Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DNA Structure
DNA Structure
Uploaded by
Shashikant VishwakarmaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DNA Structure
DNA Structure
Uploaded by
Shashikant VishwakarmaCopyright:
Available Formats
Study Materials BYJU'S Answer Scholarship BTC Buy a Course Success Stories Login
Biology Important Questions Biology MCQ's 25 Important Topics in Biology Biology Syllabus Biology Biology Article Important Diagrams
Biology > Biology Article > Dna Structure
Type your search
DNA: Structure, Function and Discovery
Nucleic acids are the organic materials present in all organisms in the form of DNA or
RNA. These nucleic acids are formed by the combination of nitrogenous bases, sugar
molecules and phosphate groups that are linked by different bonds in a series of
sequences. The DNA structure de>nes the basic genetic makeup of our body. In fact, it
de>nes the genetic makeup of nearly all life on earth.
Table of Contents
What is DNA?
Discovery
Diagram
DNA Structure
Chargaff’s Rule
DNA Replication
Function of DNA
Why DNA is called a Polynucleotide Molecule?
Read on to explore DNA meaning, structure, function, DNA discovery and diagram in
complete detail.
What is DNA?
“DNA is a group of molecules that is responsible for carrying
and transmitting the hereditary materials or the genetic
instructions from parents to offsprings.”
This is also true for viruses, as most of these entities have either RNA or DNA as their
genetic material. For instance, some viruses may have RNA as their genetic material, while
others have DNA as the genetic material. The Human Immunode>ciency Virus (HIV)
contains RNA, which is then converted into DNA after attaching itself to the host cell. CBSE Sample Papers
Apart from being responsible for the inheritance of genetic information in all living beings, CBSE Sample Papers Class 8
DNA also plays a crucial role in the production of proteins. Nuclear DNA is the DNA Science
contained within the nucleus of every cell in a eukaryotic organism. It codes for the
CBSE Sample Papers Class 9
majority of the organism’s genomes while the mitochondrial DNA and plastid DNA handles
Science
the rest.
CBSE Sample Papers Class 10
The DNA present in the mitochondria of the cell is termed mitochondrial DNA. It is
Science
inherited from the mother to the child. In humans, there are approximately 16,000 base
pairs of mitochondrial DNA. Similarly, plastids have their own DNA, and they play an CBSE Sample Papers Class 11
essential role in photosynthesis. Physics
Also Read: Difference between gene and DNA CBSE Sample Papers Class 11
Chemistry
Full-Form of DNA
CBSE Sample Papers Class 11
DNA is known as Deoxyribonucleic Acid. It is an organic compound that has a unique Biology
molecular structure. It is found in all prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells.
CBSE Sample Papers Class 12
Physics
DNA Types
CBSE Sample Papers Class 12
There are three different DNA types:
Chemistry
A-DNA: It is a right-handed double helix similar to the B-DNA form. Dehydrated DNA
CBSE Sample Papers Class 12
takes an A form that protects the DNA during extreme conditions such as
Biology
desiccation. Protein binding also removes the solvent from DNA, and the DNA takes
an A form.
B-DNA: This is the most common DNA conformation and is a right-handed helix.
The majority of DNA has a B type conformation under normal physiological
conditions.
Z-DNA: Z-DNA is a left-handed DNA where the double helix winds to the left in a zig- CBSE Previous Year Question
zag pattern. It was discovered by Andres Wang and Alexander Rich. It is found Papers
ahead of the start site of a gene and hence, is believed to play some role in gene CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
regulation. Class 10 Science
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
Who Discovered DNA? Class 12 Physics
DNA was >rst recognized and identi>ed by the Swiss biologist Johannes Friedrich
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
Miescher in 1869 during his research on white blood cells.
Class 12 Chemistry
The double helix structure of a DNA molecule was later discovered through the
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
experimental data by James Watson and Francis Crick. Finally, it was proved that DNA is
Class 12 Biology
responsible for storing genetic information in living organisms.
Also Read: Difference between deoxyribose and ribose
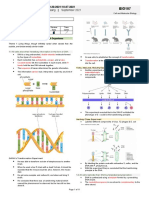
DNA Diagram
The following diagram explains the DNA structure representing the different parts of the ICSE Sample Papers
DNA. DNA comprises a sugar-phosphate backbone and the nucleotide bases (guanine, ICSE Sample Papers Class 8 Physics
cytosine, adenine and thymine).
