Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chem Review
Uploaded by
ichika lymCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chem Review
Uploaded by
ichika lymCopyright:
Available Formats
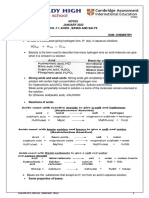
REVIEW GUIDE:
Related topics:
1. Naming and writing chemical formula
2. Writing chemical equations.
3. Balancing chemical equations.
4. Ionic bonding
5. Ionic equations
Redox
1. What is redox?
a. Process in which both oxidation and reduction takes place.
2. What is an oxidation reaction? Give examples of oxidation.
a. Gain of oxygen, loss of electrons, increase in oxidation state
3. What is the reduction reaction? Give examples of reduction.
a. Reverse process of an oxidation reaction—loss of oxygen, gain of electrons, decrease in
oxidation state
4. What is the oxidation state?
a. A number assigned to an element in a chemical combination which represents the
number of electrons lost (or gained, if the number is negative), by an atom of that
element in the compound.
5. Describe the following:
(a) Oxidizing agent, give examples
(i) A substance which oxidises another substance during a redox reaction.
(b) Reducing agent, give examples
(i) A substance which reduces another substance during a redox reaction.
Acids, Bases and Salts
6. Define acid?
a. A substance which produces hydrogen ions; H+ when dissolved in water; proton donor to
base → acceptor; water.
7. What are some of the chemical characteristics of acids? Give examples for each.
a. Metal + acid → salt + hydrogen
b. Carbonate + acid → salt + water + carbon dioxide
c. Hydroxide; oxide + acid → salt + water
8. What are some of the chemical characteristics of bases?
a. Insoluble in water
9. Why must acids be in aqueous solution OR must dissolved in water?
a. Acids only show the properties of acid when they’re dissolved in water; dissociating.
10. What are some chemical characteristics of Base?
a. Produce OH-, neutralize acids.
11. What is alkali?
a. A base that’s soluble in water; most bases aren’t alkali.
i. React with a solution of metal salt to give its metal hydroxide.
ii. Test for the presence of cations.
iii. React with acids to form salt & water only.
iv. Produce hydroxide ions when dissolved in ions.
12. What is a neutralization reaction? What indication that the reaction is complete?
a. Reaction of acids with alkalis and bases; equal number of ions.
i. Hydrogen ions from the acid and hydroxide ions from the alkali react to form
water.
1. H+ + OH- → H2O
2. Salt & water produced
13. What are oxides?
a. Compound of oxygen & another element; made by heating the element in air or oxygen.
14. What are the different types of oxides? Give examples of each.
a. Acidic oxides; non-metal → reacts with bases
i. CO2, SO2, NO2
b. Basic oxides; metal → reacts with acids
i. NaO, MgO, CuO
c. Amphoteric oxides; metal → reacts with both acids & bases
i. PbO, ZnO, Al2O3
d. Neutral oxides; non-metal → do not react
i. CO, NO, H2O
15. What are salts? Give examples of salts.
a. A compound formed when a metallic ion or an ammonium ion; NH4+ replaces one or
more hydrogen ions of an acid.
16. What are the methods to use to prepare the following salts?
(a) Soluble salts
(i) Reacting an acid with an insoluble metal, carbonate or base to make soluble salts.
