Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Under Suitable Conditions, Butane, C: © OCR 2022. You May Photocopy This
Uploaded by
Mahmud RahmanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Under Suitable Conditions, Butane, C: © OCR 2022. You May Photocopy This
Uploaded by
Mahmud RahmanCopyright:
Available Formats
1. Under suitable conditions, butane, C4H10, reacts with chlorine by radical substitution.
A mixture of organic compounds is formed,
including C4H9Cl , and compounds D and E.
i. Complete the table below to show the mechanism for the initiation and propagation stages of the reaction of C4H10 with chlorine to
form C4H9Cl .
In your equations, use molecular formulae and ‘dots‘ (·) with any radicals.
Equation
Initiation
Conditions
Propagation →
→
[3]
i. Organic compound D is formed by substitution of all the H atoms in butane by Cl atoms.
Write the equation for the formation of compound D from butane.
Use molecular formulae.
[1]
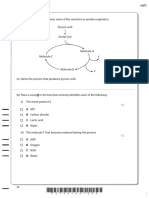
2. Which compound is unsaturated, alicyclic and contains an alkyl group?
© OCR 2022. You may photocopy this Page 1 of 13 Created in ExamBuilder
page.
C
Your answer [1]
3. A section of a polymer is shown below.
Which monomer could form this polymer?
A CH3CH(OH)CN
B HOCH2CH2CN
C H2C=CHCN
D NCCH=CHCN
Your answer [1]
(b). Hex-1-ene can also be polymerised to form poly(hex-1-ene).
i. Draw a section of poly(hex-1-ene) containing two repeat units.
[1]
i. Waste poly(hex-1-ene) can be disposed of usefully by recycling.
State two other methods of disposing of polymers that can be beneficial to the environment.
1
2
[2]
© OCR 2022. You may photocopy this Page 2 of 13 Created in ExamBuilder
page.
5. Electrons occupy orbitals which are arranged in energy levels.
In the diagram below, each box represents an orbital and each electron is shown as an arrow.
Label the sub-shells and add arrows to show how electrons occupy orbitals in an atom of oxygen.
[2]
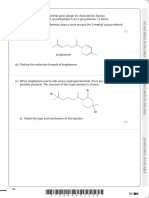
6(a). This question is about saturated hydrocarbons.
Compounds A, B and C are saturated hydrocarbons.
The structures and boiling points of A, B and C are shown below.
• Use the structures to explain what is meant by the term structural isomer.
• Explain the trend in boiling points shown by A, B and C in the table.
[5]
© OCR 2022. You may photocopy this Page 3 of 13 Created in ExamBuilder
page.
(b). Compounds A, B and C all react with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet radiation to form organic compounds with the formula
C5H11Cl.
i. Name the mechanism for this reaction.
[1]
i. Complete the table to show the number of structural isomers of C5H11Cl that could be formed from the reaction of chlorine with A
and B.
A B
Number of
structural isomers
........................ ........................
[2]
i. The reaction of compound A with excess chlorine forms a compound D, which has a molar mass of 175.5 g mol . −1
Draw a possible structure for compound D and write the equation for its formation from compound A. Use molecular formulae in the
equation.
Equation [2]
7. How many structural isomers of C6H14O are tertiary alcohols?
A 1
B 2
C 3
D 4
© OCR 2022. You may photocopy this Page 4 of 13 Created in ExamBuilder
page.
Your answer [1]
8. The structure of naphthalene is shown below.
What is the molecular formula of naphthalene?
A C10H8
B C10H10
C C12H10
D C12H12
Your answer [1]
9. Phosgene, COCl2, exists as simple molecules.
The displayed formula of a phosgene molecule is shown below.
i. Draw a ‘dot-and-cross’ diagram of a phosgene molecule.
Show outer electrons only.
[1]
i. Name the shape of a phosgene molecule and explain why it has this shape.
Name of shape
Explanation
[3]
© OCR 2022. You may photocopy this Page 5 of 13 Created in ExamBuilder
page.