ICSE Sample Papers Class 8
Chemistry
ICSE Sample Papers Class 8 Biology
ICSE Sample Papers Class 9 Physics
ICSE Sample Papers Class 9
Chemistry
ICSE Sample Papers Class 9 Biology
ICSE Sample Papers Class 10
Physics
ICSE Sample Papers Class 10
Chemistry
ICSE Sample Papers Class 10
Biology
DNA Diagram representing the DNA Structure ISC Sample Papers Class 11 Physics
ISC Sample Papers Class 11
Read more: Properties of DNA Chemistry
ISC Sample Papers Class 11 Biology
DNA Structure
ISC Sample Papers Class 12 Physics
The DNA structure can be thought of as a twisted ladder. This structure is
ISC Sample Papers Class 12
described as a double-helix, as illustrated in the >gure above. It is a nucleic
Chemistry
acid, and all nucleic acids are made up of nucleotides. The DNA molecule is
composed of units called nucleotides, and each nucleotide is composed of three different ISC Sample Papers Class 12 Biology
components such as sugar, phosphate groups and nitrogen bases.
The basic building blocks of DNA are nucleotides, which are composed of a sugar group, a
phosphate group, and a nitrogen base. The sugar and phosphate groups link the
nucleotides together to form each strand of DNA. Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Guanine (G)
and Cytosine (C) are four types of nitrogen bases. ICSE Previous Year Question
Papers
These 4 Nitrogenous bases pair together in the following way: A with T, and C with G.
These base pairs are essential for the DNA’s double helix structure, which resembles a ICSE Previous Year Question Papers
twisted ladder. Class 10 Physics
The order of the nitrogenous bases determines the genetic code or the DNA’s instructions. ICSE Previous Year Question Papers
Class 10 Chemistry
ICSE Previous Year Question Papers
Class 10 Maths
ISC Previous Year Question
Papers class 12
ISC Previous Year Question Papers
Class 12 Physics
Components of DNA Structure
ISC Previous Year Question Papers
Class 12 Chemistry
Among the three components of DNA structure, sugar is the one which forms the
backbone of the DNA molecule. It is also called deoxyribose. The nitrogenous bases of the ISC Previous Year Question Papers
opposite strands form hydrogen bonds, forming a ladder-like structure. Class 12 Biology
DNA Structure Backbone
The DNA molecule consists of 4 nitrogen bases, namely adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine
(C) and Guanine (G), which ultimately form the structure of a nucleotide. The A and G are
purines, and the C and T are pyrimidines.
The two strands of DNA run in opposite directions. These strands are held together by the Join BYJU'S Learning Program
hydrogen bond that is present between the two complementary bases. The strands are
Name
helically twisted, where each strand forms a right-handed coil, and ten nucleotides make
up a single turn.
The pitch of each helix is 3.4 nm. Hence, the distance between two consecutive base pairs Mobile Number
(i.e., hydrogen-bonded bases of the opposite strands) is 0.34 nm.
City
Grade/Exam
Email Address
Submit
The DNA coils up, forming chromosomes, and each chromosome has a single molecule of
DNA in it. Overall, human beings have around twenty-three pairs of chromosomes in the
nucleus of cells. DNA also plays an essential role in the process of cell division.
Also Read: DNA Packaging
Recommended Video:
2,358
Chargaff’s Rule
Erwin Chargaff, a biochemist, discovered that the number of nitrogenous bases in the
DNA was present in equal quantities. The amount of A is equal to T, whereas the amount of
C is equal to G.
A=T; C=G
In other words, the DNA of any cell from any organism should have a 1:1 ratio of purine and
pyrimidine bases.
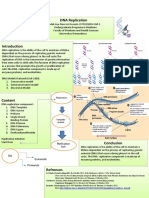
DNA Replication
DNA replication is an important process that occurs during cell division. It is also known
as semi-conservative replication, during which DNA makes a copy of itself.
DNA replication takes place in three stages:
Step 1: Initiation
The replication of DNA begins at a point known as the origin of replication. The two DNA
strands are separated by the DNA helicase. This forms the replication fork.