(ii) Titration
(b) Insoluble salts
(i) Precipitation
17. How to test for gases?
a. Ammonia; using damp litmus paper; pungent smell
b. Carbon dioxide; limewater
c. Chlorine; using damp litmus paper
d. Hydrogen; lighted splint
e. Oxygen; glowing splint
You might also like
- The 7th Meetings Material English For ChemistryDocument6 pagesThe 7th Meetings Material English For ChemistrySalsabila PutriNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and SaltsDocument6 pagesAcids Bases and SaltsHanaa AbouziedNo ratings yet
- ACIDS and BASES Notes & WorksheetDocument9 pagesACIDS and BASES Notes & WorksheetAdeenaNo ratings yet
- DC Review For Unit 3Document5 pagesDC Review For Unit 3HEY ERLNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Concepts ReviewedDocument4 pagesAcid-Base Concepts ReviewedAlif FaturrahmanNo ratings yet
- Chem - Acids and Bases and Ionic EquationsDocument23 pagesChem - Acids and Bases and Ionic EquationsYasser AliNo ratings yet
- Std10 Science EM 3 PDFDocument90 pagesStd10 Science EM 3 PDFVivek AnandanNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Solubility Rules Equations SheetDocument8 pagesAP Chemistry Solubility Rules Equations SheetssNo ratings yet
- NOTES ON Ch.2 - Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument6 pagesNOTES ON Ch.2 - Acids, Bases and SaltsMarshal XavierNo ratings yet
- NOTES ON Ch.2 - Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument6 pagesNOTES ON Ch.2 - Acids, Bases and SaltsshalomNo ratings yet
- OLvlChem Chap11 UploadDocument5 pagesOLvlChem Chap11 UploaddoullahsaqibNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument98 pagesAcids and BasesLaziNo ratings yet
- Acid Bases and Salts 2022-23Document8 pagesAcid Bases and Salts 2022-23Yasha RizviNo ratings yet
- Science Myp3 Unit 3Document7 pagesScience Myp3 Unit 3isacreudaNo ratings yet
- G10 Revised Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument81 pagesG10 Revised Acids, Bases and Saltsandrew.mooreNo ratings yet
- Learn About Acids, Bases and the pH ScaleDocument4 pagesLearn About Acids, Bases and the pH ScaleNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Acids, Bases and Non Aqueous SolventsDocument29 pagesUnit 1. Acids, Bases and Non Aqueous SolventsPrasad GutteNo ratings yet
- Class Vii CH 5 Answer KeyDocument3 pagesClass Vii CH 5 Answer Keyminakshi.pandey8No ratings yet
- Acids, Alkalis and Salts: Acids Are Substances That Form Hydrogen Ions, HDocument1 pageAcids, Alkalis and Salts: Acids Are Substances That Form Hydrogen Ions, Hsagayaamitha7388No ratings yet
- Learn About Acids and Their Key PropertiesDocument9 pagesLearn About Acids and Their Key PropertiesBirds HomeNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases..Document5 pagesAcids and Bases..rachelNo ratings yet
- Acid and Bases 2Document5 pagesAcid and Bases 2liyasariNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 2Document70 pagesChemistry Unit 2Esayas DeguNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Acids, Bases and Salts GuideDocument56 pagesChapter 10: Acids, Bases and Salts Guidejahiem wilsonNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument4 pagesAcids and BasesOmark MelvilleNo ratings yet
- Notes Acids and BasesDocument10 pagesNotes Acids and BasesRabia Ashraf - 75828/TCHR/BSSRNo ratings yet
- X - SM - Sci - Acid Bases SaltsDocument14 pagesX - SM - Sci - Acid Bases SaltsKabir AroraNo ratings yet
- Class 10 - Chemistry - Acids, Bases and Salts SolutionsDocument37 pagesClass 10 - Chemistry - Acids, Bases and Salts Solutionscharusheela charusheelaNo ratings yet