Mark scheme
Question Answer/Indicative content Marks Guidance
Dots NOT required for initiation
IGNORE temperature OR pressure
Dots required in each propagation equation
ALLOW 1 mark for BOTH propagation
equations with any dots missing or extra dots
3
Initiation
(AO1.1) e.g. C4H10 + Cl → C4H9 + HCl
C4H9• + Cl2• → C4H9Cl + Cl
Cl2 → 2Cl· AND UV ✓
DO NOT ALLOW charges
1 i Propagation
C4H10 + Cl· → C4H9· + HCl ✓
Examiner’s Comments
(AO2.5)
C4H9· + Cl2 → C4H9Cl + Cl· ✓
A minority of Many candidates scored all 3
(AO2.5) marks for this part, showing that most had
thoroughly learnt the mechanism for radical
substitution. The equation and conditions for
the initiation step were well-known but the
equations for the propagation steps often
included errors. It was common for dots to be
omitted for some radicals and C4H9Cl·, rather
than C4H9·, was often shown for one of the
products in the first propagation stage. H· was
then shown as the other product.
ALLOW structural formulae, e.g.
CH3CH2CH2CH3 + 10Cl2
→ CCl3CCl2CCl2CCl3 + 10HCl
ii C4H10 + 10 Cl2 → C4Cl10 + 10 HCl ✓ 1 (AO2.6) Examiner’s Comments
Only the highest attaining candidates were
able to write the correct equation. Although
most candidates did identify the organic
product as C4Cl10, the other product was
usually seen as 5H2 rather than 10HCl.
iii
Total 7
2 C 1 (AO1.2) Examiner’s Comments
© OCR 2022. You may photocopy this Page 6 of 13 Created in ExamBuilder
page.
Unsaturated, alicyclic and alkyl are all terms
that are introduced in AS Chemistry and about
two-thirds of candidates recognised that option
C met the three criteria. From the annotations
on scripts, most candidates ruled out the
saturated option B. A sizeable number of
candidates selected either the aromatic option
A, or structure D which does not possess an
alkyl group. It is important that candidates
learn the terms introduced in the specification
Section 4.1.1, Basic concepts in organic
chemistry.
Total 1
Examiner’s Comments
This part discriminated well. Although most
candidates did select C as the correct
structure, many were diverted into selecting
3 C 1 (AO1.2) option D, the other alternative containing a
double C=C bond. In identifying a monomer
for an addition polymer, candidates are
advised to identify the repeat unit and then to
replace the single C–C bond with a double
bond to give the monomer.
Total 1
4 a i
ii
b i 1(AO2.5) ALLOW correct structural OR displayed
OR skeletal formula
Must show two repeat units
Polymer must have side links
NOTE: C4H9– is allowed for CH3CH2CH2CH2–
IGNORE brackets and use of ‘n’
ALLOW alternating side chains, i.e.
Examiner’s Comments
Over half of the candidates answered this
question incorrectly. Many drew the wrong
repeat units or did not show two repeat units.
© OCR 2022. You may photocopy this Page 7 of 13 Created in ExamBuilder
page.
The structural diagrams were very hard to
decipher and not well drawn.
Exemplar 6
Although the connectivity is not exact, this was
allowed. Many students drew full displayed
structures which were very difficult to decipher
as they often encroached over the writing in
the question.
For energy production,
ALLOW generate electricity/heating
ALLOW as an (organic) feedstock
Examiner’s Comments
Combustion for energy production ✓
Most students did not gain many marks on
ii 2(AO1.1×2)
for production of plastics this question, with a significant number stating
OR other useful organic compounds ✓ that the plastics could be used to feed
livestock or as fertilisers. Those that
mentioned combustion, merely stated plastics
could be used as a fuel. Some candidates
made references to making them
biodegradable or recycling, but these answers
were not given.
Total 11
Sub-shells labels 2
2s (single box) AND 2p (3 boxes) ✓ (AO1.1) ALLOW single headed arrows, e.g. 1
5 Electrons as arrows Examiner’s Comments
unpaired electrons in 3 boxes: ↑↓ ↑ ↑
AND Most candidates added arrows correctly to the
Paired electrons in single box: ↑↓ ✓ (AO1.2) boxes but the sub-shell labels were sometimes
omitted. Lower attaining candidates
sometimes paired electrons, rather than
showing them singly or showed six electrons
in the 2p sub-shell. This suggested either a
lack of understanding or failure to read the
question.
Total 2
© OCR 2022. You may photocopy this Page 8 of 13 Created in ExamBuilder
page.