Step 2: Elongation
DNA polymerase III reads the nucleotides on the template strand and makes a new strand
by adding complementary nucleotides one after the other. For eg., if it reads an Adenine on
the template strand, it will add a Thymine on the complementary strand.
While adding nucleotides to the lagging strand, gaps are formed between the strands.
These gaps are known as Okazaki fragments. These gaps or nicks are sealed by ligase.
Step 3: Termination
The termination sequence present opposite to the origin of replication terminates the
replication process. The TUS protein (terminus utilization substance) binds to terminator
sequence and halts DNA polymerase movement. It induces termination.
Also Read: DNA Replication
DNA Function
DNA is the genetic material which carries all the hereditary information. Genes are the
small segments of DNA, consisting mostly of 250 – 2 million base pairs. A gene code for a
polypeptide molecule, where three nitrogenous bases sequence stands for one amino acid.
Polypeptide chains are further folded in secondary, tertiary and quaternary structures to
form different proteins. As every organism contains many genes in its DNA, different types
of proteins can be formed. Proteins are the main functional and structural molecules in
most organisms. Apart from storing genetic information, DNA is involved in:
Replication process: Transferring the genetic information from one cell to its
daughters and from one generation to the next and equal distribution of DNA during
the cell division
Mutations: The changes which occur in the DNA sequences
Transcription
Cellular Metabolism
DNA Fingerprinting
Gene Therapy
Also Read: r-factor
Why DNA is called a Polynucleotide Molecule?
The DNA is called a polynucleotide because the DNA molecule is composed of nucleotides
– deoxyadenylate (A) deoxyguanylate (G) deoxycytidylate (C) and deoxythymidylate (T),
which are combined to create long chains called a polynucleotide. As per the DNA
structure, the DNA consists of two chains of polynucleotides.
Also Read: Genetic Material
For more detailed information on DNA meaning, diagram, its types, DNA structure and
function, or any other related topics, explore at BYJU’S Biology.
Explore more
Difference between Replication and Transcription
DNA Cloning
DNA Fingerprinting
DNA As Genetic Material
DNA Structure and Polynucleotide
How is DNA inherited from each parent?
Do you get more DNA from your mother or father?
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the structure of DNA?
DNA is a double helical structure composed of nucleotides. The two helices are joined
together by hydrogen bonds. The DNA also bears a sugar-phosphate backbone.
What are the three different types of DNA?
The three different types of DNA include:
A-DNA
B-DNA
Z-DNA
How is Z-DNA different from other forms of DNA?
Z-DNA is a left-handed double helix. The helix winds to the left in a zig-zag manner. On the
contrary, A and B-DNA are right-handed DNA.
What are the functions of DNA?
The functions of DNA include:
Replication
Gene expression
Mutation
Transcription
Translation
What type of DNA is found in humans?
B-DNA is found in humans. It is a right-handed double-helical structure.
Test your Knowledge on DNA Structure!
Put your understanding of this
concept to test by answering a
few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to
begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the
“Finish” button
Check your score and answers at the end of the
quiz
Start Quiz
BIOLOGY Related Links
Forest Conservation Exocrine Glands
Bacteria Cell Diagram What Is Endangered Species
Germination Of Pollen On Stigma Fragmentation De>nition
Ellipsoid Joint What Is A Biome
Seed Dispersal By Water Human Anatomy And Physiology
11 Comments
Sagana SEPTEMBER 17, 2019 AT 1:45 AM
This was a very precise and wonderful notes in an understandable way of the
wanted part which helped a lot Thanks!
REPLY
Segun madelewi JULY 27, 2020 AT 1:52 AM
very good.
REPLY
Deep Kanwar SEPTEMBER 20, 2019 AT 8:31 PM
very informative. very helpful.
REPLY
Sheikh Shahidul Islam MARCH 20, 2020 AT 3:20 AM
Very summarized form have been highlighted. I am beni>tted.
REPLY
Oliver Joe JULY 30, 2020 AT 8:25 AM
I like the teaching on this website
REPLY
DEBORPITA BANERJEE AUGUST 18, 2020 AT 12:18 PM
Very good and informative answer. Thank you
REPLY
Williams Quainoo OCTOBER 11, 2020 AT 11:55 PM
infact am greatfull with this program and the site and it is helpful learning program
REPLY
FAHAD NOVEMBER 8, 2020 AT 3:57 PM
well explained
REPLY
Rinkal B Nith NOVEMBER 22, 2020 AT 8:32 PM
Information given here is very accurate precise and easily understandable helpful to
all those who are new to science too.