- Nota Chapter 6 Acid, Base and SaltDocument30 pagesNota Chapter 6 Acid, Base and SaltNur AfiqahNo ratings yet
- Acids and bases review quizDocument2 pagesAcids and bases review quizAnna DixonNo ratings yet
- Zaim NotesDocument5 pagesZaim NotesZafirah SuffianNo ratings yet
- Acid Base and SaltDocument15 pagesAcid Base and SaltMr. Sujan LamsalNo ratings yet
- 9.1 Acid and BasesDocument32 pages9.1 Acid and BasesUmida ZaylobiddinovaNo ratings yet
- Chem Post Lab DiscussionDocument20 pagesChem Post Lab DiscussionJules Tyrell Jobs FerolinNo ratings yet
- CH-11 Acids, Bases and Salts NotesDocument4 pagesCH-11 Acids, Bases and Salts NotesAnish KanthetiNo ratings yet
- Oxides and Its TypesDocument21 pagesOxides and Its TypesnamrataNo ratings yet
- Chemistr Y Notes: - Solencia HamiltonDocument56 pagesChemistr Y Notes: - Solencia HamiltonManushka ThomasNo ratings yet
- C10 Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument55 pagesC10 Acids, Bases and SaltsKris DookharanNo ratings yet
- AC RX of OxidesDocument4 pagesAC RX of OxidesNancy MohamedNo ratings yet
- Acid Bases and SaltsDocument26 pagesAcid Bases and SaltsTracy ChangNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes: Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument5 pagesChemistry Notes: Acids, Bases and Saltsashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- SHC IxDocument3 pagesSHC IxVishnuanand ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Acids, Alkalis & PHDocument31 pagesAcids, Alkalis & PHEdward ShawNo ratings yet
- Chem Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument27 pagesChem Acids, Bases and SaltsJun ZheNo ratings yet
- Metals & Non Metals Note Book Work 1Document2 pagesMetals & Non Metals Note Book Work 1Eeshan SharmaNo ratings yet
- X Chemistry Notes CH # 2Document7 pagesX Chemistry Notes CH # 2Rehan RafiqNo ratings yet
- Chapter Notes Acids, Bases & SaltsDocument6 pagesChapter Notes Acids, Bases & Saltsmd gayasuddinNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument7 pagesAcids and BasesM.zuhair asifNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases, Salts-IG ChemistryDocument16 pagesAcids, Bases, Salts-IG ChemistryRashi GhadiyaNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and Salts: Key Properties and ReactionsDocument5 pagesAcids, Bases and Salts: Key Properties and ReactionsIsa ShahidNo ratings yet
- All Reactions - PadhleDocument18 pagesAll Reactions - Padhlerakshitham603No ratings yet
- Chemistry ClassX AssignmentDocument6 pagesChemistry ClassX AssignmentBharatiyaNaariNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Chemistry Week 12 Lesson 1Document4 pagesGrade 10 Chemistry Week 12 Lesson 1nesiaroberts903No ratings yet
- NOTES - Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument31 pagesNOTES - Acids, Bases and SaltsKartik ChauhanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science HOTs Question BankDocument63 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science HOTs Question BankSobana Itharaji75% (4)
- Acids and Bases Chemistry GuideDocument2 pagesAcids and Bases Chemistry GuideSheri-Ann AshmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Acid and BasesDocument56 pagesChapter 7 Acid and BasesThanabalan Munuswamy100% (1)
- Acid, Bases and Salts (Prashant Kirad) - 1Document15 pagesAcid, Bases and Salts (Prashant Kirad) - 1Ashish Sharma100% (2)
- Understanding Acids and BasesDocument11 pagesUnderstanding Acids and BasesAbed AymanNo ratings yet
- Sanitary Layout Plan: Third FloorDocument1 pageSanitary Layout Plan: Third FloorFrancis KoNo ratings yet