For ‘structural’:
Structural isomers: 1 mark ALLOW different structure
OR different displayed/ skeletal formula
Different structural formulae
AND same molecular formula ✓ DO NOT ALLOW any reference to
spatial/space/3D
Same formula is not sufficient (no ‘molecular’)
Different arrangement of atoms is not
sufficient
(no ‘structure’/‘structural’)
Common molecular formula: 1 mark
ALLOW 5 carbons and 12 hydrogens
C5H12 for all 3 hydrocarbons ✓ ALLOW for 2 marks:
Different structural formulae
AND same molecular formula ✓ of C5H12
✓
Comparisons needed throughout
ORA throughout
ALLOW comparison between any alcohols,
e.g.
A is least branched and has highest b pt
6 a 5 C is most branched and has lowest b pt
ALLOW induced dipole(−dipole) interactions
Boiling point and branching:
IGNORE van der Waals’/vdw forces
ALLOW SA for surface area
1 mark
ALLOW ‘harder to overcome intermolecular
Boiling point decreases with
forces
ALLOW more energy to separate the
more branching
molecules
OR more methyl/alkyl groups/side chains IGNORE just ‘bonds’
OR shorter carbon chain ✓ intermolecular/London forces required
Examiner’s Comments
Branching and London forces: 1 mark
This question discriminated well and resulted
Could be seen anywhere within response in a full range of marks. Most candidates were
More branching gives less (surface) contact aware that structural isomers have different
structural formulae but the same molecular
AND formulae. It was common though for
fewer/weaker London forces ✓ candidates to refer to different arrangements
of atoms in space, clearly confusing with
stereoisomerism. The best candidates used
the structures (as in the question) to show that
Energy and intermolecular forces: 1 mark the common molecular formula was C5H12.
© OCR 2022. You may photocopy this Page 9 of 13 Created in ExamBuilder
page.
Candidates were expected to link the amount
of surface contact between molecules with
induced dipole–dipole forces or London
forces. ‘Contact’ or the name of the
intermolecular forces was often omitted.
Finally, candidates were expected to link the
amount of branching to the strength of the
Less energy to break London forces/ intermolecular forces and the energy needed
intermolecular forces/intermolecular to change state. Lower ability candidates often
bonds/ ✓ let themselves down by being unable to
construct a well-reasoned response. There
was often a gulf between the clear responses
of able candidates and those of lower ability
candidates.
ALLOW Free radical substitution
b i Radical substitution ✓ 1 Examiner’s Comments
Most candidates identified this reaction as
radical substitution.
Examiner’s Comments
ii A B 2 Most candidates achieved at least one mark,
3✓ 2✓ particularly for isomer A. Successful
candidates often drew structures of the
isomers alongside the table to help with their
response.
iii 2
Structure of D
ALLOW correct structural OR displayed
Structure of a trichloro isomer of A, OR skeletal formula OR mixture of the above
e.g. (as long as unambiguous)
IGNORE molecular formula
✓
ALLOW any trichloro isomer of A
CHECK carefully
Equation ALLOW multiples,
e.g. 2C5H12 + 6Cl2 → 2C5H9Cl3 + 6HCl
C5H12 + 3Cl2 → C5H9Cl3 + 3HCl ✓
Molecular formulae required
Examiner’s Comments
NO ECF from incorrect structure of D Many candidates correctly drew the structure
© OCR 2022. You may photocopy this Page 10 of 13 Created in ExamBuilder
page.
of compound D but comparatively few were
able to construct a correct equation. For this
equation, candidates needed to apply their
knowledge and understanding of
monosubstitution of alkanes to substitution of
three H atoms by three Cl atoms. This task
proved to be one of the most difficult questions
on this paper. The exemplar shows an
excellent response. The candidate has drawn
a trisubstituted structure that fits the molar
mass of 175.5 g mol−1 and a correct equation
for its formation. Many attempts at this
equation showed H2 as the second product
rather than HCl.
Exemplar 6
Total 10
ALLOW 3
Examiner’s Comments
7 C 1
The responses showed a reasonably even
split across all options with relatively few
correct responses of C. A good route to
success here is to draw out the possibilities.
Total 1
Examiner’s Comments
Many candidates added H atoms to the
8 A 1 structure to aid their choice. Most candidates
selected the correct response of A, with a
sizeable number selecting B (by adding two H
atoms where the two rings join).
Total 1
© OCR 2022. You may photocopy this Page 11 of 13 Created in ExamBuilder
page.
NOTE: O and Cl electrons MUST be shown
differently from C electrons (e.g. expected
answer)
IGNORE inner shells
ALLOW diagram with missing C, O or Cl
symbols.
