDocument4 pagesPhysics worksheet on lens and mirror imagesAmirul Hissan Che RajjabNo ratings yet
- Physics 30 Lesson 9 Optics - Thin Lenses: Refraction 2 Refraction 1Document11 pagesPhysics 30 Lesson 9 Optics - Thin Lenses: Refraction 2 Refraction 1John JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 19 Optical Instruments: Objective - IDocument6 pagesChapter - 19 Optical Instruments: Objective - IgowthamiNo ratings yet
- Geometric Optics Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument10 pagesGeometric Optics Multiple Choice QuestionsQassem MohaidatNo ratings yet
- Optics 10Document24 pagesOptics 10Uday Prakash SahuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25: Geometric OpticsDocument2 pagesChapter 25: Geometric OpticsAlarcon KendrickNo ratings yet
- All Questions Are Compulsory: Topic - Reflection & RefractionDocument3 pagesAll Questions Are Compulsory: Topic - Reflection & Refractionshivanshu kushwahaNo ratings yet
- Geometric Optics Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument14 pagesGeometric Optics Multiple Choice QuestionsqvrlenarasegtNo ratings yet
- Physuics Class 10Document9 pagesPhysuics Class 10Vidhun 8ANo ratings yet
- Back Exercise Questions NCERT LightDocument9 pagesBack Exercise Questions NCERT LightMinakshi TiwariNo ratings yet
- Lens EquationDocument9 pagesLens EquationFE LOQUILLANONo ratings yet
- Concave Mirror Problems SolvedDocument5 pagesConcave Mirror Problems SolvedLucilleDanianYarteNo ratings yet
- CK-12 Physics Concepts - Intermediate Geometric Optics Answer KeyDocument7 pagesCK-12 Physics Concepts - Intermediate Geometric Optics Answer KeyRegine AngelesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14: Geometric Optics: CK-12 Physics Concepts - Intermediate Answer KeyDocument7 pagesChapter 14: Geometric Optics: CK-12 Physics Concepts - Intermediate Answer KeyRegine AngelesNo ratings yet
- Phys Int CC CH 14 - Geometric Optics - Answers PDFDocument7 pagesPhys Int CC CH 14 - Geometric Optics - Answers PDFRegine AngelesNo ratings yet
- Mirror Equation Questions ExplainedDocument1 pageMirror Equation Questions ExplainedGian TayamoraNo ratings yet
- Mirror Equation Questions ExplainedDocument1 pageMirror Equation Questions ExplainedGian TayamoraNo ratings yet
- Final Test Alat Dan Optik (1) F5Document5 pagesFinal Test Alat Dan Optik (1) F5Windy Widyarti RahayuNo ratings yet
- Light (HOT) PDFDocument7 pagesLight (HOT) PDFEOTVNo ratings yet
- Optics - Mirror Formula - NumericalsDocument12 pagesOptics - Mirror Formula - Numericalsadimegha0% (1)
- Class 10 Physics QuestionsDocument4 pagesClass 10 Physics QuestionsNitin ChandramouleeswaranNo ratings yet
- Convex MirrorDocument3 pagesConvex MirrorMae Jane AguilarNo ratings yet
- Mirror ProblemsDocument1 pageMirror ProblemsJyotiprasad DuttaNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL 2 OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS (PHY250Document7 pagesTUTORIAL 2 OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS (PHY250adriana dahliaNo ratings yet
- Curved Mirrors Physics ExperimentDocument3 pagesCurved Mirrors Physics ExperimentRasYa DINo ratings yet
