Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1,4 Multiple Choice Questions
Uploaded by
Thiha Aung0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views13 pagesOriginal Title
APznzaajiQ9NHTPsFXnKUnRvnB8lDY9l1pJxiTSnBkmYKQlxjcveSE-hiG0qtDNETDXpVsQOCQBkfWiYv26eofN6lFf73glCDR9vIKymbeIwwve8I0PsK4VS18J1LUzg7drn4gHEjrUQ_86WQhpN8Pv1CB0U_Pd73YozajfOFqFfv4IUOrJ9dTi3Ff_TpzVbO8OttwKTFRWFXVPB3QGw2g
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views13 pagesChapter 1,4 Multiple Choice Questions
Uploaded by
Thiha AungCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
Chapter 1,4
Multiple Choice Questions
1.How many server are there in client-server architecture?
2. How many client are there in client-server architecture? three
3.Which architecture is more simpler to set up?
a. client-server architecture
b. peer-to-peer architecture
4.Machine that places the request to access the data, is generally called
as______________.
a. server machine
b. client machine
5.In which topology, every node is connected to 2 other nodes?
a.Star
b.Bus
c. Ring
6. Hub is associated with __________ network.
a.Star
b.Bus
c. Ring
7. In which topology, all nodes are connected in a single cable?
a.Star
b.Bus
c. Ring
8.In which topology, all nodes are connected in a circular closed
loop form.
a.Star
b.Bus
c. Ring
9.Star topology is basically based on a central device _________?
10.Physical or logical arrangement of network is _______.
11. In a ____ topology, a dedicated link connects a device to a central
controller.
a.Star
b.Bus
c. Ring
12. In a ________ topology, each device has a dedicated point-to-point
connection with exactly two other devices.
a. Star
b. Bus
c. Ring
13.In a client-server architecture, a single powerful
computer is called _______.
14.In a client-server architecture, multiple computers
are called____________.
15.In peer-to-peer architecture, each workstation has
equivalent _______ and _________.
16. In peer-to-peer architecture, do not
have________.
17. Peer-to-peer networks can be set up among
_______ computers.
18. _________is much simpler to set up in
comparison to client-server network.
19. The medium used for transmission of data between the
nodes on a network is called a ___________.
20. Peer-to-peer architecture is a type of network on which
each ___________ has equivalent capabilities and
responsibilities.
21. A specific type of network consisting of a single powerful
computer acting as a server, usually connected to multiple
computers called clients, is known as ___________.
22. Wireless communication is the transfer of information over
a distance without the use of ___________.
23. Microwaves, bluetooth, infrared rays are used in
__________communication.
24.A network consists of two or more computers linked together for the
purpose of sharing ________________.
25. When a network connects personal devices, it forms a _____________.
26. When computers are interconnected within a limited geographical area it
becomes a ________________.
27. A network connecting multiple LANs within the same campus is known as
________________.
28. When computers in different branches of an organisation are
interconnected within the same city, it becomes a _____________.
29. When a network is spread across cities, countries or even continents
covering a large geographical area, it becomes a ______________.
30. A __________ consists of two or more computers linked together for the
purpose of sharing resources.
A. True or false?
1. A computer requires instructions to perform any task.
2. RAD stands for Rapid Access Development.
3. BASIC supports an assembler as a translator.
4. The Interpreter converts an assembly language into a
machine
language.
5. First-generation languages use machine language.
1.-------------was used in the mid-1950s.
A. 1GL
B. 2GL
C. 3GL
D. 4GL
2.-------------is the high-level language.
A. 1GL
B. 2GL
C. 3GL
D. 4GL
3. Python, SQL and Matlab are examples of ----------------language.
A. 1GL
B. 2GL
C. 3GL
D. 4GL
4. The function and the execution of the functions in a step-by-step linear order is
called ---------------.
A. Modular Programming
B. Procedural Programming
C. Non-procedural Programming
D. Event-driven Programming
5. It is a code that executes in response to an event is called ---------------.
A. Modular Programming
B. Procedural Programming
C. Non-procedural Programming
D. Event-driven Programming
6. It is designed to detect events as they occur, and then deal with them using some event-handling
procedure.