REPLY
AUGUSTA JANUARY 29, 2021 AT 9:02 PM
NICE CONTENT KEEP IT UP
REPLY
Peddugalla ramesh JUNE 24, 2022 AT 7:47 PM
Good
REPLY
Leave a Comment
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required >elds are marked *
*
Mobile Number Send OTP
Please don't use any HTML or external links in the comment box.
Post Comment
COURSES EXAMS EXAM PREPARATION COMPANY FREE TEXTBOOK STATE BOARDS
SOLUTIONS
CBSE CAT Exam Free CAT Prep About Us NCERT Solutions Maharashtra
ICSE GATE Exam Free IAS Prep Contact Us NCERT Exemplar Gujarat
CAT IAS Exam Maths Contact our Financial NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Tamil Nadu
Partners
IAS UPSC Exam Physics NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Karnataka
Investors
JEE UPSC Syllabus Chemistry NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Kerala
Careers
NEET UPSC 2023 Biology NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Andhra Pradesh
BYJU'S in Media
Commerce UPSC 2022 JEE 2023 NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Telangana
Social Initiative -
JEE Main Bank Exam JEE Main 2022 Question NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Uttar Pradesh
Education for All
Papers with Answers
NCERT Government Exams NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Bihar
BYJU'S APP
JEE Advanced 2022 English
JEE Advanced Education News Rajasthan
Question Paper with FAQ
NCERT Solutions for Class 12
UPSC Prelims 2022 Answers Madhya Pradesh
Students Stories - The English
Question Paper CLASSES
NEET 2022 Answer Key Learning Tree West Bengal
NCERT Solutions for Class 12
UPSC Prelims 2022
Kids Learning Support
Answer Key RESOURCES RD Sharma Solutions
Class 1st - 3rd Faces of BYJU'S – Life
IAS Coaching RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions
at BYJU'S
Class 4th - 5th Worksheets
CBSE Sample Papers RS Aggarwal Solutions
Blog
Class 6th - 10th BYJU'S Answer
CBSE Question Papers ICSE Selina Solutions
BYJU'S Give
Class 11th - 12th DSSL
FOLLOW US
Home Tuition
All Products
Calculators
Formulas
US US Math Classes Math Worksheets Math Calculators Math Formulas Math Topics
1st Grade Math 1st Grade Math Volume of Cone Volume of Sphere Volume of a Cone
Worksheets Calculator Formulas
2nd Grade Math Volume of a Sphere
2nd Grade Math Volume of Sphere Probability Formulas
3rd Grade Math Volume of a Cylinder
Worksheets Calculator
Area of Rectangle
4th Grade Math Square Root
3rd Grade Math Volume of Cylinder Formulas
5th Grade Math Worksheets Calculator Pythagorean Theorem
Volume of Cylinder
6th Grade Math 4th Grade Math Traingle Area Calculator Formulas Area of a Triangle
Worksheets
7th Grade Math Area of a Circle Volume Formulas Quadrilateral
5th Grade Math Calculator
8th Grade Math Pythagorean Theorem Scienti>c Notation
Worksheets
Percent Calculator Formulas
6th Grade Math
Least Common Multiple Pro>t and Loss
Worksheets
Calculator Formulas
7th Grade Math
Slope Intercept Form Slope Formulas
Worksheets
Calculator
8th Grade Math
Hi there! Got any questions?
Worksheets I can help you...
Canada UK UK UAE UAE Mexico Mexico Australia Brazil Brazil Global
FREE
Signup
Disclaimer Privacy Policy Terms of Services Sitemap © 2022, BYJU'S. All rights reserved.