- Curved Mirror and Lenses Assignment 2021 210518 073419Document1 pageCurved Mirror and Lenses Assignment 2021 210518 073419KENNETH GERALDNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Understanding LensesDocument12 pagesLesson Plan For Understanding LensesAnonymous zzrGiWMfHZNo ratings yet
- The Lens EquationDocument22 pagesThe Lens EquationCedie SanchezNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper SolutionsDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper Solutionsr_ridhima45No ratings yet
- Physics NumericalDocument2 pagesPhysics NumericalYash Mahajan100% (1)
- Reflection Numericals TestDocument15 pagesReflection Numericals Testshalu malaniNo ratings yet
- Document (29) KhikhikhikhiDocument3 pagesDocument (29) KhikhikhikhiUTKARSH ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Salud, Juan Vicente 2017131112 PHYS101L/A2 2/11/2021Document12 pagesSalud, Juan Vicente 2017131112 PHYS101L/A2 2/11/2021yyuan ssaludNo ratings yet
- Lens FundamentalsDocument38 pagesLens FundamentalsShanta Harford100% (1)
- PDF 10TH CLASS PHYSICS IMPORTANT QUESTIONS SSC ABYASA DEEPIKADocument9 pagesPDF 10TH CLASS PHYSICS IMPORTANT QUESTIONS SSC ABYASA DEEPIKAprakashNo ratings yet
- 1993 LightDocument2 pages1993 LightAyush AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Numericals Based On Convex LensDocument2 pagesNumericals Based On Convex LensYash Saxena100% (1)
- Sci10 Q2 M4 EditedaftercontentlayoutlanguageevaluationDocument37 pagesSci10 Q2 M4 EditedaftercontentlayoutlanguageevaluationAqua AvilaNo ratings yet
- Images Formed by A Converging LensDocument5 pagesImages Formed by A Converging Lensdavid_acadecap4725No ratings yet
- 10th Reflection and Refraction of Light Cbse Test Paper Solved-4Document4 pages10th Reflection and Refraction of Light Cbse Test Paper Solved-4ashokNo ratings yet
- Luni Karlina Manik - Bilphy18 - Wave and Optic - Optical Tools II - Task Week 14Document4 pagesLuni Karlina Manik - Bilphy18 - Wave and Optic - Optical Tools II - Task Week 14Luni Karlina ManikNo ratings yet
- ProblemsDocument3 pagesProblemsKunal KishoreNo ratings yet
- LIGHT - MIRROR Practice QuestionsDocument2 pagesLIGHT - MIRROR Practice Questionsshrish000000100% (1)
- HOTS On Reflection of LightDocument2 pagesHOTS On Reflection of Lightswadhin100% (4)
- Mirror NumericalsDocument2 pagesMirror NumericalsMATHILI67% (3)
- Mirror Formula - NumericalsDocument4 pagesMirror Formula - NumericalsSen Gaming YtNo ratings yet
- Thin Lens Focus DistanceDocument13 pagesThin Lens Focus DistanceselniNo ratings yet
- PHYS 202 Lecture 16 - Optical Instruments: The Human Eye, Vision Correction, Camera, Magnifier, Microscopes & TelescopesDocument41 pagesPHYS 202 Lecture 16 - Optical Instruments: The Human Eye, Vision Correction, Camera, Magnifier, Microscopes & TelescopesSATYA NARAYAN SAHUNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Light - WorksheetDocument5 pagesReflection of Light - WorksheetDøomNo ratings yet
- Light and Geometric OpticsDocument53 pagesLight and Geometric OpticsLeah May Tamayo ManayonNo ratings yet
- Physics Light ProblemsDocument16 pagesPhysics Light ProblemsKARIKALAN D100% (2)
- 03-04-22 Class 10 cbVDseDocument2 pages03-04-22 Class 10 cbVDseArpitha AppuNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics AssgnDocument3 pagesRay Optics AssgnHimanshi GuptaNo ratings yet