For C=O bond, ALLOW sequence × × • •
9 i 1 ALLOW non-bonding electrons unpaired
CARE: Check that lone pairs on Cl and O are
included
Cl (×2) has 6 non-bonded electrons
Examiner’s Comments
(3 LPs)
O has 4 non-bonded electrons (2
Most candidates attempted a dot-and-cross
LPs)
diagram of a COCl2 molecule, with ionic
representations being rare. Candidates should
take care to include any lone pairs in their
diagrams. Omission of the O and Cl lone pairs
was the most common error.
ALLOW bp for bonded pair
Shape
Trigonal planar ✓ ALLOW 3 bonded pairs (BOD)
OR 3 sigma bonds
Number of bonded regions OR 2 bonded pairs and 1 double
(C has) 3 electron (dense) regions bond
OR 4 bonded pairs including a
double bond
OR 3 bonding regions ✓
IGNORE bonded atoms
IGNORE just 3 bonds
ii 3 ALLOW alternative phrases/words for repel
e.g. ‘push apart’
IGNORE electrons repel (pairs needed)
Electron pair repulsion (Seen anywhere)
DO NOT ALLOW atoms repel
electron pairs/bonded pairs/bonded
Examiner’s Comments
regions repel
This question discriminated well. Most
OR
candidates recognised that a COCl2 molecule
electron pairs move as far apart as
has a trigonal planar shape. The best answers
possible
OR explained this shape in terms of the three
bonds repel ✓ electron regions around the central C atom
and their repulsion.
Total 4
© OCR 2022. You may photocopy this Page 12 of 13 Created in ExamBuilder
page.
© OCR 2022. You may photocopy this Page 13 of 13 Created in ExamBuilder
page.
You might also like
- Math Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeFrom EverandMath Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 6.1.1 Aromatic Compounds QP-2Document27 pages6.1.1 Aromatic Compounds QP-2jasmeet kahlonNo ratings yet
- Catalysts Exam QDocument5 pagesCatalysts Exam QMo RonoNo ratings yet
- Y13 EPP Full PDFDocument11 pagesY13 EPP Full PDFyolanda gaoliNo ratings yet
- 12chemHL T2T1Document16 pages12chemHL T2T1oscarbecNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibrium-Jeemain - GuruDocument9 pagesIonic Equilibrium-Jeemain - Gurushitaldr767No ratings yet
- Fogler Chapter 7 On PolymerizationDocument30 pagesFogler Chapter 7 On PolymerizationKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 122 Solutions and DilutionsDocument3 pagesChemistry 122 Solutions and DilutionsITIANo ratings yet
- Science Grade 10 HOTS Questions 1573019603Document5 pagesScience Grade 10 HOTS Questions 1573019603Anonymous cQoGoqNo ratings yet
- 5090 s10 QP 21Document16 pages5090 s10 QP 21DKFBNo ratings yet
- Oct 19 Question 21Document4 pagesOct 19 Question 21hypertextassassinsftNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Expressions and CalculatingDocument7 pagesEquilibrium Expressions and CalculatingAmal JaberNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document42 pagesChapter 14NayLinNo ratings yet
- Chap7,8,9 (Worksheet)Document24 pagesChap7,8,9 (Worksheet)devil's queenNo ratings yet
- Fields of Life 04Document47 pagesFields of Life 04Ian BeardsleyNo ratings yet
- MATLABAssignmentDocument5 pagesMATLABAssignmentvenkieeNo ratings yet
- CIM and Additional Maths Assessment SolutionsDocument8 pagesCIM and Additional Maths Assessment SolutionsAditya SARMA (9CWA)No ratings yet
- Hot Spots - The Carbon Atlas: EuropeDocument1 pageHot Spots - The Carbon Atlas: EuropeNikocaNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Reactions 3Document3 pagesOxidation Reactions 3rushikesh gaikarNo ratings yet
- 3.1-Atomic Structure 2C - Edexcel IGCSE 9-1 Chemistry QP 2 AnsDocument11 pages3.1-Atomic Structure 2C - Edexcel IGCSE 9-1 Chemistry QP 2 AnsJaved UddinNo ratings yet
- WK 2Document2 pagesWK 21 2No ratings yet
- 18 Acids and Esters NotesDocument13 pages18 Acids and Esters NotesSherazNo ratings yet
- Bonding EdexcelDocument19 pagesBonding EdexcelahmedNo ratings yet
- SL & HL Questions On Lipids: EstradiolDocument1 pageSL & HL Questions On Lipids: EstradiolOmar HijaziNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding QPDocument5 pagesCovalent Bonding QPHabiba MohamedNo ratings yet
- DF1 QuestionsDocument29 pagesDF1 Questionspawico8232No ratings yet