:
You might also like
- Evolution and The Foundations of Biology: Urry - Cain - Wasserman - Minorsky - Jackson - ReeceDocument102 pagesEvolution and The Foundations of Biology: Urry - Cain - Wasserman - Minorsky - Jackson - ReeceGMEET MAG INGAYNo ratings yet
- Osmosis and Diffusion WorksheetDocument7 pagesOsmosis and Diffusion WorksheetAbir Omar25% (4)
- Molecular BiologyDocument113 pagesMolecular Biologytummalapalli venkateswara rao80% (10)
- The DNA Detective: Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Genetic CodeFrom EverandThe DNA Detective: Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Genetic CodeNo ratings yet
- 2012 ASTRO Radiation and Cancer Biology Practice Examination and Study Guide PDFDocument193 pages2012 ASTRO Radiation and Cancer Biology Practice Examination and Study Guide PDFian3yeung-2No ratings yet
- List of AbbreviationsDocument3 pagesList of Abbreviationsjuwita latiefahNo ratings yet
- Mutation & Its TypesDocument52 pagesMutation & Its TypesSunita Sangwan100% (1)
- Dna Replication & TranscriptionDocument4 pagesDna Replication & TranscriptionGarren Jude AquinoNo ratings yet
- Protein-Synthesis-Worksheet 2018Document5 pagesProtein-Synthesis-Worksheet 2018api-242868690100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Junior HighDocument7 pagesLesson Plan Junior HighMark Leo Saldua Gelizon100% (1)
- Read and Donnai 3rd EdDocument37 pagesRead and Donnai 3rd EdJessica BiwangNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On ConceptsDocument9 pagesLesson Plan On ConceptsBryanJAbulocNo ratings yet
- Dna Day 1Document3 pagesDna Day 1MaricarGabitanNo ratings yet
- Recombinant VaccinesDocument22 pagesRecombinant VaccinesjugesmangangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10. Photosynthesis AnswersDocument3 pagesChapter 10. Photosynthesis Answerskarlitarmz100% (2)
- DNA RNA COT DLL New NormalDocument6 pagesDNA RNA COT DLL New NormalConnie Joy P. Calawag100% (2)
- Enzymes Used in RDT Corrected Version EditedDocument43 pagesEnzymes Used in RDT Corrected Version EditedYuppie RajNo ratings yet
- PROTEIN SynthesisDocument37 pagesPROTEIN SynthesisChirag KothariNo ratings yet
- C11 MOLECULAR STRUCTURE OF DNA AND RNA Concepts of Genetics 12ed (Brooker)Document21 pagesC11 MOLECULAR STRUCTURE OF DNA AND RNA Concepts of Genetics 12ed (Brooker)Catalina CristinaNo ratings yet
- CV Edwin Cuppen Jan 2014 WebDocument10 pagesCV Edwin Cuppen Jan 2014 Webrasyid93No ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 10: Panpacific University Urdaneta City, Pangasinan School of Basic EducationDocument5 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 10: Panpacific University Urdaneta City, Pangasinan School of Basic EducationGomez Agustin LeslieNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Notes - 34 DNA ReplicationDocument2 pagesIB Biology Notes - 34 DNA ReplicationJohn Philip D. NapalNo ratings yet
- Day 3Document8 pagesDay 3Kinberly AnnNo ratings yet
- Difference Between DNA and Genes Definition Structure Features ComparisonDocument9 pagesDifference Between DNA and Genes Definition Structure Features Comparisonepokemon942No ratings yet
- DNA Extraction From StrawberryBananaKiwi LABORATOYDocument6 pagesDNA Extraction From StrawberryBananaKiwi LABORATOYCHALSEA DYANN JOIE GALZOTENo ratings yet
- L3+4 - DNA Replication and Genetic Code StudentDocument31 pagesL3+4 - DNA Replication and Genetic Code StudentHaris KhokharNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Notes - 33 DNA StructureDocument2 pagesIB Biology Notes - 33 DNA StructureJohn Philip D. NapalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document39 pagesChapter 9Anupa GhoseNo ratings yet
- Bio107 L01 9302021-10072021Document11 pagesBio107 L01 9302021-10072021Loyd Joredell CuritNo ratings yet
- Mol Bio-DNA-bookbasedDocument8 pagesMol Bio-DNA-bookbasedElijah Mae MundocNo ratings yet
- Ni Kadek Ayu Dewi Ari SusantiDocument1 pageNi Kadek Ayu Dewi Ari SusantiDek AyuNo ratings yet