- How to Draw Realistic Animals: Learn to Draw Using Simple Shapes and Art GridsFrom EverandHow to Draw Realistic Animals: Learn to Draw Using Simple Shapes and Art GridsRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Engr225 Pe-16Document1 pageEngr225 Pe-16ruukiNo ratings yet
- Engr225 Pe-16Document1 pageEngr225 Pe-16ruukiNo ratings yet
- Engr225 Pe-7Document1 pageEngr225 Pe-7ruukiNo ratings yet
- Session 3 Axial Load 1Document14 pagesSession 3 Axial Load 1ruukiNo ratings yet
- Engr225 Pe-5Document2 pagesEngr225 Pe-5ruukiNo ratings yet
- Engr225 Pe-6Document1 pageEngr225 Pe-6ruukiNo ratings yet
- 2021 Ex Oscillations and Communications SystemsDocument2 pages2021 Ex Oscillations and Communications SystemsruukiNo ratings yet
- AA HL - Questionbank - Calculus - EasyDocument74 pagesAA HL - Questionbank - Calculus - EasyruukiNo ratings yet
- ENGR 225 Practice Exercise 4Document2 pagesENGR 225 Practice Exercise 4ruukiNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Circuits Theorem.Document25 pagesWeek 6 Circuits Theorem.ruukiNo ratings yet
- Find circuit voltages and energies given currents and initial conditionsDocument2 pagesFind circuit voltages and energies given currents and initial conditionsruukiNo ratings yet
- Content Question Preparation G8 Part 1Document2 pagesContent Question Preparation G8 Part 1ruukiNo ratings yet
- De Anza College Physics 4B - Chiang Fall 2021Document5 pagesDe Anza College Physics 4B - Chiang Fall 2021ruukiNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Assignment Energy, Work and Power ProblemsDocument1 pageMechanics Assignment Energy, Work and Power ProblemsruukiNo ratings yet
- Sample Problem With Solution Lect 06 CIrcuit TheoremsDocument8 pagesSample Problem With Solution Lect 06 CIrcuit TheoremsruukiNo ratings yet
- Assignment #02 Electrical Engineering 02Document2 pagesAssignment #02 Electrical Engineering 02ruukiNo ratings yet
- 2018 HSC PhysicsDocument48 pages2018 HSC PhysicsruukiNo ratings yet
- Eryne Sohor - Term 2 Sound Absorption ExperimentDocument2 pagesEryne Sohor - Term 2 Sound Absorption ExperimentruukiNo ratings yet
- Homework 6 StaticsDocument2 pagesHomework 6 StaticsruukiNo ratings yet
- 4B W2021 MT1 SolutionDocument7 pages4B W2021 MT1 SolutionruukiNo ratings yet
- MEGR3210 Homework2Document3 pagesMEGR3210 Homework2ruukiNo ratings yet
- Inclass Ch5 SolveDocument2 pagesInclass Ch5 SolveruukiNo ratings yet
- MEGR3210 Homework4Document2 pagesMEGR3210 Homework4ruukiNo ratings yet
- Physics Syllabus 2020Document17 pagesPhysics Syllabus 2020Fatima PuspaNo ratings yet
- Pointers EASE 2 Physics Grade 8 2020-2021Document2 pagesPointers EASE 2 Physics Grade 8 2020-2021ruukiNo ratings yet
- HSC Physics Trial ExamDocument35 pagesHSC Physics Trial ExamruukiNo ratings yet
- NUS and NTU Physics Entrance ExamDocument152 pagesNUS and NTU Physics Entrance ExamruukiNo ratings yet
- 2012 Natural Sciences Test-421Document14 pages2012 Natural Sciences Test-421amandashn96No ratings yet
- NTU Entrance Examination Paper Requirements: Engineering & ITDocument4 pagesNTU Entrance Examination Paper Requirements: Engineering & ITDaffa WidyadhanaNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Loose Tube Cable: (Fundamental Structures)Document4 pagesOptical Fiber Loose Tube Cable: (Fundamental Structures)Must PyurNo ratings yet