- Open Fracture Classification and TreatmentDocument70 pagesOpen Fracture Classification and TreatmentKelly Khesya100% (1)
- Solutions of Mini Case Bruce HoniballDocument5 pagesSolutions of Mini Case Bruce HoniballShivshankar Yadav100% (1)
- Schutz - Subnotes PDFDocument47 pagesSchutz - Subnotes PDFJarryd RastiNo ratings yet
- The Human BodyDocument17 pagesThe Human BodyRuthie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Soal UAS Bahasa Inggris Kelas 2 SD Semester 1 (Ganjil) : A. Choose The Correct Answer by Crossing (X) A, B or C!Document7 pagesSoal UAS Bahasa Inggris Kelas 2 SD Semester 1 (Ganjil) : A. Choose The Correct Answer by Crossing (X) A, B or C!Hamizan ShopNo ratings yet
- Store Visit ChecklistDocument5 pagesStore Visit ChecklisthayeslnlNo ratings yet
- Oukfxu DH Lwpuk Ladyu@Izs'K.K GSRQ Izns"K LRJ Ij MRRJNK H Ysoy 1) 2, Oa 3 LRJ Ds VF/KDKFJ Ksa Ds Leidz LWDocument12 pagesOukfxu DH Lwpuk Ladyu@Izs'K.K GSRQ Izns"K LRJ Ij MRRJNK H Ysoy 1) 2, Oa 3 LRJ Ds VF/KDKFJ Ksa Ds Leidz LWNishant KumarNo ratings yet
- Des 415 Research 01Document29 pagesDes 415 Research 01Just scribble me For funNo ratings yet
- Mp1 Type 1 ManualDocument69 pagesMp1 Type 1 ManualJerryNo ratings yet
- WB City GateDocument7 pagesWB City GateDiegoNo ratings yet
- CRRT (RVS) One Day TrainingDocument46 pagesCRRT (RVS) One Day TrainingwantoNo ratings yet
- Attachment No 2 PDFDocument10 pagesAttachment No 2 PDFTusharRoyNo ratings yet
- Usg Iom PDFDocument56 pagesUsg Iom PDFAnonymous 7xHNgoKE6eNo ratings yet
- Ceramic Inlays A Case Presentation and LessonsDocument11 pagesCeramic Inlays A Case Presentation and LessonsStef David100% (1)
- Physical Education Week 1 ActivitiesDocument4 pagesPhysical Education Week 1 ActivitiesTummys TummieNo ratings yet
- Abstract of SURYA NAMASKARDocument23 pagesAbstract of SURYA NAMASKARSarita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ames Perception ExperimentsDocument108 pagesAmes Perception ExperimentsMichael RoseNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design Coefficients and Factors TableDocument3 pagesSeismic Design Coefficients and Factors TableJonathan ColeNo ratings yet
- Presidential Decree No. 1616 establishes Intramuros AdministrationDocument22 pagesPresidential Decree No. 1616 establishes Intramuros AdministrationRemiel Joseph Garniel BataoNo ratings yet
- 4.5.1.1 Inside and Outside Control Instructions - IG PDFDocument4 pages4.5.1.1 Inside and Outside Control Instructions - IG PDFMaksim Korsakov100% (4)
- Evaluation of Sensors: For Mine Fire Detection Using An Atmospheric Monitoring SystemDocument9 pagesEvaluation of Sensors: For Mine Fire Detection Using An Atmospheric Monitoring SystemMario GaitanNo ratings yet
- The Emerald Tablets of Thoth Toth The Atlantean - Table 05Document5 pagesThe Emerald Tablets of Thoth Toth The Atlantean - Table 05Georgiana BealcuNo ratings yet
- New American Paintings - December-January, 2019Document180 pagesNew American Paintings - December-January, 2019Fabio Nagual100% (1)
- ABR College Mechanical Mid Exam Questions on MetrologyDocument1 pageABR College Mechanical Mid Exam Questions on MetrologySrinu ArnuriNo ratings yet
- 016 Muscoril COPPDocument3 pages016 Muscoril COPPTheRoom23No ratings yet
- Statics: Vector Mechanics For EngineersDocument32 pagesStatics: Vector Mechanics For EngineersArdaNo ratings yet
- Nature 1Document6 pagesNature 1Susanty SainudinNo ratings yet
- LastDocument6 pagesLastandypressNo ratings yet
- Mushroom Umami Taste EvaluationDocument10 pagesMushroom Umami Taste EvaluationMaryam HanifNo ratings yet