- Q3 - WEEK 1 - LAS-1-Process-involved-in-Genetic-EngineeringDocument2 pagesQ3 - WEEK 1 - LAS-1-Process-involved-in-Genetic-EngineeringBernard D. Fajardo Jr.No ratings yet
- The Dna: Learning Objectives (L.O.)Document13 pagesThe Dna: Learning Objectives (L.O.)masa bedaNo ratings yet
- With The Used of Different Materials and Multimedia Presentation, The Students Should Be Able ToDocument7 pagesWith The Used of Different Materials and Multimedia Presentation, The Students Should Be Able ToAllenNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 3rd QuarterDocument6 pagesGen Bio 3rd QuarterzafmustaphaNo ratings yet
- Dna Introduction 8753Document11 pagesDna Introduction 8753shilpa SNo ratings yet
- DNA Synthesis and SequenceDocument6 pagesDNA Synthesis and SequenceInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- PDF Reference3-Lesson11-CentraldogmaofmolecularbiologyDocument10 pagesPDF Reference3-Lesson11-Centraldogmaofmolecularbiologyjg teNo ratings yet
- Biofilm PDFDocument9 pagesBiofilm PDFAlvan YogiNo ratings yet
- Alberts Molecbiolcell7-Split 4 - CompressedDocument69 pagesAlberts Molecbiolcell7-Split 4 - CompressedBryan JacomeNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of DNA Presentation in Colorful Retro Illustrative StyleDocument20 pagesStructure and Function of DNA Presentation in Colorful Retro Illustrative StylewriterseinnaaaoNo ratings yet
- Understanding Biochemistry: Structure and Function of Nucleic AcidsDocument24 pagesUnderstanding Biochemistry: Structure and Function of Nucleic AcidsluluNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet Science 9 Quarter 1 Week 3Document11 pagesLearning Activity Sheet Science 9 Quarter 1 Week 3Mabell Mingoy100% (1)
- AP Q Chapter 3Document68 pagesAP Q Chapter 3Mahra AlketbiNo ratings yet
- DNA WPS OfficeDocument7 pagesDNA WPS OfficejakevcabauatanNo ratings yet
- James Watson-: B M C LDocument34 pagesJames Watson-: B M C L정재윤No ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 (4TH Quarter) - HeredityDocument7 pagesSCIENCE 10 (4TH Quarter) - HeredityJyña Khura TanoNo ratings yet
- Overview - DNA Cloning (Article) - Khan AcademyDocument14 pagesOverview - DNA Cloning (Article) - Khan AcademyMaryem SafdarNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document10 pagesPresentation 1sharanvarmavegirajuNo ratings yet
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Fact Sheet - National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI)Document2 pagesDeoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Fact Sheet - National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI)Amit KaushikNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication in Prokayotes and EukaryDocument55 pagesDNA Replication in Prokayotes and EukarySuraj DubeyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Evolution and DNA ReplicationDocument2 pagesLecture 1 - Evolution and DNA ReplicationStacy Ann VergaraNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 4th QTDocument7 pagesGen Bio 4th QTZuri MaeNo ratings yet
- SAS For Biochemistry BIO 024 Module 6 1Document33 pagesSAS For Biochemistry BIO 024 Module 6 1vovoka449No ratings yet
- Grade-10-LAS-Week-4A-3rd - QuarterDocument5 pagesGrade-10-LAS-Week-4A-3rd - QuarterYaRNo ratings yet
- Zugibe Istc 667 Final Instructional Design ProjectDocument14 pagesZugibe Istc 667 Final Instructional Design Projectapi-705616526No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Biomolecules-Nucleic AcidsDocument10 pagesLesson Plan Biomolecules-Nucleic AcidsLeo Jude LopezNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication - BioDocument17 pagesDna Replication - Biorautshreyash22No ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 (1) Do Cell BiologyDocument23 pagesChapter - 5 (1) Do Cell BiologykikijitsuNo ratings yet
- L2 & 3 The NucleusDocument54 pagesL2 & 3 The NucleusAmarachi MaduabuchiNo ratings yet