- Digital Microscope: The World's First 4K Ultra-High Accuracy MicroscopeDocument40 pagesDigital Microscope: The World's First 4K Ultra-High Accuracy MicroscopeCARLO CAPULINo ratings yet
- Digital SLR Photography 2014-07Document150 pagesDigital SLR Photography 2014-07xistense100% (1)
- Q.NO.20 Determine The Focal Length of The Given Concave Mirror by U - V Method. Verify The Result From U-V Graph. FormulaDocument16 pagesQ.NO.20 Determine The Focal Length of The Given Concave Mirror by U - V Method. Verify The Result From U-V Graph. Formulakrishnik183No ratings yet
- TP MetrologyDocument2 pagesTP MetrologyPhilippe LeungNo ratings yet
- A' Level Physic 2 2017Document324 pagesA' Level Physic 2 2017Mwesigwa Ambrose Kajura100% (1)
- Zeiss Ikon Super Ikonta IV USER MANUALDocument35 pagesZeiss Ikon Super Ikonta IV USER MANUALOvidiu SchifirnetNo ratings yet
- Refractive Index - Convex Lens and Plain MirrorDocument5 pagesRefractive Index - Convex Lens and Plain Mirrorven230% (1)
- LP Test 2Document6 pagesLP Test 2Jade Thong EchaviaNo ratings yet
- User Manual: Model M8333Z SeriesDocument20 pagesUser Manual: Model M8333Z SeriesMarcelo WillyNo ratings yet
- Cbjescco 10Document12 pagesCbjescco 10neomatrix70100% (1)
- Images Formed by Curved Mirrors ExplainedDocument7 pagesImages Formed by Curved Mirrors ExplainedMark SalvadorNo ratings yet
- E112eq PDFDocument6 pagesE112eq PDFMingNo ratings yet
- Nicol PrismDocument2 pagesNicol PrismPushpendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Science10 Q2 Mod3 QualitativeCharacteristicsOfImagesDocument12 pagesScience10 Q2 Mod3 QualitativeCharacteristicsOfImagesKOBE BRYANT TIDOYNo ratings yet
- WIDELINE - Horizon Technical GuideDocument24 pagesWIDELINE - Horizon Technical GuideAmin AminiNo ratings yet
- Pengajuan Peralatan Fiber Optik: Fusion Splicer AI9C SIGNAL FIREDocument2 pagesPengajuan Peralatan Fiber Optik: Fusion Splicer AI9C SIGNAL FIRENanda KhoiriNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Performance Task #1 (2Nd Quarter) (MODULE 1 & 2)Document1 pageScience 7 Performance Task #1 (2Nd Quarter) (MODULE 1 & 2)Alvin GultiaNo ratings yet
- Tamron SP 24-70mm F/2.8 Di lens reviewDocument4 pagesTamron SP 24-70mm F/2.8 Di lens reviewDoc Hertzio Endoskeleton OrbeNo ratings yet
- Types of CameraDocument16 pagesTypes of CameraOsman Gumanti Ahmad AlbabNo ratings yet
- MAPEH-Arts: Quarter 3 - Module 2Document24 pagesMAPEH-Arts: Quarter 3 - Module 2Girlie Oguan LovendinoNo ratings yet
- Profile PricesDocument22 pagesProfile PricesAntonio CastilloNo ratings yet
- Parts of MicroscopeDocument4 pagesParts of MicroscopeAyela Kim PiliNo ratings yet
- Performance: Physics Light 01Document4 pagesPerformance: Physics Light 01Vijay kumar LokanadamNo ratings yet
- Performance Task Physics 10 1st GradingDocument2 pagesPerformance Task Physics 10 1st GradingIvan TabanagNo ratings yet
- Glass Survey For Interior DesignerDocument23 pagesGlass Survey For Interior DesignerShiv Kumar0% (1)
- 01212Document36 pages01212Jovan MartinovicNo ratings yet
- Transparent Translucent OpaqueDocument39 pagesTransparent Translucent OpaqueHuynh NganNo ratings yet
- Ace Edison LED Lighting Product CatalogDocument24 pagesAce Edison LED Lighting Product CatalogvijayninelNo ratings yet
- Camera Technical InformationDocument2 pagesCamera Technical InformationmarjaaaaaNo ratings yet