- AQA A Level Chem CH30 Practice Question AnswersDocument2 pagesAQA A Level Chem CH30 Practice Question AnswersMahebul MazidNo ratings yet
- Arenes PracticeDocument4 pagesArenes PracticeArda RahmainiNo ratings yet
- Heptane Combustion and ReactionsDocument46 pagesHeptane Combustion and Reactions梁瀚允No ratings yet
- Bonding, Polarity & Intermolecular Forces 2 QPDocument16 pagesBonding, Polarity & Intermolecular Forces 2 QPmNo ratings yet
- CLASS TEST 3 (Introducing Organic, Hydrocarbons) : Academic Session: 2018-2019Document4 pagesCLASS TEST 3 (Introducing Organic, Hydrocarbons) : Academic Session: 2018-2019GM Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- 9701 U4 Organic TQDocument17 pages9701 U4 Organic TQSumaira AliNo ratings yet
- Formulae, Equations, Amounts of Substance 1 QPDocument13 pagesFormulae, Equations, Amounts of Substance 1 QPtobyrathmellNo ratings yet
- Calcium looping models for CO2 capture from power plantsDocument52 pagesCalcium looping models for CO2 capture from power plantsmohsen ranjbarNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure 1 QPDocument10 pagesAtomic Structure 1 QPAsif AmdadNo ratings yet
- 28.2-Photosynthesis Photosynthesis Pigments-Qp Alevel-Edexcel-Biology UpdatedDocument14 pages28.2-Photosynthesis Photosynthesis Pigments-Qp Alevel-Edexcel-Biology UpdatedMZWAANo ratings yet
- Sat Language 3-20Document7 pagesSat Language 3-20api-438316167No ratings yet
- Official Sat Writing 9-10Document34 pagesOfficial Sat Writing 9-10Mustafa ElazazyNo ratings yet
- 2210 My9 - Dap Spring 2021Document10 pages2210 My9 - Dap Spring 2021api-644492588No ratings yet
- Chemistry: Pearson Edexcel International Advanced LevelDocument20 pagesChemistry: Pearson Edexcel International Advanced LevelRose RamisaNo ratings yet
- Group - 7 Practice Review QuestionsDocument11 pagesGroup - 7 Practice Review Questionsdosibo2378No ratings yet
- Vectors 1Document19 pagesVectors 1Fazlina MustafaNo ratings yet
- SCH Srm450v2 Schematics Amp (0029446-Xx Revh00)Document5 pagesSCH Srm450v2 Schematics Amp (0029446-Xx Revh00)John CasasNo ratings yet
- Additional Practice ExerciseDocument1 pageAdditional Practice ExerciseAlicia Jane PerasNo ratings yet
- Markscheme HL Paper2Document20 pagesMarkscheme HL Paper2dilemNo ratings yet
- Writing and Language Test: 35 Minutes, 44 QuestionsDocument16 pagesWriting and Language Test: 35 Minutes, 44 QuestionsVincent GiuntaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Monosaccharides, Disaccharides and PolysaccharidesDocument5 pagesCarbohydrates: Monosaccharides, Disaccharides and PolysaccharidesBetina De JesusNo ratings yet
- Benzene Is An Important Starting Material in The Production of Dyes, Detergents and Medicines. (A)Document9 pagesBenzene Is An Important Starting Material in The Production of Dyes, Detergents and Medicines. (A)Rayyan BariNo ratings yet
- 5 The Diagram Below Summarises Some of The Reactions in Aerobic RespirationDocument3 pages5 The Diagram Below Summarises Some of The Reactions in Aerobic RespirationEricka AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Amines 2 QPDocument9 pagesAmines 2 QPdanyNo ratings yet
- 1-June 2019 QP 21 PDFDocument2 pages1-June 2019 QP 21 PDFzuveriaNo ratings yet
- Reaction Rate EquationsDocument2 pagesReaction Rate EquationszuveriaNo ratings yet
- Microstructural Investigations in Cordierite-Mullite RefractoriesDocument16 pagesMicrostructural Investigations in Cordierite-Mullite RefractoriesuvsarathiNo ratings yet
- Biology Mock 4 Unit 1Document3 pagesBiology Mock 4 Unit 1crudecadaverNo ratings yet
- NAME-2012-2013 (L-2, T-1)Document13 pagesNAME-2012-2013 (L-2, T-1)partho RoyNo ratings yet
- Math Basic Econ LogDocument1 pageMath Basic Econ LogLiv FernandezNo ratings yet
- Potenliometrit TitrationsDocument4 pagesPotenliometrit TitrationsJuan Camilo Aguilar MayaNo ratings yet
- Writing and Language Test: 35minutes, 44questionsDocument18 pagesWriting and Language Test: 35minutes, 44questionsHaisam AwanNo ratings yet