A. Modular Programming
B. Procedural Programming
C. Non-procedural Programming
D. Event-driven Programming
7. This is a collection of binary digits or bits that the computer reads and interprets.
A. Machine Language
B. High-level Language
C. Assembly Language
D. Very high-level language
8. There are ______ generations of computer language.
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
9. Program used to convert or translate programs written in assembly code to machine code.
A. Assembler
B. Compiler
C. Interpreter
D. Coder
10. Program used to translate source code into intermediate code and immediately execute it line
by line is:
A. Assembler
B. Compiler
C. Interpreter
D. Coder
You might also like
- 2nd Periodical Examinations Computer Grade 10Document3 pages2nd Periodical Examinations Computer Grade 10Jayjay TorresNo ratings yet
- Exam 3rd Quarter 22 23Document4 pagesExam 3rd Quarter 22 23christine baraNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Year 7 NetworkDocument4 pagesAnswer Key Year 7 Networkmarwamohammed1517No ratings yet
- Computer Networks MCQsDocument42 pagesComputer Networks MCQsWaqas Javed50% (4)
- CSS Unit TestDocument2 pagesCSS Unit TestpapyoverzosaNo ratings yet
- Arizona FBLA TestDocument16 pagesArizona FBLA Test13stanleyNo ratings yet
- Rev G11Document4 pagesRev G11Ihab Hosny AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07 Test-AnswerDocument4 pagesChapter 07 Test-AnswerAlif Kap Wau InsanNo ratings yet
- EXAMDocument13 pagesEXAMjohn alNo ratings yet
- Tutooor18 RWHDocument6 pagesTutooor18 RWHR.S.G.FNo ratings yet
- CST Grade5 Term 1 Sample PaperDocument4 pagesCST Grade5 Term 1 Sample PaperZainab WajidahNo ratings yet
- Information Technology - Level 40 Newtorks Worksheet #1Document2 pagesInformation Technology - Level 40 Newtorks Worksheet #1Rana Hassan TariqNo ratings yet
- ICT QUIZ 4 1B E Sol 22062022 062532pmDocument4 pagesICT QUIZ 4 1B E Sol 22062022 062532pmLiaquat RaniaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 First Grading Exam (2019-2020)Document3 pagesGrade 10 First Grading Exam (2019-2020)Kadir YaegarNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 Chapter 6 Reading Guide FinishedDocument17 pagesCCNA 1 Chapter 6 Reading Guide FinishedShriRam HegdeNo ratings yet
- I. Multiple Choice (30 PTS.)Document3 pagesI. Multiple Choice (30 PTS.)Hanz AngeloNo ratings yet
- CN Question BankDocument57 pagesCN Question BankMohammad ImthiyazNo ratings yet
- Louiglen - P CSS-3rd-Periodical-Exam-Test-PaperDocument3 pagesLouiglen - P CSS-3rd-Periodical-Exam-Test-PaperLouiglen PacanaNo ratings yet
- Ec6802 WN MCQS On Unit 1 & 2Document10 pagesEc6802 WN MCQS On Unit 1 & 2ohmshankarNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Test css11Document2 pages2nd Quarter Test css11Cha N OtNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems Servicing: Self-Learning Module 4Document10 pagesComputer Systems Servicing: Self-Learning Module 4Jeffrey MacabareNo ratings yet
- ACN MCQ MergedDocument747 pagesACN MCQ MergedAjit RoyNo ratings yet
- Periodical Exam in ICT12&11 2018-2019 2nd QuarterDocument4 pagesPeriodical Exam in ICT12&11 2018-2019 2nd QuarterRS Dulay100% (1)
- Computer Network Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDF - December 14, 2021Document9 pagesComputer Network Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDF - December 14, 2021Amit TiwariNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems Servicing: Self-Learning Module 2Document9 pagesComputer Systems Servicing: Self-Learning Module 2Jeffrey MacabareNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ALL ABOUT CLOUD WorksheetDocument9 pagesChapter 3 ALL ABOUT CLOUD WorksheetgamersnexxNo ratings yet