- Dna Extraction SimulationDocument1 pageDna Extraction SimulationPamela Noel MartinezNo ratings yet
- Biological Data Paper 1Document6 pagesBiological Data Paper 1Medha PatelNo ratings yet
- Lebt 101Document8 pagesLebt 101remixthisworldNo ratings yet
- Week 1 DNADocument28 pagesWeek 1 DNAHonleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet
- Architecture of The Escherichia Coli NucleoidDocument35 pagesArchitecture of The Escherichia Coli NucleoidFrancisca MoralesNo ratings yet
- MLS 007 SAS Session 2 CytogeneticsDocument9 pagesMLS 007 SAS Session 2 CytogeneticsReizel GaasNo ratings yet
- DNA, Genes and ChromosomesDocument7 pagesDNA, Genes and ChromosomesblobfacewastakenNo ratings yet
- Blackline Maste - DNA - The Master Molecule of Life PDFDocument6 pagesBlackline Maste - DNA - The Master Molecule of Life PDFghacass66No ratings yet
- Nucliec AcidDocument5 pagesNucliec AcidJoyce Fraulein T. LejosNo ratings yet
- Biok - 7.1 - DNA - Structure - and Replication - AHLDocument37 pagesBiok - 7.1 - DNA - Structure - and Replication - AHLZoya PadaniyaNo ratings yet
- Python Programming - 3rd Edition - PDF - Powered by BoxDocument1 pagePython Programming - 3rd Edition - PDF - Powered by BoxShashikant VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- The Discovery of DNA - YourGenomeDocument13 pagesThe Discovery of DNA - YourGenomeShashikant VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- MAths RoadmapDocument12 pagesMAths RoadmapShashikant VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Class - 1 - Evs - Clothes-Worksheet 2Document2 pagesClass - 1 - Evs - Clothes-Worksheet 2Shashikant VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Cell Biology Practice 1: (72 Marks)Document17 pagesUnit 1 Cell Biology Practice 1: (72 Marks)Rita LimNo ratings yet
- Protein StructureDocument16 pagesProtein StructureAakash HaiderNo ratings yet
- Protein BiokimiaDocument44 pagesProtein BiokimiaAdnindya JeehanNo ratings yet
- Biology RespirationDocument20 pagesBiology Respirationhafizah_90100% (2)
- Internet-Accessible DNA Sequence Database For Identifying Fusaria From Human and Animal InfectionsDocument11 pagesInternet-Accessible DNA Sequence Database For Identifying Fusaria From Human and Animal InfectionsJose Fernando SNNo ratings yet
- Song 1996Document8 pagesSong 1996Iuliana SoldanescuNo ratings yet
- MICF Ana Raquel MateusDocument48 pagesMICF Ana Raquel MateusNonô Ribeiro da CunhaNo ratings yet
- CHT312 - Ktu QbankDocument7 pagesCHT312 - Ktu QbankJeevandersh SNo ratings yet
- Leutwiler 1984 MGG The DNA of Arabidopsis ThalianaDocument9 pagesLeutwiler 1984 MGG The DNA of Arabidopsis ThalianaAJMRNo ratings yet
- MLS 114 Lecture #3Document15 pagesMLS 114 Lecture #3NjeodoNo ratings yet
- CV David C Eustice 1-2010Document6 pagesCV David C Eustice 1-2010Teresa MortonNo ratings yet
- DNA EkstrakromosomalDocument33 pagesDNA EkstrakromosomalSoraya Aya100% (1)
- CamBeads Si Usage InstructionsDocument5 pagesCamBeads Si Usage Instructionsrohit asilNo ratings yet
- CAPE Biology Unit 1 - 13-Cell Cycle and Mitosis - 2024-FinalDocument161 pagesCAPE Biology Unit 1 - 13-Cell Cycle and Mitosis - 2024-FinalKEMEISHA MILLERNo ratings yet
- The Key Difference Between Essential and NonDocument2 pagesThe Key Difference Between Essential and NonRafael CurtesNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Molecules To Metabolism-STUDENTDocument54 pages2.1 Molecules To Metabolism-STUDENTAngel Alexandra SiregarNo ratings yet
- Membran SelDocument62 pagesMembran SelLena EnjelinaNo ratings yet
- 5 - Stories of Salicylic Acid - A Plant Defense Hormone - 2020Document17 pages5 - Stories of Salicylic Acid - A Plant Defense Hormone - 2020Rafael Rocha Ferreira RochaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid STRUCTUREDocument5 pagesNucleic Acid STRUCTUREKalel SandovalNo ratings yet
- Elastin TopicDocument29 pagesElastin TopicAaveeza KhanumNo ratings yet