- Assign - 6 - Chemical Formulae, Equations, Calculations 1 QPDocument2 pagesAssign - 6 - Chemical Formulae, Equations, Calculations 1 QPDiya JNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Online Zoom - Creative CommonsDocument1 pageComputer Science Online Zoom - Creative CommonsMahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Health and DiseaseDocument4 pagesLesson 1 - Health and DiseaseMahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument2 pagesLesson 3 - Cardiovascular DiseaseMahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - PathogensDocument2 pagesLesson 4 - PathogensMahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Online Zoom Lesson - E-Waste and EthicsDocument2 pagesComputer Science Online Zoom Lesson - E-Waste and EthicsMahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- ProjectilesDocument10 pagesProjectilesMahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- COAS P1 Ch18 ItDocument10 pagesCOAS P1 Ch18 ItMahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- COAS TR P1 18ws1Document2 pagesCOAS TR P1 18ws1Mahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Computer Misuse Act 1990 ExplainedDocument3 pagesComputer Misuse Act 1990 ExplainedMahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- AS Maths Mechanics Unit 9 TestDocument1 pageAS Maths Mechanics Unit 9 TestMahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Mahmud RAHMAN - 1.1 WorkbookDocument8 pagesMahmud RAHMAN - 1.1 WorkbookMahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry KS4 To KS5 Transition WorkDocument28 pagesChemistry KS4 To KS5 Transition WorkMahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Mahmud RAHMAN - 2.2 WorkbookDocument20 pagesMahmud RAHMAN - 2.2 WorkbookMahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Mahmud RAHMAN - 1.2 Workbook (Part 1)Document19 pagesMahmud RAHMAN - 1.2 Workbook (Part 1)Mahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Mahmud RAHMAN - 2.1 WorkbookDocument33 pagesMahmud RAHMAN - 2.1 WorkbookMahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Mahmud RAHMAN 4.4.2.1 Radioactive Decay and Nuclear RadiationDocument18 pagesMahmud RAHMAN 4.4.2.1 Radioactive Decay and Nuclear RadiationMahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Volcano Case Studies 5 & 6Document11 pagesVolcano Case Studies 5 & 6Mahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Mahmud RAHMAN - 1.2 Workbook (Part 2)Document30 pagesMahmud RAHMAN - 1.2 Workbook (Part 2)Mahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Mahmud RAHMAN - Edexcel - Biology - Health, Disease and The Development of Medicines - KnowIT - GCSE 2Document49 pagesMahmud RAHMAN - Edexcel - Biology - Health, Disease and The Development of Medicines - KnowIT - GCSE 2Mahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 QuestionsDocument20 pagesPaper 2 QuestionsMahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Mahmud RAHMAN - 2.4 WorkbookDocument19 pagesMahmud RAHMAN - 2.4 WorkbookMahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Math Revision WorksheetDocument8 pagesYear 10 Math Revision WorksheetMahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Python Task 1 Year 10Document4 pagesPython Task 1 Year 10Mahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- LMB Essay PlanDocument3 pagesLMB Essay PlanMahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Human impact threatening biosphere sustainabilityDocument6 pagesHuman impact threatening biosphere sustainabilityMahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Year 10 CS Exam Prep - Searching and Sorting AlgorithmsDocument14 pagesYear 10 CS Exam Prep - Searching and Sorting AlgorithmsMahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- SPEAKING-Booklet With Model AnswrsDocument26 pagesSPEAKING-Booklet With Model AnswrsMahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Revision Easter Worksheet SVDocument8 pagesYear 10 Revision Easter Worksheet SVMahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Computer Science November 2020Document21 pagesYear 10 Computer Science November 2020Mahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- CGLE Tier I 2022 Exam AnalysisDocument28 pagesCGLE Tier I 2022 Exam Analysisnakul yadavNo ratings yet