- WWW Ans KeyDocument2 pagesWWW Ans KeyTrijal GargNo ratings yet
- Sample G11 ExamDocument3 pagesSample G11 Examnolekay153No ratings yet
- Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Module - Form 4Document12 pagesInformation and Communication Technology (ICT) Module - Form 4Eim MiraNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Online BitsDocument34 pagesComputer Networks Online Bits06121a040191% (11)
- Chapter 2 Solutions: Review QuestionsDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Solutions: Review QuestionsOrpheo NgadimanNo ratings yet
- CC Inf106 2019Document2 pagesCC Inf106 2019Djamila Maimouna SELLY NGALOUMONo ratings yet
- I. MULTIPLE CHOICES: Read The Statement Carefully. Choose The Letter of The BestDocument3 pagesI. MULTIPLE CHOICES: Read The Statement Carefully. Choose The Letter of The Bestリアルビン シェリルNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems Servicing: Self-Learning Module 3Document8 pagesComputer Systems Servicing: Self-Learning Module 3Jeffrey MacabareNo ratings yet
- Samples of Competitive Examination Questions Part I IDocument66 pagesSamples of Competitive Examination Questions Part I IYasser AlghrafyNo ratings yet
- Networking ConceptsDocument10 pagesNetworking ConceptsdrosbeastNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1: CECS 474 Computer Network InteroperabilityDocument4 pagesQuiz 1: CECS 474 Computer Network Interoperabilityاسامه العبسيNo ratings yet
- Ictl Form 2 Final08Document11 pagesIctl Form 2 Final08tycoon96100% (1)
- CS440 Midterm V A No AnswersDocument19 pagesCS440 Midterm V A No AnswerswowNo ratings yet
- CSS 3rd Periodical Exam (Test Paper)Document3 pagesCSS 3rd Periodical Exam (Test Paper)JefersonNo ratings yet
- Discovering Computers Chapter 9 Practice TestDocument4 pagesDiscovering Computers Chapter 9 Practice TestfdgdfgNo ratings yet
- Ccna ch7Document8 pagesCcna ch7dsuntewNo ratings yet
- Cs101 Grand Quiz With SolutionDocument5 pagesCs101 Grand Quiz With Solutionfatima shahNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Network MCQDocument5 pagesData Communication Network MCQMd Siraj UddinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 TestDocument4 pagesChapter 5 TestMariaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test CSS TM1Document11 pagesPre-Test CSS TM1SUPER M SCHOOL OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGYNo ratings yet
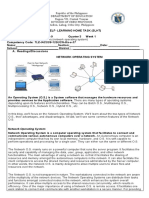
- Network Operating SystemDocument7 pagesNetwork Operating SystemLady Christianne BucsitNo ratings yet
- CH03Document5 pagesCH03MurosamaNo ratings yet
- CST101 Introduction To Computer Science. TEST 01. Name: - Theoretical Part Explain: (12 Points)Document4 pagesCST101 Introduction To Computer Science. TEST 01. Name: - Theoretical Part Explain: (12 Points)Cesar AllainNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Network and Internet WorksheetDocument3 pagesData Communication Network and Internet WorksheetGeneil ClarkeNo ratings yet
- AdnmnetDocument2 pagesAdnmnetAlebel AyalnehNo ratings yet
- Chp-6 Getting Connected InternetDocument2 pagesChp-6 Getting Connected Internetjitendragandhi250No ratings yet
- CPA Workbook (WB) Upper Sec - 28 Sep 2021 For PrintingDocument97 pagesCPA Workbook (WB) Upper Sec - 28 Sep 2021 For PrintinghayderthamhouyinNo ratings yet
- PDC Example Exam QuestionsDocument9 pagesPDC Example Exam Questionskunal singhNo ratings yet
- C Programming for the Pc the Mac and the Arduino Microcontroller SystemFrom EverandC Programming for the Pc the Mac and the Arduino Microcontroller SystemNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandOperating Systems Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet
- Mohamed Bilal NodejsDocument3 pagesMohamed Bilal NodejssheikabuNo ratings yet
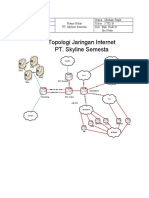
- Laporan Topologi Real (PT. Skyline Semesta)Document13 pagesLaporan Topologi Real (PT. Skyline Semesta)Ghulam Faqih HasibuanNo ratings yet
- Hezlin PHD Editted14022023Document58 pagesHezlin PHD Editted14022023hezlinNo ratings yet
- Datasheet: Gigabit Passive Optical NetworkDocument12 pagesDatasheet: Gigabit Passive Optical NetworkdrjxNo ratings yet
- Document Finder CustomizingDocument7 pagesDocument Finder CustomizingetiennehanfNo ratings yet
- The School'S Learning Resource Center: My Performance (How I Will Be Rated)Document9 pagesThe School'S Learning Resource Center: My Performance (How I Will Be Rated)johncyrus dela cruzNo ratings yet
- DeploymentGuide PulseConnectSecure-SAMLauthDocument28 pagesDeploymentGuide PulseConnectSecure-SAMLauthNetsys BilisimNo ratings yet
- FCS SyllabusDocument3 pagesFCS SyllabusrajsiddhartharapoluNo ratings yet
- MU325 Answer 4Document6 pagesMU325 Answer 4SuhendiNo ratings yet
- Prayer For Thesis Final DefenseDocument8 pagesPrayer For Thesis Final Defenseashleydavisshreveport100% (2)
- 96M-CH605 Partes y HerramientasDocument6 pages96M-CH605 Partes y HerramientasAraceli ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- PN-VC841H: Intelligent Touch BoardDocument3 pagesPN-VC841H: Intelligent Touch BoardMohamed ShawkyNo ratings yet
- WP Ot Ciso Solution SelectionDocument6 pagesWP Ot Ciso Solution SelectionPedrito OrangeNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource WasSara AlbogamiNo ratings yet
- How To Ace The Number One Question in Interviews - "Tell Me About Yourself"Document3 pagesHow To Ace The Number One Question in Interviews - "Tell Me About Yourself"Christine CaoNo ratings yet
- Technical Communication Omnipcx Enterprise: NB of Pages: 174 Date: 14 October 2005Document174 pagesTechnical Communication Omnipcx Enterprise: NB of Pages: 174 Date: 14 October 2005locuras34No ratings yet
- DSDPlusDocument11 pagesDSDPlusMariano Rubén JurczyszynNo ratings yet
- Irjet V7i9652Document6 pagesIrjet V7i9652NatashaNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Tracking System Using GPS and GSM TechnologyDocument5 pagesVehicle Tracking System Using GPS and GSM TechnologyIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- NET102 Chapter2ConfigureaNetworkOperatingSystemDocument52 pagesNET102 Chapter2ConfigureaNetworkOperatingSystemsteven EstevanNo ratings yet
- Economics Today The Micro View 18th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocument16 pagesEconomics Today The Micro View 18th Edition Miller Solutions Manualtusseh.itemm0lh100% (26)
- Porcupine Excel AssignmentDocument25 pagesPorcupine Excel AssignmentAndrea XiaoNo ratings yet
- System Analysis and Design - Lecture 9: Data Flow DiagramDocument29 pagesSystem Analysis and Design - Lecture 9: Data Flow DiagramWajiihah BaureekNo ratings yet
- Use Jack and Pulseaudio at The Same Time On Linux MintDocument3 pagesUse Jack and Pulseaudio at The Same Time On Linux MintNicola LandroNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal On A Fitness Website Project Name: Hearty HabitDocument4 pagesProject Proposal On A Fitness Website Project Name: Hearty Habitraju acharyaNo ratings yet
- Export 20220925 2044Document57 pagesExport 20220925 2044Dimas AyodyaNo ratings yet
- XT1710-Moto Z2 Play - L3 BB Troubleshooting Guide V1.0Document102 pagesXT1710-Moto Z2 Play - L3 BB Troubleshooting Guide V1.0karenchristinasantos87100% (1)
- Module 2 BCDocument11 pagesModule 2 BCJonathan Jr. BeltranNo ratings yet
- Operation/Technical ManualDocument64 pagesOperation/Technical ManualBilal AloulouNo ratings yet
- Zelev 1Document2 pagesZelev 1evansparrowNo ratings yet