- Adhesion of Polymer Mechanism and Op Tim IzationDocument17 pagesAdhesion of Polymer Mechanism and Op Tim IzationAnh QuânNo ratings yet
- SL MC Test s2 Models of Bonding - Structure (Second Test)Document7 pagesSL MC Test s2 Models of Bonding - Structure (Second Test)Amira Selpa KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Bonding in Organic MoleculesDocument62 pagesBonding in Organic Moleculesprueba gratisNo ratings yet
- High boiling point and hydrogen bonding enable water propertiesDocument37 pagesHigh boiling point and hydrogen bonding enable water propertiesMike LarguezaNo ratings yet
- Activated Carbon: PRESENTED BY Raja WajahatDocument15 pagesActivated Carbon: PRESENTED BY Raja Wajahatnusty_fairyNo ratings yet
- B. SC Hons Chemistry PDFDocument167 pagesB. SC Hons Chemistry PDFSuraj PatraNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Philippine Christian UniversityDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Philippine Christian UniversityRemar Jhon PaineNo ratings yet
- AP 2018 Thắng1Document35 pagesAP 2018 Thắng1Tran thi thanh nhaNo ratings yet
- H2 Chem Notes 9729 PDFDocument78 pagesH2 Chem Notes 9729 PDFBobNo ratings yet
- Physicalscience q1 Mod6 Effectsofintermolecularforcesonpropertiesofsubstances v2Document35 pagesPhysicalscience q1 Mod6 Effectsofintermolecularforcesonpropertiesofsubstances v2Marivic Garvida0% (1)
- 1.solid StateDocument33 pages1.solid StateBHAVITH SD VNS 06No ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and Phase ChangesDocument29 pagesIntermolecular Forces and Phase ChangesnasyieNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Paper 1CR June 2014Document23 pagesMark Scheme Paper 1CR June 2014LayonNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Properties of Water Molecular Structure and Intermolecular ForcesDocument24 pagesModule 4 Properties of Water Molecular Structure and Intermolecular ForcesKirstine Pearl AlmuenaNo ratings yet
- IMF's of Attraction Solid, Liquid and GasesDocument18 pagesIMF's of Attraction Solid, Liquid and GasesMark John GuardamanoNo ratings yet
- Ace Microbiology! - The EASY Guid - Dr. Holden HemsworthDocument265 pagesAce Microbiology! - The EASY Guid - Dr. Holden Hemsworthmie storyNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Laboratory: Basra University College of Science and Technology Pharmacy DepartmentDocument12 pagesOrganic Chemistry Laboratory: Basra University College of Science and Technology Pharmacy DepartmentcrtgyhujikNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Intermolecular ForcesDocument6 pagesOrganic Chemistry Intermolecular Forcescesia freniereNo ratings yet
- Chemie Week 5: Van-der-Waals (English-Zusammenfassung)Document2 pagesChemie Week 5: Van-der-Waals (English-Zusammenfassung)Nicolai MerckerNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Attractions and The Properties of Liquids and SolidsDocument105 pagesIntermolecular Attractions and The Properties of Liquids and SolidsRokiaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry As Revision Questions F332Document23 pagesChemistry As Revision Questions F332LilliNo ratings yet
- G12 Chemistry Quiz on Intermolecular ForcesDocument59 pagesG12 Chemistry Quiz on Intermolecular ForcesSir. Crims0n80% (5)
- Chapter13 (Liquid and Solid)Document90 pagesChapter13 (Liquid and Solid)Cathy RavinaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Types of Bonding Toward Physical Properties of SubstanceDocument3 pagesEffect of Types of Bonding Toward Physical Properties of SubstanceeilyanaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Period 3 OxidesDocument21 pagesProperties of Period 3 OxidesJayden Sue100% (1)
- ChemistryDocument4 pagesChemistryManish SainiNo ratings yet
- Class P ChemDocument79 pagesClass P Chemprashantyadavpky07No ratings yet
- Chemistry SyllabusDocument83 pagesChemistry SyllabuskameshNo ratings yet
- Physical Science: Week 3: Intermolecular ForcesDocument16 pagesPhysical Science: Week 3: Intermolecular ForcesMelvin Ranera Abila100% (1)